Remove special-casing for `SimplifiedType` for next solver
It's unnecessary due to the way that we fully normalize the self type before assembly begins.
r? lcnr
These functions are only used in `rustc_builtin_macros`, so it makes
sense for them to live there. This allows them to be changed from `pub`
to `pub(crate)`.
uses a `ProofTreeVisitor` to look into nested
goals when looking at the pending obligations
during hir typeck. Used by closure signature
inference, coercion, and for async functions.
`-Z debug-macros` is "stabilized" by enabling it by default and removing.
`-Z collapse-macro-debuginfo` is stabilized as `-C collapse-macro-debuginfo`.
It now supports all typical boolean values (`parse_opt_bool`) in addition to just yes/no.
Default value of `collapse_debuginfo` was changed from `false` to `external` (i.e. collapsed if external, not collapsed if local).
`#[collapse_debuginfo]` attribute without a value is no longer supported to avoid guessing the default.
Don't ICE when `codegen_select_candidate` returns ambiguity in new solver
Because we merge identical candidates, we may have >1 impl candidate to in `codegen_select_error` but *not* have a trait error.
r? lcnr
Detect borrow error involving sub-slices and suggest `split_at_mut`
```
error[E0499]: cannot borrow `foo` as mutable more than once at a time
--> $DIR/suggest-split-at-mut.rs:13:18
|
LL | let a = &mut foo[..2];
| --- first mutable borrow occurs here
LL | let b = &mut foo[2..];
| ^^^ second mutable borrow occurs here
LL | a[0] = 5;
| ---- first borrow later used here
|
= help: use `.split_at_mut(position)` or similar method to obtain two mutable non-overlapping sub-slices
```
Address most of #58792.
For follow up work, we should emit a structured suggestion for cases where we can identify the exact `let (a, b) = foo.split_at_mut(2);` call that is needed.
Improved code with clippy
I haven't used the bootstrapped compiler, but I think I have made some improvements using clippy. I have already made the following changes to the compiler:
Replaced `self.first().is_digit(10)` with `self.first().is_ascii_digit()` on lines 633, 664, and 680 of compiler/rust_lexer/src/lib.rs.
Removed unnecessary cast on line 262 of compiler/rustc_lexer/src/unescape.rs
Replaced ok_or_else with ok_or on line 303 of compiler/rustc_lexer/src/unescape.rs
Replaced `!std::env::var("RUSTC_BOOTSTRAP").is_ok()` with `std::env::var("RUSTC_BOOTSTRAP").is_err()` on line 4 of compiler/rustc_macros/build.rs
Removed needless borrow for generic argument `env`on line 53 of compiler/rust_llvm/build.rs
```
error[E0499]: cannot borrow `foo` as mutable more than once at a time
--> $DIR/suggest-split-at-mut.rs:13:18
|
LL | let a = &mut foo[..2];
| --- first mutable borrow occurs here
LL | let b = &mut foo[2..];
| ^^^ second mutable borrow occurs here
LL | a[0] = 5;
| ---- first borrow later used here
|
= help: use `.split_at_mut(position)` or similar method to obtain two mutable non-overlapping sub-slices
```
Address most of #58792.
For follow up work, we should emit a structured suggestion for cases where we can identify the exact `let (a, b) = foo.split_at_mut(2);` call that is needed.
Enforce closure args + return type are WF
I found this out when investigating https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/123461#issuecomment-2040894359. Turns out we don't register WF obligations for closure args and return types, leading to the ICE.
~~I think this is a useful thing to check for, but I'd like to check what the fallout is.~~ crater is complete.
~~Worst case, I think we should enforce this across an edition boundary (and possibly eventually migrate this for all editions) -- this should be super easy to do, since this is a check in HIR wfcheck, so it can be made edition dependent.~~ I believe the regressions are manageable enough to not necessitate edition-specific behavior.
Fixes#123461
Set writable and dead_on_unwind attributes for sret arguments
Set the `writable` and `dead_on_unwind` attributes for `sret` arguments. This allows call slot optimization to remove more memcpy's.
See https://llvm.org/docs/LangRef.html#parameter-attributes for the specification of these attributes. In short, the statement we're making here is that:
* The return slot is writable.
* The return slot will not be read if the function unwinds.
Fixes https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/90595.
Provide more context and suggestions in borrowck errors involving closures
Start pointing to where bindings where declared when they are captured in closures:
```
error[E0597]: `x` does not live long enough
--> $DIR/suggest-return-closure.rs:23:9
|
LL | let x = String::new();
| - binding `x` declared here
...
LL | |c| {
| --- value captured here
LL | x.push(c);
| ^ borrowed value does not live long enough
...
LL | }
| -- borrow later used here
| |
| `x` dropped here while still borrowed
```
Suggest cloning in more cases involving closures:
```
error[E0507]: cannot move out of `foo` in pattern guard
--> $DIR/issue-27282-move-ref-mut-into-guard.rs:11:19
|
LL | if { (|| { let mut bar = foo; bar.take() })(); false } => {},
| ^^ --- move occurs because `foo` has type `&mut Option<&i32>`, which does not implement the `Copy` trait
| |
| `foo` is moved here
|
= note: variables bound in patterns cannot be moved from until after the end of the pattern guard
help: consider cloning the value if the performance cost is acceptable
|
LL | if { (|| { let mut bar = foo.clone(); bar.take() })(); false } => {},
| ++++++++
```
Mention when type parameter could be Clone
```
error[E0382]: use of moved value: `t`
--> $DIR/use_of_moved_value_copy_suggestions.rs:7:9
|
LL | fn duplicate_t<T>(t: T) -> (T, T) {
| - move occurs because `t` has type `T`, which does not implement the `Copy` trait
...
LL | (t, t)
| - ^ value used here after move
| |
| value moved here
|
help: if `T` implemented `Clone`, you could clone the value
--> $DIR/use_of_moved_value_copy_suggestions.rs:4:16
|
LL | fn duplicate_t<T>(t: T) -> (T, T) {
| ^ consider constraining this type parameter with `Clone`
...
LL | (t, t)
| - you could clone this value
help: consider restricting type parameter `T`
|
LL | fn duplicate_t<T: Copy>(t: T) -> (T, T) {
| ++++++
```
The `help` is new. On ADTs, we also extend the output with span labels:
```
error[E0507]: cannot move out of static item `FOO`
--> $DIR/issue-17718-static-move.rs:6:14
|
LL | let _a = FOO;
| ^^^ move occurs because `FOO` has type `Foo`, which does not implement the `Copy` trait
|
note: if `Foo` implemented `Clone`, you could clone the value
--> $DIR/issue-17718-static-move.rs:1:1
|
LL | struct Foo;
| ^^^^^^^^^^ consider implementing `Clone` for this type
...
LL | let _a = FOO;
| --- you could clone this value
help: consider borrowing here
|
LL | let _a = &FOO;
| +
```
Suggest cloning captured binding in move closure
```
error[E0507]: cannot move out of `bar`, a captured variable in an `FnMut` closure
--> $DIR/borrowck-move-by-capture.rs:9:29
|
LL | let bar: Box<_> = Box::new(3);
| --- captured outer variable
LL | let _g = to_fn_mut(|| {
| -- captured by this `FnMut` closure
LL | let _h = to_fn_once(move || -> isize { *bar });
| ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^ ----
| | |
| | variable moved due to use in closure
| | move occurs because `bar` has type `Box<isize>`, which does not implement the `Copy` trait
| `bar` is moved here
|
help: clone the value before moving it into the closure 1
|
LL ~ let value = bar.clone();
LL ~ let _h = to_fn_once(move || -> isize { value });
|
```
```
error[E0507]: cannot move out of `bar`, a captured variable in an `FnMut` closure
--> $DIR/borrowck-move-by-capture.rs:9:29
|
LL | let bar: Box<_> = Box::new(3);
| --- captured outer variable
LL | let _g = to_fn_mut(|| {
| -- captured by this `FnMut` closure
LL | let _h = to_fn_once(move || -> isize { *bar });
| ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^ ----
| | |
| | variable moved due to use in closure
| | move occurs because `bar` has type `Box<isize>`, which does not implement the `Copy` trait
| `bar` is moved here
|
help: clone the value before moving it into the closure
|
LL ~ let value = bar.clone();
LL ~ let _h = to_fn_once(move || -> isize { value });
|
```
```
error[E0382]: use of moved value: `t`
--> $DIR/use_of_moved_value_copy_suggestions.rs:7:9
|
LL | fn duplicate_t<T>(t: T) -> (T, T) {
| - move occurs because `t` has type `T`, which does not implement the `Copy` trait
...
LL | (t, t)
| - ^ value used here after move
| |
| value moved here
|
help: if `T` implemented `Clone`, you could clone the value
--> $DIR/use_of_moved_value_copy_suggestions.rs:4:16
|
LL | fn duplicate_t<T>(t: T) -> (T, T) {
| ^ consider constraining this type parameter with `Clone`
...
LL | (t, t)
| - you could clone this value
help: consider restricting type parameter `T`
|
LL | fn duplicate_t<T: Copy>(t: T) -> (T, T) {
| ++++++
```
The `help` is new. On ADTs, we also extend the output with span labels:
```
error[E0507]: cannot move out of static item `FOO`
--> $DIR/issue-17718-static-move.rs:6:14
|
LL | let _a = FOO;
| ^^^ move occurs because `FOO` has type `Foo`, which does not implement the `Copy` trait
|
note: if `Foo` implemented `Clone`, you could clone the value
--> $DIR/issue-17718-static-move.rs:1:1
|
LL | struct Foo;
| ^^^^^^^^^^ consider implementing `Clone` for this type
...
LL | let _a = FOO;
| --- you could clone this value
help: consider borrowing here
|
LL | let _a = &FOO;
| +
```
Start pointing to where bindings were declared when they are captured in closures:
```
error[E0597]: `x` does not live long enough
--> $DIR/suggest-return-closure.rs:23:9
|
LL | let x = String::new();
| - binding `x` declared here
...
LL | |c| {
| --- value captured here
LL | x.push(c);
| ^ borrowed value does not live long enough
...
