Add a `size()` function to WASI's `MetadataExt`.
WASI's `filestat` type includes a size field, so expose it in
`MetadataExt` via a `size()` function, similar to the corresponding Unix
function.
r? ``````@alexcrichton``````
Enable API documentation for `std::os::wasi`.
This adds API documentation support for `std::os::wasi` modeled after
how `std::os::unix` works, so that WASI can be documented [here] along
with the other platforms.
[here]: https://doc.rust-lang.org/stable/std/os/index.html
Two changes of particular interest:
- This changes the `AsRawFd` for `io::Stdin` for WASI to return
`libc::STDIN_FILENO` instead of `sys::stdio::Stdin.as_raw_fd()` (and
similar for `Stdout` and `Stderr`), which matches how the `unix`
version works. `STDIN_FILENO` etc. may not always be explicitly
reserved at the WASI level, but as long as we have Rust's `std` and
`libc`, I think it's reasonable to guarantee that we'll always use
`libc::STDIN_FILENO` for stdin.
- This duplicates the `osstr2str` utility function, rather than
trying to share it across all the configurations that need it.
r? ```@alexcrichton```
library: Normalize safety-for-unsafe-block comments
Almost all safety comments are of the form `// SAFETY:`,
so normalize the rest and fix a few of them that should
have been a `/// # Safety` section instead.
Furthermore, make `tidy` only allow the uppercase form. While
currently `tidy` only checks `core`, it is a good idea to prevent
`core` from drifting to non-uppercase comments, so that later
we can start checking `alloc` etc. too.
Signed-off-by: Miguel Ojeda <ojeda@kernel.org>
Update outdated comment in unix Command.
The big comment in the `Command` struct has been incorrect for some time (at least since #46789 which removed `envp`). Rather than try to remove the allocations, this PR just updates the comment to reflect reality. There is an explanation for the reasoning at https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/31409#issuecomment-182122895, discussing the potential of being able to call `Command::exec` after `libc::fork`. That can still be done in the future, but I think for now it would be good to just correct the comment.
Add an impl of Error on `Arc<impl Error>`.
`Display` already exists so this should be a non-controversial change (famous last words).
Would have to be insta-stable.
rust_2015 and rust_2018 are just re-exports of v1.
rust_2021 is a module that for now just re-exports everything from v1,
such that we can add more things later.
Almost all safety comments are of the form `// SAFETY:`,
so normalize the rest and fix a few of them that should
have been a `/// # Safety` section instead.
Furthermore, make `tidy` only allow the uppercase form. While
currently `tidy` only checks `core`, it is a good idea to prevent
`core` from drifting to non-uppercase comments, so that later
we can start checking `alloc` etc. too.
Signed-off-by: Miguel Ojeda <ojeda@kernel.org>
This adds API documentation support for `std::os::wasi` modeled after
how `std::os::unix` works, so that WASI can be documented [here] along
with the other platforms.
[here]: https://doc.rust-lang.org/stable/std/os/index.html
Two changes of particular interest:
- This changes the `AsRawFd` for `io::Stdin` for WASI to return
`libc::STDIN_FILENO` instead of `sys::stdio::Stdin.as_raw_fd()` (and
similar for `Stdout` and `Stderr`), which matches how the `unix`
version works. `STDIN_FILENO` etc. may not always be explicitly
reserved at the WASI level, but as long as we have Rust's `std` and
`libc`, I think it's reasonable to guarantee that we'll always use
`libc::STDIN_FILENO` for stdin.
- This duplicates the `osstr2str` utility function, rather than
trying to share it across all the configurations that need it.
Update the bootstrap compiler
This updates the bootstrap compiler, notably leaving out a change to enable semicolon in macro expressions lint, because stdarch still depends on the old behavior.
- Link from `core::hash` to `HashMap` and `HashSet`
- Link from HashMap and HashSet to the module-level documentation on
when to use the collection
- Link from several collections to Wikipedia articles on the general
concept
add diagnostic items for OsString/PathBuf/Owned as well as to_vec on slice
This is adding diagnostic items to be used by rust-lang/rust-clippy#6730, but my understanding is the clippy-side change does need to be done over there since I am adding a new clippy feature.
Add diagnostic items to the following types:
OsString (os_string_type)
PathBuf (path_buf_type)
Owned (to_owned_trait)
As well as the to_vec method on slice/[T]
Make WASI's `hard_link` behavior match other platforms.
Following #78026, `std::fs::hard_link` on most platforms does not follow
symlinks. Change the WASI implementation to also not follow symlinks.
r? ```@alexcrichton```
The use of `ExitStatus` as the Rust type name for a Unix *wait
status*, not an *exit status*, is very confusing, but sadly probably
too late to change.
This area is confusing enough in Unix already (and many programmers
are already confuxed). We can at least document it.
I chose *not* to mention the way shells like to exit with signal
numbers, thus turning signal numbers into exit statuses. This is only
relevant for Rust programs using `std::process` if they run shells.
Signed-off-by: Ian Jackson <ijackson@chiark.greenend.org.uk>
Currently, on Nightly, this panics:
```
use std::process::ExitStatus;
use std::os::unix::process::ExitStatusExt;
fn main() {
let st = ExitStatus::from_raw(0x007f);
println!("st = {}", st);
}
```
This is because the impl of Display assumes that if .code() is None,
.signal() must be Some. That was a false assumption, although it was
true with buggy code before
5b1316f781
unix ExitStatus: Do not treat WIFSTOPPED as WIFSIGNALED
This is not likely to have affected many people in practice, because
`Command` will never produce such a wait status (`ExitStatus`).
Signed-off-by: Ian Jackson <ijackson@chiark.greenend.org.uk>
Provide NonZero_c_* integers
I'm pretty sure I am going want this for #73125 and it seems like an
omission that would be in any case good to remedy.
<strike>Because the raw C types are in `std`, not `core`, to achieve this we
must export the relevant macros from `core` so that `std` can use
them. That's done with a new `num_internals` perma-unstable feature.
The macros need to take more parameters for the module to get the
types from and feature attributes to use.
I have eyeballed the docs output for core, to check that my changes to
these macros have made no difference to the core docs output.</strike>
Implement RFC 2580: Pointer metadata & VTable
RFC: https://github.com/rust-lang/rfcs/pull/2580
~~Before merging this PR:~~
* [x] Wait for the end of the RFC’s [FCP to merge](https://github.com/rust-lang/rfcs/pull/2580#issuecomment-759145278).
* [x] Open a tracking issue: https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/81513
* [x] Update `#[unstable]` attributes in the PR with the tracking issue number
----
This PR extends the language with a new lang item for the `Pointee` trait which is special-cased in trait resolution to implement it for all types. Even in generic contexts, parameters can be assumed to implement it without a corresponding bound.
For this I mostly imitated what the compiler was already doing for the `DiscriminantKind` trait. I’m very unfamiliar with compiler internals, so careful review is appreciated.
This PR also extends the standard library with new unstable APIs in `core::ptr` and `std::ptr`:
```rust
pub trait Pointee {
/// One of `()`, `usize`, or `DynMetadata<dyn SomeTrait>`
type Metadata: Copy + Send + Sync + Ord + Hash + Unpin;
}
pub trait Thin = Pointee<Metadata = ()>;
pub const fn metadata<T: ?Sized>(ptr: *const T) -> <T as Pointee>::Metadata {}
pub const fn from_raw_parts<T: ?Sized>(*const (), <T as Pointee>::Metadata) -> *const T {}
pub const fn from_raw_parts_mut<T: ?Sized>(*mut (),<T as Pointee>::Metadata) -> *mut T {}
impl<T: ?Sized> NonNull<T> {
pub const fn from_raw_parts(NonNull<()>, <T as Pointee>::Metadata) -> NonNull<T> {}
/// Convenience for `(ptr.cast(), metadata(ptr))`
pub const fn to_raw_parts(self) -> (NonNull<()>, <T as Pointee>::Metadata) {}
}
impl<T: ?Sized> *const T {
pub const fn to_raw_parts(self) -> (*const (), <T as Pointee>::Metadata) {}
}
impl<T: ?Sized> *mut T {
pub const fn to_raw_parts(self) -> (*mut (), <T as Pointee>::Metadata) {}
}
/// `<dyn SomeTrait as Pointee>::Metadata == DynMetadata<dyn SomeTrait>`
pub struct DynMetadata<Dyn: ?Sized> {
// Private pointer to vtable
}
impl<Dyn: ?Sized> DynMetadata<Dyn> {
pub fn size_of(self) -> usize {}
pub fn align_of(self) -> usize {}
pub fn layout(self) -> crate::alloc::Layout {}
}
unsafe impl<Dyn: ?Sized> Send for DynMetadata<Dyn> {}
unsafe impl<Dyn: ?Sized> Sync for DynMetadata<Dyn> {}
impl<Dyn: ?Sized> Debug for DynMetadata<Dyn> {}
impl<Dyn: ?Sized> Unpin for DynMetadata<Dyn> {}
impl<Dyn: ?Sized> Copy for DynMetadata<Dyn> {}
impl<Dyn: ?Sized> Clone for DynMetadata<Dyn> {}
impl<Dyn: ?Sized> Eq for DynMetadata<Dyn> {}
impl<Dyn: ?Sized> PartialEq for DynMetadata<Dyn> {}
impl<Dyn: ?Sized> Ord for DynMetadata<Dyn> {}
impl<Dyn: ?Sized> PartialOrd for DynMetadata<Dyn> {}
impl<Dyn: ?Sized> Hash for DynMetadata<Dyn> {}
```
API differences from the RFC, in areas noted as unresolved questions in the RFC:
* Module-level functions instead of associated `from_raw_parts` functions on `*const T` and `*mut T`, following the precedent of `null`, `slice_from_raw_parts`, etc.
* Added `to_raw_parts`
I'm pretty sure I am going want this for #73125 and it seems like an
omission that would be in any case good to remedy.
It's a shame we don't have competent token pasting and case mangling
for use in macro_rules!.
Signed-off-by: Ian Jackson <ijackson@chiark.greenend.org.uk>
This file contained a lot of repetitive code. This was about to get
considerably worse, with introduction of a slew of new aliases.
No functional change. I've eyeballed the docs and they don't seem to
have changed either.
Signed-off-by: Ian Jackson <ijackson@chiark.greenend.org.uk>
Quotes the arg and not quotes the arg have different effect on Windows when the program called
are msys2/cygwin program.
Refer to https://github.com/msys2/MSYS2-packages/issues/2176
Signed-off-by: Yonggang Luo <luoyonggang@gmail.com>
Add diagnostic items to the following types:
OsString (os_string_type)
PathBuf (path_buf_type)
Owned (to_owned_trait)
As well as the to_vec method on slice/[T]
Add the following trait impls:
- `impl Extend<OsString> for OsString`
- `impl<'a> Extend<&'a OsStr> for OsString`
- `impl FromIterator<OsString> for OsString`
- `impl<'a> FromIterator<&'a OsStr> for OsString`
Because `OsString` is a platform string with no particular semantics,
concatenating them together seems acceptable.
use RWlock when accessing os::env
Multiple threads modifying the current process environment is fairly uncommon. Optimize for the more common read case.
r? ````@m-ou-se````
Upgrade wasm32 image to Ubuntu 20.04
This switches the wasm32 image, which is used to test
wasm32-unknown-emscripten, to Ubuntu 20.04. While at it, enable
most of the excluded tests, as they seem to work fine with some
minor fixes.
This method is similar to the existing `exists()` method, except it
doesn't silently ignore the errors, leading to less error-prone code.
This change intentionally does NOT touch the documentation of `exists()`
nor recommend people to use this method while it's unstable.
Such changes are reserved for stabilization to prevent confusing people.
Apart from that it avoids conflicts with #80979.
This switches the wasm32 image, which is used to test
wasm32-unknown-emscripten to Ubuntu 20.04. While at it, enable
most of the excluded tests, as they seem to work fine with some
minor fixes.
Expose correct symlink API on WASI
As described in https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/68574, the currently exposed API for symlinks is, in fact, a thin wrapper around the corresponding syscall, and not suitable for public usage.
The reason is that the 2nd param in the call is expected to be a handle of a "preopened directory" (a WASI concept for exposing dirs), and the only way to retrieve such handle right now is by tinkering with a private `__wasilibc_find_relpath` API, which is an implementation detail and definitely not something we want users to call directly.
Making matters worse, the semantics of this param aren't obvious from its name (`fd`), and easy to misinterpret, resulting in people trying to pass a handle of the target file itself (as in https://github.com/vitiral/path_abs/pull/50), which doesn't work as expected.
I did a [codesearch among open-source repos](https://sourcegraph.com/search?q=std%3A%3Aos%3A%3Awasi%3A%3Afs%3A%3Asymlink&patternType=literal), and the usage above is so far the only usage of this API at all, but we should fix it before more people start using it incorrectly.
While this is technically a breaking API change, I believe it's a justified one, as 1) it's OS-specific and 2) there was strictly no way to correctly use the previous form of the API, and if someone does use it, they're likely doing it wrong like in the example above.
The new API does not lead to the same confusion, as it mirrors `std::os::unix::fs::symlink` and `std::os::windows::fs::symlink_{file,dir}` variants by accepting source/target paths.
Fixes#68574.
r? ``@alexcrichton``
Stabilize poison API of Once, rename poisoned()
This stabilizes:
* `OnceState`
* `OnceState::is_poisoned()` (previously named `poisoned()`)
* `Once::call_once_force()`
`poisoned()` was renamed because the new name is more clear as a few
people agreed and nobody objected.
Closes#33577
Notes:
* I'm not entirely sure it's supposed to be 1.51, LMK if I did it wrong
* I failed to run tests locally, so we will have to leave it to bors or someone else can try
OsStr eq_ignore_ascii_case takes arg by value
Per a comment on #70516 this changes `eq_ignore_ascii_case` to take the generic parameter `S: AsRef<OsStr>` by value instead of by reference.
This is technically a breaking change to an unstable method. I think the only way it would break is if you called this method with an explicit type parameter, ie `my_os_str.eq_ignore_ascii_case::<str>("foo")` becomes `my_os_str.eq_ignore_ascii_case::<&str>("foo")`.
Besides that, I believe it is overall more flexible since it can now take an owned `OsString` for example.
If this change should be made in some other PR (like #80193) then please just close this.
This stabilizes:
* `OnceState`
* `OnceState::is_poisoned()` (previously named `poisoned()`)
* `Once::call_once_force()`
`poisoned()` was renamed because the new name is more clear as a few
people agreed and nobody objected.
Closes#33577
Per a comment on #70516 this changes `eq_ignore_ascii_case` to take the generic parameter `S: AsRef<OsStr>` by value instead of by reference.
This is technically a breaking change to an unstable method. I think the only way it would break is if you called this method with an explicit type parameter, ie `my_os_str.eq_ignore_ascii_case::<str>("foo")` becomes `my_os_str.eq_ignore_ascii_case::<&str>("foo")`.
