Rename BoxMeUp to PanicPayload.
"BoxMeUp" is not very clear. Let's rename that to a description of what it actually represents: a panic payload.
This PR also renames the structs that implement this trait to have more descriptive names.
Part of https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/116005
r? `@oli-obk`
Simplify/Optimize FileEncoder
FileEncoder is basically a BufWriter except that it exposes access to the not-written-to-yet region of the buffer so that some users can write directly to the buffer. This strategy is awesome because it lets us avoid calling memcpy for small copies, but the previous strategy was based on the writer accessing a `&mut [MaybeUninit<u8>; N]` and returning a `&[u8]` which is an API which currently mandates the use of unsafe code, making that interface in general not that appealing.
So this PR cleans up the FileEncoder implementation and builds on that general idea of direct buffer access in order to prevent `memcpy` calls in a few key places when encoding the dep graph and rmeta tables. The interface used here is now 100% safe, but with the caveat that internally we need to avoid trusting the number of bytes that the provided function claims to have written.
The original primary objective of this PR was to clean up the FileEncoder implementation so that the fix for the following issues would be easy to implement. The fix for these issues is to correctly update self.buffered even when writes fail, which I think it's easy to verify manually is now done, because all the FileEncoder methods are small.
Fixes https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/115298
Fixes https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/114671
Fixes https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/114045
Fixes https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/108100
Fixes https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/106787
Refactor `thread_info` to remove the `RefCell`
`thread_info` currently uses `RefCell`-based initialization. Refactor this to use `OnceCell` instead which is more performant and better suits the needs of one-time initialization.
This is nobody's bottleneck but OnceCell checks are a single `cmp` vs. `RefCell<Option>` needing runtime logic
Don't modify libstd to dump rustc ICEs
Do a much simpler thing and just dump a `std::backtrace::Backtrace` to file.
r? `@estebank` `@oli-obk`
Fixes#115610
Add initial libstd support for Xous
This patchset adds some minimal support to the tier-3 target `riscv32imac-unknown-xous-elf`. The following features are supported:
* alloc
* thread creation and joining
* thread sleeping
* thread_local
* panic_abort
* mutex
* condvar
* stdout
Additionally, internal support for the various Xous primitives surrounding IPC have been added as part of the Xous FFI. These may be exposed as part of `std::os::xous::ffi` in the future, however for now they are not public.
This represents the minimum viable product. A future patchset will add support for networking and filesystem support.
get rid of duplicate primitive_docs
Having this duplicate makes editing that file very annoying. And at least locally the generated docs still look perfectly fine...
Add `minmax{,_by,_by_key}` functions to `core::cmp`
This PR adds the following functions:
```rust
// mod core::cmp
#![unstable(feature = "cmp_minmax")]
pub fn minmax<T>(v1: T, v2: T) -> [T; 2]
where
T: Ord;
pub fn minmax_by<T, F>(v1: T, v2: T, compare: F) -> [T; 2]
where
F: FnOnce(&T, &T) -> Ordering;
pub fn minmax_by_key<T, F, K>(v1: T, v2: T, mut f: F) -> [T; 2]
where
F: FnMut(&T) -> K,
K: Ord;
```
(they are also `const` under `#[feature(const_cmp)]`, I've omitted `const` stuff for simplicity/readability)
----
Semantically these functions are equivalent to `{ let mut arr = [v1, v2]; arr.sort(); arr }`, but since they operate on 2 elements only, they are implemented as a single comparison.
Even though that's basically a sort, I think "sort 2 elements" operation is useful on it's own in many cases. Namely, it's a common pattern when you have 2 things, and need to know which one is smaller/bigger to operate on them differently.
I've wanted such functions countless times, most recently in #109402, so I thought I'd propose them.
----
r? libs-api
Small wins for formatting-related code
This PR does two small wins in fmt code:
- Override `write_char` for `PadAdapter` to use inner buffer's `write_char`
- Override some `write_fmt` implementations to avoid avoid the additional indirection and vtable generated by the default impl.
make `Debug` impl for `ascii::Char` match that of `char`
# Objective
use a more recognisable format for the `Debug` impl on `ascii::Char` than the derived one based off the enum variants. The alogorithm used is the following:
- escape `ascii::Char::{Null, CharacterTabulation, CarraigeReturn, LineFeed, ReverseSolidus, Apostrophe}` to `'\0'`, `'\t'`, `'\r'`, `'\n'`, `'\\'` and `'\''` respectively. these are the same escape codes as `<char as Debug>::fmt` uses.
