Fix for localized windows editions in testcase fn read_link() Issue#93211
This PR aims to fix the issue with localized windows versions that do not necessarily have the folder "Documents and settings" in English.
The idea was provided by `@the8472.` We check if the "CI" environment variable is set, then we always check for the "Documents and Settings"-folder, otherwise we check if the folder exists on the local machine, and if not we skip this assert.
Resoles #93211.
Improve doc wording for retain on some collections
I found the documentation wording on the various retain methods on many collections to be unusual.
I tried to invert the relation by switching `such that` with `for which` .
Use modern formatting for format! macros
This updates the standard library's documentation to use the new format_args syntax.
The documentation is worthwhile to update as it should be more idiomatic
(particularly for features like this, which are nice for users to get acquainted
with). The general codebase is likely more hassle than benefit to update: it'll
hurt git blame, and generally updates can be done by folks updating the code if
(and when) that makes things more readable with the new format.
A few places in the compiler and library code are updated (mostly just due to
already having been done when this commit was first authored).
`eprintln!("{}", e)` becomes `eprintln!("{e}")`, but `eprintln!("{}", e.kind())` remains untouched.
This updates the standard library's documentation to use the new syntax. The
documentation is worthwhile to update as it should be more idiomatic
(particularly for features like this, which are nice for users to get acquainted
with). The general codebase is likely more hassle than benefit to update: it'll
hurt git blame, and generally updates can be done by folks updating the code if
(and when) that makes things more readable with the new format.
A few places in the compiler and library code are updated (mostly just due to
already having been done when this commit was first authored).
Merge `#[deprecated]` and `#[rustc_deprecated]`
The first commit makes "reason" an alias for "note" in `#[rustc_deprecated]`, while still prohibiting it in `#[deprecated]`.
The second commit changes "suggestion" to not just be a feature of `#[rustc_deprecated]`. This is placed behind the new `deprecated_suggestion` feature. This needs a tracking issue; let me know if this PR will be approved and I can create one.
The third commit is what permits `#[deprecated]` to be used when `#![feature(staged_api)]` is enabled. This isn't yet used in stdlib (only tests), as it would require duplicating all deprecation attributes until a bootstrap occurs. I intend to submit a follow-up PR that replaces all uses and removes the remaining `#[rustc_deprecated]` code after the next bootstrap.
`@rustbot` label +T-libs-api +C-feature-request +A-attributes +S-waiting-on-review
Ignore `close_read_wakes_up` test on SGX platform
PR #94714 enabled the `close_read_wakes_up` test for all platforms. This is incorrect. This test should be ignored at least for the SGX platform.
cc: ``@mzohreva`` ``@jethrogb``
The initial stdlib modifications for L4Re just used the linux specifics
directly because they were reasonably close to L4Re's behavior.
However, this breaks when Linux-specific code relies on code that is
only available for the linux target, such as in #81825.
Put L4Re into its own platform to avoid such breakage in the future.
This uses the Linux-specific code as a starting point, which seems to be
in line with other OSes with a unix-y interface such as Fuchsia.
L4Re provides limited POSIX support which includes support for
standard I/O streams, and a limited implementation of the standard file
handling API. However, because as a capability based OS it strives to
only make a local view available to each application, there are
currently no standardized special files like /dev/null that could serve
to sanitize closed standard FDs.
For now, skip any attempts to sanitize standard streams until a more
complete POSIX runtime is available.
unix: reduce the size of DirEntry
On platforms where we call `readdir` instead of `readdir_r`, we store
the name as an allocated `CString` for variable length. There's no point
carrying around a full `dirent64` with its fixed-length `d_name` too.
Reverted atomic_mut_ptr feature removal causing compilation break
Fixes a regression introduced as part of https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/94546
Std no longer compiles on nightly while using the following commnd:
export RUSTFLAGS='-C target-feature=+atomics,+bulk-memory'
cargo build --target wasm32-unknown-unknown -Z build-std=panic_abort,std
I can help add tests to avoid future breaks but i couldn't understand the test framework
unix: Avoid name conversions in `remove_dir_all_recursive`
Each recursive call was creating an `OsString` for a `&Path`, only for
it to be turned into a `CString` right away. Instead we can directly
pass `.name_cstr()`, saving two allocations each time.
Enable `close_read_wakes_up` test on Windows
I wonder if we could/should try enabling this again? It was closed by #38867 due to #31657. I've tried running this test (along with other tests) on my machine a number of times and haven't seen this fail yet,
Caveat: the worst that can happen is this succeeds initially but then causes random hangs in CI. This is not a great failure mode and would be a reason not to do this.
If this does work out, closes#39006
r? `@Mark-Simulacrum`
On platforms where we call `readdir` instead of `readdir_r`, we store
the name as an allocated `CString` for variable length. There's no point
carrying around a full `dirent64` with its fixed-length `d_name` too.
Remove argument from closure in thread::Scope::spawn.
This implements ```@danielhenrymantilla's``` [suggestion](https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/93203#issuecomment-1040798286) for improving the scoped threads interface.
Summary:
The `Scope` type gets an extra lifetime argument, which represents basically its own lifetime that will be used in `&'scope Scope<'scope, 'env>`:
```diff
- pub struct Scope<'env> { .. };
+ pub struct Scope<'scope, 'env: 'scope> { .. }
pub fn scope<'env, F, T>(f: F) -> T
where
- F: FnOnce(&Scope<'env>) -> T;
+ F: for<'scope> FnOnce(&'scope Scope<'scope, 'env>) -> T;
```
This simplifies the `spawn` function, which now no longer passes an argument to the closure you give it, and now uses the `'scope` lifetime for everything:
```diff
- pub fn spawn<'scope, F, T>(&'scope self, f: F) -> ScopedJoinHandle<'scope, T>
+ pub fn spawn<F, T>(&'scope self, f: F) -> ScopedJoinHandle<'scope, T>
where
- F: FnOnce(&Scope<'env>) -> T + Send + 'env,
+ F: FnOnce() -> T + Send + 'scope,
- T: Send + 'env;
+ T: Send + 'scope;
```
The only difference the user will notice, is that their closure now takes no arguments anymore, even when spawning threads from spawned threads:
```diff
thread::scope(|s| {
- s.spawn(|_| {
+ s.spawn(|| {
...
});
- s.spawn(|s| {
+ s.spawn(|| {
...
- s.spawn(|_| ...);
+ s.spawn(|| ...);
});
});
```
<details><summary>And, as a bonus, errors get <em>slightly</em> better because now any lifetime issues point to the outermost <code>s</code> (since there is only one <code>s</code>), rather than the innermost <code>s</code>, making it clear that the lifetime lasts for the entire <code>thread::scope</code>.
</summary>
```diff
error[E0373]: closure may outlive the current function, but it borrows `a`, which is owned by the current function
--> src/main.rs:9:21
|
- 7 | s.spawn(|s| {
- | - has type `&Scope<'1>`
+ 6 | thread::scope(|s| {
+ | - lifetime `'1` appears in the type of `s`
9 | s.spawn(|| println!("{:?}", a)); // might run after `a` is dropped
| ^^ - `a` is borrowed here
| |
| may outlive borrowed value `a`
|
note: function requires argument type to outlive `'1`
--> src/main.rs:9:13
|
9 | s.spawn(|| println!("{:?}", a)); // might run after `a` is dropped
| ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
help: to force the closure to take ownership of `a` (and any other referenced variables), use the `move` keyword
|
9 | s.spawn(move || println!("{:?}", a)); // might run after `a` is dropped
| ++++
"
```
</details>
The downside is that the signature of `scope` and `Scope` gets slightly more complex, but in most cases the user wouldn't need to write those, as they just use the argument provided by `thread::scope` without having to name its type.
Another downside is that this does not work nicely in Rust 2015 and Rust 2018, since in those editions, `s` would be captured by reference and not by copy. In those editions, the user would need to use `move ||` to capture `s` by copy. (Which is what the compiler suggests in the error.)
Each recursive call was creating an `OsString` for a `&Path`, only for
it to be turned into a `CString` right away. Instead we can directly
pass `.name_cstr()`, saving two allocations each time.
Unix path::absolute: Fix leading "." component
Testing leading `.` and `..` components were missing from the unix tests.
This PR adds them and fixes the leading `.` case. It also fixes the test cases so that they do an exact comparison.
This problem reported by ``@axetroy``
Windows 11 no longer turn paths ending with dos device names into device paths.
E.g. `C:\path\to\COM1.txt` used to get turned into `\\.\COM1`. Whereas now the path is left as is.
UNIX `remove_dir_all()`: Try recursing first on the slow path
This only affects the _slow_ code path - if there is no `dirent.d_type` or if it is `DT_UNKNOWN`.
POSIX specifies that calling `unlink()` or `unlinkat(..., 0)` on a directory is allowed to succeed:
> The _path_ argument shall not name a directory unless the process has appropriate privileges and the implementation supports using _unlink()_ on directories.
This however can cause dangling inodes requiring an fsck e.g. on Illumos UFS, so we have to avoid that in the common case. We now just try to recurse into it first and unlink() if we can't open it as a directory.
The other two commits integrate the Macos x86-64 implementation reducing redundancy. Split into two commits for better reviewing.
Fixes#94335.
Rollup of 5 pull requests
Successful merges:
- #94362 (Add well known values to `--check-cfg` implementation)
- #94577 (only disable SIMD for doctests in Miri (not for the stdlib build itself))
- #94595 (Fix invalid `unresolved imports` errors for a single-segment import)
- #94596 (Delay bug in expr adjustment when check_expr is called multiple times)
- #94618 (Don't round stack size up for created threads in Windows)
Failed merges:
r? `@ghost`
`@rustbot` modify labels: rollup
Enable conditional compilation checking on the Rust codebase
This pull-request enable conditional compilation checking on every rust project build by the `bootstrap` tool.
To be more specific, this PR only enable well known names checking + extra names (bootstrap, parallel_compiler, ...).
r? `@Mark-Simulacrum`
Add #[track_caller] to track callers when initializing poisoned Once
This PR is for this Issue.
https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/87707
With this fix, we expect to be able to track the caller when poisoned Once is initialized.
Before calling `CreateProcessW`, stdio handles are passed through
`stdio::get_handle`, which already converts NULL to
`INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE`, so we don't need extra checks for NULL after
that point.
This addresses #90964 by making the std API consistent about presenting
absent stdio handles on Windows as NULL handles. Stdio handles may be
absent due to `#![windows_subsystem = "windows"]`, due to the console
being detached, or due to a child process having been launched from a
parent where stdio handles are absent.
Specifically, this fixes the case of child processes of parents with absent
stdio, which previously ended up with `stdin().as_raw_handle()` returning
`INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE`, which was surprising, and which overlapped with an
unrelated valid handle value. With this patch, `stdin().as_raw_handle()`
now returns null in these situation, which is consistent with what it
does in the parent process.
And, document this in the "Windows Portability Considerations" sections of
the relevant documentation.
This only affects the `slow` code path, if there is no `dirent.d_type` or if
the type is `DT_UNKNOWN`.
POSIX specifies that calling `unlink()` or `unlinkat(..., 0)` on a directory can
succeed:
> "The _path_ argument shall not name a directory unless the process has
> appropriate privileges and the implementation supports using _unlink()_ on
> directories."
This however can cause orphaned directories requiring an fsck e.g. on Illumos
UFS, so we have to avoid that in the common case. We now just try to recurse
into it first and unlink() if we can't open it as a directory.
Use `HandleOrNull` and `HandleOrInvalid` in the Windows FFI bindings.
Use the new `HandleOrNull` and `HandleOrInvalid` types that were introduced
as part of [I/O safety] in a few functions in the Windows FFI bindings.
This factors out an `unsafe` block and two `unsafe` function calls in the
Windows implementation code.
And, it helps test `HandleOrNull` and `HandleOrInvalid`, and indeed, it
turned up a bug: `OwnedHandle` also needs to be `#[repr(transparent)]`,
as it's used inside of `HandleOrNull` and `HandleOrInvalid` which are also
`#[repr(transparent)]`.
r? ```@joshtriplett```
[I/O safety]: https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/87074
Make regular stdio lock() return 'static handles
This also deletes the unstable API surface area previously added to expose this
functionality on new methods rather than built into the current set.
Closes#86845 (tracking issue for unstable API needed without this)
r? ``````@dtolnay`````` to kick off T-libs-api FCP
Clarification of default socket flags
This PR outlines the decision to disable inheritance of socket objects when possible to child processes in the documentation.
Use the new `HandleOrNull` and `HandleOrInvalid` types that were introduced
as part of [I/O safety] in a few functions in the Windows FFI bindings.
This factors out an `unsafe` block and two `unsafe` function calls in the
Windows implementation code.
And, it helps test `HandleOrNull` and `HandleOrInvalid`, which indeed turned
up a bug: `OwnedHandle` also needs to be `#[repr(transparent)]`, as it's
used inside of `HandleOrNull` and `HandleOrInvalid` which are also
`#[repr(transparent)]`.
[I/O safety]: https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/87074
Update the documentation for `{As,Into,From}Raw{Fd,Handle,Socket}`.
This change weakens the descriptions of the
`{as,into,from}_raw_{fd,handle,socket}` descriptions from saying that
they *do* express ownership relations to say that they are *typically used*
in ways that express ownership relations. This is needed since, for
example, std's own [`RawFd`] implements `{As,From,Into}Fd` without any of
the ownership relationships.
This adds proper `# Safety` comments to `from_raw_{fd,handle,socket}`,
adds the requirement that raw handles be not opened with the
`FILE_FLAG_OVERLAPPED` flag, and merges the `OwnedHandle::from_raw_handle`
comment into the main `FromRawHandle::from_raw_handle` comment.
And, this changes `HandleOrNull` and `HandleOrInvalid` to not implement
`FromRawHandle`, since they are intended for limited use in FFI situations,
and not for generic use, and they have constraints that are stronger than
the those of `FromRawHandle`.
[`RawFd`]: https://doc.rust-lang.org/stable/std/os/unix/io/type.RawFd.html
There may eventually be something to say about `FILE_FLAG_OVERLAPPED` here,
however this appears to be independent of the other changes in this PR,
so remove them from this PR so that it can be discussed separately.
Rename `BorrowedFd::borrow_raw_fd` to `BorrowedFd::borrow_raw`.
Also, rename `BorrowedHandle::borrow_raw_handle` and
`BorrowedSocket::borrow_raw_socket` to `BorrowedHandle::borrow_raw` and
`BorrowedSocket::borrow_raw`.
This is just a minor rename to reduce redundancy in the user code calling
these functions, and to eliminate an inessential difference between
`BorrowedFd` code and `BorrowedHandle`/`BorrowedSocket` code.
While here, add a simple test exercising `BorrowedFd::borrow_raw_fd`.
r? ``````@joshtriplett``````
Add documentation about `BorrowedFd::to_owned`.
Following up on #88564, this adds documentation explaining why
`BorrowedFd::to_owned` returns another `BorrowedFd` rather than an
`OwnedFd`. And similar for `BorrowedHandle` and `BorrowedSocket`.
r? `````@joshtriplett`````
this avoids parsing mountinfo which can be huge on some systems and
something might be emulating cgroup fs for sandboxing reasons which means
it wouldn't show up as mountpoint
additionally the new implementation operates on a single pathbuffer, reducing allocations
Manually tested via
```
// spawn a new cgroup scope for the current user
$ sudo systemd-run -p CPUQuota="300%" --uid=$(id -u) -tdS
// quota.rs
#![feature(available_parallelism)]
fn main() {
println!("{:?}", std:🧵:available_parallelism()); // prints Ok(3)
}
```
Caveats
* cgroup v1 is ignored
* funky mountpoints (containing spaces, newlines or control chars) for cgroupfs will not be handled correctly since that would require unescaping /proc/self/mountinfo
The escaping behavior of procfs seems to be undocumented. systemd and docker default to `/sys/fs/cgroup` so it should be fine for most systems.