Besides that, I believe it is overall more flexible since it can now take an owned `OsString` for example.
If this change should be made in some other PR (like #80193) then please just close this.
Add doc aliases for "delete"
This patch adds doc aliases for "delete". The added aliases are supposed to reference usages `delete` in other programming languages.
- `HashMap::remove`, `BTreeMap::remove` -> `Map#delete` and `delete` keyword in JavaScript.
- `HashSet::remove`, `BTreeSet::remove` -> `Set#delete` in JavaScript.
- `mem::drop` -> `delete` keyword in C++.
- `fs::remove_file`, `fs::remove_dir`, `fs::remove_dir_all`-> `File#delete` in Java, `File#delete` and `Dir#delete` in Ruby.
Before this change, searching for "delete" in documentation returned no results.
sys: use `process::abort()` instead of `arch::wasm32::unreachable()`
Rationale:
- `abort()` lowers to `wasm32::unreachable()` anyway.
- `abort()` isn't `unsafe`.
- `abort()` matches the comment better.
- `abort()` avoids confusion by future readers (e.g. https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/81527): the naming of wasm's `unreachable` instruction is a bit unfortunate because it is not related to the `unreachable()` intrinsic (intended to trigger UB).
Codegen is likely to be different since `unreachable()` is `inline` while `abort()` is `cold`. Since it doesn't look like we are expecting here to trigger this case, the latter seems better anyway.
Add AArch64 big-endian and ILP32 targets
This PR adds 3 new AArch64 targets:
- `aarch64_be-unknown-linux-gnu`
- `aarch64-unknown-linux-gnu_ilp32`
- `aarch64_be-unknown-linux-gnu_ilp32`
It also fixes some ABI issues on big-endian ARM and AArch64.
Fix calling convention for CRT startup
My PR #81478 used the wrong calling convention for a set of
functions that are called by the CRT. These functions need to use
`extern "C"`.
This would only affect x86, which is the only target (that I know of)
that has multiple calling conventions.
```@bors``` r? ```@m-ou-se```
Let io::copy reuse BufWriter buffers
This optimization will allow users to implicitly set the buffer size for io::copy by wrapping the writer into a `BufWriter` if the default block size is insufficient, which should fix#49921
Due to min_specialization limitations this approach only works with `BufWriter` but not for `BufReader<R>` since `R` is unconstrained and thus the necessary specialization on `R: Read` is not always applicable. Once specialization becomes more powerful this optimization could be extended to look at the reader and writer side and use whichever buffer is larger.
Implement Rust 2021 panic
This implements the Rust 2021 versions of `panic!()`. See https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/80162 and https://github.com/rust-lang/rfcs/pull/3007.
It does so by replacing `{std, core}::panic!()` by a bulitin macro that expands to either `$crate::panic::panic_2015!(..)` or `$crate::panic::panic_2021!(..)` depending on the edition of the caller.
This does not yet make std's panic an alias for core's panic on Rust 2021 as the RFC proposes. That will be a separate change: c5273bdfb2 That change is blocked on figuring out what to do with https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/80846 first.
My PR #81478 used the wrong calling convention for a set of
functions that are called by the CRT. These functions need to use
`extern "C"`.
This would only affect x86, which is the only target (that I know of)
that has multiple calling conventions.
This patch adds doc aliases for "delete". The added aliases are
supposed to reference usages `delete` in other programming
languages.
- `HashMap::remove`, `BTreeMap::remove` -> `Map#delete` and `delete`
keyword in JavaScript.
- `HashSet::remove`, `BTreeSet::remove` -> `Set#delete` in JavaScript.
- `mem::drop` -> `delete` keyword in C++.
- `fs::remove_file`, `fs::remove_dir`, `fs::remove_dir_all`
-> `File#delete` in Java, `File#delete` and `Dir#delete` in Ruby.
Before this change, searching for "delete" in documentation
returned no results.
Resolve DLL imports at CRT startup, not on demand
On Windows, libstd uses GetProcAddress to locate some DLL imports, so
that libstd can run on older versions of Windows. If a given DLL import
is not present, then libstd uses other behavior (such as fallback
implementations).
This commit uses a feature of the Windows CRT to do these DLL imports
during module initialization, before main() (or DllMain()) is called.
This is the ideal time to resolve imports, because the module is
effectively single-threaded at that point; no other threads can
touch the data or code of the module that is being initialized.
This avoids several problems. First, it makes the cost of performing
the DLL import lookups deterministic. Right now, the DLL imports are
done on demand, which means that application threads _might_ have to
do the DLL import during some time-sensitive operation. This is a
small source of unpredictability. Since threads can race, it's even
possible to have more than one thread running the same redundant
DLL lookup.
This commit also removes using the heap to allocate strings, during
the DLL lookups.
Stabilize raw ref macros
This stabilizes `raw_ref_macros` (https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/73394), which is possible now that https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/74355 is fixed.
However, as I already said in https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/73394#issuecomment-751342185, I am not particularly happy with the current names of the macros. So I propose we also change them, which means I am proposing to stabilize the following in `core::ptr`:
```rust
pub macro const_addr_of($e:expr) {
&raw const $e
}
pub macro mut_addr_of($e:expr) {
&raw mut $e
}
```
The macro name change means we need another round of FCP. Cc `````@rust-lang/libs`````
Fixes#73394
Add `core::stream::Stream`
[[Tracking issue: #79024](https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/79024)]
This patch adds the `core::stream` submodule and implements `core::stream::Stream` in accordance with [RFC2996](https://github.com/rust-lang/rfcs/pull/2996). The RFC hasn't been merged yet, but as requested by the libs team in https://github.com/rust-lang/rfcs/pull/2996#issuecomment-725696389 I'm filing this PR to get the ball rolling.
## Documentatation
The docs in this PR have been adapted from [`std::iter`](https://doc.rust-lang.org/std/iter/index.html), [`async_std::stream`](https://docs.rs/async-std/1.7.0/async_std/stream/index.html), and [`futures::stream::Stream`](https://docs.rs/futures/0.3.8/futures/stream/trait.Stream.html). Once this PR lands my plan is to follow this up with PRs to add helper methods such as `stream::repeat` which can be used to document more of the concepts that are currently missing. That will allow us to cover concepts such as "infinite streams" and "laziness" in more depth.
## Feature gate
The feature gate for `Stream` is `stream_trait`. This matches the `#[lang = "future_trait"]` attribute name. The intention is that only the APIs defined in RFC2996 will use this feature gate, with future additions such as `stream::repeat` using their own feature gates. This is so we can ensure a smooth path towards stabilizing the `Stream` trait without needing to stabilize all the APIs in `core::stream` at once. But also don't start expanding the API until _after_ stabilization, as was the case with `std::future`.
__edit:__ the feature gate has been changed to `async_stream` to match the feature gate proposed in the RFC.
## Conclusion
This PR introduces `core::stream::{Stream, Next}` and re-exports it from `std` as `std::stream::{Stream, Next}`. Landing `Stream` in the stdlib has been a mult-year process; and it's incredibly exciting for this to finally happen!
---
r? `````@KodrAus`````
cc/ `````@rust-lang/wg-async-foundations````` `````@rust-lang/libs`````
As described in https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/68574, the currently exposed API for symlinks is, in fact, a thin wrapper around the corresponding syscall, and not suitable for public usage.
The reason is that the 2nd param in the call is expected to be a handle of a "preopened directory" (a WASI concept for exposing dirs), and the only way to retrieve such handle right now is by tinkering with a private `__wasilibc_find_relpath` API, which is an implementation detail and definitely not something we want users to call directly.
Making matters worse, the semantics of this param aren't obvious from its name (`fd`), and easy to misinterpret, resulting in people trying to pass a handle of the target file itself (as in https://github.com/vitiral/path_abs/pull/50), which doesn't work as expected.
I did a codesearch among open-source repos, and the usage above is so far the only usage of this API at all, but we should fix it before more people start using it incorrectly.
While this is technically a breaking API change, I believe it's a justified one, as 1) it's OS-specific and 2) there was strictly no way to correctly use the previous form of the API, and if someone does use it, they're likely doing it wrong like in the example above.
The new API does not lead to the same confusion, as it mirrors `std::os::unix::fs::symlink` and `std::os::windows::fs::symlink_{file,dir}` variants by accepting source/target paths.
Fixes#68574.
Rationale:
- `abort()` lowers to `wasm32::unreachable()` anyway.
- `abort()` isn't `unsafe`.
- `abort()` matches the comment better.
- `abort()` avoids confusion by future readers (e.g.
https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/81527): the naming of wasm's
`unreachable' instruction is a bit unfortunate because it is not
related to the `unreachable()` intrinsic (intended to trigger UB).
Codegen is likely to be different since `unreachable()` is `inline`
while `abort()` is `cold`. Since it doesn't look like we are expecting
here to trigger this case, the latter seems better anyway.
Signed-off-by: Miguel Ojeda <ojeda@kernel.org>
On Windows, libstd uses GetProcAddress to locate some DLL imports, so
that libstd can run on older versions of Windows. If a given DLL import
is not present, then libstd uses other behavior (such as fallback
implementations).
This commit uses a feature of the Windows CRT to do these DLL imports
during module initialization, before main() (or DllMain()) is called.
This is the ideal time to resolve imports, because the module is
effectively single-threaded at that point; no other threads can
touch the data or code of the module that is being initialized.
This avoids several problems. First, it makes the cost of performing
the DLL import lookups deterministic. Right now, the DLL imports are
done on demand, which means that application threads _might_ have to
do the DLL import during some time-sensitive operation. This is a
small source of unpredictability. Since threads can race, it's even
possible to have more than one thread running the same redundant
DLL lookup.
This commit also removes using the heap to allocate strings, during
the DLL lookups.
Stabilize `Seek::stream_position` (feature `seek_convenience`)
Tracking issue: #59359
Unresolved questions from tracking issue:
- "Override `stream_len` for `File`?" → we can do that in the future, this does not block stabilization.
- "Rename to `len` and `position`?" → as noted in the tracking issue, both of these shorter names have problems (`len` is usually a cheap getter, `position` clashes with `Cursor`). I do think the current names are perfectly fine.
- "Rename `stream_position` to `tell`?" → as mentioned in [the comment bringing this up](https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/59359#issuecomment-559541545), `stream_position` is more descriptive. I don't think `tell` would be a good name.
What remains to decide, is whether or not adding these methods is worth it.
Trying to shrink_to greater than capacity should be no-op
Per the discussion in https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/56431, `shrink_to` shouldn't panic if you try to make a vector shrink to a capacity greater than its current capacity.
Make std::future a re-export of core::future
After 1a764a7ef5, there are no `std::future`-specific items (except for `cfg(bootstrap)` items removed in 93eed402ad). So, instead of defining `std` own module, we can re-export the `core::future` directly.
Implement Error for &(impl Error)
Opening this up just to see what it breaks. It's unfortunate that `&(impl Error)` doesn't actually implement `Error`. If this direct approach doesn't work out then I'll try something different, like an `Error::by_ref` method.
**EDIT:** This is a super low-priority experiment so feel free to cancel it for more important crater runs! 🙂
-----
# Stabilization Report
## Why?
We've been working for the last few years to try "fix" the `Error` trait, which is probably one of the most fundamental in the whole standard library. One of its issues is that we commonly expect you to work with abstract errors through `dyn Trait`, but references and smart pointers over `dyn Trait` don't actually implement the `Error` trait. If you have a `&dyn Error` or a `Box<dyn Error>` you simply can't pass it to a method that wants a `impl Error`.
## What does this do?
This stabilizes the following trait impl:
```rust
impl<'a, T: Error + ?Sized + 'static> Error for &'a T;
```
This means that `&dyn Error` will now satisfy a `impl Error` bound.
It doesn't do anything with `Box<dyn Error>` directly. We discussed how we could do `Box<dyn Error>` in the thread here (and elsewhere in the past), but it seems like we need something like lattice-based specialization or a sprinkling of snowflake compiler magic to make that work. Having said that, with this new impl you _can_ now get a `impl Error` from a `Box<dyn Error>` by dereferencing it.
## What breaks?
A crater run revealed a few crates broke with something like the following:
```rust
// where e: &'short &'long dyn Error
err.source()
```
previously we'd auto-deref that `&'short &'long dyn Error` to return a `Option<&'long dyn Error>` from `source`, but now will call directly on `&'short impl Error`, so will return a `Option<&'short dyn Error>`. The fix is to manually deref:
```rust
// where e: &'short &'long dyn Error
(*err).source()
```
In the recent Libs meeting we considered this acceptable breakage.
Remove delay-binding for Win XP and Vista
The minimum supported Windows version is now Windows 7. Windows XP
and Windows Vista are no longer supported; both are already broken, and
require extra steps to use.
This commit removes the delayed-binding support for Windows API
functions that are present on all supported Windows targets. This has
several benefits: Removes needless complexity. Removes a load and
dynamic call on hot paths in mutex acquire / release. This may have
performance benefits.
* "Drop official support for Windows XP"
https://github.com/rust-lang/compiler-team/issues/378
* "Firefox has ended support for Windows XP and Vista"
https://support.mozilla.org/en-US/kb/end-support-windows-xp-and-vista
Inline methods of Path and OsString
These methods are not generic, and therefore aren't candidates for cross-crate inlining without an `#[inline]` attribute.
Document why not use concat! in dbg! macro
Original title: Reduce code generated by `dbg!` macro
The expanded code before/after: <https://rust.godbolt.org/z/hE3j95>.
---
We cannot use `concat!` since `file!` could contains `{` or the expression is a block (`{ .. }`).
Using it will generated malformed format strings.
So let's document this reason why we don't use `concat!` macro at all.
The minimum supported Windows version is now Windows 7. Windows XP
and Windows Vista are no longer supported; both are already broken, and
require extra steps to use.
This commit removes the delayed-binding support for Windows API
functions that are present on all supported Windows targets. This has
several benefits: Removes needless complexity. Removes a load and
dynamic call on hot paths in mutex acquire / release. This may have
performance benefits.
* "Drop official support for Windows XP"
https://github.com/rust-lang/compiler-team/issues/378
* "Firefox has ended support for Windows XP and Vista"
https://support.mozilla.org/en-US/kb/end-support-windows-xp-and-vista
std: Update wasi-libc commit of the wasm32-wasi target
This brings in an implementation of `current_dir` and `set_current_dir`
(emulation in `wasi-libc`) as well as an updated version of finding
relative paths. This also additionally updates clang to the latest
release to build wasi-libc with.
BufWriter: Provide into_raw_parts
If something goes wrong, one might want to unpeel the layers of nested
Writers to perform recovery actions on the underlying writer, or reuse
its resources.
`into_inner` can be used for this when the inner writer is still
working. But when the inner writer is broken, and returning errors,
`into_inner` simply gives you the error from flush, and the same
`Bufwriter` back again.
Here I provide the necessary function, which I have chosen to call
`into_raw_parts`.