- if `u8::is_ascii_control` is false, print the character wrapped in single quotes.
- otherwise, print in the format `'\xAB'` where `A` and `B` are the hex nibbles of the byte. (`char` uses unicode escapes and this seems like the corresponding ascii format).
Tracking issue: https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/110998
impl Step for IP addresses
ACP: rust-lang/libs-team#235
Note: since this is insta-stable, it requires an FCP.
Separating out from the bit operations PR since it feels logically disjoint, and so their FCPs can be separate.
Update doc for `alloc::format!` and `core::concat!`
Closes#115551.
Used comments instead of `assert!`s as [`std::fmt`](https://doc.rust-lang.org/std/fmt/index.html#usage) uses comments.
Should all the str-related macros (`format!`, `format_args!`, `concat!`, `stringify!`, `println!`, `writeln!`, etc.) references each others? For instance, [`concat!`](https://doc.rust-lang.org/core/macro.concat.html) mentions that integers are stringified, but don't link to `stringify!`.
`@rustbot` label +A-docs +A-fmt
Specialize count for range iterators
Since `size_hint` is already specialized, it feels apt to specialize `count` as well. Without any specialized version of `ExactSizeIterator::len` or `Step::steps_between`, this feels like a more reliable way of accessing this without having to rely on knowing that `size_hint` is correct.
In my case, this is particularly useful to access the `steps_between` implementation for `char` from the standard library without having to compute it manually.
I didn't think it was worth modifying the `Step` trait to add a version of `steps_between` that used native overflow checks since this is just doing one subtraction in most cases anyway, and so I decided to make the inclusive version use `checked_add` so it didn't have this lopsided overflow-checks-but-only-sometimes logic.
clarify that unsafe code must not rely on our safe traits
This adds a disclaimer to PartialEq, Eq, PartialOrd, Ord, Hash, Deref, DerefMut.
We already have a similar disclaimer in ExactSizeIterator (worded a bit differently):
```
/// Note that this trait is a safe trait and as such does *not* and *cannot*
/// guarantee that the returned length is correct. This means that `unsafe`
/// code **must not** rely on the correctness of [`Iterator::size_hint`]. The
/// unstable and unsafe [`TrustedLen`](super::marker::TrustedLen) trait gives
/// this additional guarantee.
```
If there are any other traits that should carry such a disclaimer, please let me know.
Fixes https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/73682
Make useless_ptr_null_checks smarter about some std functions
This teaches the `useless_ptr_null_checks` lint that some std functions can't ever return null pointers, because they need to point to valid data, get references as input, etc.
This is achieved by introducing an `#[rustc_never_returns_null_ptr]` attribute and adding it to these std functions (gated behind bootstrap `cfg_attr`).
Later on, the attribute could maybe be used to tell LLVM that the returned pointer is never null. I don't expect much impact of that though, as the functions are pretty shallow and usually the input data is already never null.
Follow-up of PR #113657Fixes#114442
Rework `no_coverage` to `coverage(off)`
As discussed at the tail of https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/84605 this replaces the `no_coverage` attribute with a `coverage` attribute that takes sub-parameters (currently `off` and `on`) to control the coverage instrumentation.
Allows future-proofing for things like `coverage(off, reason="Tested live", issue="#12345")` or similar.
`thread_info` currently uses `RefCell`-based initialization. Refactor
this to use `OnceCell` instead which is more performant and better suits
the needs of one-time initialization.
Allow redirecting subprocess stdout to our stderr etc. (redux)
This is the code from #88561, tidied up, including review suggestions, and with the for-testing-only CI commit removed. FCP for the API completed in #88561.
I have made a new MR to facilitate review. The discussion there is very cluttered and the branch is full of changes (in many cases as a result of changes to other Rust stdlib APIs since then). Assuming this MR is approvedl we should close that one.
### Reviewer doing a de novo review
Just code review these four commits.. FCP discussion starts here: https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/88561#issuecomment-1640527595
Portability tests: you can see that this branch works on Windows too by looking at the CI results in #88561, which has the same code changes as this branch but with an additional "DO NOT MERGE" commit to make the Windows tests run.
### Reviewer doing an incremental review from some version of #88561
Review the new commits since your last review. I haven't force pushed the branch there.
git diff the two branches (eg `git diff 176886197d6..0842b69c219`). You'll see that the only difference is in gitlab CI files. You can also see that *this* MR doesn't touch those files.