LL | }
| -- borrow later used here
| |
| `x` dropped here while still borrowed
```
Suggest cloning in more cases involving closures:
```
error[E0507]: cannot move out of `foo` in pattern guard
--> $DIR/issue-27282-move-ref-mut-into-guard.rs:11:19
|
LL | if { (|| { let mut bar = foo; bar.take() })(); false } => {},
| ^^ --- move occurs because `foo` has type `&mut Option<&i32>`, which does not implement the `Copy` trait
| |
| `foo` is moved here
|
= note: variables bound in patterns cannot be moved from until after the end of the pattern guard
help: consider cloning the value if the performance cost is acceptable
|
LL | if { (|| { let mut bar = foo.clone(); bar.take() })(); false } => {},
| ++++++++
```
Improve diagnostic for unknown `--print` request
This PR improves the diagnostic when encountering a unknown `--print` request.
It also moves the run-make test to a simple UI test.
Stabilise inline_const
# Stabilisation Report
## Summary
This PR will stabilise `inline_const` feature in expression position. `inline_const_pat` is still unstable and will *not* be stabilised.
The feature will allow code like this:
```rust
foo(const { 1 + 1 })
```
which is roughly desugared into
```rust
struct Foo;
impl Foo {
const FOO: i32 = 1 + 1;
}
foo(Foo::FOO)
```
This feature is from https://github.com/rust-lang/rfcs/pull/2920 and is tracked in #76001 (the tracking issue should *not* be closed as it needs to track inline const in pattern position). The initial implementation is done in #77124.
## Difference from RFC
There are two major differences (enhancements) as implemented from the RFC. First thing is that the RFC says that the type of an inline const block inferred from the content *within* it, but we currently can infer the type using the information from outside the const block as well. This is a frequently requested feature to the initial implementation (e.g. #89964). The inference is implemented in #89561 and is done by treating inline const similar to a closure and therefore share inference context with its parent body.
This allows code like:
```rust
let v: Vec<i32> = const { Vec::new() };
```
Another enhancement that differs from the RFC is that we currently allow inline consts to reference generic parameters. This is implemented in #96557.
This allows code like:
```rust
fn create_none_array<T, const N: usize>() -> [Option<T>; N] {
[const { None::<T> }; N]
}
```
This enhancement also makes inline const usable as static asserts:
```rust
fn require_zst<T>() {
const { assert!(std::mem::size_of::<T>() == 0) }
}
```
## Documentation
Reference: rust-lang/reference#1295
## Unresolved issues
We still have a few issues that are not resolved, but I don't think it necessarily has to block stabilisation:
* expr fragment specifier issue: #86730
* ~~`const {}` behaves similar to `async {}` but not to `{}` and `unsafe {}` (they are treated as `ExpressionWithoutBlock` rather than `ExpressionWithBlock`): https://rust-lang.zulipchat.com/#narrow/stream/213817-t-lang/topic/const.20blocks.20differ.20from.20normal.20and.20from.20unsafe.20blocks/near/290229453~~
## Tests
There are a few tests in https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/tree/master/src/test/ui/inline-const
Macro calls are ephemeral, they should not add anything to the definition tree, even if their AST could contains something with identity.
Thankfully, macro call AST cannot contain anything like that, so these walks are just noops.
In majority of other places in def_collector / build_reduced_graph they are already not visited.
(Also, a minor match reformatting is included.)
Add diagnostic item for `std::iter::Enumerate`
This adds a diagnostic item for `std::iter::Enumerate`. The change will be used by the clippy `unused_enumerate_index` lint to move away from type paths to using diagnostic items.
see: https://github.com/rust-lang/rust-clippy/issues/5393
More DefineOpaqueTypes::Yes
This accepts more code on stable. It is now possible to have match arms return a function item `foo::<ConcreteType>` and a function item `foo::<OpaqueTypeInDefiningScope>` in another, and that will constrain `OpaqueTypeInDefiningScope` to have the hidden type `ConcreteType`. So the following function will now compile, but on master it errors with a type mismatch on the second match arm
```rust
// The function item whose generic params we want to merge.
fn foo<T>(t: T) -> T { t }
// Helper ensuring we can constrain `T` on `F` without explicitly specifying it
fn bind<T, F: FnOnce(T) -> T>(_: T, f: F) -> F { f }
fn k() -> impl Sized {
let x = match true {
true => {
// `f` is `FnDef(foo, [infer_var])`
let f = foo;
// Get a value of an opaque type on stable
let t = k();
// this returns `FnDef(foo, [k::return])`
bind(t, f)
}
false => foo::<()>,
};
todo!()
}
```
r? ``@compiler-errors``
cc https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/116652
delegation: Support renaming, and async, const, extern "ABI" and C-variadic functions
Also allow delegating to functions with opaque types (`impl Trait`).
The delegation item will refer to the original opaque type from the callee, fresh opaque type won't be created, which seems like a reasonable behavior.
(Such delegation items will cause query cycles when used in trait impls, but it can be fixed later.)
Part of https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/118212.
It's a highly misleading name, because it's completely different to
`MetaItem::name_value_literal`. Specifically, it doesn't match
`MetaItemKind::NameValue` (e.g. `#[foo = 3]`), it matches
`MetaItemKind::List` (e.g. `#[foo(3)]`).
Couldn't find documentation supporting that single-variant
`#[repr(Rust)]` enums with RHS assigned work as expected with this
change.
```rust
enum Variants {
A = 17,
} // Would this be zero sized optimized guaranteed?
```
Stop using LLVM struct types for alloca
The alloca type has no semantic meaning, only the size (and alignment, but we specify it explicitly) matter. Using `[N x i8]` is a more direct way to specify that we want `N` bytes, and avoids relying on LLVM's struct layout. It is likely that a future LLVM version will change to an untyped alloca representation.
Split out from #121577.
r? `@ghost`
restrict promotion of `const fn` calls
We only promote them in `const`/`static` initializers, but even that is still unfortunate -- we still cannot add promoteds to required_consts. But we should add them there to make sure it's always okay to evaluate every const we encounter in a MIR body. That effort of not promoting things that can fail to evaluate is tracked in https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/80619. These `const fn` calls are the last missing piece.
So I propose that we do not promote const-fn calls in const when that may fail without the entire const failing, thereby completing https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/80619. Unfortunately we can't just reject promoting these functions outright due to backwards compatibility. So let's see if we can find a hack that makes crater happy...
For the record, this is the [crater analysis](https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/80243#issuecomment-751885520) from when I tried to entirely forbid this kind of promotion. It's a tiny amount of breakage and if we had a nice alternative for code like that, we could conceivably push it through... but sadly, inline const expressions are still blocked on t-lang concerns about post-monomorphization errors and we haven't yet figured out an implementation that can resolve those concerns. So we're forced to make progress via other means, such as terrible hacks like this.
Attempt one: only promote calls on the "safe path" at the beginning of a MIR block. This is the path that starts at the start block and continues via gotos and calls, but stops at the first branch. If we had imposed this restriction before stabilizing `if` and `match` in `const`, this would have definitely been sufficient...
EDIT: Turns out that works. :)
**Here's the t-lang [nomination comment](https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/121557#issuecomment-1990902440).** And here's the [FCP comment](https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/121557#issuecomment-2010306165).
r? `@oli-obk`
Enable `CrateNum` query feeding via `TyCtxt`
Instead of having a magic function that violates some `TyCtxtFeed` invariants, add a `create_def` equivalent for `CrateNum`s.
Note that this still isn't tracked by the query system (unlike `create_def`), and that feeding most `CrateNum` queries for crates other than the local one will likely cause performance regressions.
These things should be attempted on their own separately, but this PR should stand on its own
Also allow `impl Trait` in delegated functions.
The delegation item will refer to the original opaque type from the callee, fresh opaque type won't be created.
Rollup of 3 pull requests
Successful merges:
- #124003 (Dellvmize some intrinsics (use `u32` instead of `Self` in some integer intrinsics))
- #124169 (Don't fatal when calling `expect_one_of` when recovering arg in `parse_seq`)
- #124286 (Subtree sync for rustc_codegen_cranelift)
r? `@ghost`
`@rustbot` modify labels: rollup
Subtree sync for rustc_codegen_cranelift
This fixes a crash when compiling the standard library. In addition the Cranelift update fixes all the 128bit int abi incompatibility between cg_clif and cg_llvm.
r? ``@ghost``
``@rustbot`` label +A-codegen +A-cranelift +T-compiler
Don't fatal when calling `expect_one_of` when recovering arg in `parse_seq`
In `parse_seq`, when parsing a sequence of token-separated items, if we don't see a separator, we try to parse another item eagerly in order to give a good diagnostic and recover from a missing separator:
d1a0fa5ed3/compiler/rustc_parse/src/parser/mod.rs (L900-L901)
If parsing the item itself calls `expect_one_of`, then we will fatal because of #58903:
d1a0fa5ed3/compiler/rustc_parse/src/parser/mod.rs (L513-L516)
For `precise_capturing` feature I implemented, we do end up calling `expected_one_of`:
d1a0fa5ed3/compiler/rustc_parse/src/parser/ty.rs (L712-L714)
This leads the compiler to fatal *before* having emitted the first error, leading to absolutely no useful information for the user about what happened in the parser.
This PR makes it so that we stop doing that.
Fixes#124195
Dellvmize some intrinsics (use `u32` instead of `Self` in some integer intrinsics)
This implements https://github.com/rust-lang/compiler-team/issues/693 minus what was implemented in #123226.
Note: I decided to _not_ change `shl`/... builder methods, as it just doesn't seem worth it.
r? ``@scottmcm``
Rollup of 7 pull requests
Successful merges:
- #120929 (Wrap dyn type with parentheses in suggestion)
- #122591 (Suggest using type args directly instead of equality constraint)
- #122598 (deref patterns: lower deref patterns to MIR)
- #123048 (alloc::Layout: explicitly document size invariant on the type level)
- #123993 (Do `check_coroutine_obligations` once per typeck root)
- #124218 (Allow nesting subdiagnostics in #[derive(Subdiagnostic)])
- #124285 (Mark ``@RUSTC_BUILTIN`` search path usage as unstable)
r? `@ghost`
`@rustbot` modify labels: rollup
Do `check_coroutine_obligations` once per typeck root
We only need to do `check_coroutine_obligations` once per typeck root, especially since the new solver can't really (easily) associate which obligations correspond to which coroutines.