I had to do something with `panicked`. Returning it to the caller as
a boolean seemed rather bare. Throwing the buffered data away in this
situation also seems unfriendly: maybe the programmer knows something
about the underlying writer and can recover somehow.
So I went for a custom Error. This may be overkill, but it does have
the nice property that a caller who actually wants to look at the
buffered data, rather than simply extracting the inner writer, will be
told by the type system if they forget to handle the panicked case.
If a caller doesn't need the buffer, it can just be discarded. That
WriterPanicked is a newtype around Vec<u8> means that hopefully the
layouts of the Ok and Err variants can be very similar, with just a
boolean discriminant. So this custom error type should compile down
to nearly no code.
*If this general idea is felt appropriate, I will open a tracking issue, etc.*
Don't use posix_spawn_file_actions_addchdir_np on macOS.
There is a bug on macOS where using `posix_spawn_file_actions_addchdir_np` with a relative executable path will cause `posix_spawnp` to return ENOENT, even though it successfully spawned the process in the given directory.
`posix_spawn_file_actions_addchdir_np` was introduced in macOS 10.15 first released in Oct 2019. I have tested macOS 10.15.7 and 11.0.1.
Example offending program:
```rust
use std::fs;
use std::os::unix::fs::PermissionsExt;
use std::process::*;
fn main() {
fs::create_dir_all("bar").unwrap();
fs::create_dir_all("foo").unwrap();
fs::write("foo/foo.sh", "#!/bin/sh\necho hello ${PWD}\n").unwrap();
let perms = fs::Permissions::from_mode(0o755);
fs::set_permissions("foo/foo.sh", perms).unwrap();
let c = Command::new("../foo/foo.sh").current_dir("bar").spawn();
eprintln!("{:?}", c);
}
```
This prints:
```
Err(Os { code: 2, kind: NotFound, message: "No such file or directory" })
hello /Users/eric/Temp/bar
```
I wanted to open this PR to get some feedback on possible solutions. Alternatives:
* Do nothing.
* Document the bug.
* Try to detect if the executable is a relative path on macOS, and avoid using `posix_spawn_file_actions_addchdir_np` only in that case.
I looked at the [XNU source code](https://opensource.apple.com/source/xnu/xnu-6153.141.1/bsd/kern/kern_exec.c.auto.html), but I didn't see anything obvious that would explain the behavior. The actual chdir succeeds, it is something else further down that fails, but I couldn't see where.
EDIT: I forgot to mention, relative exe paths with `current_dir` in general are discouraged (see #37868). I don't know if #37868 is fixable, since normalizing it would change the semantics for some platforms. Another option is to convert the executable to an absolute path with something like joining the cwd with the new cwd and the executable, but I'm uncertain about that.
Clarify what the effects of a 'logic error' are
This clarifies what a 'logic error' is (which is a term used to describe what happens if you put things in a hash table or btree and then use something like a refcell to break the internal ordering). This tries to be as vague as possible, as we don't really want to promise what happens, except "bad things, but not UB". This was discussed in #80657
This brings in an implementation of `current_dir` and `set_current_dir`
(emulation in `wasi-libc`) as well as an updated version of finding
relative paths. This also additionally updates clang to the latest
release to build wasi-libc with.
Deprecate atomic::spin_loop_hint in favour of hint::spin_loop
For https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/55002
We wanted to leave `atomic::spin_loop_hint` alone when stabilizing `hint::spin_loop` so folks had some time to migrate. This now deprecates `atomic_spin_loop_hint`.
Fix handling of malicious Readers in read_to_end
A malicious `Read` impl could return overly large values from `read`, which would result in the guard's drop impl setting the buffer's length to greater than its capacity! ~~To fix this, the drop impl now uses the safe `truncate` function instead of `set_len` which ensures that this will not happen. The result of calling the function will be nonsensical, but that's fine given the contract violation of the `Read` impl.~~
~~The `Guard` type is also used by `append_to_string` which does not pass untrusted values into the length field, so I've copied the guard type into each function and only modified the one used by `read_to_end`. We could just keep a single one and modify it, but it seems a bit cleaner to keep the guard code close to the functions and related specifically to them.~~
To fix this, we now assert that the returned length is not larger than the buffer passed to the method.
For reference, this bug has been present for ~2.5 years since 1.20: ecbb896b9e.
Closes#80894.
Add a `std::io::read_to_string` function
I recognize that you're usually supposed to open an issue first, but the
implementation is very small so it's okay if this is closed and it was 'wasted
work' :)
-----
The equivalent of `std::fs::read_to_string`, but generalized to all
`Read` impls.
As the documentation on `std::io::read_to_string` says, the advantage of
this function is that it means you don't have to create a variable first
and it provides more type safety since you can only get the buffer out
if there were no errors. If you use `Read::read_to_string`, you have to
remember to check whether the read succeeded because otherwise your
buffer will be empty.
It's friendlier to newcomers and better in most cases to use an explicit
return value instead of an out parameter.
Add missing methods to unix ExitStatusExt
These are the methods corresponding to the remaining exit status examination macros from `wait.h`. `WCOREDUMP` isn't in SuS but is it is very standard. I have not done portability testing to see if this builds everywhere, so I may need to Do Something if it doesn't.
There is also a bugfix and doc improvement to `.signal()`, and an `.into_raw()` accessor.
This would fix#73128 and fix#73129. Please let me know if you like this direction, and if so I will open the tracking issue and so on.
If this MR goes well, I may tackle #73125 next - I have an idea for how to do it.
This is not particularly pretty but the current situation is a mess
and I don't think I'm making it significantly worse.
Signed-off-by: Ian Jackson <ijackson@chiark.greenend.org.uk>
As discussed in #79982.
I think the "new interfaces", ie the new trait and impl, must be
insta-stable. This seems OK because we are, in fact, adding a new
restriction to the stable API.
Signed-off-by: Ian Jackson <ijackson@chiark.greenend.org.uk>
We need to be clear that this never returns WSTOPSIG. That is, if
WIFSTOPPED, the return value is None.
Signed-off-by: Ian Jackson <ijackson@chiark.greenend.org.uk>
A unix wait status can contain, at least, exit statuses, termination
signals, and stop signals.
WTERMSIG is only valid if WIFSIGNALED.
https://pubs.opengroup.org/onlinepubs/9699919799/functions/wait.html
It will not be easy to experience this bug with `Command`, because
that doesn't pass WUNTRACED. But you could make an ExitStatus
containing, say, a WIFSTOPPED, from a call to one of the libc wait
functions.
(In the WIFSTOPPED case, there is WSTOPSIG. But a stop signal is
encoded differently to a termination signal, so WTERMSIG and WSTOPSIG
are by no means the same.)
Signed-off-by: Ian Jackson <ijackson@chiark.greenend.org.uk>
use Once instead of Mutex to manage capture resolution
For #78299
This allows us to return borrows of the captured backtrace frames that are tied to a borrow of the Backtrace itself, instead of to some short-lived Mutex guard.
We could alternatively share `&Mutex<Capture>`s and lock on-demand, but then we could potentially forget to call `resolve()` before working with the capture. It also makes it semantically clearer what synchronization is needed on the capture.
cc `@seanchen1991` `@rust-lang/project-error-handling`
Fix safety comment
The size assertion in the comment was inverted compared to the code. After fixing that the implication that `(new_size >= old_size) => new_size != 0` still doesn't hold so explain why `old_size != 0` at this point.
Rustdoc: Fix macros 2.0 and built-in derives being shown at the wrong path
Fixes#74355
- ~~waiting on author + draft PR since my code ought to be cleaned up _w.r.t._ the way I avoid the `.unwrap()`s:~~
- ~~dummy items may avoid the first `?`,~~
- ~~but within the module traversal some tests did fail (hence the second `?`), meaning the crate did not possess the exact path of the containing module (`extern` / `impl` blocks maybe? I'll look into that).~~
r? `@jyn514`
Optimize away some path lookups in the generic `fs::copy` implementation
This also eliminates a use of a `Path` convenience function, in support
of #80741, refactoring `std::path` to focus on pure data structures and
algorithms.
Stabilize slice::strip_prefix and slice::strip_suffix
These two methods are useful. The corresponding methods on `str` are already stable.
I believe that stablising these now would not get in the way of, in the future, extending these to take a richer pattern API a la `str`'s patterns.
Tracking PR: #73413. I also have an outstanding PR to improve the docs for these two functions and the corresponding ones on `str`: #75078
I have tried to follow the [instructions in the dev guide](https://rustc-dev-guide.rust-lang.org/stabilization_guide.html#stabilization-pr). The part to do with `compiler/rustc_feature` did not seem applicable. I assume that's because these are just library features, so there is no corresponding machinery in rustc.
The size assertion in the comment was inverted compared to the code. After fixing that the implication that `(new_size >= old_size) => new_size != 0` still doesn't hold so explain why `old_size != 0` at this point.
This also eliminates a use of a `Path` convenience function, in support
of #80741, refactoring `std::path` to focus on pure data structures and
algorithms.
The heading style for `std::prelude` is to be consistent with the
headings for `std` and `core`: `# The Rust Standard Library` and
`# The Rust Core Library`, respectively.
This allows us to return borrows of the captured backtrace frames
that are tied to a borrow of the Backtrace itself, instead of to
some short-lived Mutex guard.
It also makes it semantically clearer what synchronization is needed
on the capture.
slightly more typed interface to panic implementation
The panic payload is currently being passed around as a `usize`. However, it actually is a pointer, and the involved types are available on all ends of this API, so I propose we use the proper pointer type to avoid some casts. Avoiding int-to-ptr casts also makes this code work with `miri -Zmiri-track-raw-pointers`.
Fix intra-doc links for non-path primitives
This does *not* currently work for associated items that are
auto-implemented by the compiler (e.g. `never::eq`), because they aren't
present in the source code. I plan to fix this in a follow-up PR.
Fixes https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/63351 using the approach mentioned in https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/63351#issuecomment-683352130.
r? `@Manishearth`
cc `@petrochenkov` - this makes `rustc_resolve::Res` public, is that ok? I'd just add an identical type alias in rustdoc if not, which seems a waste.
We hope later to extend `core::str::Pattern` to slices too, perhaps as
part of stabilising that. We want to minimise the amount of type
inference breakage when we do that, so we don't want to stabilise
strip_prefix and strip_suffix taking a simple `&[T]`.
@KodrAus suggested the approach of introducing a new perma-unstable
trait, which reduces this future inference break risk.
I found it necessary to make two impls of this trait, as the unsize
coercion don't apply when hunting for trait implementations.
Since SlicePattern's only method returns a reference, and the whole
trait is just a wrapper for slices, I made the trait type be the
non-reference type [T] or [T;N] rather than the reference. Otherwise
the trait would have a lifetime parameter.
I marked both the no-op conversion functions `#[inline]`. I'm not
sure if that is necessary but it seemed at the very least harmless.
Signed-off-by: Ian Jackson <ijackson@chiark.greenend.org.uk>
Stabilize `core::slice::fill`
Tracking issue https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/70758
Stabilizes the `core::slice::fill` API in Rust 1.50, adding a `memset` doc alias so people coming from C/C++ looking for this operation can find it in the docs. This API hasn't seen any changes since we changed the signature in https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/71165/, and it seems like the right time to propose stabilization. Thanks!
r? `@m-ou-se`
This caught several bugs where people expected `slice` to link to the
primitive, but it linked to the module instead.
This also uses `cfg_attr(bootstrap)` since the ambiguity only occurs
when compiling with stage 1.
Add array search aliases
Missed this in https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/80068. This one will really fix https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/46075.
The last alias especially I'm a little unsure about - maybe fuzzy search should be fixed in rustdoc instead? Happy to make that change although I'd have to figure out how.
r? ``@m-ou-se`` although cc ``@GuillaumeGomez`` for the search issue.
Fix failing build of std on armv5te-unknown-linux-uclibceabi due to missing cmsg_len_zero
I'm getting the following error when trying to build `std` on `armv5te-unknown-linux-uclibceabi`:
```
error[E0425]: cannot find value `cmsg_len_zero` in this scope
--> /home/operutka/.rustup/toolchains/nightly-x86_64-unknown-linux-gnu/lib/rustlib/src/rust/library/std/src/sys/unix/ext/net/ancillary.rs:376:47
|
376 | let data_len = (*cmsg).cmsg_len - cmsg_len_zero;
| ^^^^^^^^^^^^^ not found in this scope
```
Obviously, this branch:
```rust
cfg_if::cfg_if! {
if #[cfg(any(target_os = "android", all(target_os = "linux", target_env = "gnu")))] {
let cmsg_len_zero = libc::CMSG_LEN(0) as libc::size_t;
} else if #[cfg(any(
target_os = "dragonfly",
target_os = "emscripten",
target_os = "freebsd",
all(target_os = "linux", target_env = "musl",),
target_os = "netbsd",
target_os = "openbsd",
))] {
let cmsg_len_zero = libc::CMSG_LEN(0) as libc::socklen_t;
}
}
```
does not cover the case `all(target_os = "linux", target_env = "uclibc")`.
Mark `-1` as an available niche for file descriptors
Based on discussion from <https://internals.rust-lang.org/t/can-the-standard-library-shrink-option-file/12768>, the file descriptor `-1` is chosen based on the POSIX API designs that use it as a sentinel to report errors. A bigger niche could've been chosen, particularly on Linux, but would not necessarily be portable.
This PR also adds a test case to ensure that the -1 niche (which is kind of hacky and has no obvious test case) works correctly. It requires the "upper" bound, which is actually -1, to be expressed in two's complement.
The equivalent of `std::fs::read_to_string`, but generalized to all
`Read` impls.
As the documentation on `std::io::read_to_string` says, the advantage of
this function is that it means you don't have to create a variable first
and it provides more type safety since you can only get the buffer out
if there were no errors. If you use `Read::read_to_string`, you have to
remember to check whether the read succeeded because otherwise your
buffer will be empty.
It's friendlier to newcomers and better in most cases to use an explicit
return value instead of an out parameter.
Move {f32,f64}::clamp to core.
`clamp` was recently stabilized (tracking issue: https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/44095). But although `Ord::clamp` was added in `core` (because `Ord` is in `core`), the versions for the `f32` and `f64` primitives were added in `std` (together with `floor`, `sin`, etc.), not in `core` (together with `min`, `max`, `from_bits`, etc.).
This change moves them to `core`, such that `clamp` on floats is available in `no_std` programs as well.
Stabilize all stable methods of `Ipv4Addr`, `Ipv6Addr` and `IpAddr` as const
This PR stabilizes all currently stable methods of `Ipv4Addr`, `Ipv6Addr` and `IpAddr` as const.