This implementation is wrong. Like the impl for From<File>, it is
forced to panic because process::Stdio in unsupported/process.rs
doesn't have a suitable variant.
The root cause of the problem is that process::Stdio in
unsupported/process.rs has any information in it at all.
I'm pretty sure that it should just be a unit struct. However,
making that build on all platforms is going to be a lot of work,
iterating through CI and/or wrestling Docker.
I don't think this extra panic is making things significantly worse.
For now I have added some TODOs.
Clarify stability guarantee for lifetimes in enum discriminants
Since `std::mem::Discriminant` erases lifetimes, it should be clarified that changing the concrete value of a lifetime parameter does not change the value of an enum discriminant for a given variant. This is useful as it guarantees that it is safe to transmute `Discriminant<Foo<'a>>` to `Discriminant<Foo<'b>>` for any combination of `'a` and `'b`. This also holds for type-generics as long as the type parameters do not change, e.g. `Discriminant<Foo<T, 'a>>` can be transmuted to `Discriminant<Foo<T, 'b>>`.
Side note: Is what I've written actually enough to imply soundness (or rather codify it), or should it specifically be spelled out that it's OK to transmute in the above way?
Lint on invalid usage of `UnsafeCell::raw_get` in reference casting
This PR proposes to take into account `UnsafeCell::raw_get` method call for non-Freeze types for the `invalid_reference_casting` lint.
The goal of this is to catch those kind of invalid reference casting:
```rust
fn as_mut<T>(x: &T) -> &mut T {
unsafe { &mut *std::cell::UnsafeCell::raw_get(x as *const _ as *const _) }
//~^ ERROR casting `&T` to `&mut T` is undefined behavior
}
```
r? `@est31`
Update stdarch submodule and remove special handling in cranelift codegen for some AVX and SSE2 LLVM intrinsics
https://github.com/rust-lang/stdarch/pull/1463 reimplemented some x86 intrinsics to avoid using some x86-specific LLVM intrinsics:
* Store unaligned (`_mm*_storeu_*`) use `<*mut _>::write_unaligned` instead of `llvm.x86.*.storeu.*`.
* Shift by immediate (`_mm*_s{ll,rl,ra}i_epi*`) use `if` (srl, sll) or `min` (sra) to simulate the behaviour when the RHS is out of range. RHS is constant, so the `if`/`min` will be optimized away.
This PR updates the stdarch submodule to pull these changes and removes special handling for those LLVM intrinsics from cranelift codegen. I left gcc codegen untouched because there are some autogenerated lists.
Move RawOsError defination to sys
This was originally a part of https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/105861, but I feel it should be its own PR since the raw os error is still unstable.
Outline panicking code for `RefCell::borrow` and `RefCell::borrow_mut`
This outlines panicking code for `RefCell::borrow` and `RefCell::borrow_mut` to reduce code size.
Use std::io::Error::is_interrupted everywhere
In https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/115228 I introduced this helper and started using it, this PR uses it to replace all applicable uses of `std::io::Error::kind`. The justification is the same; for whatever reason LLVM totally flops optimizing `Error::kind` so it's nice to use it less.
FYI ``@mkroening`` I swear the hermit changes look good, but I was so sure about the previous PR.
RangeFull: Remove parens around .. in documentation snippet
I’ve removed unnecessary parentheses in a documentation snippet documenting `RangeFull`. It could’ve lead people to believe the parentheses were necessary.
Also stabilizes saturating_int_assign_impl, gh-92354.
And also make pub fns const where the underlying saturating_*
fns became const in the meantime since the Saturating type was
created.
kmc-solid: Fix `is_interrupted`
Follow-up to #115228. Fixes a build error in [`*-kmc-solid_*`](https://doc.rust-lang.org/nightly/rustc/platform-support/kmc-solid.html) Tier 3 targets.