* quota will be ignored when `sched_getaffinity` doesn't work
* assumes procfs is mounted under `/proc` and cgroupfs mounted and readable somewhere in the directory tree
The ability to interoperate with C code via FFI is not limited to crates
using std; this allows using these types without std.
The existing types in `std::os::raw` become type aliases for the ones in
`core::ffi`. This uses type aliases rather than re-exports, to allow the
std types to remain stable while the core types are unstable.
This also moves the currently unstable `NonZero_` variants and
`c_size_t`/`c_ssize_t`/`c_ptrdiff_t` types to `core::ffi`, while leaving
them unstable.
use BOOL for TCP_NODELAY setsockopt value on Windows
This issue was found by the Wine project and mitigated there [^1].
Windows' setsockopt expects a BOOL (a typedef for int) for TCP_NODELAY
[^2]. Windows itself is forgiving and will accept any positive optlen and
interpret the first byte of *optval as the value, so this bug does not
affect Windows itself, but does affect systems implementing Windows'
interface more strictly, such as Wine. Wine was previously passing this
through to the host's setsockopt, where, e.g., Linux requires that
optlen be correct for the chosen option, and TCP_NODELAY expects an int.
[^1]: d6ea38f32d
[^2]: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/win32/api/winsock/nf-winsock-setsockopt
Some improvements to the async docs
The goal here is to make the docs overall a little bit more comprehensive and add more links between the things.
One thing that's not working yet is the links to the keywords. Somehow I couldn't get them to work.
r? ````@GuillaumeGomez```` do you know how I could get the keyword links to work?
This issue was found by the Wine project and mitigated there [1].
Windows' documented interface for `setsockopt` expects a `BOOL` (a
`typedef` for `int`) for `TCP_NODELAY` [2]. Windows is forgiving and
will accept any positive length and interpret the first byte of
`*option_value` as the value, so this bug does not affect Windows
itself, but does affect systems implementing Windows' interface more
strictly, such as Wine. Wine was previously passing this through to the
host's `setsockopt`, where, e.g., Linux requires that `option_len` be
correct for the chosen option, and `TCP_NODELAY` expects an `int`.
[1]: d6ea38f32d
[2]: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/win32/api/winsock/nf-winsock-setsockopt
POSIX allows `getsockopt` to set `*option_len` to a smaller value if
necessary. Windows will set `*option_len` to 1 for boolean options even
when the caller passes a `BOOL` (`int`) with `*option_len` as 4.
Previously `level` was named `opt` and `option_name` was named `val`,
then extra names of `payload` or `slot` were used for the option value.
This change aligns the wrapper parameters with their names in POSIX.
Winsock uses similar but more abbreviated names: `level`, `optname`,
`optval`, `optlen`.
Fix miniz_oxide types showing up in std docs
Fixes#90526.
Thanks to ```````@camelid,``````` I rediscovered `doc(masked)`, allowing us to prevent `miniz_oxide` type to show up in std docs.
r? ```````@notriddle```````
removing architecture requirements for RustyHermit
RustHermit and HermitCore is able to run on aarch64 and x86_64. In the future these operating systems will also support RISC-V. Consequently, the dependency to a specific target should be removed.
The build process of `hermit-abi` fails if the architecture isn't supported.
Add debug assertions to validate NUL terminator in c strings
The `unchecked` variants from the stdlib usually perform the check anyway if debug assertions are on (for example, `unwrap_unchecked`). This PR does the same thing for `CStr` and `CString`, validating the correctness for the NUL byte in debug mode.
Destabilise entry_insert
See: https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/90345
I didn't revert the rename that was done in that PR, I left it as `entry_insert`.
Additionally, before that PR, `VacantEntry::insert_entry` seemingly had no stability attribute on it? I kept the attribute, just made it an unstable one, same as the one on `Entry`.
There didn't seem to be any mention of this in the RELEASES.md, so I don't think there's anything for me to do other than this?
kmc-solid: Use the filesystem thread-safety wrapper
Fixes the thread unsafety of the `std::fs` implementation used by the [`*-kmc-solid_*`](https://doc.rust-lang.org/nightly/rustc/platform-support/kmc-solid.html) Tier 3 targets.
Neither the SOLID filesystem API nor built-in filesystem drivers guarantee thread safety by default. Although this may suffice in general embedded-system use cases, and in fact the API can be used from multiple threads without any problems in many cases, this has been a source of unsoundness in `std::sys::solid::fs`.
This commit updates the implementation to leverage the filesystem thread-safety wrapper (which uses a pluggable synchronization mechanism) to enforce thread safety. This is done by prefixing all paths passed to the filesystem API with `\TS`. (Note that relative paths aren't supported in this platform.)
Add MAIN_SEPARATOR_STR
Currently, if someone needs access to the path separator as a str, they need to go through this mess:
```rust
unsafe {
std::str::from_utf8_unchecked(slice::from_ref(&(MAIN_SEPARATOR as u8)))
}
```
This PR just re-exports an existing path separator str API.
Add documentation to more `From::from` implementations.
For users looking at documentation through IDE popups, this gives them relevant information rather than the generic trait documentation wording “Performs the conversion”. For users reading the documentation for a specific type for any reason, this informs them when the conversion may allocate or copy significant memory versus when it is always a move or cheap copy.
Notes on specific cases:
* The new documentation for `From<T> for T` explains that it is not a conversion at all.
* Also documented `impl<T, U> Into<U> for T where U: From<T>`, the other central blanket implementation of conversion.
* The new documentation for construction of maps and sets from arrays of keys mentions the handling of duplicates. Future work could be to do this for *all* code paths that convert an iterable to a map or set.
* I did not add documentation to conversions of a specific error type to a more general error type.
* I did not add documentation to unstable code.
This change was prepared by searching for the text "From<... for" and so may have missed some cases that for whatever reason did not match. I also looked for `Into` impls but did not find any worth documenting by the above criteria.
RustHermit and HermitCore is able to run on aarch64 and x86_64.
In the future these operating systems will also support RISC-V.
Consequently, the dependency to a specific target should be removed.
Building hermit-abi fails if the architecture isn't supported.
make `Instant::{duration_since, elapsed, sub}` saturating and remove workarounds
This removes all mutex/atomic-based workarounds for non-monotonic clocks and makes the previously panicking methods saturating instead. Additionally `saturating_duration_since` becomes deprecated since `duration_since` now fills that role.
Effectively this moves the fixup from `Instant` construction to the comparisons.
This has some observable effects, especially on platforms without monotonic clocks:
* Incorrectly ordered Instant comparisons no longer panic in release mode. This could hide some programming errors, but since debug mode still panics tests can still catch them.
* `checked_duration_since` will now return `None` in more cases. Previously it only happened when one compared instants obtained in the wrong order or manually created ones. Now it also does on backslides.
* non-monotonic intervals will not be transitive, i.e. `b.duration_since(a) + c.duration_since(b) != c.duration_since(a)`
The upsides are reduced complexity and lower overhead of `Instant::now`.
## Motivation
Currently we must choose between two poisons. One is high worst-case latency and jitter of `Instant::now()` due to explicit synchronization; see #83093 for benchmarks, the worst-case overhead is > 100x. The other is sporadic panics on specific, rare combinations of CPU/hypervisor/operating system due to platform bugs.
Use-cases where low-overhead, fine-grained timestamps are needed - such as syscall tracing, performance profiles or sensor data acquisition (drone flight controllers were mentioned in a libs meeting) in multi-threaded programs - are negatively impacted by the synchronization.
The panics are user-visible (program crashes), hard to reproduce and can be triggered by any dependency that might be using Instants for any reason.
A solution that is fast _and_ doesn't panic is desirable.
----
closes#84448closes#86470
This removes all mutex/atomics based workarounds for non-monotonic clocks and makes the previously panicking methods saturating instead.
Effectively this moves the monotonization from `Instant` construction to the comparisons.
This has some observable effects, especially on platforms without monotonic clocks:
* Incorrectly ordered Instant comparisons no longer panic. This may hide some programming errors until someone actually looks at the resulting `Duration`
* `checked_duration_since` will now return `None` in more cases. Previously it only happened when one compared instants obtained in the wrong order or
manually created ones. Now it also does on backslides.
The upside is reduced complexity and lower overhead of `Instant::now`.
Fix hashing for windows paths containing a CurDir component
* the logic only checked for / but not for \
* verbatim paths shouldn't skip items at all since they don't get normalized
* the extra branches get optimized out on unix since is_sep_byte is a trivial comparison and is_verbatim is always-false
* tests lacked windows coverage for these cases
That lead to equal paths not having equal hashes and to unnecessary collisions.
Rollup of 10 pull requests
Successful merges:
- #90955 (Rename `FilenameTooLong` to `InvalidFilename` and also use it for Windows' `ERROR_INVALID_NAME`)
- #91607 (Make `span_extend_to_prev_str()` more robust)
- #92895 (Remove some unused functionality)
- #93635 (Add missing platform-specific information on current_dir and set_current_dir)
- #93660 (rustdoc-json: Add some tests for typealias item)
- #93782 (Split `pauth` target feature)
- #93868 (Fix incorrect register conflict detection in asm!)
- #93888 (Implement `AsFd` for `&T` and `&mut T`.)
- #93909 (Fix typo: explicitely -> explicitly)
- #93910 (fix mention of moved function in `rustc_hir` docs)
Failed merges:
r? `@ghost`
`@rustbot` modify labels: rollup
Implement `AsFd` for `&T` and `&mut T`.
Add implementations of `AsFd` for `&T` and `&mut T`, so that users can
write code like this:
```rust
pub fn fchown<F: AsFd>(fd: F, uid: Option<u32>, gid: Option<u32>) -> io::Result<()> {
```
with `fd: F` rather than `fd: &F`.
And similar for `AsHandle` and `AsSocket` on Windows.
Also, adjust the `fchown` example to pass the file by reference. The
code can work either way now, but passing by reference is more likely
to be what users will want to do.
This is an alternative to #93869, and is a simpler way to achieve the
same goals: users don't need to pass borrowed-`BorrowedFd` arguments,
and it prevents a pitfall in the case where users write `fd: F` instead
of `fd: &F`.
r? ```@joshtriplett```
Rename `FilenameTooLong` to `InvalidFilename` and also use it for Windows' `ERROR_INVALID_NAME`
Address https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/90940#issuecomment-970157931
`ERROR_INVALID_NAME` (i.e. "The filename, directory name, or volume label syntax is incorrect") happens if we pass an invalid filename, directory name, or label syntax, so mapping as `InvalidInput` is reasonable to me.
Stabilise `is_aarch64_feature_detected!` under `simd_aarch64` feature
Initial implementation, looking for feedback on the approach here. https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/86941
One point I noticed was that I haven't seen different "since" versions for the same feature - does this mean that other features can't be added to to the `simd_aarch64` feature once this is in stable? If so it might need a more specific name.
r? `@Amanieu`
Add implementations of `AsFd` for `&T` and `&mut T`, so that users can
write code like this:
```rust
pub fn fchown<F: AsFd>(fd: F, uid: Option<u32>, gid: Option<u32>) -> io::Result<()> {
```
with `fd: F` rather than `fd: &F`.
And similar for `AsHandle` and `AsSocket` on Windows.
Also, adjust the `fchown` example to pass the file by reference. The
code can work either way now, but passing by reference is more likely
to be what users will want to do.
This is an alternative to #93869, and is a simpler way to achieve the
same goals: users don't need to pass borrowed-`BorrowedFd` arguments,
and it prevents a pitfall in the case where users write `fd: F` instead
of `fd: &F`.
kmc-solid: Fix wait queue manipulation errors in the `Condvar` implementation
This PR fixes a number of bugs in the `Condvar` wait queue implementation used by the [`*-kmc-solid_*`](https://doc.rust-lang.org/nightly/rustc/platform-support/kmc-solid.html) Tier 3 targets. These bugs can occur when there are multiple threads waiting on the same `Condvar` and sometimes manifest as an `unwrap` failure.
Neither the SOLID filesystem API nor built-in filesystems guarantee
thread safety by default. Although this may suffice in general embedded-
system use cases, and in fact the API can be used from multiple threads
without any problems in many cases, this has been a source of
unsoundness in `std::sys::solid::fs`.
This commit updates the `std` code to leverage the filesystem thread-
safety wrapper to enforce thread safety. This is done by prefixing all
paths passed to the filesystem API with `\TS`. (Note that relative paths
aren't supported in this platform.)
Use `NtCreateFile` instead of `NtOpenFile` to open a file
Generally the internal `Nt*` functions should be avoided but when we do need to use one we should stick to the most commonly used for the job. To that end, this PR replaces `NtOpenFile` with `NtCreateFile`.
NOTE: The initial version of this comment hypothesised that this may help with some recent false positives from malware scanners. This hypothesis proved wrong. Sorry for the distraction.
Make io::Error use 64 bits on targets with 64 bit pointers.
I've wanted this for a long time, but didn't see a good way to do it without having extra allocation. When looking at it yesterday, it was more clear what to do for some reason.
This approach avoids any additional allocations, and reduces the size by half (8 bytes, down from 16). AFAICT it doesn't come additional runtime cost, and the compiler seems to do a better job with code using it.
Additionally, this `io::Error` has a niche (still), so `io::Result<()>` is *also* 64 bits (8 bytes, down from 16), and `io::Result<usize>` (used for lots of io trait functions) is 2x64 bits (16 bytes, down from 24 — this means on x86_64 it can use the nice rax/rdx 2-reg struct return). More generally, it shaves a whole 64 bit integer register off of the size of basically any `io::Result<()>`.
(For clarity: Improving `io::Result` (rather than io::Error) was most of the motivation for this)
On 32 bit (or other non-64bit) targets we still use something equivalent the old repr — I don't think think there's improving it, since one of the fields it stores is a `i32`, so we can't get below that, and it's already about as close as we can get to it.
---
### Isn't Pointer Tagging Dodgy?
The details of the layout, and why its implemented the way it is, are explained in the header comment of library/std/src/io/error/repr_bitpacked.rs. There's probably more details than there need to be, but I didn't trim it down that much, since there's a lot of stuff I did deliberately, that might have not seemed that way.
There's actually only one variant holding a pointer which gets tagged. This one is the (holder for the) user-provided error.
I believe the scheme used to tag it is not UB, and that it preserves pointer provenance (even though often pointer tagging does not) because the tagging operation is just `core::ptr::add`, and untagging is `core::ptr::sub`. The result of both operations lands inside the original allocation, so it would follow the safety contract of `core::ptr::{add,sub}`.
The other pointer this had to encode is not tagged — or rather, the tagged repr is equivalent to untagged (it's tagged with 0b00, and has >=4b alignment, so we can reuse the bottom bits). And the other variants we encode are just integers, which (which can be untagged using bitwise operations without worry — they're integers).
CC `@RalfJung` for the stuff in repr_bitpacked.rs, as my comments are informed by a lot of the UCG work, but it's possible I missed something or got it wrong (even if the implementation is okay, there are parts of the header comment that says things like "We can't do $x" which could be false).
---
### Why So Many Changes?
The repr change was mostly internal, but changed one widely used API: I had to switch how `io::Error::new_const` works.
This required switching `io::Error::new_const` to take the full message data (including the kind) as a `&'static`, rather than just the string. This would have been really tedious, but I made a macro that made it much simpler, but it was a wide change since `io::Error::new_const` is used everywhere.
This included changing files for a lot of targets I don't have easy access to (SGX? Haiku? Windows? Who has heard of these things), so I expect there to be spottiness in CI initially, unless luck is on my side.
Anyway this large only tangentially-related change is all in the first commit (although that commit also pulls the previous repr out into its own file), whereas the packing stuff is all in commit 2.
---
P.S. I haven't looked at all of this since writing it, and will do a pass over it again later, sorry for any obvious typos or w/e. I also definitely repeat myself in comments and such.