This requires us to move the checks for sized coroutine fields into `mir_coroutine_witnesses`, but that's fine imo.
r? lcnr
deref patterns: lower deref patterns to MIR
This lowers deref patterns to MIR. This is a bit tricky because this is the first kind of pattern that requires storing a value in a temporary. Thanks to https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/123324 false edges are no longer a problem.
The thing I'm not confident about is the handling of fake borrows. This PR ignores any fake borrows inside a deref pattern. We are guaranteed to at least fake borrow the place of the first pointer value, which could be enough, but I'm not certain.
Suggest using type args directly instead of equality constraint
When type arguments are written erroneously using an equality constraint we suggest specifying them directly without the equality constraint.
Fixes#122162
Changes the diagnostic in the issue from:
```rust
error[E0229]: associated type bindings are not allowed here
9 | impl std::cmp::PartialEq<Rhs = T> for S {
| ^^^^^^^ associated type not allowed here
|
```
to
```rust
error[E0229]: associated type bindings are not allowed here
9 | impl std::cmp::PartialEq<Rhs = T> for S {
| ^^^^^^^ associated type not allowed here
|
help: to use `T` as a generic argument specify it directly
|
| impl std::cmp::PartialEq<T> for S {
| ~
```
Use fulfillment in method probe, not evaluation
This PR reworks method probing to use fulfillment instead of a `for`-loop of `evaluate_predicate` calls, and moves normalization from method candidate assembly into the `consider_probe`, where it's applied to *all* candidates. This last part coincidentally fixes https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/121643#issuecomment-1975371248.
Regarding *why* this large rewrite is done: In general, it's an anti-pattern to do `for o in obligations { evaluate(o); }` because it's not compatible with the way that the new solver emits alias-relate obligations which constrain variables that may show up in other predicates.
r? lcnr
Disallow ambiguous attributes on expressions
This implements the suggestion in [#15701](https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/15701#issuecomment-2033124217) to disallow ambiguous outer attributes on expressions. This should resolve one of the concerns blocking the stabilization of `stmt_expr_attributes`.
weak lang items are not allowed to be #[track_caller]
For instance the panic handler will be called via this import
```rust
extern "Rust" {
#[lang = "panic_impl"]
fn panic_impl(pi: &PanicInfo<'_>) -> !;
}
```
A `#[track_caller]` would add an extra argument and thus make this the wrong signature.
The 2nd commit is a consistency rename; based on the docs [here](https://doc.rust-lang.org/unstable-book/language-features/lang-items.html) and [here](https://rustc-dev-guide.rust-lang.org/lang-items.html) I figured "lang item" is more widely used. (In the compiler output, "lang item" and "language item" seem to be pretty even.)
panic_str only exists for the migration to 2021 panic macros
The only caller is `expect_failed`, which is already a cold inline(never) function, so inlining into that function should be fine. (And indeed `panic_str` was `#[inline]` anyway.)
The existence of panic_str risks someone calling it when they should call `panic` instead, and I can't see a reason why this footgun should exist.
I also extended the comment in `panic` to explain why it needs a `'static` string -- I know I've wondered about this in the past and it took me quite a while to understand.
Rollup of 7 pull requests
Successful merges:
- #123680 (Deny gen keyword in `edition_2024_compat` lints)
- #124057 (Fix ICE when ADT tail has type error)
- #124168 (Use `DefiningOpaqueTypes::Yes` in rustdoc, where the `InferCtxt` is guaranteed to have no opaque types it can define)
- #124197 (Move duplicated code in functions in `tests/rustdoc-gui/notable-trait.goml`)
- #124200 (Improve handling of expr->field errors)
- #124220 (Miri: detect wrong vtables in wide pointers)
- #124266 (remove an unused type from the reentrant lock tests)
r? `@ghost`
`@rustbot` modify labels: rollup
Improve handling of expr->field errors
The current message for "`->` used for field access" is the following:
```rust
error: expected one of `!`, `.`, `::`, `;`, `?`, `{`, `}`, or an operator, found `->`
--> src/main.rs:2:6
|
2 | a->b;
| ^^ expected one of 8 possible tokens
```
([playground link](https://play.rust-lang.org/?version=stable&mode=debug&edition=2021&gist=7f8b6f4433aa7866124123575456f54e))
This PR tries to address this by adding a dedicated error message and recovery. The proposed error message is:
```
error: `->` used for field access or method call
--> ./tiny_test.rs:2:6
|
2 | a->b;
| ^^ help: try using `.` instead
|
= help: the `.` operator will dereference the value if needed
```
(feel free to bikeshed it as much as necessary)
Use `DefiningOpaqueTypes::Yes` in rustdoc, where the `InferCtxt` is guaranteed to have no opaque types it can define
r? `@lcnr`
I manually checked there it's always `tcx.infer_ctxt().build()`
Deny gen keyword in `edition_2024_compat` lints
Splits the `keyword_idents` lint into two -- `keyword_idents_2018` and `keyword_idents_2024` -- since each corresponds to a future-compat warning in a different edition. Group these together into a new `keyword_idents` lint group, and add the latter to the `rust_2024_compatibility` so that `gen` is ready for the 2024 edition.
cc `@traviscross` `@ehuss`
Add simple async drop glue generation
This is a prototype of the async drop glue generation for some simple types. Async drop glue is intended to behave very similar to the regular drop glue except for being asynchronous. Currently it does not execute synchronous drops but only calls user implementations of `AsyncDrop::async_drop` associative function and awaits the returned future. It is not complete as it only recurses into arrays, slices, tuples, and structs and does not have same sensible restrictions as the old `Drop` trait implementation like having the same bounds as the type definition, while code assumes their existence (requires a future work).
This current design uses a workaround as it does not create any custom async destructor state machine types for ADTs, but instead uses types defined in the std library called future combinators (deferred_async_drop, chain, ready_unit).
Also I recommend reading my [explainer](https://zetanumbers.github.io/book/async-drop-design.html).
This is a part of the [MCP: Low level components for async drop](https://github.com/rust-lang/compiler-team/issues/727) work.
Feature completeness:
- [x] `AsyncDrop` trait
- [ ] `async_drop_in_place_raw`/async drop glue generation support for
- [x] Trivially destructible types (integers, bools, floats, string slices, pointers, references, etc.)
- [x] Arrays and slices (array pointer is unsized into slice pointer)
- [x] ADTs (enums, structs, unions)
- [x] tuple-like types (tuples, closures)
- [ ] Dynamic types (`dyn Trait`, see explainer's [proposed design](https://github.com/zetanumbers/posts/blob/main/async-drop-design.md#async-drop-glue-for-dyn-trait))
- [ ] coroutines (https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/123948)
- [x] Async drop glue includes sync drop glue code
- [x] Cleanup branch generation for `async_drop_in_place_raw`
- [ ] Union rejects non-trivially async destructible fields
- [ ] `AsyncDrop` implementation requires same bounds as type definition
- [ ] Skip trivially destructible fields (optimization)
- [ ] New [`TyKind::AdtAsyncDestructor`](https://github.com/zetanumbers/posts/blob/main/async-drop-design.md#adt-async-destructor-types) and get rid of combinators
- [ ] [Synchronously undroppable types](https://github.com/zetanumbers/posts/blob/main/async-drop-design.md#exclusively-async-drop)
- [ ] Automatic async drop at the end of the scope in async context
Improve ICE message for forbidden dep-graph reads.
The new message mentions the main context that the ICE might occur in and it mentions the query/dep-node that is being read.
cc https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/123781, where this would have been helpful.
coverage: Prepare for improved branch coverage
When trying to rebase my new branch coverage work (including #124154) on top of the introduction of MC/DC coverage (#123409), I found it a lot harder than anticipated. With the benefit of hindsight, the branch coverage code and MC/DC code have become more interdependent than I'm happy with.
This PR therefore disentangles them a bit, so that it will be easier for both areas of code to evolve independently without interference.
---
This PR also includes a few extra branch coverage tests that I had sitting around from my current branch coverage work. They mostly just demonstrate that certain language constructs listed in #124118 currently don't have branch coverage support.
``@rustbot`` label +A-code-coverage
[cleanup] [llvm backend] Prevent creating the same `Instance::mono` multiple times
Just a little thing I came across while going through the code.
r? ```@oli-obk```
The error mentions `///`, when it's actually `//!`:
error[E0658]: attributes on expressions are experimental
--> test.rs:4:9
|
4 | //! wah
| ^^^^^^^
|
= note: see issue #15701 <https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/15701> for more information
= help: add `#![feature(stmt_expr_attributes)]` to the crate attributes to enable
= help: `///` is for documentation comments. For a plain comment, use `//`.
The current message for "`->` used for field access" is the following:
```rust
error: expected one of `!`, `.`, `::`, `;`, `?`, `{`, `}`, or an operator, found `->`
--> src/main.rs:2:6
|
2 | a->b;
| ^^ expected one of 8 possible tokens
```
(playground link[1])
This PR tries to address this by adding a dedicated error message and recovery. The proposed error message is:
```
error: `->` used for field access or method call
--> ./tiny_test.rs:2:6
|
2 | a->b;
| ^^ help: try using `.` instead
|
= help: the `.` operator will dereference the value if needed
```
(feel free to bikeshed it as much as necessary)
[1]: https://play.rust-lang.org/?version=stable&mode=debug&edition=2021&gist=7f8b6f4433aa7866124123575456f54e
Signed-off-by: Sasha Pourcelot <sasha.pourcelot@protonmail.com>
Ignore `-C strip` on MSVC
tl;dr - Define `-Cstrip` to only ever affect the binary; no other build artifacts.
This is necessary to improve cross-platform behavior consistency: if someone wanted debug information to be contained only in separate files on all platforms, they would set `-Cstrip=symbols` and `-Csplit-debuginfo=packed`, but this would result in no PDB files on MSVC.