```
error[E0603]: function `is_interrupted` is private
--> library\std\src\sys\solid\mod.rs:77:12
|
77 | error::is_interrupted(code)
| ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^ private function
|
note: the function `is_interrupted` is defined here
--> library\std\src\sys\solid\error.rs:35:1
|
35 | fn is_interrupted(er: abi::ER) -> bool {
| ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
```
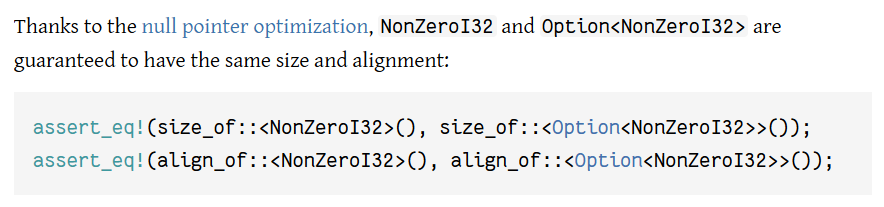
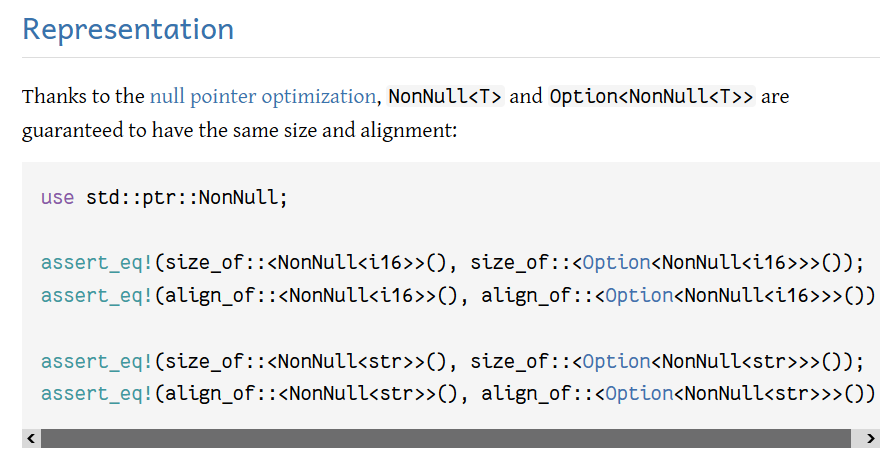
Add alignment to the NPO guarantee
This PR [changes](https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/114845#discussion_r1294363357) "same size" to "same size and alignment" in the option module's null pointer optimization docs in <https://doc.rust-lang.org/std/option/#representation>.
As far as I know, this has been true for a long time in the actual rustc implementation, but it's not in the text of those docs, so I figured I'd bring this up to FCP it.
I also see no particular reason that we'd ever *want* to have higher alignment on these. In many of the cases it's impossible, as the minimum alignment is already the size of the type, but even if we *could* do things like on 32-bit we could say that `NonZeroU64` is 4-align but `Option<NonZeroU64>` is 8-align, I just don't see any value in doing that, so feel completely fine closing this door for the few things on which the NPO is already guaranteed. These are basically all primitives, and should end up with the same size & alignment as those primitives.
(There's no layout guarantee for something like `Option<[u8; 3]>`, where it'd be at least plausible to consider raising the alignment from 1 to 4 on, say, some hypothetical target that doesn't have efficient unaligned 4-byte load/stores. And even if we ever did start to offer some kind of guarantee around such a type, I doubt we'd put it under the "null pointer" optimization header.)
Screenshots for the new examples:
Implement Step for ascii::Char
This allows iterating over ranges of `ascii::Char`, similarly to ranges of `char`.
Note that `ascii::Char` is still unstable, tracked in #110998.
docs: improve std::fs::read doc
#### What does this PR do
1. Rephrase a confusing sentence in the document of `std::fs::read()`
-----
Closes#114432
cc `@Dexus0` `@saethlin`
Currently, `CStr::from_ptr` contains its own implementation of `strlen`
that uses `const_eval_select` to either call libc's `strlen` or use a
naive Rust implementation. Refactor that into its own function so we can
use it elsewhere in the module.
Add note that Vec::as_mut_ptr() does not materialize a reference to the internal buffer
See discussion on https://github.com/thomcc/rust-typed-arena/issues/62 and [t-opsem](https://rust-lang.zulipchat.com/#narrow/stream/136281-t-opsem/topic/is.20this.20typed_arena.20code.20sound.20under.20stacked.2Ftree.20borrows.3F)
This method already does the correct thing here, but it is worth guaranteeing that it does so it can be used more freely in unsafe code without having to worry about potential Stacked/Tree Borrows violations. This moves one more unsafe usage pattern from the "very likely sound but technically not fully defined" box into "definitely sound", and currently our surface area of the latter is woefully small.
I'm not sure how best to word this, opening this PR as a way to start discussion.