(It probably could use more tests too. I did some basic testing, and made it so we `debug_assert!` in cases the decode isn't what we encoded, but I don't know the degree which I can assume libstd's testing of IO would exercise this. That is: it wouldn't be surprising to me if libstds IO testing were minimal, especially around error cases, although I have no idea).
* the logic only checked for / but not for \
* verbatim paths shouldn't skip items at all since they don't get normalized
* the extra branches get optimized out on unix since is_sep_byte is a trivial comparison and is_verbatim is always-false
* tests lacked windows coverage for these cases
That lead to equal paths not having equal hashes and to unnecessary collisions.
Also, rename `BorrowedHandle::borrow_raw_handle` and
`BorrowedSocket::borrow_raw_socket` to `BorrowedHandle::borrow_raw` and
`BorrowedSocket::borrow_raw`.
This is just a minor rename to reduce redundancy in the user code calling
these functions, and to eliminate an inessential difference between
`BorrowedFd` code and `BorrowedHandle`/`BorrowedSocket` code.
While here, add a simple test exercising `BorrowedFd::borrow_raw_fd`.
kmc-solid: Fix off-by-one error in `SystemTime::now`
Fixes a miscalculation of `SystemTime` on the [`*-kmc-solid_*`](https://doc.rust-lang.org/nightly/rustc/platform-support/kmc-solid.html) Tier 3 targets.
Unlike the identically-named libc counterpart `tm::tm_mon`, `SOLID_RTC_TIME::tm_mon` contains a 1-based month number.
Link `try_exists` docs to `Path::exists`
Links to the existing `Path::exists` method from both `std::Path::try_exists` and `std::fs:try_exists`.
Tracking issue for `path_try_exists`: #83186
pub use std::simd::StdFloat;
Syncs portable-simd up to commit rust-lang/portable-simd@03f6fbb21e,
Diff: 533f0fc81a...03f6fbb21e
This sync requires a little bit more legwork because it also introduces a trait into `std::simd`, so that it is no longer simply a reexport of `core::simd`. Out of simple-minded consistency and to allow more options, I replicated the pattern for the way `core::simd` is integrated in the first place, however this is not necessary if it doesn't acquire any interdependencies inside `std`: it could be a simple crate reexport. I just don't know yet if that will happen or not.
To summarize other misc changes:
- Shifts no longer panic, now wrap on too-large shifts (like `Simd` integers usually do!)
- mask16x32 will now be many i16s, not many i32s... 🙃
- `#[must_use]` is spread around generously
- Adjusts division, float min/max, and `Mask::{from,to}_array` internally to be faster
- Adds the much-requested `Simd::cast::<U>` function (equivalent to `simd.to_array().map(|lane| lane as U)`)
Support configuring whether to capture backtraces at runtime
Tracking issue: https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/93346
This adds a new API to the `std::panic` module which configures whether and how the default panic hook will emit a backtrace when a panic occurs.
After discussion with `@yaahc` on [Zulip](https://rust-lang.zulipchat.com/#narrow/stream/219381-t-libs/topic/backtrace.20lib.20vs.2E.20panic), this PR chooses to avoid adjusting or seeking to provide a similar API for the (currently unstable) std::backtrace API. It seems likely that the users of that API may wish to expose more specific settings rather than just a global one (e.g., emulating the `env_logger`, `tracing` per-module configuration) to avoid the cost of capture in hot code. The API added here could plausibly be copied and/or re-exported directly from std::backtrace relatively easily, but I don't think that's the right call as of now.
```rust
mod panic {
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
#[non_exhaustive]
pub enum BacktraceStyle {
Short,
Full,
Off,
}
fn set_backtrace_style(BacktraceStyle);
fn get_backtrace_style() -> Option<BacktraceStyle>;
}
```
Several unresolved questions:
* Do we need to move to a thread-local or otherwise more customizable strategy for whether to capture backtraces? See [this comment](https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/79085#issuecomment-727845826) for some potential use cases for this.
* Proposed answer: no, leave this for third-party hooks.
* Bikeshed on naming of all the options, as usual.
* Should BacktraceStyle be moved into `std::backtrace`?
* It's already somewhat annoying to import and/or re-type the `std::panic::` prefix necessary to use these APIs, probably adding a second module to the mix isn't worth it.
Note that PR #79085 proposed a much simpler API, but particularly in light of the desire to fully replace setting environment variables via `env::set_var` to control the backtrace API, a more complete API seems preferable. This PR likely subsumes that one.
Fix incorrect panic message in example
The panic message when calling the `connect()` should probably be a message about connection failure, not a message about binding address failure.
Document valid values of the char type
As discussed at #93392, the current documentation on what constitutes a valid char isn't very detailed and is partly on the MAX constant rather than the type itself.
This PR expands on that information, stating the actual numerical range, giving examples of what won't work, and also mentions how a `char` might be a valid USV but still not be a defined character (terminology checked against [Unicode 14.0, table 2-3](https://www.unicode.org/versions/Unicode14.0.0/ch02.pdf#M9.61673.TableTitle.Table.22.Types.of.Code.Points)).
This change weakens the descriptions of the
`{as,into,from}_raw_{fd,handle,socket}` descriptions from saying that
they *do* express ownership relations to say that they are *typically used*
in ways that express ownership relations. This needed needed since, for
example, std's own [`RawFd`] implements `{As,From,Into}Fd` without any of
the ownership relationships.
This adds proper `# Safety` comments to `from_raw_{fd,handle,socket}`,
adds the requirement that raw handles be not opened with the
`FILE_FLAG_OVERLAPPED` flag, and merges the `OwnedHandle::from_raw_handle`
comment into the main `FromRawHandle::from_raw_handle` comment.
And, this changes `HandleOrNull` and `HandleOrInvalid` to not implement
`FromRawHandle`, since they are intended for limited use in FFI situations,
and not for generic use, and they have constraints that are stronger than
the those of `FromRawHandle`.
[`RawFd`]: https://doc.rust-lang.org/stable/std/os/unix/io/type.RawFd.html
Change Termination::report return type to ExitCode
Related to https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/43301
The goal of this change is to minimize the forward compatibility risks in stabilizing Termination. By using the opaque type `ExitCode` instead of an `i32` we leave room for us to evolve the API over time to provide what cross-platform consistency we can / minimize footguns when working with exit codes, where as stabilizing on `i32` would limit what changes we could make in the future in how we represent and construct exit codes.
kmc-solid: Increase the default stack size
This PR increases the default minimum stack size on the [`*-kmc-solid_*`](https://doc.rust-lang.org/nightly/rustc/platform-support/kmc-solid.html) Tier 3 targets to 64KiB (Arm) and 128KiB (AArch64).
This value was chosen as a middle ground between supporting a relatively complex program (e.g., an application using a full-fledged off-the-shelf web server framework) with no additional configuration and minimizing resource consumption for the embedded platform that doesn't support lazily-allocated pages nor over-commitment (i.e., wasted stack spaces are wasted physical memory). If the need arises, the users can always set the `RUST_MIN_STACK` environmental variable to override the default stack size or use the platform API directly.
Errors from pthread_sigmask(3) were handled using cvt(), which expects a
return value of -1 on error and uses errno.
However, pthread_sigmask(3) returns 0 on success and an error number
otherwise.
Fix it by replacing cvt() with cvt_nz().
kmc-solid: Inherit the calling task's base priority in `Thread::new`
This PR fixes the initial priority calculation of spawned threads on the [`*-kmc-solid_*`](https://doc.rust-lang.org/nightly/rustc/platform-support/kmc-solid.html) Tier 3 targets.
Fixes a spawned task (an RTOS object on top of which threads are implemented for this target; unrelated to async tasks) getting an unexpectedly higher priority if it's spawned by a task whose priority is temporarily boosted by a priority-protection mutex.
unix: Use metadata for `DirEntry::file_type` fallback
When `DirEntry::file_type` fails to match a known `d_type`, we should
fall back to `DirEntry::metadata` instead of a bare `lstat`, because
this is faster and more reliable on targets with `fstatat`.
Fixes a spawned task getting an unexpectedly higher priority if it's
spawned by a task whose priority is temporarily boosted by a priority-
protection mutex.
When `DirEntry::file_type` fails to match a known `d_type`, we should
fall back to `DirEntry::metadata` instead of a bare `lstat`, because
this is faster and more reliable on targets with `fstatat`.
fs: Don't copy d_name from struct dirent
The dirent returned from readdir() is only guaranteed to be valid for
d_reclen bytes on common platforms. Since we copy the name separately
anyway, we can copy everything except d_name into DirEntry::entry.
Fixes#93384.
Move unstable is_{arch}_feature_detected! macros to std::arch
These macros are unstable, except for `is_x86_feature_detected` which is still exported from the crate root for backwards-compatibility.
This should unblock the stabilization of `is_aarch64_feature_detected`.
r? ```@m-ou-se```
The dirent returned from readdir() is only guaranteed to be valid for
d_reclen bytes on common platforms. Since we copy the name separately
anyway, we can copy everything except d_name into DirEntry::entry.
Fixes#93384.
kmc-solid: Implement `net::FileDesc::duplicate`
This PR implements `std::sys::solid::net::FileDesc::duplicate`, which was accidentally left out when this target was added by #86191.
Bump libc and fix remove_dir_all on Fuchsia after CVE fix
With the previous `is_dir` impl, we would attempt to unlink
a directory in the None branch, but Fuchsia supports returning
ENOTEMPTY from unlinkat() without the AT_REMOVEDIR flag because
we don't currently differentiate unlinking files and directories
by default.
On the Fuchsia side I've opened https://fxbug.dev/92273 to discuss
whether this is the correct behavior, but it doesn't seem like
addressing the error code is necessary to make our tests happy.
Depends on https://github.com/rust-lang/libc/pull/2654 since we
apparently haven't needed to reference DT_UNKNOWN before this.
With the previous `is_dir` impl, we would attempt to unlink
a directory in the None branch, but Fuchsia supports returning
ENOTEMPTY from unlinkat() without the AT_REMOVEDIR flag because
we don't currently differentiate unlinking files and directories
by default.
On the Fuchsia side I've opened https://fxbug.dev/92273 to discuss
whether this is the correct behavior, but it doesn't seem like
addressing the error code is necessary to make our tests happy.
Updates std's libc crate to include DT_UNKNOWN for Fuchsia.
Avoid double panics when using `TempDir` in tests
`TempDir` could panic on drop if `remove_dir_all` returns an error. If this happens while already panicking, the test process would abort and therefore not show the test results.
This PR tries to avoid such double panics.
Add os::unix::net::SocketAddr::from_path
Creates a new SocketAddr from a path, supports both regular paths and
abstract namespaces.
Note that `SocketAddr::from_abstract_namespace` could be removed after this as `SocketAddr::unix` also supports abstract namespaces.
Updates #65275
Unblocks https://github.com/tokio-rs/mio/issues/1527
r? `@m-ou-se`
With the addition of `sock_accept()` to snapshot1, simple networking via
a passed `TcpListener` is possible. This patch implements the basics to
make a simple server work.
Signed-off-by: Harald Hoyer <harald@profian.com>
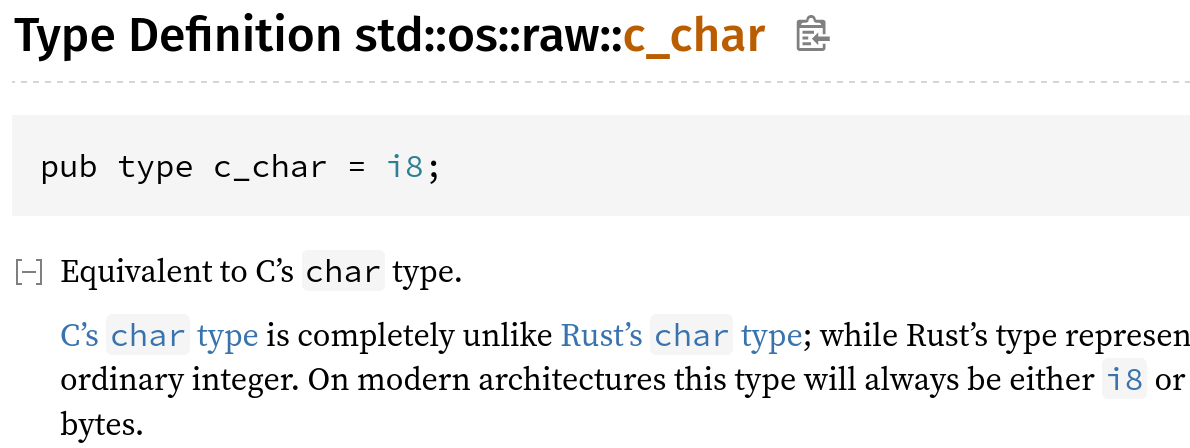
Define c_char using cfg_if rather than repeating 40-line cfg
Libstd has a 40-line cfg that defines the targets on which `c_char` is unsigned, and then repeats the same cfg with `not(…)` for the targets on which `c_char` is signed.
This PR replaces it with a `cfg_if!` in which an `else` takes care of the signed case.
I confirmed that `x.py doc library/std` inlines the type alias because c_char_definition is not a publicly accessible path:
Make available the remaining float intrinsics that require runtime support
from a platform's libm, and thus cannot be included in a no-deps libcore,
by exposing them through a sealed trait, `std::simd::StdFloat`.
We might use the trait approach a bit more in the future, or maybe not.
Ideally, this trait doesn't stick around, even if so.
If we don't need to intermesh it with std, it can be used as a crate,
but currently that is somewhat uncertain.
The creation of libc::sockaddr_un is a safe operation, no need for it to
be unsafe.
This also uses the more performant copy_nonoverlapping instead of an
iterator.
Following up on #88564, this adds documentation explaining why
`BorrowedFd::to_owned` returns another `BorrowedFd` rather than an
`OwnedFd`. And similar for `BorrowedHandle` and `BorrowedSocket`.
Add a `try_clone()` function to `OwnedFd`.
As suggested in #88564. This adds a `try_clone()` to `OwnedFd` by
refactoring the code out of the existing `File`/`Socket` code.
r? ``@joshtriplett``
Fix STD compilation for the ESP-IDF target (regression from CVE-2022-21658)
Commit 54e22eb7db broke the compilation of STD for the ESP-IDF embedded "unix-like" Tier 3 target, because the fix for [CVE-2022-21658](https://blog.rust-lang.org/2022/01/20/Rust-1.58.1.html) uses [libc flags](https://github.com/esp-rs/esp-idf-svc/runs/4892221554?check_suite_focus=true) which are not supported on the ESP-IDF platform.
This PR simply redirects the ESP-IDF compilation to the "classic" implementation, similar to REDOX. This should be safe because:
* Neither of the two filesystems supported by ESP-IDF (spiffs and fatfs) support [symlinks](https://github.com/natevw/fatfs/blob/master/README.md) in the first place
* There is no notion of fs permissions at all, as the ESP-IDF is an embedded platform that does not have the notion of users, groups, etc.
* Similarly, ESP-IDF has just one "process" - the firmware itself - which contains the user code and the "OS" fused together and running with all permissions
Print a helpful message if unwinding aborts when it reaches a nounwind function
This is implemented by routing `TerminatorKind::Abort` back through the panic handler, but with a special flag in the `PanicInfo` which indicates that the panic handler should *not* attempt to unwind the stack and should instead abort immediately.
This is useful for the planned change in https://github.com/rust-lang/lang-team/issues/97 which would make `Drop` impls `nounwind` by default.