Resolves#114215
This clears the way for larger changes to how branches are handled by the
coverage instrumentor, in order to support branch coverage for more language
constructs.
Fix ICE when there is a non-Unicode entry in the incremental crate directory
Fix the ICE that occurs when there is a non-Unicode entry in the incremental crate directory by replacing uses of `to_string_lossy` + `assert_no_characters_lost` with `to_str`. The added test would cause the compiler to ICE before this PR.
Add an intrinsic for `ptr::from_raw_parts(_mut)`
Fixes#123174
cc `@CAD97` `@saethlin`
r? `@cjgillot`
As suggested in https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/123190#issuecomment-2028717967, this adds a new `AggregateKind::RawPtr` for creating a pointer from its data pointer and its metadata.
That means that `slice::from_raw_parts` and friends no longer need to hard-code pointer layout into `libcore`, and because it no longer does union hacks the MIR is shorter and more amenable to optimizations.
fix normalizing in different `ParamEnv`s with the same `InferCtxt`
This PR changes the key of the projection cache from just `AliasTy` to `(AliasTy, ParamEnv)` to allow normalizing in different `ParamEnv`s without resetting caches. Previously, normalizing the same alias in different param envs would always reuse the cached result from the first normalization, which is incorrect if the projection clauses in the param env have changed.
Fixing this bug allows us to get rid of `InferCtxt::clear_caches`, which was only used by the `AutoTraitFinder`, because it requires normalizing in different param envs.
r? `@fmease`
Upcoming mingw-w64 releases will contain small math functions refactor which moved implementation around.
As a result functions like `lgamma`
now depend on libraries in this order:
`libmingwex.a` -> `libmsvcrt.a` -> `libmingwex.a`.
Fixes#124221
Fix trait solver overflow with `non_local_definitions` lint
This PR fixes the trait solver overflow with the `non_local_definitions` lint reported in https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/123573 using the suggestion from `@lcnr:` https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/123573#issuecomment-2041348320 to use the next trait solver.
~~I have not (yet) tried to create a minimized repro~~ ``@compiler-errors`` did the minimization (thanks you) but I have manually tested on the `starlark-rust` project that it fixes the issue.
Fixes#123573
r? `@lcnr`
Flip spans for precise capturing syntax not capturing a ty/const param, and for implicit captures of lifetime params
Make the primary span point to the opaque, rather than the param which might be very far away (e.g. in an impl header hundreds of lines above).
Give a name to each distinct manipulation of pretty-printer FixupContext
There are only 7 distinct ways that the AST pretty-printer interacts with FixupContext: 3 constructors (including Default), 2 transformations, and 2 queries.
This PR turns these into associated functions which can be documented with examples.
This PR unblocks https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/119427#discussion_r1439481201. In order to improve the pretty-printer's behavior regarding parenthesization of braced macro calls in match arms, which have different grammar than macro calls in statements, FixupContext needs to be extended with 2 new fields. In the previous approach, that would be onerous. In the new approach, all it entails is 1 new constructor (`FixupContext::new_match_arm()`).
This handles using deref patterns to choose the correct match arm. This
does not handle bindings or guards.
Co-authored-by: Deadbeef <ent3rm4n@gmail.com>
PatRangeBoundary::compare_with: als add a fast-path for signed integers
Not sure if we have a benchmark that hits this... but it seems odd to only do this for unsigned integers.
Fix capturing duplicated lifetimes via parent in `precise_captures` (`impl use<'...>`)
For technical reasons related to the way that `Self` and `T::Assoc` are lowered from HIR -> `rustc_middle::ty`, an opaque may mention in its bounds both the original early-bound lifetime from the parent `impl`/`fn`, *and* the *duplicated* early-bound lifetime on the opaque.
This is fine -- and has been fine since `@cjgillot` rewrote the way we handled opaque lifetime captures, and we went further to allow this behavior explicitly in https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/115659. It's worthwhile to read this PR's technical section to recall how this duplication works and when it acts surprisingly.
The problem here is that the check that make sure that `impl use<'a, 'b>` lists all of the opaque's captured lifetimes wasn't smart enough to consider both these captured lifetimes and the original lifetimes they're duplicated from to be equal. This PR fixes that.
r? oli-obk
Implement Modified Condition/Decision Coverage
This is an implementation based on llvm backend support (>= 18) by `@evodius96` and branch coverage support by `@Zalathar.`
### Major changes:
* Add -Zcoverage-options=mcdc as switch. Now coverage options accept either `no-branch`, `branch`, or `mcdc`. `mcdc` also enables `branch` because it is essential to work.
* Add coverage mapping for MCDCBranch and MCDCDecision. Note that MCDCParameter evolves from llvm 18 to llvm 19. The mapping in rust side mainly references to 19 and is casted to 18 types in llvm wrapper.
* Add wrapper for mcdc instrinc functions from llvm. And inject associated statements to mir.
* Add BcbMappingKind::Decision, I'm not sure is it proper but can't find a better way temporarily.
* Let coverage-dump support parsing MCDCBranch and MCDCDecision from llvm ir.
* Add simple tests to check whether mcdc works.
* Same as clang, currently rustc does not generate instrument for decision with more than 6 condtions or only 1 condition due to considerations of resource.
### Implementation Details
1. To get information about conditions and decisions, `MCDCState` in `BranchInfoBuilder` is used during hir lowering to mir. For expressions with logical op we call `Builder::visit_coverage_branch_operation` to record its sub conditions, generate condition ids for them and save their spans (to construct the span of whole decision). This process mainly references to the implementation in clang and is described in comments over `MCDCState::record_conditions`. Also true marks and false marks introduced by branch coverage are used to detect where the decision evaluation ends: the next id of the condition == 0.
2. Once the `MCDCState::decision_stack` popped all recorded conditions, we can ensure that the decision is checked over and push it into `decision_spans`. We do not manually insert decision span to avoid complexity from then_else_break in nested if scopes.
3. When constructing CoverageSpans, add condition info to BcbMappingKind::Branch and decision info to BcbMappingKind::Decision. If the branch mapping has non-zero condition id it will be transformed to MCDCBranch mapping and insert `CondBitmapUpdate` statements to its evaluated blocks. While decision bcb mapping will insert `TestVectorBitmapUpdate` in all its end blocks.
### Usage
```bash
echo "[build]\nprofiler=true" >> config.toml
./x build --stage 1
./x test tests/coverage/mcdc_if.rs
```
to build the compiler and run tests.
```shell
export PATH=path/to/llvm-build:$PATH
rustup toolchain link mcdc build/host/stage1
cargo +mcdc rustc --bin foo -- -Cinstrument-coverage -Zcoverage-options=mcdc
cd target/debug
LLVM_PROFILE_FILE="foo.profraw" ./foo
llvm-profdata merge -sparse foo.profraw -o foo.profdata
llvm-cov show ./foo -instr-profile=foo.profdata --show-mcdc
```
to check "foo" code.
### Problems to solve
For now decision mapping will insert statements to its all end blocks, which may be optimized by inserting a final block of the decision. To do this we must also trace the evaluated value at each end of the decision and join them separately.
This implementation is not heavily tested so there should be some unrevealed issues. We are going to check our rust products in the next. Please let me know if you had any suggestions or comments.
Disable SimplifyToExp in MatchBranchSimplification
Due to the miscompilation mentioned in #124150, We need to disable MatchBranchSimplification temporarily.
To fully resolve this issue, my plan is:
1. Disable SimplifyToExp in MatchBranchSimplification (this PR).
2. Remove all potentially unclear transforms in #124122.
3. Gradually add back the removed transforms (possibly multiple PRs).
r? `@Nilstrieb` or `@oli-obk`
Rollup of 5 pull requests
Successful merges:
- #123571 (Correctly change type when adding adjustments on top of `NeverToAny`)
- #123729 (run-make: refactor out command wrappers for `clang` and `llvm-readobj`)
- #124106 (Don't repeatedly duplicate TAIT lifetimes for each subsequently nested TAIT)
- #124149 (rustdoc-search: fix description on aliases in results)
- #124155 (bootstrap: don't use rayon for sysinfo)
r? `@ghost`
`@rustbot` modify labels: rollup
Don't repeatedly duplicate TAIT lifetimes for each subsequently nested TAIT
Make it so that nested TAITs inherit the lifetimes from their parent item, not their parent TAIT. This is because we don't need to re-duplicate lifetimes for nested TAITs over and over, since the only lifetimes they can capture are from the parent item anyways.
This mirrors how RPITs work. This is **not** a functional change that should be observable, since the whole point of duplicating lifetimes and marking the shadowed ones (and uncaptured ones) as bivariant is designed to *not* be observable.
r? oli-obk
Rollup of 7 pull requests
Successful merges:
- #123406 (Force exhaustion in iter::ArrayChunks::into_remainder)
- #123752 (Properly handle emojis as literal prefix in macros)
- #123935 (Don't inline integer literals when they overflow - new attempt)
- #123980 ( Add an opt-in to store incoming edges in `VecGraph` + misc)
- #124019 (Use raw-dylib for Windows synchronization functions)
- #124110 (Fix negating `f16` and `f128` constants)
- #124116 (when suggesting RUST_BACKTRACE=1, add a special note for Miri's env var isolation)
r? `@ghost`
`@rustbot` modify labels: rollup
Use raw-dylib for Windows synchronization functions
Fixes#123999 by using the raw-dylib feature to specify the DLL to load the Windows futex functions from (e.g. [`WaitOnAddress`](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/win32/api/synchapi/nf-synchapi-waitonaddress)). This avoids reliance on the import library causing that issue.
With apologies to ``@bjorn3,`` as it's currently necessary to revert this for cranelift.
Don't inline integer literals when they overflow - new attempt
Basically #116633 but I implemented the suggested changes.
Fixes#115423. Fixes#116631.
This is my first contribution to this repo so please let me know if I'm supposed to change something :)
Properly handle emojis as literal prefix in macros
Do not accept the following
```rust
macro_rules! lexes {($($_:tt)*) => {}}
lexes!(🐛"foo");
```
Before, invalid emoji identifiers were gated during parsing instead of lexing in all cases, but this didn't account for macro pre-expansion of literal prefixes.