Tracking issue: #76205
`Ipv4Addr` (`const_ipv4`):
- `octets`
- `is_loopback`
- `is_private`
- `is_link_local`
- `is_multicast`
- `is_broadcast`
- `is_docmentation`
- `to_ipv6_compatible`
- `to_ipv6_mapped`
`Ipv6Addr` (`const_ipv6`):
- `segments`
- `is_unspecified`
- `is_loopback`
- `is_multicast`
- `to_ipv4`
`IpAddr` (`const_ip`):
- `is_unspecified`
- `is_loopback`
- `is_multicast`
## Motivation
The ip methods seem like prime candidates to be made const: their behavior is defined by an external spec, and based solely on the byte contents of an address. These methods have been made unstable const in the beginning of September, after the necessary const integer arithmetic was stabilized.
There is currently a PR open (#78802) to change the internal representation of `IpAddr{4,6}` from `libc` types to a byte array. This does not have any impact on the constness of the methods.
## Implementation
Most of the stabilizations are straightforward, with the exception of `Ipv6Addr::segments`, which uses the unstable feature `const_fn_transmute`. The code could be rewritten to equivalent stable code, but this leads to worse code generation (#75085).
This is why `segments` gets marked with `#[rustc_allow_const_fn_unstable(const_fn_transmute)]`, like the already const-stable `Ipv6Addr::new`, the justification being that a const-stable alternative implementation exists https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/76206#issuecomment-685044184.
## Future posibilities
This PR const-stabilizes all currently stable ip methods, however there are also a number of unstable methods under the `ip` feature (#27709). These methods are already unstable const. There is a PR open (#76098) to stabilize those methods, which could include const-stabilization. However, stabilizing those methods as const is dependent on `Ipv4Addr::octets` and `Ipv6Addr::segments` (covered by this PR).
Add the "async" and "promise" doc aliases to `core::future::Future`
Adds the "async" and "promise" doc aliases to `core::future::Future`. This enables people who search for "async" or "promise" to find `Future`, which is Rust's core primitive for async programming. Thanks!
Stabilize or_insert_with_key
Stabilizes the `or_insert_with_key` feature from https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/71024. This allows inserting key-derived values when a `HashMap`/`BTreeMap` entry is vacant.
The difference between this and `.or_insert_with(|| ... )` is that this provides a reference to the key to the closure after it is moved with `.entry(key_being_moved)`, avoiding the need to copy or clone the key.
Edit formatting in Rust Prelude docs
Use consistent punctuation and capitalization in the list of things re-exported in the prelude.
Also adds a (possibly missing) word.
Refactor and fix `parse_prefix` on Windows
This PR is an extension of #78692 as well as a general refactor of `parse_prefix`:
**Fixes**:
There are two errors in the current implementation of `parse_prefix`:
Firstly, in the current implementation only `\` is recognized as a separator character in device namespace prefixes. This behavior is only correct for verbatim paths; `"\\.\C:/foo"` should be parsed as `"C:"` instead of `"C:/foo"`.
Secondly, the current implementation only handles single separator characters. In non-verbatim paths a series of separator characters should be recognized as a single boundary, e.g. the UNC path `"\\localhost\\\\\\C$\foo"` should be parsed as `"\\localhost\\\\\\C$"` and then `UNC(server: "localhost", share: "C$")`, but currently it is not parsed at all, because it starts being parsed as `\\localhost\` and then has an invalid empty share location.
Paths like `"\\.\C:/foo"` and `"\\localhost\\\\\\C$\foo"` are valid on Windows, they are equivalent to just `"C:\foo"`.
**Refactoring**:
All uses of `&[u8]` within `parse_prefix` are extracted to helper functions and`&OsStr` is used instead. This reduces the number of places unsafe is used:
- `get_first_two_components` is adapted to the more general `parse_next_component` and used in more places
- code for parsing drive prefixes is extracted to `parse_drive`
Add fast futex-based thread parker for Windows.
This adds a fast futex-based thread parker for Windows. It either uses WaitOnAddress+WakeByAddressSingle or NT Keyed Events (NtWaitForKeyedEvent+NtReleaseKeyedEvent), depending on which is available. Together, this makes this thread parker work for Windows XP and up. Before this change, park()/unpark() did not work on Windows XP: it needs condition variables, which only exist since Windows Vista.
---
Unfortunately, NT Keyed Events are an undocumented Windows API. However:
- This API is relatively simple with obvious behaviour, and there are several (unofficial) articles documenting the details. [1]
- parking_lot has been using this API for years (on Windows versions before Windows 8). [2] Many big projects extensively use parking_lot, such as servo and the Rust compiler itself.
- It is the underlying API used by Windows SRW locks and Windows critical sections. [3] [4]
- The source code of the implementations of Wine, ReactOs, and Windows XP are available and match the expected behaviour.
- The main risk with an undocumented API is that it might change in the future. But since we only use it for older versions of Windows, that's not a problem.
- Even if these functions do not block or wake as we expect (which is unlikely, see all previous points), this implementation would still be memory safe. The NT Keyed Events API is only used to sleep/block in the right place.
[1]\: http://www.locklessinc.com/articles/keyed_events/
[2]\: https://github.com/Amanieu/parking_lot/commit/43abbc964e
[3]\: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/archive/msdn-magazine/2012/november/windows-with-c-the-evolution-of-synchronization-in-windows-and-c
[4]\: Windows Internals, Part 1, ISBN 9780735671300
---
The choice of fallback API is inspired by parking_lot(_core), but the implementation of this thread parker is different. While parking_lot has no use for a fast path (park() directly returning if unpark() was already called), this implementation has a fast path that returns without even checking which waiting/waking API to use, as the same atomic variable with compatible states is used in all cases.
doc(array,vec): add notes about side effects when empty-initializing
Copying some context from a conversation in the Rust discord:
* Both `vec![T; 0]` and `[T; 0]` are syntactically valid, and produce empty containers of their respective types
* Both *also* have side effects:
```rust
fn side_effect() -> String {
println!("side effect!");
"foo".into()
}
fn main() {
println!("before!");
let x = vec![side_effect(); 0];
let y = [side_effect(); 0];
println!("{:?}, {:?}", x, y);
}
```
produces:
```
before!
side effect!
side effect!
[], []
```
This PR just adds two small notes to each's documentation, warning users that side effects can occur.
I've also submitted a clippy proposal: https://github.com/rust-lang/rust-clippy/issues/6439
Link loop/for keyword
Even though the reference already have all of these, I am just adding related keywords in the see also to let others easily click on the related keyword.
Windows TLS: ManuallyDrop instead of mem::forget
The Windows TLS implementation still used `mem::forget` instead of `ManuallyDrop`, leading to the usual problem of "using" the `Box` when it should not be used any more.
Dogfood `str_split_once()`
Part of https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/74773.
Beyond increased clarity, this fixes some instances of a common confusion with how `splitn(2)` behaves: the first element will always be `Some()`, regardless of the delimiter, and even if the value is empty.
Given this code:
```rust
fn main() {
let val = "...";
let mut iter = val.splitn(2, '=');
println!("Input: {:?}, first: {:?}, second: {:?}", val, iter.next(), iter.next());
}
```
We get:
```
Input: "no_delimiter", first: Some("no_delimiter"), second: None
Input: "k=v", first: Some("k"), second: Some("v")
Input: "=", first: Some(""), second: Some("")
```
Using `str_split_once()` makes more clear what happens when the delimiter is not found.
Make the kernel_copy tests more robust/concurrent.
These tests write to the same filenames in /tmp and in some cases these files don't get cleaned up properly. This caused issues for us when different users run the tests on the same system, e.g.:
```
---- sys::unix::kernel_copy::tests::bench_file_to_file_copy stdout ----
thread 'sys::unix::kernel_copy::tests::bench_file_to_file_copy' panicked at 'called `Result::unwrap()` on an `Err` value: Os { code: 13, kind: PermissionDenied, message: "Permission denied" }', library/std/src/sys/unix/kernel_copy/tests.rs:71:10
---- sys::unix::kernel_copy::tests::bench_file_to_socket_copy stdout ----
thread 'sys::unix::kernel_copy::tests::bench_file_to_socket_copy' panicked at 'called `Result::unwrap()` on an `Err` value: Os { code: 13, kind: PermissionDenied, message: "Permission denied" }', library/std/src/sys/unix/kernel_copy/tests.rs💯10
```
Use `std::sys_common::io__test::tmpdir()` to solve this.
CC ``@the8472.``
Improve documentation for `std::{f32,f64}::mul_add`
Makes it more clear that performance improvement is not guaranteed when using FMA, even when the target architecture supports it natively.
Enforce no-move rule of ReentrantMutex using Pin and fix UB in stdio
A `sys_common::ReentrantMutex` may not be moved after initializing it with `.init()`. This was not enforced, but only stated as a requirement in the comments on the unsafe functions. This change enforces this no-moving rule using `Pin`, by changing `&self` to a `Pin` in the `init()` and `lock()` functions.
This uncovered a bug I introduced in #77154: stdio.rs (the only user of ReentrantMutex) called `init()` on its ReentrantMutexes while constructing them in the intializer of `SyncOnceCell::get_or_init`, which would move them afterwards. Interestingly, the ReentrantMutex unit tests already had the same bug, so this invalid usage has been tested on all (CI-tested) platforms for a long time. Apparently this doesn't break badly on any of the major platforms, but it does break the rules.\*
To be able to keep using SyncOnceCell, this adds a `SyncOnceCell::get_or_init_pin` function, which makes it possible to work with pinned values inside a (pinned) SyncOnceCell. Whether this function should be public or not and what its exact behaviour and interface should be if it would be public is something I'd like to leave for a separate issue or PR. In this PR, this function is internal-only and marked with `pub(crate)`.
\* Note: That bug is now included in 1.48, while this patch can only make it to ~~1.49~~ 1.50. We should consider the implications of 1.48 shipping with a wrong usage of `pthread_mutex_t` / `CRITICAL_SECTION` / .. which technically invokes UB according to their specification. The risk is very low, considering the objects are not 'used' (locked) before the move, and the ReentrantMutex unit tests have verified this works fine in practice.
Edit: This has been backported and included in 1.48. And soon 1.49 too.
---
In future changes, I want to push this usage of Pin further inside `sys` instead of only `sys_common`, and apply it to all 'unmovable' objects there (`Mutex`, `Condvar`, `RwLock`). Also, while `sys_common`'s mutexes and condvars are already taken care of by #77147 and #77648, its `RwLock` should still be made movable or get pinned.
Based on discussion from https://internals.rust-lang.org/t/can-the-standard-library-shrink-option-file/12768,
the file descriptor -1 is chosen based on the POSIX API designs that use it as a sentinel to report errors.
A bigger niche could've been chosen, particularly on Linux, but would not necessarily be portable.
This PR also adds a test case to ensure that the -1 niche
(which is kind of hacky and has no obvious test case) works correctly.
It requires the "upper" bound, which is actually -1, to be expressed in two's complement.
implement better availability probing for copy_file_range
Followup to https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/75428#discussion_r469616547
Previously syscall detection was overly pessimistic. Any attempt to copy to an immutable file (EPERM) would disable copy_file_range support for the whole process.
The change tries to copy_file_range on invalid file descriptors which will never run into the immutable file case and thus we can clearly distinguish syscall availability.
ext/ucred: Support PID in peer creds on macOS
This is a follow-up to https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/75148 (RFC: https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/42839).
The original PR used `getpeereid` on macOS and the BSDs, since they don't (generally) support the `SO_PEERCRED` mechanism that Linux supplies.
This PR splits the macOS/iOS implementation of `peer_cred()` from that of the BSDs, since macOS supplies the `LOCAL_PEERPID` sockopt as a source of the missing PID. It also adds a `cfg`-gated tests that ensures that platforms with support for PIDs in `UCred` have the expected data.
Use is_write_vectored to optimize the write_vectored implementation for BufWriter
In case when the underlying writer does not have an efficient implementation `write_vectored`, the present implementation of
`write_vectored` for `BufWriter` may still forward vectored writes directly to the writer depending on the total length of the data. This misses the advantage of buffering, as the actually written slice may be small.
Provide an alternative code path for the non-vectored case, where the slices passed to `BufWriter` are coalesced in the buffer before being flushed to the underlying writer with plain `write` calls. The buffer is only bypassed if an individual slice's length is at least as large as the buffer.
Remove a FIXME comment referring to #72919 as the issue has been closed with an explanation provided.
The code in io::stdio before this change misused the ReentrantMutexes,
by calling init() on them and moving them afterwards. Now that
ReentrantMutex requires Pin for init(), this mistake is no longer easy
to make.
Fix incorrect io::Take's limit resulting from io::copy specialization
The specialization introduced in #75272 fails to update `io::Take` wrappers after performing the copy syscalls which bypass those wrappers. The buffer flushing before the copy does update them correctly, but the bytes copied after the initial flush weren't subtracted.
The fix is to subtract the bytes copied from each `Take` in the chain of wrappers, even when an error occurs during the syscall loop. To do so the `CopyResult` enum now has to carry the bytes copied so far in the error case.
Provide IntoInnerError::into_parts
Hi. This is an updated version of the IntoInnerError bits of my previous portmanteau MR #78689. Thanks to `@jyn514` and `@m-ou-se` for helpful comments there.
I have made this insta-stable since it seems like it will probably be uncontroversial, but that is definitely something that someone from the libs API team should be aware of and explicitly consider.
I included a tangentially-related commit providing documentation of the buffer full behaviiour of `&mut [u8] as Write`; the behaviour I am documenting is relied on by the doctest for `into_parts`.
In particular, IntoIneerError only currently provides .error() which
returns a reference, not an owned value. This is not helpful and
means that a caller of BufWriter::into_inner cannot acquire an owned
io::Error which seems quite wrong.
Signed-off-by: Ian Jackson <ijackson@chiark.greenend.org.uk>
If something goes wrong, one might want to unpeel the layers of nested
Writers to perform recovery actions on the underlying writer, or reuse
its resources.
`into_inner` can be used for this when the inner writer is still
working. But when the inner writer is broken, and returning errors,
`into_inner` simply gives you the error from flush, and the same
`Bufwriter` back again.
Here I provide the necessary function, which I have chosen to call
`into_raw_parts`.
I had to do something with `panicked`. Returning it to the caller as
a boolean seemed rather bare. Throwing the buffered data away in this
situation also seems unfriendly: maybe the programmer knows something
about the underlying writer and can recover somehow.
So I went for a custom Error. This may be overkill, but it does have
the nice property that a caller who actually wants to look at the
buffered data, rather than simply extracting the inner writer, will be
told by the type system if they forget to handle the panicked case.
If a caller doesn't need the buffer, it can just be discarded. That
WriterPanicked is a newtype around Vec<u8> means that hopefully the
layouts of the Ok and Err variants can be very similar, with just a
boolean discriminant. So this custom error type should compile down
to nearly no code.
Signed-off-by: Ian Jackson <ijackson@chiark.greenend.org.uk>
Use more std:: instead of core:: in docs for consistency
``@rustbot`` label T-doc
Some cleanup work to use `std::` instead of `core::` in docs as much as possible. This helps with terminology and consistency, especially for newcomers from other languages that have often heard of `std` to describe the standard library but not of `core`.