### Code
```rust
#![feature(c_unwind)]
fn panic() {
panic!()
}
extern "C" fn nounwind() {
panic();
}
fn main() {
nounwind();
}
```
### Before
```
$ ./test
thread 'main' panicked at 'explicit panic', test.rs:4:5
note: run with `RUST_BACKTRACE=1` environment variable to display a backtrace
Illegal instruction (core dumped)
```
### After
```
$ ./test
thread 'main' panicked at 'explicit panic', test.rs:4:5
note: run with `RUST_BACKTRACE=1` environment variable to display a backtrace
thread 'main' panicked at 'panic in a function that cannot unwind', test.rs:7:1
stack backtrace:
0: 0x556f8f86ec9b - <std::sys_common::backtrace::_print::DisplayBacktrace as core::fmt::Display>::fmt::hdccefe11a6ac4396
1: 0x556f8f88ac6c - core::fmt::write::he152b28c41466ebb
2: 0x556f8f85d6e2 - std::io::Write::write_fmt::h0c261480ab86f3d3
3: 0x556f8f8654fa - std::panicking::default_hook::{{closure}}::h5d7346f3ff7f6c1b
4: 0x556f8f86512b - std::panicking::default_hook::hd85803a1376cac7f
5: 0x556f8f865a91 - std::panicking::rust_panic_with_hook::h4dc1c5a3036257ac
6: 0x556f8f86f079 - std::panicking::begin_panic_handler::{{closure}}::hdda1d83c7a9d34d2
7: 0x556f8f86edc4 - std::sys_common::backtrace::__rust_end_short_backtrace::h5b70ed0cce71e95f
8: 0x556f8f865592 - rust_begin_unwind
9: 0x556f8f85a764 - core::panicking::panic_no_unwind::h2606ab3d78c87899
10: 0x556f8f85b910 - test::nounwind::hade6c7ee65050347
11: 0x556f8f85b936 - test::main::hdc6e02cb36343525
12: 0x556f8f85b7e3 - core::ops::function::FnOnce::call_once::h4d02663acfc7597f
13: 0x556f8f85b739 - std::sys_common::backtrace::__rust_begin_short_backtrace::h071d40135adb0101
14: 0x556f8f85c149 - std::rt::lang_start::{{closure}}::h70dbfbf38b685e93
15: 0x556f8f85c791 - std::rt::lang_start_internal::h798f1c0268d525aa
16: 0x556f8f85c131 - std::rt::lang_start::h476a7ee0a0bb663f
17: 0x556f8f85b963 - main
18: 0x7f64c0822b25 - __libc_start_main
19: 0x556f8f85ae8e - _start
20: 0x0 - <unknown>
thread panicked while panicking. aborting.
Aborted (core dumped)
```
delete `Stdin::split` forwarder
Part of #87096. Delete the `Stdin::split` forwarder because it's seen as too niche to expose at this level.
`@rustbot` label T-libs-api A-io
Improve `Arc` and `Rc` documentation
This makes two changes (I can split the PR if necessary, but the changes are pretty small):
1. A bunch of trait implementations claimed to be zero cost; however, they use the `Arc<T>: From<Box<T>>` impl which is definitely not free, especially for large dynamically sized `T`.
2. The code in deferred initialization examples unnecessarily used excessive amounts of `unsafe`. This has been reduced.
readdir() is preferred over readdir_r() on Linux and many other
platforms because it more gracefully supports long file names. Both
glibc and musl (and presumably all other Linux libc implementations)
guarantee that readdir() is thread-safe as long as a single DIR* is not
accessed concurrently, which is enough to make a readdir()-based
implementation of ReadDir safe. This implementation is already used for
some other OSes including Fuchsia, Redox, and Solaris.
See #40021 for more details. Fixes#86649. Fixes#34668.
Help optimize out backtraces when disabled
The comment in `rust_backtrace_env` says:
> // If the `backtrace` feature of this crate isn't enabled quickly return
> // `None` so this can be constant propagated all over the place to turn
> // optimize away callers.
but this optimization has regressed, because the only caller of this function had an alternative path that unconditionally (and pointlessly) asked for a full backtrace, so the disabled state couldn't propagate.
I've added a getter for the full format that respects the feature flag, so that the caller will now be able to really optimize out the disabled backtrace path. I've also made `rust_backtrace_env` trivially inlineable when backtraces are disabled.
Little improves in CString `new` when creating from slice
Old code already contain optimization for cases with `&str` and `&[u8]` args. This commit adds a specialization for `&mut[u8]` too.
Also, I added usage of old slice in search for zero bytes instead of new buffer because it produce better code for constant inputs on Windows LTO builds. For other platforms, this wouldn't cause any difference because it calls `libc` anyway.
Inlined `_new` method into spec trait to reduce amount of code generated to `CString::new` callers.
Remove deprecated LLVM-style inline assembly
The `llvm_asm!` was deprecated back in #87590 1.56.0, with intention to remove
it once `asm!` was stabilized, which already happened in #91728 1.59.0. Now it
is time to remove `llvm_asm!` to avoid continued maintenance cost.
Closes#70173.
Closes#92794.
Closes#87612.
Closes#82065.
cc `@rust-lang/wg-inline-asm`
r? `@Amanieu`
Add diagnostic items for macros
For use in Clippy, it adds diagnostic items to all the stable public macros
Clippy has lints that look for almost all of these (currently by name or path), but there are a few that aren't currently part of any lint, I could remove those if it's preferred to add them as needed rather than ahead of time
Implement `panic::update_hook`
Add a new function `panic::update_hook` to allow creating panic hooks that forward the call to the previously set panic hook, without race conditions. It works by taking a closure that transforms the old panic hook into a new one, while ensuring that during the execution of the closure no other thread can modify the panic hook. This is a small function so I hope it can be discussed here without a formal RFC, however if you prefer I can write one.
Consider the following example:
```rust
let prev = panic::take_hook();
panic::set_hook(Box::new(move |info| {
println!("panic handler A");
prev(info);
}));
```
This is a common pattern in libraries that need to do something in case of panic: log panic to a file, record code coverage, send panic message to a monitoring service, print custom message with link to github to open a new issue, etc. However it is impossible to avoid race conditions with the current API, because two threads can execute in this order:
* Thread A calls `panic::take_hook()`
* Thread B calls `panic::take_hook()`
* Thread A calls `panic::set_hook()`
* Thread B calls `panic::set_hook()`
And the result is that the original panic hook has been lost, as well as the panic hook set by thread A. The resulting panic hook will be the one set by thread B, which forwards to the default panic hook. This is not considered a big issue because the panic handler setup is usually run during initialization code, probably before spawning any other threads.
Using the new `panic::update_hook` function, this race condition is impossible, and the result will be either `A, B, original` or `B, A, original`.
```rust
panic::update_hook(|prev| {
Box::new(move |info| {
println!("panic handler A");
prev(info);
})
});
```
I found one real world use case here: 988cf403e7/src/detection.rs (L32) the workaround is to detect the race condition and panic in that case.
The pattern of `take_hook` + `set_hook` is very common, you can see some examples in this pull request, so I think it's natural to have a function that combines them both. Also using `update_hook` instead of `take_hook` + `set_hook` reduces the number of calls to `HOOK_LOCK.write()` from 2 to 1, but I don't expect this to make any difference in performance.
### Unresolved questions:
* `panic::update_hook` takes a closure, if that closure panics the error message is "panicked while processing panic" which is not nice. This is a consequence of holding the `HOOK_LOCK` while executing the closure. Could be avoided using `catch_unwind`?
* Reimplement `panic::set_hook` as `panic::update_hook(|_prev| hook)`?
Remove `&mut` from `io::read_to_string` signature
``@m-ou-se`` [realized][1] that because `Read` is implemented for `&mut impl
Read`, there's no need to take `&mut` in `io::read_to_string`.
Removing the `&mut` from the signature allows users to remove the `&mut`
from their calls (and thus pass an owned reader) if they don't use the
reader later.
r? `@m-ou-se`
[1]: https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/80218#issuecomment-874322129
Inline std::os::unix::ffi::OsStringExt methods
Those methods essentially do nothing at assembly level. On Unix systems, `OsString` is represented as a `Vec` without performing any transformations.
Partially stabilize `maybe_uninit_extra`
This covers:
```rust
impl<T> MaybeUninit<T> {
pub unsafe fn assume_init_read(&self) -> T { ... }
pub unsafe fn assume_init_drop(&mut self) { ... }
}
```
It does not cover the const-ness of `write` under `const_maybe_uninit_write` nor the const-ness of `assume_init_read` (this commit adds `const_maybe_uninit_assume_init_read` for that).
FCP: https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/63567#issuecomment-958590287.
Signed-off-by: Miguel Ojeda <ojeda@kernel.org>
`@m-ou-se` [realized][1] that because `Read` is implemented for `&mut impl
Read`, there's no need to take `&mut` in `io::read_to_string`.
Removing the `&mut` from the signature allows users to remove the `&mut`
from their calls (and thus pass an owned reader) if they don't use the
reader later.
[1]: https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/80218#issuecomment-874322129
Add `std::error::Report` type
This is a continuation of https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/90174, split into a separate PR since I cannot push to ```````@seanchen1991``````` 's fork
Simpilfy thread::JoinInner.
`JoinInner`'s `native` field was an `Option`, but that's unnecessary.
Also, thanks to `Arc::get_mut`, there's no unsafety needed in `JoinInner::join()`.
`WSADuplicateSocketW` returns 0 on success, which differs from
handle-oriented functions which return 0 on error. Use `sys::net::cvt`
to handle its return value, which handles the socket convention of
returning 0 on success, rather than `sys::cvt`, which handles the
handle-oriented convention of returning 0 on failure.
Eliminate "boxed" wording in `std::error::Error` documentation
In commit 29403ee, documentation for the methods on `std::any::Any` was
modified so that they referred to the concrete value behind the trait
object as the "inner" value. This is a more accurate wording than
"boxed": while putting trait objects inside boxes is arguably the most
common use, they can also be placed behind other pointer types like
`&mut` or `std::sync::Arc`.
This commit does the same documentation changes for `std::error::Error`.
Improve documentation for File::options to give a more likely example
`File::options().read(true).open(...)` is equivalent to just
`File::open`. Change the example to set the `append` flag instead, and
then change the filename to something more likely to be written in
append mode.
This covers:
impl<T> MaybeUninit<T> {
pub unsafe fn assume_init_read(&self) -> T { ... }
pub unsafe fn assume_init_drop(&mut self) { ... }
}
It does not cover the const-ness of `write` under
`const_maybe_uninit_write` nor the const-ness of
`assume_init_read` (this commit adds
`const_maybe_uninit_assume_init_read` for that).
FCP: https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/63567#issuecomment-958590287.
Signed-off-by: Miguel Ojeda <ojeda@kernel.org>
Replace usages of vec![].into_iter with [].into_iter
`[].into_iter` is idiomatic over `vec![].into_iter` because its simpler and faster (unless the vec is optimized away in which case it would be the same)
So we should change all the implementation, documentation and tests to use it.
I skipped:
* `src/tools` - Those are copied in from upstream
* `src/test/ui` - Hard to tell if `vec![].into_iter` was used intentionally or not here and not much benefit to changing it.
* any case where `vec![].into_iter` was used because we specifically needed a `Vec::IntoIter<T>`
* any case where it looked like we were intentionally using `vec![].into_iter` to test it.
`File::options().read(true).open(...)` is equivalent to just
`File::open`. Change the example to set the `append` flag instead, and
then change the filename to something more likely to be written in
append mode.
In commit 29403ee, documentation for the methods on `std::any::Any` was
modified so that they referred to the concrete value behind the trait
object as the "inner" value. This is a more accurate wording than
"boxed": while putting trait objects inside boxes is arguably the most
common use, they can also be placed behind other pointer types like
`&mut` or `std::sync::Arc`.
This commit does the same documentation changes for `std::error::Error`.
Mak DefId to AccessLevel map in resolve for export
hir_id to accesslevel in resolve and applied in privacy
using local def id
removing tracing probes
making function not recursive and adding comments
Move most of Exported/Public res to rustc_resolve
moving public/export res to resolve
fix missing stability attributes in core, std and alloc
move code to access_levels.rs
return for some kinds instead of going through them
Export correctness, macro changes, comments
add comment for import binding
add comment for import binding
renmae to access level visitor, remove comments, move fn as closure, remove new_key
fmt
fix rebase
fix rebase
fmt
fmt
fix: move macro def to rustc_resolve
fix: reachable AccessLevel for enum variants
fmt
fix: missing stability attributes for other architectures
allow unreachable pub in rustfmt
fix: missing impl access level + renaming export to reexport
Missing impl access level was found thanks to a test in clippy
Previously suggested in https://github.com/rust-lang/rfcs/issues/2854.
It makes sense to have this since `char` implements `From<u8>`. Likewise
`u32`, `u64`, and `u128` (since #79502) implement `From<char>`.
Rollup of 7 pull requests
Successful merges:
- #92092 (Drop guards in slice sorting derive src pointers from &mut T, which is invalidated by interior mutation in comparison)
- #92388 (Fix a minor mistake in `String::try_reserve_exact` examples)
- #92442 (Add negative `impl` for `Ord`, `PartialOrd` on `LocalDefId`)
- #92483 (Stabilize `result_cloned` and `result_copied`)
- #92574 (Add RISC-V detection macro and more architecture instructions)
- #92575 (ast: Always keep a `NodeId` in `ast::Crate`)
- #92583 (⬆️ rust-analyzer)
Failed merges:
r? `@ghost`
`@rustbot` modify labels: rollup
intra-doc: Make `Receiver::into_iter` into a clickable link
The documentation on `std::sync::mpsc::Iter` and `std::sync::mpsc::TryIter` provides links to the corresponding `Receiver` methods, unlike `std::sync::mpsc::IntoIter` does.
This was left out in c59b188aae
Related to #29377
Modifications to `std::io::Stdin` on Windows so that there is no longer a 4-byte buffer minimum in read().
This is an attempted fix of issue #91722, where a too-small buffer was passed to the read function of stdio on Windows. This caused an error to be returned when `read_to_end` or `read_to_string` were called. Both delegate to `std::io::default_read_to_end`, which creates a buffer that is of length >0, and forwards it to `std::io::Stdin::read()`. The latter method returns an error if the length of the buffer is less than 4, as there might not be enough space to allocate a UTF-16 character. This creates a problem when the buffer length is in `0 < N < 4`, causing the bug.
The current modification creates an internal buffer, much like the one used for the write functions
I'd also like to acknowledge the help of ``@agausmann`` and ``@hkratz`` in detecting and isolating the bug, and for suggestions that made the fix possible.
Couple disclaimers:
- Firstly, I didn't know where to put code to replicate the bug found in the issue. It would probably be wise to add that case to the testing suite, but I'm afraid that I don't know _where_ that test should be added.
- Secondly, the code is fairly fundamental to IO operations, so my fears are that this may cause some undesired side effects ~or performance loss in benchmarks.~ The testing suite runs on my computer, and it does fix the issue noted in #91722.
- Thirdly, I left the "surrogate" field in the Stdin struct, but from a cursory glance, it seems to be serving the same purpose for other functions. Perhaps merging the two would be appropriate.
Finally, this is my first pull request to the rust language, and as such some things may be weird/unidiomatic/plain out bad. If there are any obvious improvements I could do to the code, or any other suggestions, I would appreciate them.
Edit: Closes#91722
It now panic!()s on its own, rather than resume_unwind'ing the panic
payload from the thread. Using resume_unwind skips the panic_handler,
meaning that the main thread would never have a panic handler run, which
can get confusing.
- Do not `#[doc(hidden)]` the `#[derive]` macro attribute
- Add a link to the reference section to `derive`'s inherent docs
- Do the same for `#[test]` and `#[global_allocator]`
- Fix `GlobalAlloc` link (why is it on `core` and not `alloc`?)
- Try `no_inline`-ing the `std` reexports from `core`
- Revert "Try `no_inline`-ing the `std` reexports from `core`"
- Address PR review
- Also document the unstable macros
The documentation on `std::sync::mpsc::Iter` and `std::sync::mpsc::TryIter` provides links to the corresponding `Receiver` methods, unlike `std::sync::mpsc::IntoIter` does.