Fix#123696.
Introduce perma-unstable `wasm-c-abi` flag
Now that `wasm-bindgen` v0.2.88 supports the spec-compliant C ABI, the idea is to switch to that in a future version of Rust. In the meantime it would be good to let people test and play around with it.
This PR introduces a new perma-unstable `-Zwasm-c-abi` compiler flag, which switches to the new spec-compliant C ABI when targeting `wasm32-unknown-unknown`.
Alternatively, we could also stabilize this and then deprecate it when we switch. I will leave this to the Rust maintainers to decide.
This is a companion PR to #117918, but they could be merged independently.
MCP: https://github.com/rust-lang/compiler-team/issues/703
Tracking issue: https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/122532
Add support for Arm64EC to the Standard Library
Adds the final pieces so that the standard library can be built for arm64ec-pc-windows-msvc (initially added in #119199)
* Bumps `windows-sys` to 0.56.0, which adds support for Arm64EC.
* Correctly set the `isEC` parameter for LLVM's `writeArchive` function.
* Add `#![feature(asm_experimental_arch)]` to library crates where Arm64EC inline assembly is used, as it is currently unstable.
Move confusing comment about otherwise blocks in `lower_match_tree`
This comment was historically inside a block guarded by `if let Some(otherwise_block) = otherwise`.
When #120978 made the “otherwise block” non-optional, it also flattened that region of code. Doing so left this comment awkwardly stranded above an unrelated line of code, without its original context.
We can restore that context by moving it above the declaration of `otherwise`.
r? ``@Nadrieril``
Match ergonomics 2024: miscellaneous code cleanups
- Store `ByRef` instead of `BindingAnnotation` in `PatInfo`
- Rename `BindingAnnotation` to `BindingMode`
r? ``@Nadrieril``
cc #123076
``@rustbot`` label A-patterns
Delay interning errors to after validation
fixes https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/122398fixes#122548
This improves diagnostics since validation errors are usually more helpful compared with interning errors that just make broad statements about the entire constant
r? `@RalfJung`
Codegen ZSTs without an allocation
This makes sure that &[] is equivalent to unsafe code (from_raw_parts(dangling, 0)). No new stable guarantee is intended about whether or not we do this, this is just an optimization.
This regressed in #67000 (no comments I can see about that regression in the PR, though it did change the test modified here). We had previously performed this optimization since #63635.
interpret: pass MemoryKind to adjust_alloc_base_pointer
Another puzzle piece for https://github.com/rust-lang/miri/pull/3475.
The 2nd commit renames base_pointer -> root_pointer; that's how Tree Borrows already calls them and I think the term is more clear than "base pointer". In particular, this distinguishes it from "base address", since a root pointer can point anywhere into an allocation, not just its base address.
https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/124018 has been rolled up already so I couldn't add it there any more.
r? ```@oli-obk```
This comment was historically inside a block guarded by
`if let Some(otherwise_block) = otherwise`.
When #120978 made the otherwise block non-optional, it also flattened that
region of code. Doing so left this comment awkwardly stranded above an
unrelated line of code, without its original context.
We can restore that context by moving it above the declaration of `otherwise`.
Delay span bug when `Self` kw resolves to `DefKind::{Mod,Trait}`
Catch the case where `kw::Self` is recovered in the parser and causes us to subsequently resolve `&self`'s implicit type to something that's not a type.
This check could be made more accurate, though I'm not sure how hard we have to try here.
Fixes#123988
This makes sure that &[] is just as efficient as indirecting through
unsafe code (from_raw_parts). No new stable guarantee is intended about
whether or not we do this, this is just an optimization.
Co-authored-by: Ralf Jung <post@ralfj.de>
Rollup of 7 pull requests
Successful merges:
- #123673 (Don't ICE for kind mismatches during error rendering)
- #123675 (Taint const qualifs if a static is referenced that didn't pass wfcheck)
- #123975 (Port the 2 `rust-lld` run-make tests to `rmake`)
- #124000 (Use `/* value */` as a placeholder)
- #124013 (Box::into_raw: make Miri understand that this is a box-to-raw cast)
- #124027 (Prefer identity equality over equating types during coercion.)
- #124036 (Remove `default_hidden_visibility: false` from wasm targets)
r? `@ghost`
`@rustbot` modify labels: rollup
This PR removes the static check that disallowed extern functions
with ellipsis (varargs) as the only parameter since this is now
valid in C23.
Also, adds a doc comment for `check_decl_cvariadic_pos()` and
fixes the name of the function (`varadic` -> `variadic`).
Remove `default_hidden_visibility: false` from wasm targets
To the best of my ability I believe that this is no longer necessary. I don't fully recall why this was first added but I believe it had to do with symbols all being exported by default and this was required to undo that. Regardless nowadays the default output of rustc seems suitable so it seems best to keep wasm in line with other targets.
Prefer identity equality over equating types during coercion.
These types are always generic only over their own generic parameters with no inference variables involved.
r? `@compiler-errors`
I love touching code that [hasn't changed meaningfully since 2016](https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/41937)
Use `/* value */` as a placeholder
The expression `value` isn't a valid suggestion; let's use `/* value */` as a placeholder (which is also invalid) since it more clearly signals to the user that they need to fill it in with something meaningful. This parallels the suggestions we have in a couple other places, like arguments.
We could also print the type name instead of `/* value */`, especially if it's suggestable, but I don't care strongly about that.
Taint const qualifs if a static is referenced that didn't pass wfcheck
It is correct to only check the signature here, as the ICE is caused by `USE_WITH_ERROR` trying to allocate memory to store the result of `WITH_ERROR` before evaluating it.
fixes#123153
To the best of my ability I believe that this is no longer necessary. I
don't fully recall why this was first added but I believe it had to do
with symbols all being exported by default and this was required to undo
that. Regardless nowadays the default output of rustc seems suitable so
it seems best to keep wasm in line with other targets.
Allow workproducts without object files.
This pull request partially reverts changes from e16c3b4a44
Original motivation for this assert was described with "A WorkProduct without a saved file is useless"
which was true at the time but now it is possible to have work products with other types of files
(llvm-ir, asm, etc) and there are bugreports for this failure:
For example: https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/123695
Fixes https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/123234
Now existing `assert` and `.unwrap_or_else` are unified into a single
check that emits slightly more user friendly error message if an object
files was meant to be produced but it's missing
Outline default query and hook provider function implementations
The default query and hook provider functions call `bug!` with a decently long message.
Due to argument inlining in `format_args!` ([`flatten_format_args`](https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/78356)), this ends up duplicating the message for each query, adding ~90KB to `librustc_driver.so` of unreachable panic messages.
To avoid this, we can outline the common `bug!` logic.
Subtype predicates only exist on inference types, so we can allow them to register opaque types within them.
We were unable to come up with an example where this could be reached (subtype predicates with either side not being an infer var gets consumed during any `select_where_possible` invocation, of which we have a lot in typeck). To ensure we don't silently accept new behaviour in case we missed a situation where this could occur, I have added an assert that prevents opaque types from having their hidden type constrained.
r? `@compiler-errors`
interpret: remove outdated comment
In https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/107756, allocation became generally fallible, so the "only panic if there is provenance" no longer applies.
r? ``@oli-obk``
Change a diagnostics-path-only `DefineOpaqueTypes` to `Yes`.
This can't possibly affect compilation, so it's safe to flip, even if I couldn't come up with an affected test
r? ``@compiler-errors``
Stabilize checking of cfgs at compile-time: `--check-cfg` option
This PR stabilize the `--check-cfg` CLI option of `rustc` (and `rustdoc`) 🎉.
In particular this PR does two things:
1. it makes the `--check-cfg` option stable
2. and it moves the documentation to the stable books
FCP: https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/82450#issuecomment-1965328542Resolves#82450
``@rustbot`` labels +S-blocked +F-check-cfg
r? ``@petrochenkov``
This pull request partially reverts changes from e16c3b4a44
Original motivation for this assert was described with "A WorkProduct without a saved file is useless"
which was true at the time but now it is possible to have work products with other types of files
(llvm-ir, asm, etc) and there are bugreports for this failure:
For example: https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/123695
Fixes https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/123234
Now existing `assert` and `.unwrap_or_else` are unified into a single
check that emits slightly more user friendly error message if an object
files was meant to be produced but it's missing
Move size assertions for `mir::syntax` types into the same file
A redundant size assertion for `StatementKind` was added in #122937, because the existing assertion was in a different file.
This PR cleans that up, and also moves the `TerminatorKind` assertion into the same file where it belongs, to avoid the same thing happening again.
r? `@nnethercote`
Opaque types have no namespace
Opaques are never referenced by name -- even when we have `type X = impl Sized;`, `X` is the name of the type alias, not the opaque.
Make `suggest_deref_closure_return` more idiomatic/easier to understand
The only functional change here really is just making it not use a fresh type variable for upvars. I'll point that out in the code.
The rest of the changes are just stylistic, because reading this code was really confusing me (variable names were vague, ways of accessing types were unidiomatic, order of operations was kind of strange, etc).
This is stacked on #123989.
r? oli-obk since you approved #122213
Better graphviz output for SCCs and NLL constraints
This PR modifies the output for `-Z dump-mir-graphviz=yes`. Specifically, it changes the output of the files `.-------.nll.0.regioncx.all.dot` and `nll.0.regioncx.scc.dot` to be easier to read and contain some information that helped me during debugging. In particular:
- SCC indices are contracted to `SCC(n)` instead of `ConstraintSccIndex(n)` to compress the nodes
- SCC regions are in `{}` rather than `[]` (controversial since they are technically ordered by index, but I figured they're more sets than arrays conceptually since they're equivalence classes).