Edit: I also added more intra doc links when I saw the opportunity.
These tests write to the same filenames in /tmp and in some cases these
files don't get cleaned up properly. This caused issues for us when
different users run the tests on the same system, e.g.:
```
---- sys::unix::kernel_copy::tests::bench_file_to_file_copy stdout ----
thread 'sys::unix::kernel_copy::tests::bench_file_to_file_copy' panicked at 'called `Result::unwrap()` on an `Err` value: Os { code: 13, kind: PermissionDenied, message: "Permission denied" }', library/std/src/sys/unix/kernel_copy/tests.rs:71:10
---- sys::unix::kernel_copy::tests::bench_file_to_socket_copy stdout ----
thread 'sys::unix::kernel_copy::tests::bench_file_to_socket_copy' panicked at 'called `Result::unwrap()` on an `Err` value: Os { code: 13, kind: PermissionDenied, message: "Permission denied" }', library/std/src/sys/unix/kernel_copy/tests.rs💯10
```
Use `std::sys_common::io__test::tmpdir()` to solve this.
unix: Extend UnixStream and UnixDatagram to send and receive file descriptors
Add the functions `recv_vectored_fds` and `send_vectored_fds` to `UnixDatagram` and `UnixStream`. With this functions `UnixDatagram` and `UnixStream` can send and receive file descriptors, by using `recvmsg` and `sendmsg` system call.
std::io: Use sendfile for UnixStream
`UnixStream` was forgotten in #75272 .
Benchmark yields the following results.
Before:
`running 1 test
test sys::unix::kernel_copy::tests::bench_file_to_uds_copy ... bench: 54,399 ns/iter (+/- 6,817) = 2409 MB/s`
After:
`running 1 test
test sys::unix::kernel_copy::tests::bench_file_to_uds_copy ... bench: 18,627 ns/iter (+/- 6,007) = 7036 MB/s`
Rename `optin_builtin_traits` to `auto_traits`
They were originally called "opt-in, built-in traits" (OIBITs), but
people realized that the name was too confusing and a mouthful, and so
they were renamed to just "auto traits". The feature flag's name wasn't
updated, though, so that's what this PR does.
There are some other spots in the compiler that still refer to OIBITs,
but I don't think changing those now is worth it since they are internal
and not particularly relevant to this PR.
Also see <https://rust-lang.zulipchat.com/#narrow/stream/131828-t-compiler/topic/opt-in.2C.20built-in.20traits.20(auto.20traits).20feature.20name>.
r? `@oli-obk` (feel free to re-assign if you're not the right reviewer for this)
Fix typo in `keyword` docs for traits
This PR fixes a small typo in the `keyword_docs.rs` file, describing the differences between the 2015 and 2018 editions of traits.
They were originally called "opt-in, built-in traits" (OIBITs), but
people realized that the name was too confusing and a mouthful, and so
they were renamed to just "auto traits". The feature flag's name wasn't
updated, though, so that's what this PR does.
There are some other spots in the compiler that still refer to OIBITs,
but I don't think changing those now is worth it since they are internal
and not particularly relevant to this PR.
Also see <https://rust-lang.zulipchat.com/#narrow/stream/131828-t-compiler/topic/opt-in.2C.20built-in.20traits.20(auto.20traits).20feature.20name>.
Drop support for all cloudabi targets
`cloudabi` is a tier-3 target, and [it is no longer being maintained upstream][no].
This PR drops supports for cloudabi targets. Those targets are:
* aarch64-unknown-cloudabi
* armv7-unknown-cloudabi
* i686-unknown-cloudabi
* x86_64-unknown-cloudabi
Since this drops supports for a target, I'd like somebody to tag `relnotes` label to this PR.
Some other issues:
* The tidy exception for `cloudabi` crate is still remained because
* `parking_lot v0.9.0` and `parking_lot v0.10.2` depends on `cloudabi v0.0.3`.
* `parking_lot v0.11.0` depends on `cloudabi v0.1.0`.
[no]: https://github.com/NuxiNL/cloudabi#note-this-project-is-unmaintained
Stabilize `IpAddr::is_ipv4` and `is_ipv6` as const
Insta-stabilize the methods `is_ipv4` and `is_ipv6` of `std::net::IpAddr` as const, in the same way as [PR#76198](https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/76198).
Possible because of the recent stabilization of const control flow.
Part of #76225 and #76205.
Insta-stabilize the methods `is_ipv4` and `is_ipv6` of `IpAddr`.
Possible because of the recent stabilization of const control flow.
Also adds a test for these methods in a const context.
Do what write does and optimize for the most likely case:
slices are much smaller than the buffer. If a slice does not fit
completely in the remaining capacity of the buffer, it is left out
rather than buffered partially. Special treatment is only left for
oversized slices that are written directly to the underlying writer.
Now that BufWriter always claims to support vectored writes,
look through it at the wrapped writer to decide whether to
use vectored writes for LineWriter.
If the underlying writer does not support efficient vectored output,
do it differently: always try to coalesce the slices in the buffer
until one comes that does not fit entirely. Flush the buffer before
the first slice if needed.
Stabilize clamp
Tracking issue: https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/44095
Clamp has been merged and unstable for about a year and a half now. How do we feel about stabilizing this?
rustc_expand: Mark inner `#![test]` attributes as soft-unstable
Custom inner attributes are feature gated (https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/54726) except for attributes having name `test` literally, which are not gated for historical reasons.
`#![test]` is an inner proc macro attribute, so it has all the issues described in https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/54726 too.
This PR gates it with the `soft_unstable` lint.
unix/weak: pass arguments to syscall at the given type
Given that we know the type the argument should have, it seems a bit strange not to use that information.
r? `@m-ou-se` `@cuviper`
Add lint for panic!("{}")
This adds a lint that warns about `panic!("{}")`.
`panic!(msg)` invocations with a single argument use their argument as panic payload literally, without using it as a format string. The same holds for `assert!(expr, msg)`.
This lints checks if `msg` is a string literal (after expansion), and warns in case it contained braces. It suggests to insert `"{}", ` to use the message literally, or to add arguments to use it as a format string.
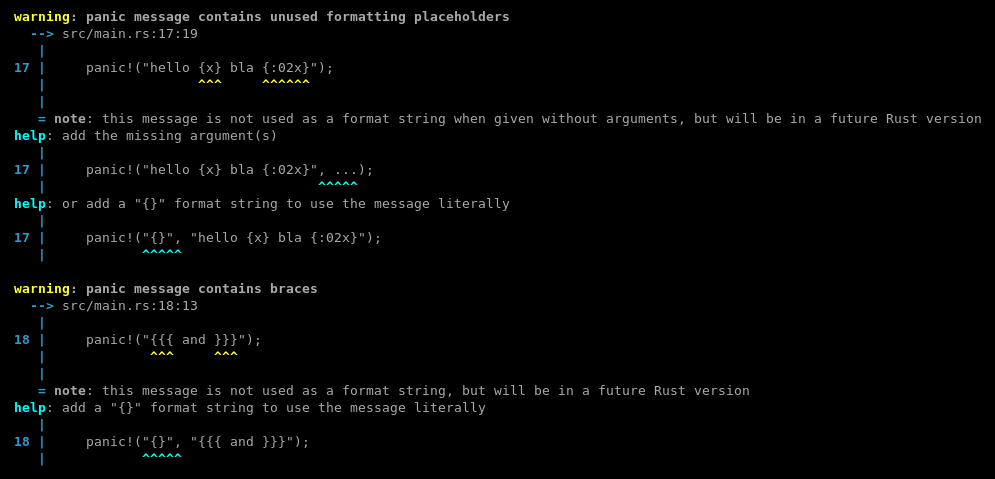
This lint is also a good starting point for adding warnings about `panic!(not_a_string)` later, once [`panic_any()`](https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/74622) becomes a stable alternative.
Fix typo in `std::io::Write` docs
These referred to a “`Write`er”—extra *e*. Presumably a copy-paste
holdover from “`Read`er”.
Test Plan:
Running ``git grep '`\?[Ww]rite`\?er'`` no longer finds any results.
wchargin-branch: io-write-docs
Tighten the bounds on atomic Ordering in std::sys::unix::weak::Weak
This moves reading this from multiple SeqCst reads to Relaxed read + Acquire fence if we are actually going to use the data.
Would love to avoid the Acquire fence, but doing so would need Ordering::Consume, which neither Rust, nor LLVM supports (a shame, since this fence is hardly free on ARM, which is what I was hoping to improve).
r? ``@Amanieu`` (Sorry for always picking you, but I know a lot of people wouldn't feel comfortable reviewing atomic ordering changes)
linux: try to use libc getrandom to allow interposition
We'll try to use a weak `getrandom` symbol first, because that allows
things like `LD_PRELOAD` interposition. For example, perf measurements
might want to disable randomness to get reproducible results. If the
weak symbol is not found, we fall back to a raw `SYS_getrandom` call.
These referred to a “`Write`er”—extra *e*. Presumably a copy-paste
holdover from “`Read`er”.
Test Plan:
Running ``git grep '`\?[Ww]rite`\?er'`` no longer finds any results.
wchargin-branch: io-write-docs
Rollup of 9 pull requests
Successful merges:
- #77939 (Ensure that the source code display is working with DOS backline)
- #78138 (Upgrade dlmalloc to version 0.2)
- #78967 (Make codegen tests compatible with extra inlining)
- #79027 (Limit storage duration of inlined always live locals)
- #79077 (document that __rust_alloc is also magic to our LLVM fork)
- #79088 (clarify `span_label` documentation)
- #79097 (Code block invalid html tag lint)
- #79105 (std: Fix test `symlink_hard_link` on Windows)
- #79107 (build-manifest: strip newline from rustc version)
Failed merges:
r? `@ghost`
`@rustbot` modify labels: rollup
std: Fix test `symlink_hard_link` on Windows
The test was introduced in https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/78026 and fails depending on Windows version and admin rights.
Other similar tests check for symlink creation permissions before doing anything, this PR performs the same check for `symlink_hard_link` as well.
Upgrade dlmalloc to version 0.2
In preparation of adding dynamic memory management support for SGXv2-enabled platforms, the dlmalloc crate has been refactored. More specifically, support has been added to implement platform specification outside of the dlmalloc crate. (see https://github.com/alexcrichton/dlmalloc-rs/pull/15)
This PR upgrades dlmalloc to version 0.2 for the `wasm` and `sgx` targets.
As the dlmalloc changes have received a positive review, but have not been merged yet, this PR contains a commit to prevent tidy from aborting CI prematurely.
cc: `@jethrogb`
Make the libstd build script smaller
Of all sysroot crates currently only compiler_builtins, miniz_oxide and std require a build script. compiler_builtins uses to conditionally enable certain features and possibly compile a C version ([source](63ccaf11f0/build.rs)), miniz_oxide only uses it to detect if liballoc is supported as the MSRV is 1.34.0 instead of the 1.36.0 which stabilized liballoc ([source](28514ec09f/miniz_oxide/build.rs)). std now only uses it to enable `freebsd12` when the `RUST_STD_FREEBSD_12_ABI` env var is set, to determine if `restricted-std` should be set, to set the `STD_ENV_ARCH` env var identical to `CARGO_CFG_TARGET_ARCH`, and to unconditionally enable `backtrace_in_libstd`.
If all build scripts were to be removed, it would be possible for rustc to completely compile it's own sysroot. It currently requires a rustc version that already has an available libstd to compile the build scripts. If rustc can completely compile it's own sysroot, rustbuild could be simplified to not forcefully use the bootstrap compiler for build scripts.
`@rustbot` modify labels: +T-compiler +libs-impl
We'll try to use a weak `getrandom` symbol first, because that allows
things like `LD_PRELOAD` interposition. For example, perf measurements
might want to disable randomness to get reproducible results. If the
weak symbol is not found, we fall back to a raw `SYS_getrandom` call.
Simplify output capturing
This is a sequence of incremental improvements to the unstable/internal `set_panic` and `set_print` mechanism used by the `test` crate:
1. Remove the `LocalOutput` trait and use `Arc<Mutex<dyn Write>>` instead of `Box<dyn LocalOutput>`. In practice, all implementations of `LocalOutput` were just `Arc<Mutex<..>>`. This simplifies some logic and removes all custom `Sink` implementations such as `library/test/src/helpers/sink.rs`. Also removes a layer of indirection, as the outermost `Box` is now gone. It also means that locking now happens per `write_fmt`, not per individual `write` within. (So `"{} {}\n"` now results in one `lock()`, not four or more.)
2. Since in all cases the `dyn Write`s were just `Vec<u8>`s, replace the type with `Arc<Mutex<Vec<u8>>>`. This simplifies things more, as error handling and flushing can be removed now. This also removes the hack needed in the default panic handler to make this work with `::realstd`, as (unlike `Write`) `Vec<u8>` is from `alloc`, not `std`.
3. Replace the `RefCell`s by regular `Cell`s. The `RefCell`s were mostly used as `mem::replace(&mut *cell.borrow_mut(), something)`, which is just `Cell::replace`. This removes an unecessary bookkeeping and makes the code a bit easier to read.
4. Merge `set_panic` and `set_print` into a single `set_output_capture`. Neither the test crate nor rustc (the only users of this feature) have a use for using these separately. Merging them simplifies things even more. This uses a new function name and feature name, to make it clearer this is internal and not supposed to be used by other crates.
Might be easier to review per commit.
Rename/Deprecate LayoutErr in favor of LayoutError
Implements rust-lang/wg-allocators#73.
This patch renames LayoutErr to LayoutError, and uses a type alias to support users using the old name.
The new name will be instantly stable in release 1.49 (current nightly), the type alias will become deprecated in release 1.51 (so that when the current nightly is 1.51, 1.49 will be stable).
This is the only error type in `std` that ends in `Err` rather than `Error`, if this PR lands all stdlib error types will end in `Error` 🥰
Fix an intrinsic invocation on threaded wasm
This looks like it was forgotten to get updated in #74482 and wasm with
threads isn't built on CI so we didn't catch this by accident.
specialize io::copy to use copy_file_range, splice or sendfile
Fixes#74426.
Also covers #60689 but only as an optimization instead of an official API.
The specialization only covers std-owned structs so it should avoid the problems with #71091
Currently linux-only but it should be generalizable to other unix systems that have sendfile/sosplice and similar.
There is a bit of optimization potential around the syscall count. Right now it may end up doing more syscalls than the naive copy loop when doing short (<8KiB) copies between file descriptors.
The test case executes the following:
```
[pid 103776] statx(3, "", AT_STATX_SYNC_AS_STAT|AT_EMPTY_PATH, STATX_ALL, {stx_mask=STATX_ALL|STATX_MNT_ID, stx_attributes=0, stx_mode=S_IFREG|0644, stx_size=17, ...}) = 0
[pid 103776] write(4, "wxyz", 4) = 4
[pid 103776] write(4, "iklmn", 5) = 5
[pid 103776] copy_file_range(3, NULL, 4, NULL, 5, 0) = 5
```
0-1 `stat` calls to identify the source file type. 0 if the type can be inferred from the struct from which the FD was extracted
𝖬 `write` to drain the `BufReader`/`BufWriter` wrappers. only happen when buffers are present. 𝖬 ≾ number of wrappers present. If there is a write buffer it may absorb the read buffer contents first so only result in a single write. Vectored writes would also be an option but that would require more invasive changes to `BufWriter`.