This was left out in c59b188aae
Related to #29377
Rollup of 7 pull requests
Successful merges:
- #84083 (Clarify the guarantees that ThreadId does and doesn't make.)
- #91593 (Remove unnecessary bounds for some Hash{Map,Set} methods)
- #92297 (Reduce compile time of rustbuild)
- #92332 (Add test for where clause order)
- #92438 (Enforce formatting for rustc_codegen_cranelift)
- #92463 (Remove pronunciation guide from Vec<T>)
- #92468 (Emit an error for `--cfg=)`)
Failed merges:
r? `@ghost`
`@rustbot` modify labels: rollup
Remove unnecessary bounds for some Hash{Map,Set} methods
This PR moves `HashMap::{into_keys,into_values,retain}` and `HashSet::retain` from `impl` blocks with `K: Eq + Hash, S: BuildHasher` into the blocks without them. It doesn't seem to me there is any reason these methods need to be bounded by that. This change brings `HashMap::{into_keys,into_values}` on par with `HashMap::{keys,values,values_mut}` which are not bounded either.
Clarify the guarantees that ThreadId does and doesn't make.
The existing documentation does not spell out whether `ThreadId`s are unique during the lifetime of a thread or of a process. I had to examine the source code to realise (pleasingly!) that they're unique for the lifetime of a process. That seems worth documenting clearly, as it's a strong guarantee.
Examining the way `ThreadId`s are created also made me realise that the `as_u64` method on `ThreadId` could be a trap for the unwary on those platforms where the platform's notion of a thread identifier is also a 64 bit integer (particularly if they happen to use a similar identifier scheme to `ThreadId`). I therefore think it's worth being even clearer that there's no relationship between the two.
Remove CommandEnv::apply
It's not being used and uses unsound set_var and remove_var functions. This is an internal function that isn't exported (even with `process_internals` feature), so this shouldn't break anything.
Also see #92365. Note that this isn't the only use of those methods in standard library, so that particular pull request will need more changes than just this to work (in particular, `test_capture_env_at_spawn` is using `set_var` and `remove_var`).
It appears `find_max_slow` comes from the BinaryHeap docs, where the
try_reserve example is a slow implementation of find_max. It has no
relevance to this code in OsString though.
Old code already contain optimization for cases with `&str` and `&[u8]` args. This commit adds a specialization for `&mut[u8]` too.
Also, I added usage of old slice in search for zero bytes instead of new buffer because it produce better code for Windows on LTO builds. For other platforms, this wouldn't cause any difference because it calls `libc` anyway.
Inlined `_new` method into spec trait to reduce amount of code generated to `CString::new` callers.
Quote bat script command line
Fixes#91991
[`CreateProcessW`](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/win32/api/processthreadsapi/nf-processthreadsapi-createprocessw#parameters) should only be used to run exe files but it does have some (undocumented) special handling for files with `.bat` and `.cmd` extensions. Essentially those magic extensions will cause the parameters to be automatically rewritten. Example pseudo Rust code (note that `CreateProcess` starts with an optional application name followed by the application arguments):
```rust
// These arguments...
CreateProcess(None, `@"foo.bat` "hello world""`@,` ...);
// ...are rewritten as
CreateProcess(Some(r"C:\Windows\System32\cmd.exe"), `@""foo.bat` "hello world"""`@,` ...);
```
However, when setting the first parameter (the application name) as we now do, it will omit the extra level of quotes around the arguments:
```rust
// These arguments...
CreateProcess(Some("foo.bat"), `@"foo.bat` "hello world""`@,` ...);
// ...are rewritten as
CreateProcess(Some(r"C:\Windows\System32\cmd.exe"), `@"foo.bat` "hello world""`@,` ...);
```
This means the arguments won't be passed to the script as intended.
Note that running batch files this way is undocumented but people have relied on this so we probably shouldn't break it.
Change Backtrace::enabled atomic from SeqCst to Relaxed
This atomic is not synchronizing anything outside of its own value, so we don't need the `Acquire`/`Release` guarantee that all memory operations prior to the store are visible after the subsequent load, nor the `SeqCst` guarantee of all threads seeing all of the sequentially consistent operations in the same order.
Using `Relaxed` reduces the overhead of `Backtrace::capture()` in the case that backtraces are not enabled.
## Benchmark
```rust
#![feature(backtrace)]
use std::backtrace::Backtrace;
use std::sync::atomic::{AtomicUsize, Ordering};
use std::thread;
use std::time::Instant;
fn main() {
let begin = Instant::now();
let mut threads = Vec::new();
for _ in 0..64 {
threads.push(thread::spawn(|| {
for _ in 0..10_000_000 {
let _ = Backtrace::capture();
static LOL: AtomicUsize = AtomicUsize::new(0);
LOL.store(1, Ordering::Release);
}
}));
}
for thread in threads {
let _ = thread.join();
}
println!("{:?}", begin.elapsed());
}
```
**Before:** 6.73 seconds
**After:** 5.18 seconds
Update stdlib to the 2021 edition
progress towards https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/88638
I couldnt find a way to run the 2018 style panic tests against 2018 so I just deleted them, maybe theres a way to do it that I missed though?
Add `io::Error::other`
This PR adds a small utility constructor, `io::Error::other`, a shorthand for `io::Error::new(io::ErrorKind::Other, err)`, something I find myself writing often.
For some concrete stats, a quick search on [grep.app](https://grep.app) shows that more than half of the uses of `io::Error::new` use `ErrorKind::Other`:
```
Error::new\((?:std::)?(?:io::)?ErrorKind:: => 3,898 results
Error::new\((?:std::)?(?:io::)?ErrorKind::Other => 2,186 results
```
Stabilize `iter::zip`
Hello all!
As the tracking issue (#83574) for `iter::zip` completed the final commenting period without any concerns being raised, I hereby submit this stabilization PR on the issue.
As the pull request that introduced the feature (#82917) states, the `iter::zip` function is a shorter way to zip two iterators. As it's generally a quality-of-life/ergonomic improvement, it has been integrated into the codebase without any trouble, and has been
used in many places across the rust compiler and standard library since March without any issues.
For more details, I would refer to `@cuviper's` original PR, or the [function's documentation](https://doc.rust-lang.org/std/iter/fn.zip.html).
Stabilize asm! and global_asm!
Tracking issue: #72016
It's been almost 2 years since the original [RFC](https://github.com/rust-lang/rfcs/pull/2850) was posted and we're finally ready to stabilize this feature!
The main changes in this PR are:
- Removing `asm!` and `global_asm!` from the prelude as per the decision in #87228.
- Stabilizing the `asm` and `global_asm` features.
- Removing the unstable book pages for `asm` and `global_asm`. The contents are moved to the [reference](https://github.com/rust-lang/reference/pull/1105) and [rust by example](https://github.com/rust-lang/rust-by-example/pull/1483).
- All links to these pages have been removed to satisfy the link checker. In a later PR these will be replaced with links to the reference or rust by example.
- Removing the automatic suggestion for using `llvm_asm!` instead of `asm!` if you're still using the old syntax, since it doesn't work anymore with `asm!` no longer being in the prelude. This only affects code that predates the old LLVM-style `asm!` being renamed to `llvm_asm!`.
- Updating `stdarch` and `compiler-builtins`.
- Updating all the tests.
r? `@joshtriplett`
They are also removed from the prelude as per the decision in
https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/87228.
stdarch and compiler-builtins are updated to work with the new, stable
asm! and global_asm! macros.
Rollup of 11 pull requests
Successful merges:
- #91668 (Remove the match on `ErrorKind::Other`)
- #91678 (Add tests fixed by #90023)
- #91679 (Move core/stream/stream/mod.rs to core/stream/stream.rs)
- #91681 (fix typo in `intrinsics::raw_eq` docs)
- #91686 (Fix `Vec::reserve_exact` documentation)
- #91697 (Delete Utf8Lossy::from_str)
- #91706 (Add unstable book entries for parts of asm that are not being stabilized)
- #91709 (Replace iterator-based set construction by *Set::From<[T; N]>)
- #91716 (Improve x.py logging and defaults a bit more)
- #91747 (Add pierwill to .mailmap)
- #91755 (Fix since attribute for const_linked_list_new feature)
Failed merges:
r? `@ghost`
`@rustbot` modify labels: rollup
Update documentation to use `from()` to initialize `HashMap`s and `BTreeMap`s
As of Rust 1.56, `HashMap` and `BTreeMap` both have associated `from()` functions. I think using these in the documentation cleans things up a bit. It allows us to remove some of the `mut`s and avoids the Initialize-Then-Modify anti-pattern.
Implement most of RFC 2930, providing the ReadBuf abstraction
This replaces the `Initializer` abstraction for permitting reading into uninitialized buffers, closing #42788.
This leaves several APIs described in the RFC out of scope for the initial implementation:
* read_buf_vectored
* `ReadBufs`
Closes#42788, by removing the relevant APIs.
Update std::env::temp_dir to use GetTempPath2 on Windows when available.
As a security measure, Windows 11 introduces a new temporary directory API, GetTempPath2.
When the calling process is running as SYSTEM, a separate temporary directory
will be returned inaccessible to non-SYSTEM processes. For non-SYSTEM processes
the behavior will be the same as before.
This can help mitigate against attacks such as this one:
https://medium.com/csis-techblog/cve-2020-1088-yet-another-arbitrary-delete-eop-a00b97d8c3e2
Compatibility risk: Software which relies on temporary files to communicate between SYSTEM and non-SYSTEM
processes may be affected by this change. In many cases, such patterns may be vulnerable to the very
attacks the new API was introduced to harden against.
I'm unclear on the Rust project's tolerance for such change-of-behavior in the standard library. If anything,
this PR is meant to raise awareness of the issue and hopefully start the conversation.
How tested: Taking the example code from the documentation and running it through psexec (from SysInternals) on
Win10 and Win11.
On Win10:
C:\test>psexec -s C:\test\main.exe
<...>
Temporary directory: C:\WINDOWS\TEMP\
On Win11:
C:\test>psexec -s C:\test\main.exe
<...>
Temporary directory: C:\Windows\SystemTemp\
Implement concat_bytes!
This implements the unstable `concat_bytes!` macro, which has tracking issue #87555. It can be used like:
```rust
#![feature(concat_bytes)]
fn main() {
assert_eq!(concat_bytes!(), &[]);
assert_eq!(concat_bytes!(b'A', b"BC", [68, b'E', 70]), b"ABCDEF");
}
```
If strings or characters are used where byte strings or byte characters are required, it suggests adding a `b` prefix. If a number is used outside of an array it suggests arrayifying it. If a boolean is used it suggests replacing it with the numeric value of that number. Doubly nested arrays of bytes are disallowed.
Emphasise that an OsStr[ing] is not necessarily a platform string
Fixes#53261
Since that issue was filed, #56141 added a further clarification to the `OsString` docs. However the ffi docs may still leave the impression that an `OsStr` is in the platform native form. This PR aims to further emphasise that an `OsStr` is not necessarily a platform string.
Add support for riscv64gc-unknown-freebsd
For https://doc.rust-lang.org/nightly/rustc/target-tier-policy.html#tier-3-target-policy:
* A tier 3 target must have a designated developer or developers (the "target maintainers") on record to be CCed when issues arise regarding the target. (The mechanism to track and CC such developers may evolve over time.)
For all Rust targets on FreeBSD, it's [rust@FreeBSD.org](mailto:rust@FreeBSD.org).
* Targets must use naming consistent with any existing targets; for instance, a target for the same CPU or OS as an existing Rust target should use the same name for that CPU or OS. Targets should normally use the same names and naming conventions as used elsewhere in the broader ecosystem beyond Rust (such as in other toolchains), unless they have a very good reason to diverge. Changing the name of a target can be highly disruptive, especially once the target reaches a higher tier, so getting the name right is important even for a tier 3 target.
Done.
* Target names should not introduce undue confusion or ambiguity unless absolutely necessary to maintain ecosystem compatibility. For example, if the name of the target makes people extremely likely to form incorrect beliefs about what it targets, the name should be changed or augmented to disambiguate it.
Done
* Tier 3 targets may have unusual requirements to build or use, but must not create legal issues or impose onerous legal terms for the Rust project or for Rust developers or users.
Done.
* The target must not introduce license incompatibilities.
Done.
* Anything added to the Rust repository must be under the standard Rust license (MIT OR Apache-2.0).
Fine with me.
* The target must not cause the Rust tools or libraries built for any other host (even when supporting cross-compilation to the target) to depend on any new dependency less permissive than the Rust licensing policy. This applies whether the dependency is a Rust crate that would require adding new license exceptions (as specified by the tidy tool in the rust-lang/rust repository), or whether the dependency is a native library or binary. In other words, the introduction of the target must not cause a user installing or running a version of Rust or the Rust tools to be subject to any new license requirements.
Done.
* If the target supports building host tools (such as rustc or cargo), those host tools must not depend on proprietary (non-FOSS) libraries, other than ordinary runtime libraries supplied by the platform and commonly used by other binaries built for the target. For instance, rustc built for the target may depend on a common proprietary C runtime library or console output library, but must not depend on a proprietary code generation library or code optimization library. Rust's license permits such combinations, but the Rust project has no interest in maintaining such combinations within the scope of Rust itself, even at tier 3.
Done.
* Targets should not require proprietary (non-FOSS) components to link a functional binary or library.
Done.
* "onerous" here is an intentionally subjective term. At a minimum, "onerous" legal/licensing terms include but are not limited to: non-disclosure requirements, non-compete requirements, contributor license agreements (CLAs) or equivalent, "non-commercial"/"research-only"/etc terms, requirements conditional on the employer or employment of any particular Rust developers, revocable terms, any requirements that create liability for the Rust project or its developers or users, or any requirements that adversely affect the livelihood or prospects of the Rust project or its developers or users.
Fine with me.
* Neither this policy nor any decisions made regarding targets shall create any binding agreement or estoppel by any party. If any member of an approving Rust team serves as one of the maintainers of a target, or has any legal or employment requirement (explicit or implicit) that might affect their decisions regarding a target, they must recuse themselves from any approval decisions regarding the target's tier status, though they may otherwise participate in discussions.
Ok.
* This requirement does not prevent part or all of this policy from being cited in an explicit contract or work agreement (e.g. to implement or maintain support for a target). This requirement exists to ensure that a developer or team responsible for reviewing and approving a target does not face any legal threats or obligations that would prevent them from freely exercising their judgment in such approval, even if such judgment involves subjective matters or goes beyond the letter of these requirements.
Ok.
* Tier 3 targets should attempt to implement as much of the standard libraries as possible and appropriate (core for most targets, alloc for targets that can support dynamic memory allocation, std for targets with an operating system or equivalent layer of system-provided functionality), but may leave some code unimplemented (either unavailable or stubbed out as appropriate), whether because the target makes it impossible to implement or challenging to implement. The authors of pull requests are not obligated to avoid calling any portions of the standard library on the basis of a tier 3 target not implementing those portions.
std is implemented.
* The target must provide documentation for the Rust community explaining how to build for the target, using cross-compilation if possible. If the target supports running tests (even if they do not pass), the documentation must explain how to run tests for the target, using emulation if possible or dedicated hardware if necessary.
Building is possible the same way as other Rust on FreeBSD targets.
* Tier 3 targets must not impose burden on the authors of pull requests, or other developers in the community, to maintain the target. In particular, do not post comments (automated or manual) on a PR that derail or suggest a block on the PR based on a tier 3 target. Do not send automated messages or notifications (via any medium, including via `@)` to a PR author or others involved with a PR regarding a tier 3 target, unless they have opted into such messages.
Ok.
* Backlinks such as those generated by the issue/PR tracker when linking to an issue or PR are not considered a violation of this policy, within reason. However, such messages (even on a separate repository) must not generate notifications to anyone involved with a PR who has not requested such notifications.