- For regions in other universes than the root, also show the region universe (as ?8/U1)
- For regions with external names, show the external name in parenthesis
- For the region graph where edges are locations, render the All variant of the enum without the file since it's extremely long and often destroys the rendering
- For region graph edge annotations for single locations, remove the wrapping around the Location variant and just add its contents since this can be unambiguously done
Example output (from the function `foo()` of `tests/ui/error-codes/E0582.rs`) for an SCC graph:
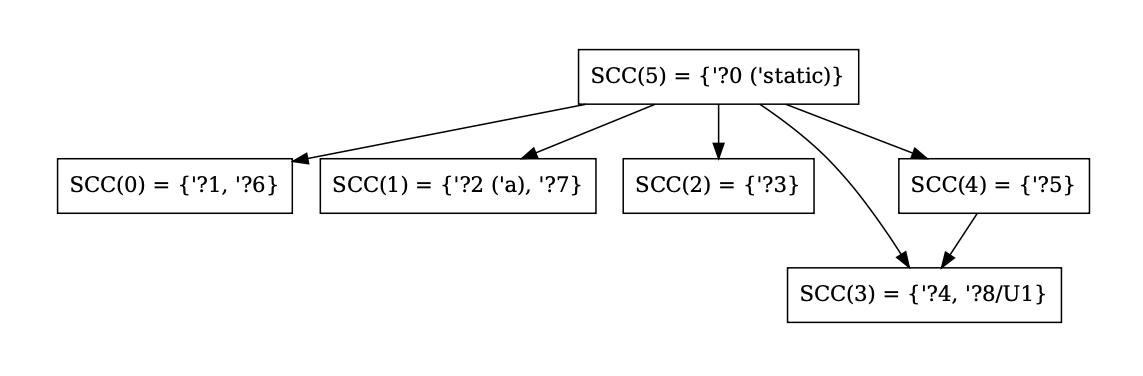
...and for the constraints:
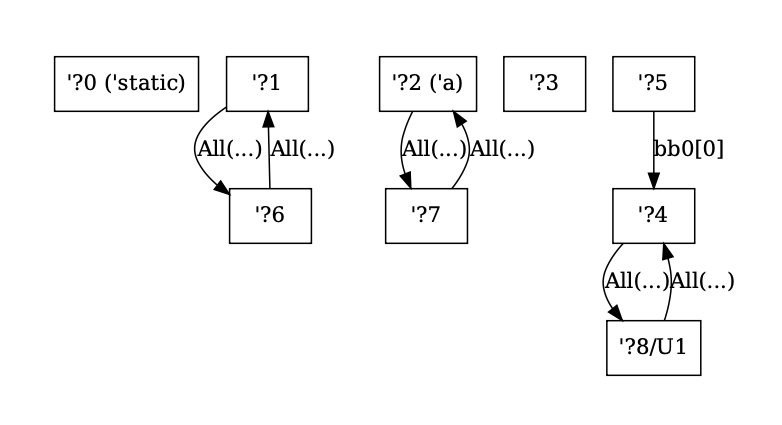
This PR also gives `UniverseIndex`es the `is_root()` method since this is now an operation that happens three times in the borrowck crate.
Update ar_archive_writer to 0.2.0
This adds a whole bunch of tests checking for any difference with llvm's archive writer. It also fixes two mistakes in the porting from C++ to Rust. The first one causes a divergence for Mach-O archives which may or may not be harmless. The second will definitively cause issues, but only applies to thin archives, which rustc currently doesn't create.
Implement syntax for `impl Trait` to specify its captures explicitly (`feature(precise_capturing)`)
Implements `impl use<'a, 'b, T, U> Sized` syntax that allows users to explicitly list the captured parameters for an opaque, rather than inferring it from the opaque's bounds (or capturing *all* lifetimes under 2024-edition capture rules). This allows us to exclude some implicit captures, so this syntax may be used as a migration strategy for changes due to #117587.
We represent this list of captured params as `PreciseCapturingArg` in AST and HIR, resolving them between `rustc_resolve` and `resolve_bound_vars`. Later on, we validate that the opaques only capture the parameters in this list.
We artificially limit the feature to *require* mentioning all type and const parameters, since we don't currently have support for non-lifetime bivariant generics. This can be relaxed in the future.
We also may need to limit this to require naming *all* lifetime parameters for RPITIT, since GATs have no variance. I have to investigate this. This can also be relaxed in the future.
r? `@oli-obk`
Tracking issue:
- https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/123432
Trait predicates for types which have errors may still
evaluate to OK leading to downstream ICEs. Now we return
a selection error for such types in candidate assembly and
thereby prevent such issues
A redundant size assertion for `StatementKind` was added in #122937, because
the existing assertion was in a different file.
This patch cleans that up, and also moves the `TerminatorKind` assertion into
the same file where it belongs, to avoid the same thing happening again.
Currently it's a method on `EarlyDiagCtxt`, which is not the right place
for it at all -- `EarlyDiagCtxt` is used to issue diagnostics, but
shouldn't be doing any of the actual checking.
This commit moves it into a standalone function that takes an
`EarlyDiagCtxt` as an argument, which is more sensible. This does
require adding `EarlyDiagCtxt::early_struct_warn`, so a warning can be
returned and then modified with a note. (And that likely explains why
somebody put `initialize_checked_jobserver` into `EarlyDiagCtxt` in the
first place.)
Currently `SourceMap` is constructed slightly later than
`SessionGlobals`, and inserted. This commit changes things so they are
done at the same time.
Benefits:
- `SessionGlobals::source_map` changes from
`Lock<Option<Lrc<SourceMap>>>` to `Option<Lrc<SourceMap>>`. It's still
optional, but mutability isn't required because it's initialized at
construction.
- `set_source_map` is removed, simplifying `run_compiler`, which is
good because that's a critical function and it's nice to make it
simpler.
This requires moving things around a bit, so the necessary inputs are
available when `SessionGlobals` is created, in particular the `loader`
and `hash_kind`, which are no longer computed by `build_session`. These
inputs are captured by the new `SourceMapInputs` type, which is threaded
through various places.
Fix pretty HIR for anon consts in diagnostics
This removes the `NoAnn` printer which skips over nested bodies altogether, which is confusing, and requires users of `{ty|qpath|pat}_to_string` to pass in `&tcx` which now impleemnts `hir_pretty::PpAnn`.
There's one case where this "regresses" by actually printing out the body of the anon const -- we could suppress that, but I don't expect people to actually get anon consts like that unless they're fuzzing, tbh.
r? estebank
Don't even parse an intrinsic unless the feature gate is enabled
Don't return true in `tcx.is_intrinsic` if the function is defined locally and `#![feature(intrinsics)]` is not enabled. This is a slightly more general fix than #123526, since #123587 shows that we have simplifying assumptions about intrinsics elsewhere in the compiler.
This will make the code ICE again if the user **enables** `#[feature(intrinsics)]`, but I kind of feel like if we want to fix that, we should make the `INTERNAL_FEATURES` lint `Deny` again. Perhaps we could do that on non-nightly compilers. Or we should just stop compilation altogether if they have `#![feature]` enabled on a non-nightly compiler.
As for the UX of *real* cases of hitting these ICEs, I believe pretty strongly that if a compiler/stdlib dev is modifying internal intrinsics (intentionally, like when making a change to rustc) we have no guarantee to make the ICE better looking for them. Honestly, *not* spitting out a stack trace is probably a disservice to the people who hit those ICEs in that case.
r? `@Nilstrieb` `@estebank`
Cleanup: Rename `ModSep` to `PathSep`
`::` is usually referred to as the *path separator* (citation needed).
The existing name `ModSep` for *module separator* is a bit misleading since it in fact separates the segments of arbitrary path segments, not only ones resolving to modules. Let me just give a shout-out to associated items (`T::Assoc`, `<Ty as Trait>::function`) and enum variants (`Option::None`).
Motivation: Reduce friction for new contributors, prevent potential confusion.
cc `@petrochenkov`
r? nnethercote or compiler
Remove `TypeVariableOriginKind` and `ConstVariableOriginKind`
It's annoying to have to import `TypeVariableOriginKind` just to fill it with `MiscVariable` for almost every use. Every other usage other than `TypeParameterDefinition` wasn't even used -- I can see how it may have been useful once for debugging, but I do quite a lot of typeck debugging and I've never really needed it.
So let's just remove it, and keep around the only useful thing which is the `DefId` of the param for `var_for_def`.
This is based on #123006, which removed the special use of `TypeVariableOriginKind::OpaqueInference`, which I'm pretty sure I was the one that added.
r? lcnr or re-roll to types
Fix various bugs in `ty_kind_suggestion`
Consolidates two implementations of `ty_kind_suggestion`
Fixes some misuse of the empty param-env
Fixes a problem where we suggested `(42)` instead of `(42,)` for tuple suggestions
Suggest a value when `return;`, making it consistent with `break;`
Fixes#123906
Fix UB in LLVM FFI when passing zero or >1 bundle
Rust passes a `*const &OperandBundleDef` to these APIs, usually from a `Vec<&OperandBundleDef>` or so. Previously we were dereferencing that pointer and passing it to the ArrayRef constructor with some length (N).
This meant that if the length was 0, we were dereferencing a pointer to nowhere (if the vector on the Rust side didn't actually get allocated or so), and if the length was >1 then loading the *second* element somewhere in LLVM would've been reading past the end.
Since Rust can't hold OperandBundleDef by-value we're forced to indirect through a vector that copies out the OperandBundleDefs from the by-reference list on the Rust side in order to match the LLVM expected API.
move the LargeAssignments lint logic into its own file
The collector is a file full of very subtle logic, so let's try to keep that separate from the logic that only serves to implement this lint.
Remove magic constants when using `base_n`.
Some use cases of `base_n` use number literals instead of the predefined constants. The latter are more descriptive so it might be better to use those instead.
builtin-derive: tag → discriminant
As far as I can tell, all of this operates on the discriminant, not the tag. After all, with something like `Option<&T>`, the "tag" of the `Some` variant is basically just the reference value, which is never what you want to compare when figuring out which variant the enum is in.
See [here](https://rustc-dev-guide.rust-lang.org/appendix/glossary.html) for an explanation of the difference between tag and discriminant.