𝖭 `copy_file_range`/`splice`/`sendfile` until file size, EOF or the byte limit from `Take` is reached. This should generally be *much* more efficient than the read-write loop and also have other benefits such as DMA offload or extent sharing.
## Benchmarks
```
OLD
test io::tests::bench_file_to_file_copy ... bench: 21,002 ns/iter (+/- 750) = 6240 MB/s [ext4]
test io::tests::bench_file_to_file_copy ... bench: 35,704 ns/iter (+/- 1,108) = 3671 MB/s [btrfs]
test io::tests::bench_file_to_socket_copy ... bench: 57,002 ns/iter (+/- 4,205) = 2299 MB/s
test io::tests::bench_socket_pipe_socket_copy ... bench: 142,640 ns/iter (+/- 77,851) = 918 MB/s
NEW
test io::tests::bench_file_to_file_copy ... bench: 14,745 ns/iter (+/- 519) = 8889 MB/s [ext4]
test io::tests::bench_file_to_file_copy ... bench: 6,128 ns/iter (+/- 227) = 21389 MB/s [btrfs]
test io::tests::bench_file_to_socket_copy ... bench: 13,767 ns/iter (+/- 3,767) = 9520 MB/s
test io::tests::bench_socket_pipe_socket_copy ... bench: 26,471 ns/iter (+/- 6,412) = 4951 MB/s
```
Previously EOVERFLOW handling was only applied for io::copy specialization
but not for fs::copy sharing the same code.
Additionally we lower the chunk size to 1GB since we have a user report
that older kernels may return EINVAL when passing 0x8000_0000
but smaller values succeed.
Android builds use feature level 14, the libc wrapper for splice is gated
on feature level 21+ so we have to invoke the syscall directly.
Additionally the emulator doesn't seem to support it so we also have to
add ENOSYS checks.
Update thread and futex APIs to work with Emscripten
This updates the thread and futex APIs in `std` to match the APIs exposed by
Emscripten. This allows threads to run on `wasm32-unknown-emscripten` and the
thread parker to compile without errors related to the missing `futex` module.
To make use of this, Rust code must be compiled with `-C target-feature=atomics`
and Emscripten must link with `-pthread`.
I have confirmed this works well locally when building multithreaded crates.
Attempting to enable `std` thread tests currently fails for seemingly obscure
reasons and Emscripten is currently disabled in CI, so further work is needed to
have proper test coverage here.
This updates the thread and futex APIs in `std` to match the APIs exposed by
Emscripten. This allows threads to run on `wasm32-unknown-emscripten` and the
thread parker to compile without errors related to the missing `futex` module.
To make use of this, Rust code must be compiled with `-C target-feature=atomics`
and Emscripten must link with `-pthread`.
I have confirmed this works well locally when building multithreaded crates.
Attempting to enable `std` thread tests currently fails for seemingly obscure
reasons and Emscripten is currently disabled in CI, so further work is needed to
have proper test coverage here.
Duration::zero() -> Duration::ZERO
In review for #72790, whether or not a constant or a function should be favored for `#![feature(duration_zero)]` was seen as an open question. In https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/73544#issuecomment-691701670 an invitation was opened to either stabilize the methods or propose a switch to the constant value, supplemented with reasoning. Followup comments suggested community preference leans towards the const ZERO, which would be reason enough.
ZERO also "makes sense" beside existing associated consts for Duration. It is ever so slightly awkward to have a series of constants specifying 1 of various units but leave 0 as a method, especially when they are side-by-side in code. It seems unintuitive for the one non-dynamic value (that isn't from Default) to be not-a-const, which could hurt discoverability of the associated constants overall. Elsewhere in `std`, methods for obtaining a constant value were even deprecated, as seen with [std::u32::min_value](https://doc.rust-lang.org/std/primitive.u32.html#method.min_value).
Most importantly, ZERO costs less to use. A match supports a const pattern, but const fn can only be used if evaluated through a const context such as an inline `const { const_fn() }` or a `const NAME: T = const_fn()` declaration elsewhere. Likewise, while https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/73544#issuecomment-691949373 notes `Duration::zero()` can optimize to a constant value, "can" is not "will". Only const contexts have a strong promise of such. Even without that in mind, the comment in question still leans in favor of the constant for simplicity. As it costs less for a developer to use, may cost less to optimize, and seems to have more of a community consensus for it, the associated const seems best.
r? ```@LukasKalbertodt```
The discussion seems to have resolved that this lint is a bit "noisy" in
that applying it in all places would result in a reduction in
readability.
A few of the trivial functions (like `Path::new`) are fine to leave
outside of closures.
The general rule seems to be that anything that is obviously an
allocation (`Box`, `Vec`, `vec![]`) should be in a closure, even if it
is a 0-sized allocation.
It was only ever used with Vec<u8> anyway. This simplifies some things.
- It no longer needs to be flushed, because that's a no-op anyway for
a Vec<u8>.
- Writing to a Vec<u8> never fails.
- No #[cfg(test)] code is needed anymore to use `realstd` instead of
`std`, because Vec comes from alloc, not std (like Write).
Define `fs::hard_link` to not follow symlinks.
POSIX leaves it [implementation-defined] whether `link` follows symlinks.
In practice, for example, on Linux it does not and on FreeBSD it does.
So, switch to `linkat`, so that we can pick a behavior rather than
depending on OS defaults.
Pick the option to not follow symlinks. This is somewhat arbitrary, but
seems the less surprising choice because hard linking is a very
low-level feature which requires the source and destination to be on
the same mounted filesystem, and following a symbolic link could end
up in a different mounted filesystem.
[implementation-defined]: https://pubs.opengroup.org/onlinepubs/9699919799/functions/link.html
Refactor `get_first_two_components` to `get_next_component`.
Fixes the following behaviour of `parse_prefix`:
- series of separator bytes in a prefix are correctly parsed as a single separator
- device namespace prefixes correctly recognize both `\\` and `/` as separators
Use Intra-doc links for std::io::buffered
Helps with #75080. I used the implicit link style for intrinsics, as that was what `minnumf32` and others already had.
``@rustbot`` modify labels: T-doc, A-intra-doc-links
r? ``@jyn514``
`#![deny(unsafe_op_in_unsafe_fn)]` in sys/hermit
Partial fix of #73904.
This encloses ``unsafe`` operations in ``unsafe fn`` in ``sys/hermit``.
Some unsafe blocks are not well documented because some system-based functions lack documents.
Partially fix#55002, deprecate in another release
Co-authored-by: Ashley Mannix <kodraus@hey.com>
Update stable version for stabilize_spin_loop
Co-authored-by: Joshua Nelson <joshua@yottadb.com>
Use better example for spinlock
As suggested by KodrAus
Remove renamed_spin_loop already available in master
Fix spin loop example
fix various aliasing issues in the standard library
This fixes various cases where the standard library either used raw pointers after they were already invalidated by using the original reference again, or created raw pointers for one element of a slice and used it to access neighboring elements.
Add note to process::arg[s] that args shouldn't be escaped or quoted
This came out of discussion on [forum](https://users.rust-lang.org/t/how-to-get-full-output-from-command/50626), where I recently asked a question and it turned out that the problem was redundant quotation:
```rust
Command::new("rg")
.arg("\"pattern\"") // this will look for "pattern" with quotes included
```
This is something that has bitten me few times already (in multiple languages actually), so It'd be grateful to have it in the docs, even though it's not sctrictly Rust specific problem. Other users also agreed.
This can be really annoying to debug, because in many cases (inluding mine), quotes can be legal part of the argument, so the command doesn't fail, it just behaves unexpectedly. Not everybody (including me) knows that quotes around arguments are part of the shell and not part of the called program. Coincidentally, somoene had the same problem [yesterday](https://www.reddit.com/r/rust/comments/jkxelc/going_crazy_over_running_a_curl_process_from_rust/) on reddit.
I am not a native speaker, so I welcome any corrections or better formulation, I don't expect this to be merged as is. I was also reminded that this is platform/shell specific behaviour, but I didn't find a good way to formulate that briefly, any ideas welcome.
It's also my first PR here, so I am not sure I did everything correctly, I did this just from Github UI.
make exp_m1 and ln_1p examples more representative of use
With this PR, the examples for `exp_m1` would fail if `x.exp() - 1.0` is used instead of `x.exp_m1()`, and the examples for `ln_1p` would fail if `(x + 1.0).ln()` is used instead of `x.ln_1p()`.
Add std::panic::panic_any.
The discussion of #67984 lead to the conclusion that there should be a macro or function separate from `std::panic!()` for throwing arbitrary payloads, to make it possible to deprecate or disallow (in edition 2021) `std::panic!(arbitrary_payload)`.
Alternative names:
- `panic_with!(..)`
- ~~`start_unwind(..)`~~ (panicking doesn't always unwind)
- `throw!(..)`
- `panic_throwing!(..)`
- `panic_with_value(..)`
- `panic_value(..)`
- `panic_with(..)`
- `panic_box(..)`
- `panic(..)`
The equivalent (private, unstable) function in `libstd` is called `std::panicking::begin_panic`.
I suggest `panic_any`, because it allows for any (`Any + Send`) type.
_Tracking issue: #78500_
Uplift `temporary-cstring-as-ptr` lint from `clippy` into rustc
The general consensus seems to be that this lint covers a common enough mistake to warrant inclusion in rustc.
The diagnostic message might need some tweaking, as I'm not sure the use of second-person perspective matches the rest of rustc, but I'd like to hear others' thoughts on that.
(cc #53224).
r? `@oli-obk`
Capture output from threads spawned in tests
This is revival of #75172.
Original text:
> Fixes#42474.
>
> r? `@dtolnay` since you expressed interest in this, but feel free to redirect if you aren't the right person anymore.
---
Closes#75172.
`#[deny(unsafe_op_in_unsafe_fn)]` in sys/wasm
This is part of #73904.
This encloses unsafe operations in unsafe fn in `libstd/sys/wasm`.
@rustbot modify labels: F-unsafe-block-in-unsafe-fn
replace `#[allow_internal_unstable]` with `#[rustc_allow_const_fn_unstable]` for `const fn`s
`#[allow_internal_unstable]` is currently used to side-step feature gate and stability checks.
While it was originally only meant to be used only on macros, its use was expanded to `const fn`s.
This pr adds stricter checks for the usage of `#[allow_internal_unstable]` (only on macros) and introduces the `#[rustc_allow_const_fn_unstable]` attribute for usage on `const fn`s.
This pr does not change any of the functionality associated with the use of `#[allow_internal_unstable]` on macros or the usage of `#[rustc_allow_const_fn_unstable]` (instead of `#[allow_internal_unstable]`) on `const fn`s (see https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/69399#issuecomment-712911540).
Note: The check for `#[rustc_allow_const_fn_unstable]` currently only validates that the attribute is used on a function, because I don't know how I would check if the function is a `const fn` at the place of the check. I therefore openend this as a 'draft pull request'.
Closesrust-lang/rust#69399
r? @oli-obk
Throw core::panic!("message") as &str instead of String.
This makes `core::panic!("message")` consistent with `std::panic!("message")`, which throws a `&str` and not a `String`.
This also makes any other panics from `core::panicking::panic` result in a `&str` rather than a `String`, which includes compiler-generated panics such as the panics generated for `mem::zeroed()`.
---
Demonstration:
```rust
use std::panic;
use std::any::Any;
fn main() {
panic::set_hook(Box::new(|panic_info| check(panic_info.payload())));
check(&*panic::catch_unwind(|| core::panic!("core")).unwrap_err());
check(&*panic::catch_unwind(|| std::panic!("std")).unwrap_err());
}
fn check(msg: &(dyn Any + Send)) {
if let Some(s) = msg.downcast_ref::<String>() {
println!("Got a String: {:?}", s);
} else if let Some(s) = msg.downcast_ref::<&str>() {
println!("Got a &str: {:?}", s);
}
}
```
Before:
```
Got a String: "core"
Got a String: "core"
Got a &str: "std"
Got a &str: "std"
```
After:
```
Got a &str: "core"
Got a &str: "core"
Got a &str: "std"
Got a &str: "std"
```
revise Hermit's mutex interface to support the behaviour of StaticMutex
rust-lang/rust#77147 simplifies things by splitting this Mutex type into two types matching the two use cases: StaticMutex and MovableMutex. To support the new behavior of StaticMutex, we move part of the mutex implementation into libstd.
The interface to the OS changed. Consequently, I removed a few functions, which aren't longer needed.
According to [the bionic status page], `linkat` has only been available
since API level 21. Since Android is based on Linux and Linux's `link`
doesn't follow symlinks, just use `link` on Android.
[the bionic status page]: https://android.googlesource.com/platform/bionic/+/master/docs/status.md
Duration::ZERO composes better with match and various other things,
at the cost of an occasional parens, and results in less work for the
optimizer, so let's use that instead.
This expands time's test suite to use more and in more places the
range of methods and constants added to Duration in recent
proposals for the sake of testing more API surface area and
improving legibility.
const keyword: brief paragraph on 'const fn'
`const fn` were mentioned in the title, but called "deterministic functions" which is not their main property (though at least currently it is a consequence of being const-evaluable). This adds a brief paragraph discussing them, also in the hopes of clarifying that they do *not* have any effect on run-time uses.
If pthread mutex initialization fails, the failure will go unnoticed unless
debug assertions are enabled. Any subsequent use of mutex will also silently
fail, since return values from lock & unlock operations are similarly checked
only through debug assertions.
In some implementations the mutex initialization requires a memory
allocation and so it does fail in practice.
Check that initialization succeeds to ensure that mutex guarantees
mutual exclusion.
Add std:🧵:available_concurrency
This PR adds a counterpart to [C++'s `std:🧵:hardware_concurrency`](https://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/thread/thread/hardware_concurrency) to Rust, tracking issue https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/74479.
cc/ `@rust-lang/libs`
## Motivation
Being able to know how many hardware threads a platform supports is a core part of building multi-threaded code. In C++ 11 this has become available through the [`std:🧵:hardware_concurrency`](https://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/thread/thread/hardware_concurrency) API. Currently in Rust most of the ecosystem depends on the [`num_cpus` crate](https://docs.rs/num_cpus/1.13.0/num_cpus/) ([no.35 in top 500 crates](https://docs.google.com/spreadsheets/d/1wwahRMHG3buvnfHjmPQFU4Kyfq15oTwbfsuZpwHUKc4/edit#gid=1253069234)) to provide this functionality. This PR proposes an API to provide access to the number of hardware threads available on a given platform.