Ok.
* Patches adding or updating tier 3 targets must not break any existing tier 2 or tier 1 target, and must not knowingly break another tier 3 target without approval of either the compiler team or the maintainers of the other tier 3 target.
Ok.
* In particular, this may come up when working on closely related targets, such as variations of the same architecture with different features. Avoid introducing unconditional uses of features that another variation of the target may not have; use conditional compilation or runtime detection, as appropriate, to let each target run code supported by that target.
Ok.
std: Stabilize the `thread_local_const_init` feature
This commit is intended to follow the stabilization disposition of the
FCP that has now finished in #84223. This stabilizes the ability to flag
thread local initializers as `const` expressions which enables the macro
to generate more efficient code for accessing it, notably removing
runtime checks for initialization.
More information can also be found in #84223 as well as the tests where
the feature usage was removed in this PR.
Closes#84223
For users looking at documentation through IDE popups, this gives them
relevant information rather than the generic trait documentation wording
“Performs the conversion”. For users reading the documentation for a
specific type for any reason, this informs them when the conversion may
allocate or copy significant memory versus when it is always a move or
cheap copy.
Notes on specific cases:
* The new documentation for `From<T> for T` explains that it is not a
conversion at all.
* Also documented `impl<T, U> Into<U> for T where U: From<T>`, the other
central blanket implementation of conversion.
* I did not add documentation to conversions of a specific error type to
a more general error type.
* I did not add documentation to unstable code.
This change was prepared by searching for the text "From<... for" and so
may have missed some cases that for whatever reason did not match. I
also looked for `Into` impls but did not find any worth documenting by
the above criteria.
suppress warning about set_errno being unused on DragonFly
Other targets allow this function to be unused, DragonFly just misses out due to providing a specialization.
This fixes a build error for DragonFly.
Document how `last_os_error` should be used
It should be made clear that the state of the last OS error could change if another function call is made before the call to `Error::last_os_error()`.
Fixes: #53155
Bump compiler_builtins to 0.1.55 to bring in fixes for targets lackin…
…g atomic support.
This fixes a "Cannot select" LLVM error when compiling `compiler_builtins` for targets lacking atomics, like MSP430. Se https://github.com/rust-lang/compiler-builtins/issues/441 for more info. This PR is a more general version of #91248.
This commit is intended to follow the stabilization disposition of the
FCP that has now finished in #84223. This stabilizes the ability to flag
thread local initializers as `const` expressions which enables the macro
to generate more efficient code for accessing it, notably removing
runtime checks for initialization.
More information can also be found in #84223 as well as the tests where
the feature usage was removed in this PR.
Closes#84223
Expand `available_parallelism` docs in anticipation of cgroup quota support
The "fixed" in "fixed steady state limits" means to exclude load-dependent resource prioritization
that would calculate to 100% of capacity on an idle system and less capacity on a loaded system.
Additionally I also exclude "system load" since it would be silly to try to identify
other, perhaps higher priority, processes hogging some CPU cores that aren't explicitly excluded
by masks/quotas/whatever.
Refactor weak symbols in std::sys::unix
This makes a few changes to the weak symbol macros in `sys::unix`:
- `dlsym!` is added to keep the functionality for runtime `dlsym`
lookups, like for `__pthread_get_minstack@GLIBC_PRIVATE` that we don't
want to show up in ELF symbol tables.
- `weak!` now uses `#[linkage = "extern_weak"]` symbols, so its runtime
behavior is just a simple null check. This is also used by `syscall!`.
- On non-ELF targets (macos/ios) where that linkage is not known to
behave, `weak!` is just an alias to `dlsym!` for the old behavior.
- `raw_syscall!` is added to always call `libc::syscall` on linux and
android, for cases like `clone3` that have no known libc wrapper.
The new `weak!` linkage does mean that you'll get versioned symbols if
you build with a newer glibc, like `WEAK DEFAULT UND statx@GLIBC_2.28`.
This might seem problematic, but old non-weak symbols can tie the build
to new versions too, like `dlsym@GLIBC_2.34` from their recent library
unification. If you build with an old glibc like `dist-x86_64-linux`
does, you'll still get unversioned `WEAK DEFAULT UND statx`, which may
be resolved based on the runtime glibc.
I also found a few functions that don't need to be weak anymore:
- Android can directly use `ftruncate64`, `pread64`, and `pwrite64`, as
these were added in API 12, and our baseline is API 14.
- Linux can directly use `splice`, added way back in glibc 2.5 and
similarly old musl. Android only added it in API 21 though.
If the thread does not get the lock in the short term, yield the CPU
Reduces on [RustyHermit](https://github.com/hermitcore/rusty-hermit) the amount of wasted processor cycles
According to documentation, the listed errnos should only occur
if the `copy_file_range` call cannot be made at all, so the
assert be correct. However, since in practice file system
drivers (incl. FUSE etc.) can return any errno they want, we
should not panic here.
Fixes#91152
Mention std::io::Error::from(ErrorKind) in Error::new() docs
This conversion is not very discoverable for the cases
where an error is required without extra payload.
Simplify `for` loop desugar
Basically two intermediate bindings are inlined. I could have left one intermediate binding in place as this would simplify some diagnostic logic, but I think the difference in that regard would be negligible, so it is better to have a minimal HIR.
For checking that the pattern is irrefutable, I added a special case when the `match` is found to be non-exhaustive.
The reordering of the arms is purely stylistic. I don't *think* there are any perf implications.
```diff
match IntoIterator::into_iter($head) {
mut iter => {
$label: loop {
- let mut __next;
match Iterator::next(&mut iter) {
- Some(val) => __next = val,
None => break,
+ Some($pat) => $block,
}
- let $pat = __next;
- $block
}
}
}
```
The functions are now `unsafe` and they use `Option::unwrap_unchecked` instead of `unwrap_or_0`
`unwrap_or_0` was added in 42357d772b. I guess `unwrap_unchecked` was not available back then.
Given this example:
```rust
pub fn first_char(s: &str) -> Option<char> {
s.chars().next()
}
```
Previously, the following assembly was produced:
```asm
_ZN7example10first_char17ha056ddea6bafad1cE:
.cfi_startproc
test rsi, rsi
je .LBB0_1
movzx edx, byte ptr [rdi]
test dl, dl
js .LBB0_3
mov eax, edx
ret
.LBB0_1:
mov eax, 1114112
ret
.LBB0_3:
lea r8, [rdi + rsi]
xor eax, eax
mov r9, r8
cmp rsi, 1
je .LBB0_5
movzx eax, byte ptr [rdi + 1]
add rdi, 2
and eax, 63
mov r9, rdi
.LBB0_5:
mov ecx, edx
and ecx, 31
cmp dl, -33
jbe .LBB0_6
cmp r9, r8
je .LBB0_9
movzx esi, byte ptr [r9]
add r9, 1
and esi, 63
shl eax, 6
or eax, esi
cmp dl, -16
jb .LBB0_12
.LBB0_13:
cmp r9, r8
je .LBB0_14
movzx edx, byte ptr [r9]
and edx, 63
jmp .LBB0_16
.LBB0_6:
shl ecx, 6
or eax, ecx
ret
.LBB0_9:
xor esi, esi
mov r9, r8
shl eax, 6
or eax, esi
cmp dl, -16
jae .LBB0_13
.LBB0_12:
shl ecx, 12
or eax, ecx
ret
.LBB0_14:
xor edx, edx
.LBB0_16:
and ecx, 7
shl ecx, 18
shl eax, 6
or eax, ecx
or eax, edx
ret
```
After this change, the assembly is reduced to:
```asm
_ZN7example10first_char17h4318683472f884ccE:
.cfi_startproc
test rsi, rsi
je .LBB0_1
movzx ecx, byte ptr [rdi]
test cl, cl
js .LBB0_3
mov eax, ecx
ret
.LBB0_1:
mov eax, 1114112
ret
.LBB0_3:
mov eax, ecx
and eax, 31
movzx esi, byte ptr [rdi + 1]
and esi, 63
cmp cl, -33
jbe .LBB0_4
movzx edx, byte ptr [rdi + 2]
shl esi, 6
and edx, 63
or edx, esi
cmp cl, -16
jb .LBB0_7
movzx ecx, byte ptr [rdi + 3]
and eax, 7
shl eax, 18
shl edx, 6
and ecx, 63
or ecx, edx
or eax, ecx
ret
.LBB0_4:
shl eax, 6
or eax, esi
ret
.LBB0_7:
shl eax, 12
or eax, edx
ret
```
Adds IEEE 754-2019 minimun and maximum functions for f32/f64
IEEE 754-2019 removed the `minNum` (`min` in Rust) and `maxNum` (`max` in Rust) operations in favor of the newly created `minimum` and `maximum` operations due to their [non-associativity](https://grouper.ieee.org/groups/msc/ANSI_IEEE-Std-754-2019/background/minNum_maxNum_Removal_Demotion_v3.pdf) that cannot be fix in a backwards compatible manner. This PR adds `fN::{minimun,maximum}` functions following the new rules.
### IEEE 754-2019 Rules
> **minimum(x, y)** is x if x < y, y if y < x, and a quiet NaN if either operand is a NaN, according to 6.2.
For this operation, −0 compares less than +0. Otherwise (i.e., when x = y and signs are the same)
it is either x or y.
> **maximum(x, y)** is x if x > y, y if y > x, and a quiet NaN if either operand is a NaN, according to 6.2.
For this operation, +0 compares greater than −0. Otherwise (i.e., when x = y and signs are the
same) it is either x or y.
"IEEE Standard for Floating-Point Arithmetic," in IEEE Std 754-2019 (Revision of IEEE 754-2008) , vol., no., pp.1-84, 22 July 2019, doi: 10.1109/IEEESTD.2019.8766229.
### Implementation
This implementation is inspired by the one in [`glibc` ](90f0ac10a7/math/s_fminimum_template.c) (it self derived from the C2X draft) expect that:
- it doesn't use `copysign` because it's not available in `core` and also because `copysign` is unnecessary (we only want to check the sign, no need to create a new float)
- it also prefer `other > self` instead of `self < other` like IEEE 754-2019 does
I originally tried to implement them [using intrinsics](1d8aa13bc3) but LLVM [error out](https://godbolt.org/z/7sMrxW49a) when trying to lower them to machine intructions, GCC doesn't yet have built-ins for them, only cranelift support them nativelly (as it doesn't support the nativelly the old sementics).
Helps with https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/83984
Windows: Resolve `process::Command` program without using the current directory
Currently `std::process::Command` searches many directories for the executable to run, including the current directory. This has lead to a [CVE for `ripgrep`](https://cve.circl.lu/cve/CVE-2021-3013) but presumably other command line utilities could be similarly vulnerable if they run commands. This was [discussed on the internals forum](https://internals.rust-lang.org/t/std-command-resolve-to-avoid-security-issues-on-windows/14800). Also discussed was [which directories should be searched](https://internals.rust-lang.org/t/windows-where-should-command-new-look-for-executables/15015).
EDIT: This PR originally removed all implicit paths. They've now been added back as laid out in the rest of this comment.
## Old Search Strategy
The old search strategy is [documented here][1]. Additionally Rust adds searching the child's paths (see also #37519). So the full list of paths that were searched was:
1. The directories that are listed in the child's `PATH` environment variable.
2. The directory from which the application loaded.
3. The current directory for the parent process.
4. The 32-bit Windows system directory.
5. The 16-bit Windows system directory.
6. The Windows directory.
7. The directories that are listed in the PATH environment variable.
## New Search Strategy
The new strategy removes the current directory from the searched paths.
1. The directories that are listed in the child's PATH environment variable.
2. The directory from which the application loaded.
3. The 32-bit Windows system directory.
4. The Windows directory.
5. The directories that are listed in the parent's PATH environment variable.
Note that it also removes the 16-bit system directory, mostly because there isn't a function to get it. I do not anticipate this being an issue in modern Windows.
## Impact
Removing the current directory should fix CVE's like the one linked above. However, it's possible some Windows users of affected Rust CLI applications have come to expect the old behaviour.
This change could also affect small Windows-only script-like programs that assumed the current directory would be used. The user would need to use `.\file.exe` instead of the bare application name.
This PR could break tests, especially those that test the exact output of error messages (e.g. Cargo) as this does change the error messages is some cases.
[1]: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/win32/api/processthreadsapi/nf-processthreadsapi-createprocessa#parameters
Makes docs for references a little less confusing
- Make clear that the `Pointer` trait is related to formatting
- Make clear that the `Pointer` trait is implemented for references (previously it was confusing to first see that it's implemented and then see it in "expect")
- Make clear that `&T` (shared reference) implements `Send` (if `T: Send + Sync`)
The "fixed" in "fixed steady state limits" means to exclude load-dependent resource prioritization
that would calculate to 100% of capacity on an idle system and less capacity on a loaded system.
Additionally I also exclude "system load" since it would be silly to try to identify
other, perhaps higher priority, processes hogging some CPU cores that aren't explicitly excluded
by masks/quotas/whatever.
std: Tweak expansion of thread-local const
This commit tweaks the expansion of `thread_local!` when combined with a
`const { ... }` value to help ensure that the rules which apply to
`const { ... }` blocks will be the same as when they're stabilized.
Previously with this invocation:
thread_local!(static NAME: Type = const { init_expr });
this would generate (on supporting platforms):
#[thread_local]
static NAME: Type = init_expr;
instead the macro now expands to:
const INIT_EXPR: Type = init_expr;
#[thread_local]
static NAME: Type = INIT_EXPR;
with the hope that because `init_expr` is defined as a `const` item then
it's not accidentally allowing more behavior than if it were put into a
`static`. For example on the stabilization issue [this example][ex] now
gives the same error both ways.
[ex]: https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/84223#issuecomment-953384298
std: Get the standard library compiling for wasm64
This commit goes through and updates various `#[cfg]` as appropriate to
get the wasm64-unknown-unknown target behaving similarly to the
wasm32-unknown-unknown target. Most of this is just updating various
conditions for `target_arch = "wasm32"` to also account for `target_arch
= "wasm64"` where appropriate. This commit also lists `wasm64` as an
allow-listed architecture to not have the `restricted_std` feature
enabled, enabling experimentation with `-Z build-std` externally.
The main goal of this commit is to enable playing around with
`wasm64-unknown-unknown` externally via `-Z build-std` in a way that's
similar to the `wasm32-unknown-unknown` target. These targets are
effectively the same and only differ in their pointer size, but wasm64
is much newer and has much less ecosystem/library support so it'll still
take time to get wasm64 fully-fledged.
Rename WASI's `is_character_device` to `is_char_device`.
Rename WASI's `FileTypeExt::is_character_device` to
`FileTypeExt::is_char_device`, for consistency with the Unix
`FileTypeExt::is_char_device`.
Also, add a `FileTypeExt::is_socket` function, for consistency with the
Unix `FileTypeExt::is_socket` function.
r? `@alexcrichton`
Stabilize `const_raw_ptr_deref` for `*const T`
This stabilizes dereferencing immutable raw pointers in const contexts.
It does not stabilize `*mut T` dereferencing. This is behind the
same feature gate as mutable references.
closes https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/51911
pub use core::simd;
A portable abstraction over SIMD has been a major pursuit in recent years for several programming languages. In Rust, `std::arch` offers explicit SIMD acceleration via compiler intrinsics, but it does so at the cost of having to individually maintain each and every single such API, and is almost completely `unsafe` to use. `core::simd` offers safe abstractions that are resolved to the appropriate SIMD instructions by LLVM during compilation, including scalar instructions if that is all that is available.