Fix implementation of `Duration::checked_div`
I ran across this while running some sanity checks on `time`. Quickcheck immediately found a bug, and as I'd modified the code from `std` I knew there was a bug here as well.
tl;dr this code fails ([playground](https://play.rust-lang.org/?version=stable&mode=debug&edition=2021&gist=1189a3efcdfc192c27d6d87815359353))
```rust
use std::time::Duration;
fn main() {
assert_eq!(
Duration::new(1, 1).checked_div(7),
Some(Duration::new(0, 142_857_143)),
);
}
```
The existing code determines that 1/7 = 0 (seconds), 1/7 = 0 (nanoseconds), 1 billion / 7 = 142,857,142 (extra nanoseconds). The billion comes from multiplying the remainder of the seconds (1) by the number of nanoseconds in a second. However, **this wrongly ignores any remaining nanoseconds**. This PR takes that into consideration, adds a test, and also changes the roundabout way of calculating the remainder into directly computing it.
Note: This is _not_ a rounding error. This result divides evenly.
`@rustbot` label +A-time +C-bug +S-waiting-on-reviewer +T-libs
Document that SystemTime does not count leap seconds
Fixes#77994
This may not be entirely uncontroversial. I know that `@Ekleog` is going to disagree. However, in support of this docs change:
This documents the current behaviour. The alternative would be to plan to *change* the behaviour.
There are many programs which need to get a POSIX time (a `time_t`). Right now, `duration_since(UNIX_EPOCH)` is the only facility in std that does that. So, that is what programs use. Changing the behaviour would break[1] all of those programs. We would need to define a new API that can be used to get a POSIX time, and get everyone to use it. This seems highly unpalatable.
And, even if we wanted to do that, time with leap seconds is a lot less easy to work with. We would need to arrange to have a leap seconds table available to `std` somehow, and make sure that it was kept up to date. Currently we don't offer to do that for timezone data, which has similar needs. There are other complications. So it seems it would be awkwarrd to *implement* a facility that provides time including leap seconds, and the resulting value would be hard for applications to work with.
Therefore, I think it's clear that we don't want to plan to ever change `SystemTime`. We should plan to keep it the way it is. Providing TAI (for example) should be left to external crates, or additional APIs we may add in the future.
For more discussion see #77994 and in particular `@fanf2's` https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/77994#issuecomment-1409448174
[1] Of course, by "break" we really only mean *future* breakage in the case where there is, in fact, ever another leap second. There may well not be: they are in the process of being abolished (although this is of course being contested). But if we decide that `SystemTime::now().duraton_since(UNIX_EPOCH)` counts leap seconds, it would start to return `Durations`s that are 27s different to the current answers. That's clearly unacceptable. And we can hardly change `UNIX_EPOCH` by 27s.
wasi: round up the size for `aligned_alloc`
C11 `aligned_alloc` requires that the size be a multiple of the
alignment. This is enforced in the wasi-libc emmalloc implementation,
which always returns NULL if the size is not a multiple.
(The default `MALLOC_IMPL=dlmalloc` does not currently check this.)
Correct and expand documentation of `handle_alloc_error` and `set_alloc_error_hook`.
The primary goal of this change is to remove the false claim that `handle_alloc_error` always aborts; instead, code should be prepared for `handle_alloc_error` to possibly unwind, and be sound under that condition.
I saw other opportunities for improvement, so I have added all the following information:
* `handle_alloc_error` may panic instead of aborting. (Fixes#114898)
* What happens if a hook returns rather than diverging.
* A hook may panic. (This was already demonstrated in an example, but not stated in prose.)
* A hook must be sound to call — it cannot assume that it is only called by the runtime, since its function pointer can be retrieved by safe code.
I've checked these statements against the source code of `alloc` and `std`, but there may be nuances I haven't caught, so a careful review is welcome.
Go into more detail about panicking in drop.
This patch was sitting around in my drafts. I don't recall the motivation, but I think it was someone expressing confusion over “will likely abort” (since, in fact, a panicking drop _not_ caused by dropping while panicking will predictably _not_ abort).
I hope that the new text will leave people well-informed about why not to panic and when it is reasonable to panic.
C11 `aligned_alloc` requires that the size be a multiple of the
alignment. This is enforced in the wasi-libc emmalloc implementation,
which always returns NULL if the size is not a multiple.
(The default `MALLOC_IMPL=dlmalloc` does not currently check this.)
Make `rustc_on_unimplemented` std-agnostic for `alloc::rc`
See https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/112923
Just a few lines related to `alloc:rc` for `Send` and `Sync`.