Migrate some diagnostics in `rustc_resolve` to session diagnostic
Hello, I migrated some diagnostics in `rustc_resolve` to session diagnostic.
r? ``@davidtwco``
Remove a HACK by instead inferring opaque types during expected/formal type checking
I was wondering why I couldn't come up with a test that hits the code path of the argument check checking the types we inferred from the return type... Turns out we reject those attempts early during fudging.
I have absolutely no information for you as to what kind of type inference changes this may incur, but I think we should just land this out of two reasons:
* had I found the other place to use opaque type inference on before I added the hack, we'd be using that today and this PR would never have happened
* if it is possible to hit this path, it requires some god awful recursive RPIT logic that I doubt anyone would have written without actively trying to write obscure code
r? ``@ghost``
Add the missing inttoptr when we ptrtoint in ptr atomics
Ralf noticed this here: https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/122220#discussion_r1535172094
Our previous codegen forgot to add the cast back to integer type. The code compiles anyway, because of course all locals are in-memory to start with, so previous codegen would do the integer atomic, store the integer to a local, then load a pointer from that local. Which is definitely _not_ what we wanted: That's an integer-to-pointer transmute, so all pointers returned by these `AtomicPtr` methods didn't have provenance. Yikes.
Here's the IR for `AtomicPtr::fetch_byte_add` on 1.76: https://godbolt.org/z/8qTEjeraY
```llvm
define noundef ptr `@atomicptr_fetch_byte_add(ptr` noundef nonnull align 8 %a, i64 noundef %v) unnamed_addr #0 !dbg !7 {
start:
%0 = alloca ptr, align 8, !dbg !12
%val = inttoptr i64 %v to ptr, !dbg !12
call void `@llvm.lifetime.start.p0(i64` 8, ptr %0), !dbg !28
%1 = ptrtoint ptr %val to i64, !dbg !28
%2 = atomicrmw add ptr %a, i64 %1 monotonic, align 8, !dbg !28
store i64 %2, ptr %0, align 8, !dbg !28
%self = load ptr, ptr %0, align 8, !dbg !28
call void `@llvm.lifetime.end.p0(i64` 8, ptr %0), !dbg !28
ret ptr %self, !dbg !33
}
```
r? `@RalfJung`
cc `@nikic`
Rust passes a *const &OperandBundleDef to these APIs, usually from a
Vec<&OperandBundleDef> or so. Previously we were dereferencing that
pointer and passing it to the ArrayRef constructor with some length (N).
This meant that if the length was 0, we were dereferencing a pointer to
nowhere, and if the length was >1 then loading the *second* element
somewhere in LLVM would've been reading past the end.
Since Rust can't hold OperandBundleDef by-value we're forced to indirect
through a vector that copies out the OperandBundleDefs from the
by-reference list on the Rust side in order to match the LLVM expected
API.
Discard overflow obligations in `impl_may_apply`
Hacky fix for #123493. Throws away obligations that are overflowing in `impl_may_apply` when we recompute if an impl applies, since those will lead to fatal overflow if processed during fulfillment.
Something about #114811 (I think it's the predicate reordering) caused us to evaluate predicates differently in error reporting leading to fatal overflow, though I believe the underlying overflow is possible to hit since this code was rewritten to use fulfillment.
Fixes#123493
Does not necessarily change much, but we never overwrite it, so I see no reason
for it to be in the `Successors` trait. (+we already have a similar `is_cyclic`)
Add add/sub methods that only panic with debug assertions to rustc
This mitigates the perf impact of enabling overflow checks on rustc. The change to use overflow checks will be done in a later PR.
For rust-lang/compiler-team#724, based on data gathered in #119440.
Rollup of 7 pull requests
Successful merges:
- #123530 (Enable building tier2 target riscv32im-unknown-none-elf)
- #123642 (do not allow using local llvm while using rustc from ci)
- #123716 (Update documentation of Path::to_path_buf and Path::ancestors)
- #123876 (Update backtrace submodule)
- #123888 (Replace a `DefiningOpaqueTypes::No` with `Yes` by asserting that one side of the comparison is a type variable.)
- #123890 (removed (mostly) unused code)
- #123891 (Miri subtree update)
r? `@ghost`
`@rustbot` modify labels: rollup
Replace a `DefiningOpaqueTypes::No` with `Yes` by asserting that one side of the comparison is a type variable.
Thus there will never be an opaque type involved in a way that constrains its hidden type, as the other side of the comparison is always a generator witness type
r? ``@compiler-errors``
Linker flavors next steps: linker features
This is my understanding of the first step towards `@petrochenkov's` vision for the future of linker flavors, described in https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/119906#issuecomment-1895693162 and the discussion that followed.
To summarize: having `Cc` and `Lld` embedded in linker flavors creates tension about naming, and a combinatorial explosion of flavors for each new linker feature we'd want to use. Linker features are an extension mechanism that is complementary to principal flavors, with benefits described in #119906.
The most immediate use of this flag would be to turn self-contained linking on and off via features instead of flavors. For example, `-Clinker-features=+/-lld` would toggle using lld instead of selecting a precise flavor, and would be "generic" and work cross-platform (whereas linker flavors are currently more tied to targets). Under this scheme, MCP510 is expected to be `-Clink-self-contained=+linker -Zlinker-features=+lld -Zunstable-options` (though for the time being, the original flags using lld-cc flavors still work).
I purposefully didn't add or document CLI support for `+/-cc`, as it would be a noop right now. I only expect that we'd initially want to stabilize `+/-lld` to begin with.
r? `@petrochenkov`
You had requested that minimal churn would be done to the 230 target specs and this does none yet: the linker features are inferred from the flavor since they're currently isomorphic. We of course expect this to change sooner rather than later.
In the future, we can allow targets to define linker features independently from their flavor, and remove the cc and lld components from the flavors to use the features instead, this actually doesn't need to block stabilization, as we discussed.
(Best reviewed per commit)
Detect borrow checker errors where `.clone()` would be an appropriate user action
When a value is moved twice, suggest cloning the earlier move:
```
error[E0509]: cannot move out of type `U2`, which implements the `Drop` trait
--> $DIR/union-move.rs:49:18
|
LL | move_out(x.f1_nocopy);
| ^^^^^^^^^^^
| |
| cannot move out of here
| move occurs because `x.f1_nocopy` has type `ManuallyDrop<RefCell<i32>>`, which does not implement the `Copy` trait
|
help: consider cloning the value if the performance cost is acceptable
|
LL | move_out(x.f1_nocopy.clone());
| ++++++++
```
When a value is borrowed by an `fn` call, consider if cloning the result of the call would be reasonable, and suggest cloning that, instead of the argument:
```
error[E0505]: cannot move out of `a` because it is borrowed
--> $DIR/variance-issue-20533.rs:53:14
|
LL | let a = AffineU32(1);
| - binding `a` declared here
LL | let x = bat(&a);
| -- borrow of `a` occurs here
LL | drop(a);
| ^ move out of `a` occurs here
LL | drop(x);
| - borrow later used here
|
help: consider cloning the value if the performance cost is acceptable
|
LL | let x = bat(&a).clone();
| ++++++++
```
otherwise, suggest cloning the argument:
```
error[E0505]: cannot move out of `a` because it is borrowed
--> $DIR/variance-issue-20533.rs:59:14
|
LL | let a = ClonableAffineU32(1);
| - binding `a` declared here
LL | let x = foo(&a);
| -- borrow of `a` occurs here
LL | drop(a);
| ^ move out of `a` occurs here
LL | drop(x);
| - borrow later used here
|
help: consider cloning the value if the performance cost is acceptable
|
LL - let x = foo(&a);
LL + let x = foo(a.clone());
|
```
This suggestion doesn't attempt to square out the types between what's cloned and what the `fn` expects, to allow the user to make a determination on whether to change the `fn` call or `fn` definition themselves.
Special case move errors caused by `FnOnce`:
```
error[E0382]: use of moved value: `blk`
--> $DIR/once-cant-call-twice-on-heap.rs:8:5
|
LL | fn foo<F:FnOnce()>(blk: F) {
| --- move occurs because `blk` has type `F`, which does not implement the `Copy` trait
LL | blk();
| ----- `blk` moved due to this call
LL | blk();
| ^^^ value used here after move
|
note: `FnOnce` closures can only be called once
--> $DIR/once-cant-call-twice-on-heap.rs:6:10
|
LL | fn foo<F:FnOnce()>(blk: F) {
| ^^^^^^^^ `F` is made to be an `FnOnce` closure here
LL | blk();
| ----- this value implements `FnOnce`, which causes it to be moved when called
```
Account for redundant `.clone()` calls in resulting suggestions:
```
error[E0507]: cannot move out of dereference of `S`
--> $DIR/needs-clone-through-deref.rs:15:18
|
LL | for _ in self.clone().into_iter() {}
| ^^^^^^^^^^^^ ----------- value moved due to this method call
| |
| move occurs because value has type `Vec<usize>`, which does not implement the `Copy` trait
|
note: `into_iter` takes ownership of the receiver `self`, which moves value
--> $SRC_DIR/core/src/iter/traits/collect.rs:LL:COL
help: you can `clone` the value and consume it, but this might not be your desired behavior
|
LL | for _ in <Vec<usize> as Clone>::clone(&self).into_iter() {}
| ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ ~
```
We use the presence of `&mut` values in a move error as a proxy for the user caring about side effects, so we don't emit a clone suggestion in that case:
```
error[E0505]: cannot move out of `s` because it is borrowed
--> $DIR/borrowck-overloaded-index-move-index.rs:53:7
|
LL | let mut s = "hello".to_string();
| ----- binding `s` declared here
LL | let rs = &mut s;
| ------ borrow of `s` occurs here
...
LL | f[s] = 10;
| ^ move out of `s` occurs here
...
LL | use_mut(rs);
| -- borrow later used here
```
We properly account for `foo += foo;` errors where we *don't* suggest `foo.clone() += foo;`, instead suggesting `foo += foo.clone();`.
---
Each commit can be reviewed in isolation. There are some "cleanup" commits, but kept them separate in order to show *why* specific changes were being made, and their effect on tests' output.
Fix#49693, CC #64167.