`core::simd` is enabled by the `#![portable_simd]` nightly feature tracked in https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/86656 and is introduced here by pulling in the https://github.com/rust-lang/portable-simd repository as a subtree. We built the repository out-of-tree to allow faster compilation and a stochastic test suite backed by the proptest crate to verify that different targets, features, and optimizations produce the same result, so that using this library does not introduce any surprises. As these tests are technically non-deterministic, and thus can introduce overly interesting Heisenbugs if included in the rustc CI, they are visible in the commit history of the subtree but do nothing here. Some tests **are** introduced via the documentation, but these use deterministic asserts.
There are multiple unsolved problems with the library at the current moment, including a want for better documentation, technical issues with LLVM scalarizing and lowering to libm, room for improvement for the APIs, and so far I have not added the necessary plumbing for allowing the more experimental or libm-dependent APIs to be used. However, I thought it would be prudent to open this for review in its current condition, as it is both usable and it is likely I am going to learn something else needs to be fixed when bors tries this out.
The major types are
- `core::simd::Simd<T, N>`
- `core::simd::Mask<T, N>`
There is also the `LaneCount` struct, which, together with the SimdElement and SupportedLaneCount traits, limit the implementation's maximum support to vectors we know will actually compile and provide supporting logic for bitmasks. I'm hoping to simplify at least some of these out of the way as the compiler and library evolve.
This enables programmers to use a safe alternative to the current
`extern "platform-intrinsics"` API for writing portable SIMD code.
This is `#![feature(portable_simd)]` as tracked in #86656
This makes a few changes to the weak symbol macros in `sys::unix`:
- `dlsym!` is added to keep the functionality for runtime `dlsym`
lookups, like for `__pthread_get_minstack@GLIBC_PRIVATE` that we don't
want to show up in ELF symbol tables.
- `weak!` now uses `#[linkage = "extern_weak"]` symbols, so its runtime
behavior is just a simple null check. This is also used by `syscall!`.
- On non-ELF targets (macos/ios) where that linkage is not known to
behave, `weak!` is just an alias to `dlsym!` for the old behavior.
- `raw_syscall!` is added to always call `libc::syscall` on linux and
android, for cases like `clone3` that have no known libc wrapper.
The new `weak!` linkage does mean that you'll get versioned symbols if
you build with a newer glibc, like `WEAK DEFAULT UND statx@GLIBC_2.28`.
This might seem problematic, but old non-weak symbols can tie the build
to new versions too, like `dlsym@GLIBC_2.34` from their recent library
unification. If you build with an old glibc like `dist-x86_64-linux`
does, you'll still get unversioned `WEAK DEFAULT UND statx`, which may
be resolved based on the runtime glibc.
I also found a few functions that don't need to be weak anymore:
- Android can directly use `ftruncate64`, `pread64`, and `pwrite64`, as
these were added in API 12, and our baseline is API 14.
- Linux can directly use `splice`, added way back in glibc 2.5 and
similarly old musl. Android only added it in API 21 though.
Rename WASI's `FileTypeExt::is_character_device` to
`FileTypeExt::is_char_device`, for consistency with the Unix
`FileTypeExt::is_char_device`.
Also, add a `FileTypeExt::is_socket` function, for consistency with the
Unix `FileTypeExt::is_socket` function.
As discussed here
https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/88300#issuecomment-936097710
I felt this was the best place to put this (rather than next to
ExitStatusExt). After all, it's a property of the ExitStatus type on
Unix.
Signed-off-by: Ian Jackson <ijackson@chiark.greenend.org.uk>
As discussed here
https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/88300#issuecomment-936085371
exit is (conventionally) a library function, with _exit being the
actual system call.
I have checked the other references and they say "if the process
terminated by calling `exti`". I think despite the slight
imprecision (strictly, it should read iff ... `_exit`), this is
clearer. Anyone who knows about the distinction between `exit` and
`_exit` will not be confused.
`_exit` is the correct traditional name for the system call, despite
Linux calling it `exit_group` or `exit`:
https://www.freebsd.org/cgi/man.cgi?query=_exit&sektion=2&n=1
Signed-off-by: Ian Jackson <ijackson@chiark.greenend.org.uk>
Fix assertion failures in `OwnedHandle` with `windows_subsystem`.
As discussed in #88576, raw handle values in Windows can be null, such
as in `windows_subsystem` mode, or when consoles are detached from a
process. So, don't use `NonNull` to hold them, don't assert that they're
not null, and remove `OwnedHandle`'s `repr(transparent)`. Introduce a
new `HandleOrNull` type, similar to `HandleOrInvalid`, to cover the FFI
use case.
r? `@joshtriplett`
Only use `clone3` when needed for pidfd
In #89522 we learned that `clone3` is interacting poorly with Gentoo's
`sandbox` tool. We only need that for the unstable pidfd extensions, so
otherwise avoid that and use a normal `fork`.
This is a re-application of beta #89924, now that we're aware that we need
more than just a temporary release fix. I also reverted 12fbabd27f, as
that was just fallout from using `clone3` instead of `fork`.
r? `@Mark-Simulacrum`
cc `@joshtriplett`
This commit tweaks the expansion of `thread_local!` when combined with a
`const { ... }` value to help ensure that the rules which apply to
`const { ... }` blocks will be the same as when they're stabilized.
Previously with this invocation:
thread_local!(static NAME: Type = const { init_expr });
this would generate (on supporting platforms):
#[thread_local]
static NAME: Type = init_expr;
instead the macro now expands to:
const INIT_EXPR: Type = init_expr;
#[thread_local]
static NAME: Type = INIT_EXPR;
with the hope that because `init_expr` is defined as a `const` item then
it's not accidentally allowing more behavior than if it were put into a
`static`. For example on the stabilization issue [this example][ex] now
gives the same error both ways.
[ex]: https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/84223#issuecomment-953384298
This commit goes through and updates various `#[cfg]` as appropriate to
get the wasm64-unknown-unknown target behaving similarly to the
wasm32-unknown-unknown target. Most of this is just updating various
conditions for `target_arch = "wasm32"` to also account for `target_arch
= "wasm64"` where appropriate. This commit also lists `wasm64` as an
allow-listed architecture to not have the `restricted_std` feature
enabled, enabling experimentation with `-Z build-std` externally.
The main goal of this commit is to enable playing around with
`wasm64-unknown-unknown` externally via `-Z build-std` in a way that's
similar to the `wasm32-unknown-unknown` target. These targets are
effectively the same and only differ in their pointer size, but wasm64
is much newer and has much less ecosystem/library support so it'll still
take time to get wasm64 fully-fledged.
Update books
## nomicon
1 commits in 358e6a61d5f4f0496d0a81e70cdcd25d05307342..c6b4bf831e9a40aec34f53067d20634839a6778b
2021-10-20 11:23:12 -0700 to 2021-11-09 02:30:56 +0900
- Replace some use of variant with covariant (rust-lang/nomicon#322)
## book
11 commits in fd9299792852c9a368cb236748781852f75cdac6..5c5dbc5b196c9564422b3193264f3288d2a051ce
2021-10-22 21:59:46 -0400 to 2021-11-09 19:30:43 -0500
- Fix constants link.
- Fix updated anchor
- Propagate edits to chapter 2 back
- Edits to nostarch's chapter 3 edits
- ch 3 from nostarch
- Fix Cargo.toml snippet about custom derive macros
- Snapshot of chapter 9 for nostarch
- Create tmp/src for converting quotes, not sure why this broke but ok
- Update question mark to better explain where it can be used
- Clarify sentence about Results in functions that don't return Result. Fixesrust-lang/book#2912.
- Merge pull request rust-lang/book#2913 from covariant/patch-1
## rust-by-example
2 commits in 27f1ff5e440ef78828b68ab882b98e1b10d9af32..e9d45342d7a6c1def4731f1782d87ea317ba30c3
2021-10-13 08:04:40 -0300 to 2021-11-02 13:33:03 -0500
- Enums: Linked-List Needs Re-Wording (rust-lang/rust-by-example#1469)
- fix: Use the point as top left corner for `square` (rust-lang/rust-by-example#1471)
## rustc-dev-guide
13 commits in b06008731af0f7d07cd0614e820c8276dfed1c18..196ef69aa68f2cef44f37566ee7db37daf00301b
2021-10-21 15:13:09 -0500 to 2021-11-07 07:48:47 -0600
- Fix typo: [upv.rs_mentioned] -> [upvars_mentioned]
- Add note to emphasize replacing TARGET_TRIPLE (rust-lang/rustc-dev-guide#1250)
- Remove some legacy test suites.
- tiny capitalization fix
- Fix date
- Update some date-check comments
- Ensure date-check cron job is using latest stable Rust
- enhance subtree docs, link to clippy docs
- Edit introduction to bootstrapping
- Some minor adjustments to the diagnostic documentation
- Edit "About this guide" for semantic line feeds
- Fix `rustc_mir` related links (rust-lang/rustc-dev-guide#1228)
- Add documentation for LLVM CFI support
## edition-guide
3 commits in 7c0088ca744d293a5f4b1e2ac378e7c23d30fe55..27f4a84d3852e9416cae5861254fa53a825c56bd
2021-10-05 13:28:05 +0200 to 2021-11-08 10:13:20 -0500
- Add a missing period (rust-lang/edition-guide#271)
- Fix syntax error in code example (rust-lang/edition-guide#270)
- Fixed an example error of prelude.md (rust-lang/edition-guide#269)
Hashing does not have to use the whole Components parsing machinery because we only need it to match the
normalizations that Components does.
* stripping redundant separators -> skipping separators
* stripping redundant '.' directories -> skipping '.' following after a separator
That's all it takes.
And instead of hashing individual slices for each component we feed the bytes directly into the hasher which avoids
hashing the length of each component in addition to its contents.
Make `std:🧵:available_concurrency` support process-limited number of CPUs
Use `libc::sched_getaffinity` and count the number of CPUs in the returned mask. This handles cases where the process doesn't have access to all CPUs, such as when limited via `taskset` or similar.
This also covers cgroup cpusets.
This stabilizes dereferencing immutable raw pointers in const contexts.
It does not stabilize `*mut T` dereferencing. This is placed behind the
`const_raw_mut_ptr_deref` feature gate.
In #89522 we learned that `clone3` is interacting poorly with Gentoo's
`sandbox` tool. We only need that for the unstable pidfd extensions, so
otherwise avoid that and use a normal `fork`.
Replace `std::os::raw::c_ssize_t` with `std::os::raw::c_ptrdiff_t`
The discussions in #88345 brought up that `ssize_t` is not actually the signed index type defined in stddef.h, but instead it's `ptrdiff_t`. It seems pretty clear that the use of `ssize_t` here was a mistake on my part, and that if we're going to bother having a isize-alike for FFI in `std::os::raw`, it should be `ptrdiff_t` and not `ssize_t`.
Anyway, both this and `c_size_t` are dubious in the face of the discussion in https://internals.rust-lang.org/t/pre-rfc-usize-is-not-size-t/15369, and any RFC/project-group/etc that handles those issues there should contend with these types in some manner, but that doesn't mean we shouldn't fix something wrong like this, even if it is unstable.
All that said, `size_t` is *vastly* more common in function signatures than either `ssize_t` or `ptrdiff_t`, so I'm going to update the tracking issue's list of unresolved questions to note that perhaps we only want `c_size_t` — I mostly added the signed version for symmetry, rather than to meet a need. (Given this, I'm also fine with modifying this patch to instead remove `c_ssize_t` without a replacement)
CC `@magicant` (who brought the issue up)
CC `@chorman0773` (who has a significantly firmer grasp on the minutae of the C standard than I do)
r? `@joshtriplett` (original reviewer, active in the discussions around this)
Windows thread-local keyless drop
`#[thread_local]` allows us to maintain a per-thread list of destructors. This also avoids the need to synchronize global data (which is particularly tricky within the TLS callback function).
r? `@alexcrichton`
Add JoinHandle::is_running.
This adds:
```rust
impl<T> JoinHandle<T> {
/// Checks if the the associated thread is still running its main function.
///
/// This might return `false` for a brief moment after the thread's main
/// function has returned, but before the thread itself has stopped running.
pub fn is_running(&self) -> bool;
}
```
The usual way to check if a background thread is still running is to set some atomic flag at the end of its main function. We already do that, in the form of dropping an Arc which will reduce the reference counter. So we might as well expose that information.
This is useful in applications with a main loop (e.g. a game, gui, control system, ..) where you spawn some background task, and check every frame/iteration whether the background task is finished to .join() it in that frame/iteration while keeping the program responsive.
`#[thread_local]` allows us to maintain a per-thread list of destructors. This also avoids the need to synchronize global data (which is particularly tricky within the TLS callback function).
Add #[must_use] to remaining std functions (O-Z)
I've run out of compelling reasons to group functions together across crates so I'm just going to go module-by-module. This is half of the remaining items from the `std` crate, from O-Z.
`panicking::take_hook` has a side effect: it unregisters the current panic hook, returning it. I almost ignored it, but the documentation example shows `let _ = panic::take_hook();`, so following suit I went ahead and added a `#[must_use]`.
```rust
std::panicking fn take_hook() -> Box<dyn Fn(&PanicInfo<'_>) + 'static + Sync + Send>;
```
I added these functions that clippy did not flag:
```rust
std::path::Path fn starts_with<P: AsRef<Path>>(&self, base: P) -> bool;
std::path::Path fn ends_with<P: AsRef<Path>>(&self, child: P) -> bool;
std::path::Path fn with_file_name<S: AsRef<OsStr>>(&self, file_name: S) -> PathBuf;
std::path::Path fn with_extension<S: AsRef<OsStr>>(&self, extension: S) -> PathBuf;
```
Parent issue: #89692
r? `@joshtriplett`
Add #[must_use] to expensive computations
The unifying theme for this commit is weak, admittedly. I put together a list of "expensive" functions when I originally proposed this whole effort, but nobody's cared about that criterion. Still, it's a decent way to bite off a not-too-big chunk of work.
Given the grab bag nature of this commit, the messages I used vary quite a bit. I'm open to wording changes.
For some reason clippy flagged four `BTreeSet` methods but didn't say boo about equivalent ones on `HashSet`. I stared at them for a while but I can't figure out the difference so I added the `HashSet` ones in.
```rust
// Flagged by clippy.
alloc::collections::btree_set::BTreeSet<T> fn difference<'a>(&'a self, other: &'a BTreeSet<T>) -> Difference<'a, T>;
alloc::collections::btree_set::BTreeSet<T> fn symmetric_difference<'a>(&'a self, other: &'a BTreeSet<T>) -> SymmetricDifference<'a, T>
alloc::collections::btree_set::BTreeSet<T> fn intersection<'a>(&'a self, other: &'a BTreeSet<T>) -> Intersection<'a, T>;
alloc::collections::btree_set::BTreeSet<T> fn union<'a>(&'a self, other: &'a BTreeSet<T>) -> Union<'a, T>;
// Ignored by clippy, but not by me.
std::collections::HashSet<T, S> fn difference<'a>(&'a self, other: &'a HashSet<T, S>) -> Difference<'a, T, S>;
std::collections::HashSet<T, S> fn symmetric_difference<'a>(&'a self, other: &'a HashSet<T, S>) -> SymmetricDifference<'a, T, S>
std::collections::HashSet<T, S> fn intersection<'a>(&'a self, other: &'a HashSet<T, S>) -> Intersection<'a, T, S>;
std::collections::HashSet<T, S> fn union<'a>(&'a self, other: &'a HashSet<T, S>) -> Union<'a, T, S>;
```
Parent issue: #89692
r? ```@joshtriplett```
Stabilize `is_symlink()` for `Metadata` and `Path`
I'm not fully sure about `since` version, correct me if I'm wrong
Needs update after stabilization: [cargo-test-support](8063672238/crates/cargo-test-support/src/paths.rs (L202))
Linked issue: #85748
Use libc::sched_getaffinity and count the number of CPUs in the returned
mask. This handles cases where the process doesn't have access to all
CPUs, such as when limited via taskset or similar.
Automatically convert paths to verbatim for filesystem operations that support it
This allows using longer paths without the user needing to `canonicalize` or manually prefix paths. If the path is already verbatim then this has no effect.