__edit (2020-07-24):__ The purpose of this PR is to provide a hint for how many threads to spawn to saturate the processor. There's value in introducing APIs for NUMA and Windows processor groups, but those are intentionally out of scope for this PR. See: https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/74480#issuecomment-662116186.
## Naming
Discussing the naming of the API on Zulip surfaced two options:
- `std:🧵:hardware_concurrency`
- `std:🧵:hardware_threads`
Both options seemed acceptable, but overall people seem to gravitate the most towards `hardware_threads`. Additionally `@jonas-schievink` pointed out that the "hardware threads" terminology is well-established and is used in among other the [RISC-V specification](https://riscv.org/specifications/isa-spec-pdf/) (page 20):
> A component is termed a core if it contains an independent instruction fetch unit. A RISC-V-compatible core might support multiple RISC-V-compatible __hardware threads__, or harts, through multithreading.
It's also worth noting that [the original paper introducing C++'s `std::thread` submodule](http://www.open-std.org/jtc1/sc22/wg21/docs/papers/2007/n2320.html) unfortunately doesn't feature any discussion on the naming of `hardware_concurrency`, so we can't use that to help inform our decision here.
## Return type
An important consideration `@joshtriplett` brought up is that we don't want to default to `1` for platforms where the number of available threads cannot be retrieved. Instead we want to inform the users of the fact that we don't know and allow them to handle that case. Which is why this PR uses `Option<NonZeroUsize>` as its return type, where `None` is returned on platforms where we don't know the number of hardware threads available.
The reasoning for `NonZeroUsize` vs `usize` is that if the number of threads for a platform are known, they'll always be at least 1. As evidenced by the example the `NonZero*` family of APIs may currently not be the most ergonomic to use, but improving the ergonomics of them is something that I think we can address separately.
## Implementation
`@Mark-Simulacrum` pointed out that most of the code we wanted to expose here was already available under `libtest`. So this PR mostly moves the internal code of libtest into a public API.
Use posix_spawn() on unix if program is a path
Previously `Command::spawn` would fall back to the non-posix_spawn based
implementation if the `PATH` environment variable was possibly changed.
On systems with a modern (g)libc `posix_spawn()` can be significantly
faster. If program is a path itself the `PATH` environment variable is
not used for the lookup and it should be safe to use the
`posix_spawnp()` method. [1]
We found this, because we have a cli application that effectively runs a
lot of subprocesses. It would sometimes noticeably hang while printing
output. Profiling showed that the process was spending the majority of
time in the kernel's `copy_page_range` function while spawning
subprocesses. During this time the process is completely blocked from
running, explaining why users were reporting the cli app hanging.
Through this we discovered that `std::process::Command` has a fast and
slow path for process execution. The fast path is backed by
`posix_spawnp()` and the slow path by fork/exec syscalls being called
explicitly. Using fork for process creation is supposed to be fast, but
it slows down as your process uses more memory. It's not because the
kernel copies the actual memory from the parent, but it does need to
copy the references to it (see `copy_page_range` above!). We ended up
using the slow path, because the command spawn implementation in falls
back to the slow path if it suspects the PATH environment variable was
changed.
Here is a smallish program demonstrating the slowdown before this code
change:
```
use std::process::Command;
use std::time::Instant;
fn main() {
let mut args = std::env::args().skip(1);
if let Some(size) = args.next() {
// Allocate some memory
let _xs: Vec<_> = std::iter::repeat(0)
.take(size.parse().expect("valid number"))
.collect();
let mut command = Command::new("/bin/sh");
command
.arg("-c")
.arg("echo hello");
if args.next().is_some() {
println!("Overriding PATH");
command.env("PATH", std::env::var("PATH").expect("PATH env var"));
}
let now = Instant::now();
let child = command
.spawn()
.expect("failed to execute process");
println!("Spawn took: {:?}", now.elapsed());
let output = child.wait_with_output().expect("failed to wait on process");
println!("Output: {:?}", output);
} else {
eprintln!("Usage: prog [size]");
std::process::exit(1);
}
()
}
```
Running it and passing different amounts of elements to use to allocate
memory shows that the time taken for `spawn()` can differ quite
significantly. In latter case the `posix_spawnp()` implementation is 30x
faster:
```
$ cargo run --release 10000000
...
Spawn took: 324.275µs
hello
$ cargo run --release 10000000 changepath
...
Overriding PATH
Spawn took: 2.346809ms
hello
$ cargo run --release 100000000
...
Spawn took: 387.842µs
hello
$ cargo run --release 100000000 changepath
...
Overriding PATH
Spawn took: 13.434677ms
hello
```
[1]: 5f72f9800b/posix/execvpe.c (L81)
Deny broken intra-doc links in linkchecker
Since rustdoc isn't warning about these links, check for them manually.
This also fixes the broken links that popped up from the lint.
stabilize union with 'ManuallyDrop' fields and 'impl Drop for Union'
As [discussed by @SimonSapin and @withoutboats](https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/55149#issuecomment-634692020), this PR proposes to stabilize parts of the `untagged_union` feature gate:
* It will be possible to have a union with field type `ManuallyDrop<T>` for any `T`.
* While at it I propose we also stabilize `impl Drop for Union`; to my knowledge, there are no open concerns around this feature.
In the RFC discussion, we also talked about allowing `&mut T` as another non-`Copy` non-dropping type, but that felt to me like an overly specific exception so I figured we'd wait if there is actually any use for such a special case.
Some things remain unstable and still require the `untagged_union` feature gate:
* Union with fields that do not drop, are not `Copy`, and are not `ManuallyDrop<_>`. The reason to not stabilize this is to avoid semver concerns around libraries adding `Drop` implementations later. (This is already not fully semver compatible as, to my knowledge, the borrow checker will exploit the non-dropping nature of any type, but it seems prudent to avoid further increasing the amount of trouble adding an `impl Drop` can cause.)
Due to this, quite a few tests still need the `untagged_union` feature, but I think the ones where I could remove the feature flag provide good test coverage for the stable part.
Cc @rust-lang/lang
POSIX leaves it implementation-defined whether `link` follows symlinks.
In practice, for example, on Linux it does not and on FreeBSD it does.
So, switch to `linkat`, so that we can pick a behavior rather than
depending on OS defaults.
Pick the option to not follow symlinks. This is somewhat arbitrary, but
seems the less surprising choice because hard linking is a very
low-level feature which requires the source and destination to be on
the same mounted filesystem, and following a symbolic link could end
up in a different mounted filesystem.
Cleanup cloudabi mutexes and condvars
This gets rid of lots of unnecessary unsafety.
All the AtomicU32s were wrapped in UnsafeCell or UnsafeCell<MaybeUninit>, and raw pointers were used to get to the AtomicU32 inside. This change cleans that up by using AtomicU32 directly.
Also replaces a UnsafeCell<u32> by a safer Cell<u32>.
@rustbot modify labels: +C-cleanup
Static mutex is static
StaticMutex is only ever used with as a static (as the name already suggests). So it doesn't have to be generic over a lifetime, but can simply assume 'static.
This 'static lifetime guarantees the object is never moved, so this is no longer a manually checked requirement for unsafe calls to lock().
@rustbot modify labels: +T-libs +A-concurrency +C-cleanup
For backtrace, use StaticMutex instead of a raw sys Mutex.
The code used the very unsafe `sys::mutex::Mutex` directly, and built its own unlock-on-drop wrapper around it. The StaticMutex wrapper already provides that and is easier to use safely.
@rustbot modify labels: +T-libs +C-cleanup
Use futex-based thread-parker for Wasm32.
This uses the existing `sys_common/thread_parker/futex.rs` futex-based thread parker (that was already used for Linux) for wasm32 as well (if the wasm32 atomics target feature is enabled, which is not the case by default).
Wasm32 provides the basic futex operations as instructions: https://webassembly.github.io/threads/syntax/instructions.html
These are now exposed from `sys::futex::{futex_wait, futex_wake}`, just like on Linux. So, `thread_parker/futex.rs` stays completely unmodified.
Refactor io/buffered.rs into submodules
This pull request splits `BufWriter`, `BufReader`, `LineWriter`, and `LineWriterShim` (along with their associated tests) into separate submodules. It contains no functional changes. This change is being made in anticipation of adding another type of buffered writer which can be switched between line- and block-buffering mode.
Part of a series of pull requests resolving #60673.
StaticMutex is only ever used with as a static (as the name already
suggests). So it doesn't have to be generic over a lifetime, but can
simply assume 'static.
This 'static lifetime guarantees the object is never moved, so this is
no longer a manually checked requirement for unsafe calls to lock().
The comment said it's UB to call lock() while it is locked. That'd be
quite a useless Mutex. :) It was supposed to say 'locked by the same
thread', not just 'locked'.
warning: the operation is ineffective. Consider reducing it to
`self.segments()[0]`
--> library/std/src/net/ip.rs:1265:9
|
1265 | (self.segments()[0] & 0xffff) == 0xfe80
| ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
|
= note: `#[warn(clippy::identity_op)]` on by default
= help: for further information visit
https://rust-lang.github.io/rust-clippy/master/index.html#identity_op
warning: the operation is ineffective. Consider reducing it to
`self.segments()[1]`
--> library/std/src/net/ip.rs:1266:16
|
1266 | && (self.segments()[1] & 0xffff) == 0
| ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
|
= help: for further information visit
https://rust-lang.github.io/rust-clippy/master/index.html#identity_op
warning: the operation is ineffective. Consider reducing it to
`self.segments()[2]`
--> library/std/src/net/ip.rs:1267:16
|
1267 | && (self.segments()[2] & 0xffff) == 0
| ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
|
= help: for further information visit
https://rust-lang.github.io/rust-clippy/master/index.html#identity_op
warning: the operation is ineffective. Consider reducing it to
`self.segments()[3]`
--> library/std/src/net/ip.rs:1268:16
|
1268 | && (self.segments()[3] & 0xffff) == 0
| ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
|
= help: for further information visit
https://rust-lang.github.io/rust-clippy/master/index.html#identity_op
Signed-off-by: wcampbell <wcampbell1995@gmail.com>
warning: struct update has no effect, all the fields in the struct have
already been specified
--> library/std/src/net/addr.rs:367:19
|
367 | ..unsafe { mem::zeroed() }
| ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
|
= note: `#[warn(clippy::needless_update)]` on by default
= help: for further information visit
https://rust-lang.github.io/rust-clippy/master/index.html#needless_update
Remove unsafety from sys/unsupported and add deny(unsafe_op_in_unsafe_fn).
Replacing `UnsafeCell`s by a `Cell`s simplifies things and makes the mutex and rwlock implementations safe. Other than that, only unsafety in strlen() contained unsafe code.
@rustbot modify labels: +F-unsafe-block-in-unsafe-fn +C-cleanup
Implement `AsRawFd` for `StdinLock` etc. on WASI.
WASI implements `AsRawFd` for `Stdin`, `Stdout`, and `Stderr`, so
implement it for `StdinLock`, `StdoutLock`, and `StderrLock` as well.
r? @alexcrichton
Avoid SeqCst or static mut in mach_timebase_info and QueryPerformanceFrequency caches
This patch went through a couple iterations but the end result is replacing a pattern where an `AtomicUsize` (updated with many SeqCst ops) guards a `static mut` with a single `AtomicU64` that is known to use 0 as a value indicating that it is not initialized.
The code in both places exists to cache values used in the conversion of Instants to Durations on macOS, iOS, and Windows.
I have no numbers to prove that this improves performance (It seems a little futile to benchmark something like this), but it's much simpler, safer, and in practice we'd expect it to be faster everywhere where Relaxed operations on AtomicU64 are cheaper than SeqCst operations on AtomicUsize, which is a lot of places.
Anyway, it also removes a bunch of unsafe code and greatly simplifies the logic, so IMO that alone would be worth it unless it was a regression.
If you want to take a look at the assembly output though, see https://godbolt.org/z/rbr6vn for x86_64, https://godbolt.org/z/cqcbqv for aarch64 (Note that this just the output of the mac side, but i'd expect the windows part to be the same and don't feel like doing another godbolt for it). There are several versions of this function in the godbolt:
- `info_new`: version in the current patch
- `info_less_new`: version in initial PR
- `info_original`: version currently in the tree
- `info_orig_but_better_orderings`: a version that just tries to change the original code's orderings from SeqCst to the (probably) minimal orderings required for soundness/correctness.
The biggest concern I have here is if we can use AtomicU64, or if there are targets that dont have it that this code supports. AFAICT: no. (If that changes in the future, it's easy enough to do something different for them)
r? `@Amanieu` because he caught a couple issues last time I tried to do a patch reducing orderings 😅
---
<details>
<summary>I rewrote this whole message so the original is inside here</summary>
I happened to notice the code we use for caching the result of mach_timebase_info uses SeqCst exclusively.
However, thinking a little more, it's actually pretty easy to avoid the static mut by packing the timebase info into an AtomicU64.
This entirely avoids needing to do the compare_exchange. The AtomicU64 can be read/written using Relaxed ops, which on current macos/ios platforms (x86_64/aarch64) have no overhead compared to direct loads/stores. This simplifies the code and makes it a lot safer too.
I have no numbers to prove that this improves performance (It seems a little futile to benchmark something like this), although it should do that on both targets it applies to.
That said, it also removes a bunch of unsafe code and simplifies the logic (arguably at least — there are only two states now, initialized or not), so I think it's a net win even without concrete numbers.
If you want to take a look at the assembly output though, see below. It has the new version, the original, and a version of the original with lower Orderings (which is still worse than the version in this PR)
- godbolt.org/z/obfqf9 x86_64-apple-darwin
- godbolt.org/z/Wz5cWc aarch64-unknown-linux-gnu (godbolt can't do aarch64-apple-ios but that doesn't matter here)
A different (and more efficient) option than this would be to just use the AtomicU64 and use the knowledge that after initialization the denominator should be nonzero... That felt like it's relying on too many things I'm not confident in, so I didn't want to do that.
</details>
rust-lang/rust#77147 simplifies things by splitting this Mutex type
into two types matching the two use cases: StaticMutex and MovableMutex.
To support the behavior of StaticMutex, we move part of the mutex
implementation into libstd.
doc: disambiguate stat in MetadataExt::as_raw_stat
A few architectures in `os::linux::raw` import `libc::stat`, rather than
defining that type directly. However, that also imports the _function_
called `stat`, which makes this doc link ambiguous:
error: `crate::os::linux::raw::stat` is both a struct and a function
--> library/std/src/os/linux/fs.rs:21:19
|
21 | /// [`stat`]: crate::os::linux::raw::stat
| ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^ ambiguous link
|
= note: `-D broken-intra-doc-links` implied by `-D warnings`
help: to link to the struct, prefix with the item type
|
21 | /// [`stat`]: struct@crate::os::linux::raw::stat
| ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
help: to link to the function, add parentheses
|
21 | /// [`stat`]: crate::os::linux::raw::stat()
| ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
We want the `struct`, so it's now prefixed accordingly.