That seems to be all of the `... = "std::..."` issues found, but there a few notes with `std::` inside them still.
r? `@WaffleLapkin`
Add a new helper to avoid calling io::Error::kind
On `cfg(unix)`, `Error::kind` emits an enormous jump table that LLVM seems unable to optimize out. I don't really understand why, but see for yourself: https://godbolt.org/z/17hY496KG
This change lets us check for `ErrorKind::Interrupted` without going through a big match. I've checked the codegen locally, and it has the desired effect on the codegen for `BufReader::read_exact`.
This implements the ability to add arbitrary attributes to a command on Windows targets using a new `raw_attribute` method on the [`CommandExt`](https://doc.rust-lang.org/stable/std/os/windows/process/trait.CommandExt.html) trait. Setting these attributes provides extended configuration options for Windows processes.
Co-authored-by: Tyler Ruckinger <t.ruckinger@gmail.com>
kmc-solid: Import `std::sync::PoisonError` in `std::sys::solid::os`
Follow-up to #114968. Fixes a missing import in [`*-kmc-solid_*`](https://doc.rust-lang.org/nightly/rustc/platform-support/kmc-solid.html) Tier 3 targets.
```
error[E0433]: failed to resolve: use of undeclared type `PoisonError`
C:\Users\xxxxx\.rustup\toolchains\nightly-2023-08-23-x86_64-pc-windows-gnu\lib\rustlib\src\rust\library\std\src\sys\solid\os.rs(85,36)
|
85 | ENV_LOCK.read().unwrap_or_else(PoisonError::into_inner)
| ^^^^^^^^^^^ use of undeclared type `PoisonError`
|
```
Add support for `ptr::write`s for the `invalid_reference_casting` lint
This PR adds support for `ptr::write` and others for the `invalid_reference_casting` lint.
Detecting instances where instead of using the deref (`*`) operator to assign someone uses `ptr::write`, `ptr::write_unaligned` or `ptr::write_volatile`.
```rust
let data_len = 5u64;
std::ptr::write(
std::mem::transmute::<*const u64, *mut u64>(&data_len),
new_data_len,
);
```
r? ``@est31``
I tried working with `UdpSocket` and ran into `EINVAL` errors with no
clear indication of what causes the error. Also, it was uncharacteristically
hard to figure this module out, compared to other Rust `std` modules.
1. `send` and `send_to` return a `usize`
This one is just clarity. Usually, returned `usize`s indicate that the
buffer might have only been sent partially. This is not the case with
UDP. Since that `usize` must always be `buffer.len()`, I have documented
that.
2. `bind` limits `connect` and `send_to`
When you bind to a limited address space like localhost, you can only
`connect` to addresses in that same address space. Error kind:
`AddrNotAvailable`.
3. `connect`ing to localhost locks you to localhost
On Linux, if you first `connect` to localhost, subsequent `connect`s to
non-localhost addresses fail. Error kind: `InvalidInput`.
Co-authored-by: Jubilee <46493976+workingjubilee@users.noreply.github.com>
Xous passes slice pointers around in order to manipulate memory.
This is feature-gated behind `slice_ptr_len`. Xous is currently
the only target to use this feature, so gate it behind an OS flag.
Signed-off-by: Sean Cross <sean@xobs.io>
Add an implementation of thread local storage. This uses a container
that is pointed to by the otherwise-unsed `$tp` register. This container
is allocated on-demand, so threads that use no TLS will not allocate
this extra memory.
Signed-off-by: Sean Cross <sean@xobs.io>
Add support for determining the current time. This connects to the
ticktimer server in order to get the system uptime.
Signed-off-by: Sean Cross <sean@xobs.io>
Add support for stdout. This enables basic console printing via
`println!()`. Output is written to the log server.
Signed-off-by: Sean Cross <sean@xobs.io>
Xous has a concept of `services` that provide various features.
Processes may connect to these services by name or by address. Most
services require a name server in order to connect.
Add a file with the most common services, and provide a way to connect
to a service by querying the name server.
Signed-off-by: Sean Cross <sean@xobs.io>
Basic alloc support on Xous is supported by the `dlmalloc` crate. This
necessitates bumping the dlmalloc version to 0.2.4.
Signed-off-by: Sean Cross <sean@xobs.io>
Add the basics to get the operating system running, including how to
exit the operating system.
Since Xous has no libc, there is no default entrypoint. Add a `_start`
entrypoint to the system-specific os module.
Signed-off-by: Sean Cross <sean@xobs.io>