Fixes: #32689
Rollup of 5 pull requests
Successful merges:
- #90239 (Consistent big O notation in map.rs)
- #90267 (fix: inner attribute followed by outer attribute causing ICE)
- #90288 (Add hint for people missing `TryFrom`, `TryInto`, `FromIterator` import pre-2021)
- #90304 (Add regression test for #75961)
- #90344 (Add tracking issue number to const_cstr_unchecked)
Failed merges:
r? `@ghost`
`@rustbot` modify labels: rollup
Clean up special function const checks
Mark them as const and `#[rustc_do_not_const_check]` instead of hard-coding them in const-eval checks.
r? `@oli-obk`
`@rustbot` label A-const-eval T-compiler
Remove fNN::lerp
Lerp is [surprisingly complex with multiple tradeoffs depending on what guarantees you want to provide](https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/86269#issuecomment-869108301) (and what you're willing to drop for raw speed), so we don't have consensus on what implementation to use, let alone what signature - `t.lerp(a, b)` nicely puts `a, b` together, but makes dispatch to lerp custom types with the same signature basically impossible, and major ecosystem crates (e.g. nalgebra, glium) use `a.lerp(b, t)`, which is easily confusable. It was suggested to maybe provide a `Lerp<T>` trait and `t.lerp([a, b])`, which _could_ be implemented by downstream math libraries for their types, but also significantly raises the bar from a simple fNN method to a full trait, and does nothing to solve the implementation question. (It also raises the question of whether we'd support higher-order bezier interpolation.)
The only consensus we have is the lack of consensus, and the [general temperature](https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/86269#issuecomment-951347135) is that we should just remove this method (giving the method space back to 3rd party libs) and revisit this if (and likely only if) IEEE adds lerp to their specification.
If people want a lerp, they're _probably_ already using (or writing) a math support library, which provides a lerp function for its custom math types and can provide the same lerp implementation for the primitive types via an extension trait.
See also [previous Zulip discussion](https://rust-lang.zulipchat.com/#narrow/stream/219381-t-libs/topic/lerp.20API.20design)
cc ``@clarfonthey`` (original PR author), ``@m-ou-se`` (original r+), ``@scottmcm`` (last voice in tracking issue, prompted me to post this)
Closes#86269 (removed)
Stabilise unix_process_wait_more, extra ExitStatusExt methods
This stabilises the feature `unix_process_wait_more`. Tracking issue #80695, FCP needed.
This was implemented in #79982 and merged in January.
My change to use `Type::def_id()` (formerly `Type::def_id_full()`) in
more places caused some docs to show up that used to be missed by
rustdoc. Those docs contained unescaped square brackets, which triggered
linkcheck errors. This commit escapes the square brackets and adds this
particular instance to the linkcheck exception list.
Inline CStr::from_ptr
Inlining this function is valuable, as it allows LLVM to apply `strlen`-specific optimizations without having to enable LTO.
For instance, the following function:
```rust
pub fn f(p: *const c_char) -> Option<u8> {
unsafe { CStr::from_ptr(p) }.to_bytes().get(0).copied()
}
```
Looks like this if `CStr::from_ptr` is allowed to be inlined.
```asm
before:
push rax
call qword ptr [rip + std::ffi::c_str::CStr::from_ptr@GOTPCREL]
mov rcx, rax
cmp rdx, 1
sete dl
test rax, rax
sete al
or al, dl
jne .LBB1_2
mov dl, byte ptr [rcx]
.LBB1_2:
xor al, 1
pop rcx
ret
after:
mov dl, byte ptr [rdi]
test dl, dl
setne al
ret
```
Note that optimization turned this from O(N) to O(1) in terms of performance, as LLVM knows that it doesn't really need to call `strlen` to determine whether a string is empty or not.
Stabilize feature `saturating_div` for rust 1.58.0
The tracking issue is #89381
This seems like a reasonable simple change(?). The feature `saturating_div` was added as part of the ongoing effort to implement a `Saturating` integer type (see #87921). The implementation has been discussed [here](https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/87921#issuecomment-899357720) and [here](https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/87921#discussion_r691888556). It extends the list of saturating operations on integer types (like `saturating_add`, `saturating_sub`, `saturating_mul`, ...) by the function `fn saturating_div(self, rhs: Self) -> Self`.
The stabilization of the feature `saturating_int_impl` (for the `Saturating` type) needs to have this stabilized first.
Closes#89381
Previously, it wasn't clear whether "This could include" was referring
to logic errors, or undefined behaviour. Tweak wording to clarify this
sentence does not relate to UB.
Stabilize CString::from_vec_with_nul[_unchecked]
Closes the tracking issue #73179. I am keeping this in _draft_ mode until the FCP has ended.
This is my first time stabilizing a feature, so I would appreciate any guidance on things I should do differently.
Closes#73179
Remove unnecessary condition in Barrier::wait()
This is my first pull request for Rust, so feel free to call me out if anything is amiss.
After some examination, I realized that the second condition of the "spurious-wakeup-handler" loop in ``std::sync::Barrier::wait()`` should always evaluate to ``true``, making it redundant in the ``&&`` expression.
Here is the affected function before the fix:
```rust
#[stable(feature = "rust1", since = "1.0.0")]
pub fn wait(&self) -> BarrierWaitResult {
let mut lock = self.lock.lock().unwrap();
let local_gen = lock.generation_id;
lock.count += 1;
if lock.count < self.num_threads {
// We need a while loop to guard against spurious wakeups.
// https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Spurious_wakeup
while local_gen == lock.generation_id && lock.count < self.num_threads { // fixme
lock = self.cvar.wait(lock).unwrap();
}
BarrierWaitResult(false)
} else {
lock.count = 0;
lock.generation_id = lock.generation_id.wrapping_add(1);
self.cvar.notify_all();
BarrierWaitResult(true)
}
}
```
At first glance, it seems that the check that ``lock.count < self.num_threads`` would be necessary in order for a thread A to detect when another thread B has caused the barrier to reach its thread count, making thread B the "leader".
However, the control flow implicitly results in an invariant that makes observing ``!(lock.count < self.num_threads)``, i.e. ``lock.count >= self.num_threads`` impossible from thread A.
When thread B, which will be the leader, calls ``.wait()`` on this shared instance of the ``Barrier``, it locks the mutex in the first line and saves the ``MutexGuard`` in the ``lock`` variable. It then increments the value of ``lock.count``. However, it then proceeds to check if ``lock.count < self.num_threads``. Since it is the leader, it is the case that (after the increment of ``lock.count``), the lock count is *equal* to the number of threads. Thus, the second branch is immediately taken and ``lock.count`` is zeroed. Additionally, the generation ID is incremented (with wrap). Then, the condition variable is signalled. But, the other threads are waiting at the line ``lock = self.cvar.wait(lock).unwrap();``, so they cannot resume until thread B's call to ``Barrier::wait()`` returns, which drops the ``MutexGuard`` acquired in the first ``let`` statement and unlocks the mutex.
The order of events is thus:
1. A thread A calls `.wait()`
2. `.wait()` acquires the mutex, increments `lock.count`, and takes the first branch
3. Thread A enters the ``while`` loop since the generation ID has not changed and the count is less than the number of threads for the ``Barrier``
3. Spurious wakeups occur, but both conditions hold, so the thread A waits on the condition variable
4. This process repeats for N - 2 additional times for non-leader threads A'
5. *Meanwhile*, Thread B calls ``Barrier::wait()`` on the same barrier that threads A, A', A'', etc. are waiting on. The thread count reaches the number of threads for the ``Barrier``, so all threads should now proceed, with B being the leader. B acquires the mutex and increments the value ``lock.count`` only to find that it is not less than ``self.num_threads``. Thus, it immediately clamps ``self.num_threads`` back down to 0 and increments the generation. Then, it signals the condvar to tell the A (prime) threads that they may continue.
6. The A, A', A''... threads wake up and attempt to re-acquire the ``lock`` as per the internal operation of a condition variable. When each A has exclusive access to the mutex, it finds that ``lock.generation_id`` no longer matches ``local_generation`` **and the ``&&`` expression short-circuits -- and even if it were to evaluate it, ``self.count`` is definitely less than ``self.num_threads`` because it has been reset to ``0`` by thread B *before* B dropped its ``MutexGuard``**.
Therefore, it my understanding that it would be impossible for the non-leader threads to ever see the second boolean expression evaluate to anything other than ``true``. This PR simply removes that condition.
Any input would be appreciated. Sorry if this is terribly verbose. I'm new to the Rust community and concurrency can be hard to explain in words. Thanks!
Reject octal zeros in IPv4 addresses
This fixes#86964 by rejecting octal zeros in IP addresses, such that `192.168.00.00000000` is rejected with a parse error, since having leading zeros in front of another zero indicates it is a zero written in octal notation, which is not allowed in the strict mode specified by RFC 6943 3.1.1. Octal rejection was implemented in #83652, but due to the way it was implemented octal zeros were still allowed.
As a security measure, Windows 11 introduces a new temporary directory API, GetTempPath2.
When the calling process is running as SYSTEM, a separate temporary directory
will be returned inaccessible to non-SYSTEM processes. For non-SYSTEM processes
the behavior will be the same as before.
removing TLS support in x86_64-unknown-none-hermitkernel
HermitCore's kernel itself doesn't support TLS. Consequently, the entries in x86_64-unknown-none-hermitkernel should be removed. This commit should help to finalize #89062.
linux/aarch64 Now() should be actually_monotonic()
While issues have been seen on arm64 platforms the Arm architecture requires
that the counter monotonically increases and that it must provide a uniform
view of system time (e.g. it must not be possible for a core to receive a
message from another core with a time stamp and observe time going backwards
(ARM DDI 0487G.b D11.1.2). While there have been a few 64bit SoCs that have
bugs (#49281, #56940) which cause time to not monotonically increase, these have
been fixed in the Linux kernel and we shouldn't penalize all Arm SoCs for those
who refuse to update their kernels:
SUN50I_ERRATUM_UNKNOWN1 - Allwinner A64 / Pine A64 - fixed in 5.1
FSL_ERRATUM_A008585 - Freescale LS2080A/LS1043A - fixed in 4.10
HISILICON_ERRATUM_161010101 - Hisilicon 1610 - fixed in 4.11
ARM64_ERRATUM_858921 - Cortex A73 - fixed in 4.12
255a3f3e18 std: Force `Instant::now()` to be monotonic added a Mutex to work around
this problem and a small test program using glommio shows the majority of time spent
acquiring and releasing this Mutex. 3914a7b0da tries to improve this, but actually
makes it worse on big systems as for 128b atomics a ldxp/stxp pair (and successful loop)
for v8.4 systems that don't support FEAT_LSE2 is required which is expensive as a lock
and because of how the load/store-exclusives scale on large Arm systems is both unfair
to threads and tends to go backwards in performance.
A small sample program using glommio improves by 70x on a 32 core Graviton2
system with this change.
[fuchsia] Update process info struct
The fuchsia platform is in the process of softly transitioning over to
using a new value for ZX_INFO_PROCESS with a new corresponding struct.
This change migrates libstd.
See [fxrev.dev/510478](https://fxrev.dev/510478) and [fxbug.dev/30751](https://fxbug.dev/30751) for more detail.
Add abstract namespace support for Unix domain sockets
Hello! The other day I wanted to mess around with UDS in Rust and found that abstract namespaces ([unix(7)](https://man7.org/linux/man-pages/man7/unix.7.html)) on Linux still needed development. I took the approach of adding `_addr` specific public functions to reduce conflicts.
Feature name: `unix_socket_abstract`
Tracking issue: #85410
Further context: #42048
## Non-platform specific additions
`UnixListener::bind_addr(&SocketAddr) -> Result<UnixListener>`
`UnixStream::connect_addr(&SocketAddr) -> Result<()>`
`UnixDatagram::bind_addr(&SocketAddr) -> Result<UnixDatagram>`
`UnixDatagram::connect_addr(&SocketAddr) -> Result<()>`
`UnixDatagram::send_to_addr(&self, &[u8], &SocketAddr) -> Result<usize>`
## Platform-specific (Linux) additions
`SocketAddr::from_abstract_namespace(&[u8]) -> SocketAddr`
`SockerAddr::as_abstract_namespace() -> Option<&[u8]>`
## Example
```rust
#![feature(unix_socket_abstract)]
use std::os::unix::net::{UnixListener, SocketAddr};
fn main() -> std::io::Result<()> {
let addr = SocketAddr::from_abstract_namespace(b"namespace")?; // Linux only
let listener = match UnixListener::bind_addr(&addr) {
Ok(sock) => sock,
Err(err) => {
println!("Couldn't bind: {:?}", err);
return Err(err);
}
};
Ok(())
}
```
## Further Details
The main inspiration for the implementation came from the [nix-rust](https://github.com/nix-rust/nix/blob/master/src/sys/socket/addr.rs#L558) crate but there are also other [historical](c4db0685b1) [attempts](https://github.com/tormol/uds/blob/master/src/addr.rs#L324) with similar approaches.
A comment I did have was with this change, we now allow a `SocketAddr` to be constructed explicitly rather than just used almost as a handle for the return of `peer_addr` and `local_addr`. We could consider adding other explicit constructors (e.g. `SocketAddr::from_pathname`, `SockerAddr::from_unnamed`).
Cheers!
Use BCryptGenRandom instead of RtlGenRandom on Windows.
This removes usage of RtlGenRandom on Windows, in favour of BCryptGenRandom.
BCryptGenRandom isn't available on XP, but we dropped XP support a while ago.
The fuchsia platform is in the process of softly transitioning over to
using a new value for ZX_INFO_PROCESS with a new corresponding struct.
This change migrates libstd.
See fxrev.dev/510478 and fxbug.dev/30751 for more detail.
Fix ctrl-c causing reads of stdin to return empty on Windows.
Pressing ctrl+c (or ctrl+break) on Windows caused a blocking read of stdin to unblock and return empty, unlike other platforms which continue to block.
On ctrl-c, `ReadConsoleW` will return success, but also set `LastError` to `ERROR_OPERATION_ABORTED`.
This change detects this case, and re-tries the call to `ReadConsoleW`.
Fixes#89177. See issue for further details.
Tested on Windows 7 and Windows 10 with both MSVC and GNU toolchains
Improve `std:🧵:available_parallelism` docs
_Tracking issue: https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/74479_
This PR reworks the documentation of `std:🧵:available_parallelism`, as requested [here](https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/89324#issuecomment-934343254).
## Changes
The following changes are made:
- We've removed prior mentions of "hardware threads" and instead centers the docs around "parallelism" as a resource available to a program.
- We now provide examples of when `available_parallelism` may return numbers that differ from the number of CPU cores in the host machine.
- We now mention that the amount of available parallelism may change over time.
- We make note of which platform components we don't take into account which more advanced users may want to take note of.
- The example has been updated, which should be a bit easier to use.
- We've added a docs alias to `num-cpus` which provides similar functionality to `available_parallelism`, and is one of the most popular crates on crates.io.
---
Thanks!
r? `@BurntSushi`
The unifying theme for this commit is weak, admittedly. I put together a
list of "expensive" functions when I originally proposed this whole
effort, but nobody's cared about that criterion. Still, it's a decent
way to bite off a not-too-big chunk of work.
Given the grab bag nature of this commit, the messages I used vary quite
a bit.
Add #[must_use] to is_condition tests
I threw in `std::path::Path::has_root` for funsies.
A continuation of #89718.
Parent issue: #89692
r? ```@joshtriplett```
Add #[must_use] to non-mutating verb methods
These are methods that could be misconstrued to mutate their input, similar to #89694. I gave each one a different custom message.
I wrote that `upgrade` and `downgrade` don't modify the input pointers. Logically they don't, but technically they do...
Parent issue: #89692
r? ```@joshtriplett```