Link to documentation-specific guidelines.
Changed contribution information URL because it's not obvious how to get from the current URL to the documentation-specific content.
The current URL points to this "Getting Started" page, which contains nothing specific about documentation[*] and instead launches into how to *build* `rustc` which is not a strict prerequisite for contributing documentation fixes:
* https://rustc-dev-guide.rust-lang.org/getting-started.html
[*] The most specific content is a "Writing documentation" bullet point which is not itself a link to anything (I guess a patch for that might be helpful too).
### Why?
Making this change will make it easier for people who wish to make small "drive by" documentation fixes (and read contribution guidelines ;) ) which I find are often how I start contributing to a project. (Exhibit A: https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/77050 :) )
### Background
My impression is the change of content linked is an unintentional change due to a couple of other changes:
* Originally, the link pointed to `contributing.md` which started with a "table of contents" linking to each section. But the content in `contributing.md` was removed and replaced with a link to the "Getting Started" section here:
* 3f6928f1f6 (diff-6a3371457528722a734f3c51d9238c13L1)
But the changed link doesn't actually point to the equivalent content, which is now located here:
* https://rustc-dev-guide.rust-lang.org/contributing.html
(If the "Guide to Rustc Development" is now considered the canonical location of "How to Contribute" content it might be a good idea to merge some of the "Contributing" Introduction section into the "Getting Started" section.)
* This was then compounded by changing the link from `contributing.md` to `contributing.html` here:
* https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/74037/files#diff-242481015141f373dcb178e93cffa850L88
In order to even find the new location of the previous `contributing.md` content I ended up needing to do a GitHub search of the `rust-lang` org for the phrase "Documentation improvements are very welcome". :D
Fix error checking in posix_spawn implementation of Command
* Check for errors returned from posix_spawn*_init functions
* Check for non-zero return value from posix_spawn functions
A few architectures in `os::linux::raw` import `libc::stat`, rather than
defining that type directly. However, that also imports the _function_
called `stat`, which makes this doc link ambiguous:
error: `crate::os::linux::raw::stat` is both a struct and a function
--> library/std/src/os/linux/fs.rs:21:19
|
21 | /// [`stat`]: crate::os::linux::raw::stat
| ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^ ambiguous link
|
= note: `-D broken-intra-doc-links` implied by `-D warnings`
help: to link to the struct, prefix with the item type
|
21 | /// [`stat`]: struct@crate::os::linux::raw::stat
| ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
help: to link to the function, add parentheses
|
21 | /// [`stat`]: crate::os::linux::raw::stat()
| ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
We want the `struct`, so it's now prefixed accordingly.
`DirEntry` contains a `ReadDir` handle, which used to just be a wrapper
on `Arc<InnerReadDir>`. Commit af75314ecd added `end_of_stream: bool`
which is not needed by `DirEntry`, but adds 8 bytes after padding. We
can let `DirEntry` have an `Arc<InnerReadDir>` directly to avoid that.
The posix_spawnattr_init & posix_spawn_file_actions_init might fail,
but their return code is not checked.
Check for non-zero return code and destroy only succesfully initialized
objects.
The cvt function compares the argument with -1 and when equal returns a new
io::Error constructed from errno. It is used together posix_spawn_* functions.
This is incorrect. Those functions do not set errno. Instead they return
non-zero error code directly.
Check for non-zero return code and use it to construct a new io::Error.
(docs): make mutex error comment consistent with codebase
Although exceptionally minor, I found this stands out from other error reporting language used in doc comments. With the existence of the `failure` crate, I suppose this could be slightly ambiguous. In any case, this change brings the particular comment into a consistent state with other mentions of returning errors.
Support static linking with glibc and target-feature=+crt-static
With this change, it's possible to build on a linux-gnu target and pass
RUSTFLAGS='-C target-feature=+crt-static' or the equivalent via a
`.cargo/config.toml` file, and get a statically linked executable.
Update to libc 0.2.78, which adds support for static linking with glibc.
Add `crt_static_respected` to the `linux_base` target spec.
Update `android_base` and `linux_musl_base` accordingly. Avoid enabling
crt_static_respected on Android platforms, since that hasn't been
tested.
Closes https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/65447.
Minor `hash_map` doc adjustments + item attribute orderings
This PR is really a couple visual changes glued together:
1. Some of the doc comments for items in `std::collections::hash_map` referenced the names of types without escaping their formatting (e.g. using "VacantEntry" instead of "`VacantEntry`") - the ones I could find were changed to the latter
2. The vast majority of pre-item attributes seem to place doc comments as the first attribute (instead of things like `#[feature(...)]`), so the few that had the other order were changed.
3. Also ordering related: the general trend seems to be that `#[feature]` attributes follow `#[inline]`, so I swapped the two lines in places where that ordering was reversed. This is primarily a change based on stylistic continuity and aesthetics - I'm not sure how important that actually is / should be.
I figured this would be pretty uncontroversial, but some of these might have been intentional for reasons I don't know about - if so, I'd be happy to remove the relevant changes. Of these, the final set of changes is probably the most unnecessary, so it also might be better to leave those out (in favor of reducing code churn).
Unbox mutexes and condvars on some platforms
Both mutexes and condition variables contained a Box containing the actual os-specific object. This was done because moving these objects may cause undefined behaviour on some platforms.
However, this is not needed on Windows[1], Wasm[2], cloudabi[2], and 'unsupported'[3], were the box was only needlessly making them less efficient.
This change gets rid of the box on those platforms.
On those platforms, `Condvar` can no longer verify it is only used with one `Mutex`, as mutexes no longer have a stable address. This was addressed and considered acceptable in #76932.
[1]\: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/win32/api/synchapi/nf-synchapi-initializesrwlock
[2]\: These are just a single atomic integer together with futex wait/wake calls/instructions.
[3]\: The `unsupported` platform doesn't support multiple threads at all.
Only use LOCAL_{STDOUT,STDERR} when set_{print/panic} is used.
The thread local `LOCAL_STDOUT` and `LOCAL_STDERR` are only used by the `test` crate to capture output from tests when running them in the same process in differen threads. However, every program will check these variables on every print, even outside of testing.
This involves allocating a thread local key, and registering a thread local destructor. This can be somewhat expensive.
This change keeps a global flag (`LOCAL_STREAMS`) which will be set to `true` when either of these local streams is used. (So, effectively only in test and benchmark runs.) When this flag is off, these thread locals are not even looked at and therefore will not be initialized on the first output on every thread, which also means no thread local destructors will be registered.
---
Together with https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/77154, this should make output a little bit more efficient.
Fix Debug implementations of some of the HashMap and BTreeMap iterator types
HashMap's `ValuesMut`, BTreeMaps `ValuesMut`, IntoValues and `IntoKeys` structs were printing both keys and values on their Debug implementations. But they are iterators over either keys or values. Irrelevant values should not be visible. With this PR, they only show relevant fields.
This fixes#75297.
[Here's an example code.](https://play.rust-lang.org/?version=nightly&mode=debug&edition=2018&gist=0c79356ed860e347a0c1a205616f93b7) This prints this on nightly:
```
ValuesMut { inner: IterMut { range: [(1, "hello"), (2, "goodbye")], length: 2 } }
IntoKeys { inner: [(1, "hello"), (2, "goodbye")] }
IntoValues { inner: [(1, "hello"), (2, "goodbye")] }
[(2, "goodbye"), (1, "hello")]
```
After the patch this example prints these instead:
```
["hello", "goodbye"]
["hello", "goodbye"]
[1, 2]
["hello", "goodbye"]
```
I didn't add test cases for them, since I couldn't see any tests for Debug implementations anywhere. But please let me know if I should add it to a specific place.
r? @dtolnay
Use posix_spawn on musl targets
The posix_spawn had been available in a form suitable for use in a
Command implementation since musl 0.9.12. Use it in a preference to a
fork when possible, to benefit from CLONE_VM|CLONE_VFORK used there.
Previously `Command::spawn` would fall back to the non-posix_spawn based
implementation if the `PATH` environment variable was possibly changed.
On systems with a modern (g)libc `posix_spawn()` can be significantly
faster. If program is a path itself the `PATH` environment variable is
not used for the lookup and it should be safe to use the
`posix_spawnp()` method. [1]
We found this, because we have a cli application that effectively runs a
lot of subprocesses. It would sometimes noticeably hang while printing
output. Profiling showed that the process was spending the majority of
time in the kernel's `copy_page_range` function while spawning
subprocesses. During this time the process is completely blocked from
running, explaining why users were reporting the cli app hanging.
Through this we discovered that `std::process::Command` has a fast and
slow path for process execution. The fast path is backed by
`posix_spawnp()` and the slow path by fork/exec syscalls being called
explicitly. Using fork for process creation is supposed to be fast, but
it slows down as your process uses more memory. It's not because the
kernel copies the actual memory from the parent, but it does need to
copy the references to it (see `copy_page_range` above!). We ended up
using the slow path, because the command spawn implementation in falls
back to the slow path if it suspects the PATH environment variable was
changed.
Here is a smallish program demonstrating the slowdown before this code
change:
```
use std::process::Command;
use std::time::Instant;
fn main() {
let mut args = std::env::args().skip(1);
if let Some(size) = args.next() {
// Allocate some memory
let _xs: Vec<_> = std::iter::repeat(0)
.take(size.parse().expect("valid number"))
.collect();
let mut command = Command::new("/bin/sh");
command
.arg("-c")
.arg("echo hello");
if args.next().is_some() {
println!("Overriding PATH");
command.env("PATH", std::env::var("PATH").expect("PATH env var"));
}
let now = Instant::now();
let child = command
.spawn()
.expect("failed to execute process");
println!("Spawn took: {:?}", now.elapsed());
let output = child.wait_with_output().expect("failed to wait on process");
println!("Output: {:?}", output);
} else {
eprintln!("Usage: prog [size]");
std::process::exit(1);
}
()
}
```
Running it and passing different amounts of elements to use to allocate
memory shows that the time taken for `spawn()` can differ quite
significantly. In latter case the `posix_spawnp()` implementation is 30x
faster:
```
$ cargo run --release 10000000
...
Spawn took: 324.275µs
hello
$ cargo run --release 10000000 changepath
...
Overriding PATH
Spawn took: 2.346809ms
hello
$ cargo run --release 100000000
...
Spawn took: 387.842µs
hello
$ cargo run --release 100000000 changepath
...
Overriding PATH
Spawn took: 13.434677ms
hello
```
[1]: 5f72f9800b/posix/execvpe.c (L81)
Add accessors to Command.
This adds some accessor methods to `Command` to provide a way to access the values set when building the `Command`. An example where this can be useful is to display the command to be executed. This is roughly based on the [`ProcessBuilder`](13b73cdaf7/src/cargo/util/process_builder.rs (L105-L134)) in Cargo.
Possible concerns about the API:
- Values with NULs on Unix will be returned as `"<string-with-nul>"`. I don't think it is practical to avoid this, since otherwise a whole separate copy of all the values would need to be kept in `Command`.
- Does not handle `arg0` on Unix. This can be awkward to support in `get_args` and is rarely used. I figure if someone really wants it, it can be added to `CommandExt` as a separate method.
- Does not offer a way to detect `env_clear`. I'm uncertain if it would be useful for anyone.
- Does not offer a way to get an environment variable by name (`get_env`). I figure this can be added later if anyone really wants it. I think the motivation for this is weak, though. Also, the API could be a little awkward (return a `Option<Option<&OsStr>>`?).
- `get_envs` could skip "cleared" entries and just return `&OsStr` values instead of `Option<&OsStr>`. I'm on the fence here. My use case is to display a shell command, and I only intend it to be roughly equivalent to the actual execution, and I probably won't display `None` entries. I erred on the side of providing extra information, but I suspect many situations will just filter out the `None`s.
- Could implement more iterator stuff (like `DoubleEndedIterator`).
I have not implemented new std items before, so I'm uncertain if the existing issue should be reused, or if a new tracking issue is needed.
cc #44434
Fix is_absolute on WASI
WASI does not match `cfg(unix)`, but its paths are Unix-like (`/some/path`) and don't have Windows-like prefixes.
Without this change, `is_absolute` for any paths, including `/some/path`, was returning `false`on a WASI target, which is obviously not true and undesirable.
Split sys_common::Mutex in StaticMutex and MovableMutex.
The (unsafe) `Mutex` from `sys_common` had a rather complicated interface. You were supposed to call `init()` manually, unless you could guarantee it was neither moved nor used reentrantly.
Calling `destroy()` was also optional, although it was unclear if 1) resources might be leaked or not, and 2) if `destroy()` should only be called when `init()` was called.
This allowed for a number of interesting (confusing?) different ways to use this `Mutex`, all captured in a single type.
In practice, this type was only ever used in two ways:
1. As a static variable. In this case, neither `init()` nor `destroy()` are called. The variable is never moved, and it is never used reentrantly. It is only ever locked using the `LockGuard`, never with `raw_lock`.
2. As a `Box`ed variable. In this case, both `init()` and `destroy()` are called, it will be moved and possibly used reentrantly.
No other combinations are used anywhere in `std`.
This change simplifies things by splitting this `Mutex` type into two types matching the two use cases: `StaticMutex` and `MovableMutex`.
The interface of both new types is now both safer and simpler. The first one does not call nor expose `init`/`destroy`, and the second one calls those automatically in its `new()` and `Drop` functions. Also, the locking functions of `MovableMutex` are no longer unsafe.
---
This will also make it easier to conditionally box mutexes later, by moving that decision into sys/sys_common. Some of the mutex implementations (at least those of Wasm and 'sys/unsupported') are safe to move, so wouldn't need a box. ~~(But that's blocked on #76932 for now.)~~ (See #77380.)
Improve std::sys::windows::compat
Improves the compat_fn macro in sys::windows, which is used for conditionally loading APIs that might not be available.
- The module (dll) name can now be any string, not just an ident. (Not all Windows api modules are valid Rust identifiers. E.g. `WaitOnAddress` comes from `API-MS-Win-Core-Synch-l1-2-0.dll`.)
- Adds `FuncName::is_available()` for checking if a function is really available without having to do a duplicate lookup.
- Add comment explaining the lack of locking.
- Use `$_:block` to simplify the macro_rules.
- Apply `allow(unused_variables)` only to the fallback instead of everything.
---
The second point (`is_available()`) simplifies code that needs to pick an implementation depening on what is available, like `sys/windows/mutex.rs`. Before this change, it'd do its own lookup and keep its own `AtomicUsize` to track the result. Now it can just use `c::AcquireSRWLockExclusive::is_available()` directly.
This will also be useful when park/unpark/CondVar/etc. get improved implementations (e.g. from parking_lot or something else), as the best APIs for those are not available before Windows 8.
Make RawFd implement the RawFd traits
This PR makes `RawFd` implement `AsRawFd`, `IntoRawFd` and `FromRawFd`, so it can be passed to interfaces that use one of those traits as a bound.