Thus there will never be an opaque type involved in a way that constrains its hidden type, as the other side of the comparison is always a generator witness type
Re-enable `has_thread_local` for i686-msvc
A few years back, `has_thread_local` was disabled as a workaround for a compiler issue. While the exact cause was never tracked down, it was suspected to be caused by the compiler inlining a thread local access across a dylib boundary. This should be fixed now so let's try again.
Add `/System/iOSSupport` to the library search path on Mac Catalyst
On macOS, `/System/iOSSupport` contains iOS frameworks like UIKit, which is the whole idea of Mac Catalyst.
To link to these, we need to explicitly tell the linker about the support library stubs provided in the macOS SDK under the same path.
Concretely, when building a binary for Mac Catalyst, Xcode passes the following flags to the linker:
```
-iframework /Applications/Xcode.app/Contents/Developer/Platforms/MacOSX.platform/Developer/SDKs/MacOSX14.2.sdk/System/iOSSupport/System/Library/Frameworks
-L/Applications/Xcode.app/Contents/Developer/Platforms/MacOSX.platform/Developer/SDKs/MacOSX14.2.sdk/System/iOSSupport/usr/lib
```
This is not something that can be disabled (it's enabled as soon as you enable `SUPPORTS_MACCATALYST`), so I think it's pretty safe to say that we don't need an option to turn these off.
I've chosen to slightly deviate from what Xcode does and use `-F` instead of `-iframework`, since we don't need to change the header search path, and this way the flags nicely match on all the linkers. From what I could tell by reading Clang sources, there shouldn't be a difference when just running the linker.
CC `@BlackHoleFox,` `@shepmaster` (I accidentally let rustbot choose the reviewer).
typeck: fix `?` suggestion span
Noticed in <https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/112043#issuecomment-2043565292>, if the
```
use the `?` operator to extract the `Result<(), std::fmt::Error>` value, propagating a `Result::Err` value to the caller
```
suggestion is applied to a macro that comes from a non-local crate (e.g. the stdlib), the suggestion span can become non-local, which will cause newer rustfix versions to fail.
This PR tries to remedy the problem by recursively probing ancestors of the expression span, trying to identify the most ancestor span that is (1) still local, and (2) still shares the same syntax context as the expression.
This is the same strategy used in https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/112043.
The test unfortunately cannot `//@ run-rustfix` because there are two conflicting MaybeIncorrect suggestions that when collectively applied, cause the fixed source file to become non-compilable.
Also avoid running `//@ run-rustfix` for `tests/ui/typeck/issue-112007-leaked-writeln-macro-internals.rs` because that also contains conflicting suggestions.
cc `@ehuss` who noticed this. This question mark span fix + not running rustfix on the tests containing conflicting MaybeIncorrect suggestions should hopefully unblock rustfix from updating.
The suggestion to use `let else` with an uninitialized refutable `let`
statement was erroneous: `let else` cannot be used with deferred
initialization.
Improve diagnostic by suggesting to remove visibility qualifier
Resolves#123529
This PR improve diagnostic by suggesting to remove visibility qualifier.
Fix invalid silencing of parsing error
Given
```rust
macro_rules! a {
( ) => {
impl<'b> c for d {
e::<f'g>
}
};
}
```
ensure an error is emitted.
Fix#123079.
While they're isomorphic, we can flip the lld component where
applicable, so that downstream doesn't have to check both the flavor and
the linker features.
They are a flexible complementary mechanism to linker flavors,
that also avoid the combinatorial explosion of mapping linking features
to actual linker flavors.
Don't delay a bug if we suggest adding a semicolon to the RHS of an assign operator
It only makes sense to delay a bug based on the assumption that "[we] defer to the later error produced by `check_lhs_assignable`" *if* the expression we're erroring actually is an LHS; otherwise, we should still report the error since it's both useful and required.
Fixes#123722
Make `PlaceRef` and `OperandValue::Ref` share a common `PlaceValue` type
Both `PlaceRef` and `OperandValue::Ref` need the triple of the backend pointer immediate, the optional backend metadata for DSTs, and the actual alignment of the place (since it can differ from the ABI alignment).
This PR introduces a new `PlaceValue` type for those three values, leaving [`PlaceRef`](https://doc.rust-lang.org/nightly/nightly-rustc/rustc_codegen_ssa/mir/place/struct.PlaceRef.html) with the `TyAndLayout` and a `PlaceValue`, just like how [`OperandRef`](https://doc.rust-lang.org/nightly/nightly-rustc/rustc_codegen_ssa/mir/operand/struct.OperandRef.html) is a `TyAndLayout` and an `OperandValue`.
This means that various places that use `Ref`s as places can just pass the `PlaceValue` along, like in the below excerpt from the diff:
```diff
match operand.val {
- OperandValue::Ref(ptr, meta, align) => {
- debug_assert_eq!(meta, None);
+ OperandValue::Ref(source_place_val) => {
+ debug_assert_eq!(source_place_val.llextra, None);
debug_assert!(matches!(operand_kind, OperandValueKind::Ref));
- let fake_place = PlaceRef::new_sized_aligned(ptr, cast, align);
+ let fake_place = PlaceRef { val: source_place_val, layout: cast };
Some(bx.load_operand(fake_place).val)
}
```
There's more refactoring that I'd like to do after this, but I wanted to stop the PR here where it's hopefully easy (albeit probably not quick) to review since I tried to keep every change line-by-line clear. (Most are just adding `.val` to get to a field.)
You can also go commit-at-a-time if you'd like. Each passed tidy and the codegen tests on my machine (though I didn't run the cg_gcc ones).
Rollup of 8 pull requests
Successful merges:
- #122882 (Avoid a panic in `set_output_capture` in the default panic handler)
- #123523 (Account for trait/impl difference when suggesting changing argument from ref to mut ref)
- #123744 (Silence `unused_imports` for redundant imports)
- #123784 (Replace `document.write` with `document.head.insertAdjacent`)
- #123798 (Avoid invalid socket address in length calculation)
- #123804 (Stop using `HirId` for fn-like parents since closures are not `OwnerNode`s)
- #123806 (Panic on overflow in `BorrowedCursor::advance`)
- #123820 (Add my former address to .mailmap)
r? `@ghost`
`@rustbot` modify labels: rollup
Stop using `HirId` for fn-like parents since closures are not `OwnerNode`s
This is a minimal fix for #123273.
I'm overall pretty disappointed w/ the state of this code; although it's "just diagnostics", it still should be maintainable and understandable and neither of those are true. I believe this code really needs some major overhauling before anything more should be added to it, because there are subtle invariants that are being exercised and subsequently broken all over the place, and I don't think we should just paper over them (e.g.) by delaying bugs or things like that. I wouldn't be surprised if fixing up this code would also yield better diagnostics.
Silence `unused_imports` for redundant imports
Quick fix for https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/121708#issuecomment-2048105393
r? `@petrochenkov` cc `@joshtriplett`
I think this is right, would like confirmation. I also think it's weird that we're using `=` to assign to `is_redundant` but using `per_ns` for the actual spans. Seems like this could be weirdly order dependent, but that's unrelated to this change.
Account for trait/impl difference when suggesting changing argument from ref to mut ref
Do not ICE when encountering a lifetime error involving an argument with an immutable reference of a method that differs from the trait definition.
Fix#123414.
Deduplicate some function implementations between the parser and AST/HIR
These functions already existed on parser binops, so just convert back to them back and invoke the equivalent method.
Reduce Size of `ModifierInfo`
I added `ModifierInfo` in #121940 and had used a `u64` for the `size` field even though the largest value it holds is `512`.
This PR changes the type of the `size` field to `u16`.
We attempt to suggest an appropriate clone for move errors on expressions
like `S { ..s }` where a field isn't `Copy`. If we can't suggest, we still don't
emit the incorrect suggestion of `S { ..s }.clone()`.
```
error[E0509]: cannot move out of type `S<K>`, which implements the `Drop` trait
--> $DIR/borrowck-struct-update-with-dtor.rs:28:19
|
LL | let _s2 = S { a: 2, ..s0 };
| ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
| |
| cannot move out of here
| move occurs because `s0.c` has type `K`, which does not implement the `Copy` trait
|
help: clone the value from the field instead of using the spread operator syntax
|
LL | let _s2 = S { a: 2, c: s0.c.clone(), ..s0 };
| +++++++++++++++++
```
```
error[E0509]: cannot move out of type `S<()>`, which implements the `Drop` trait
--> $DIR/borrowck-struct-update-with-dtor.rs:20:19
|
LL | let _s2 = S { a: 2, ..s0 };
| ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
| |
| cannot move out of here
| move occurs because `s0.b` has type `B`, which does not implement the `Copy` trait
|
note: `B` doesn't implement `Copy` or `Clone`
--> $DIR/borrowck-struct-update-with-dtor.rs:4:1
|
LL | struct B;
| ^^^^^^^^
help: if `B` implemented `Clone`, you could clone the value from the field instead of using the spread operator syntax
|
LL | let _s2 = S { a: 2, b: s0.b.clone(), ..s0 };
| +++++++++++++++++
```
```
error[E0382]: use of moved value: `blk`
--> $DIR/once-cant-call-twice-on-heap.rs:8:5
|
LL | fn foo<F:FnOnce()>(blk: F) {
| --- move occurs because `blk` has type `F`, which does not implement the `Copy` trait
LL | blk();
| ----- `blk` moved due to this call
LL | blk();
| ^^^ value used here after move
|
note: `FnOnce` closures can only be called once
--> $DIR/once-cant-call-twice-on-heap.rs:6:10
|
LL | fn foo<F:FnOnce()>(blk: F) {
| ^^^^^^^^ `F` is made to be an `FnOnce` closure here
LL | blk();
| ----- this value implements `FnOnce`, which causes it to be moved when called
```
```
error[E0505]: cannot move out of `a` because it is borrowed
--> $DIR/variance-issue-20533.rs:28:14
|
LL | let a = AffineU32(1);
| - binding `a` declared here
LL | let x = foo(&a);
| -- borrow of `a` occurs here
LL | drop(a);
| ^ move out of `a` occurs here
LL | drop(x);
| - borrow later used here
|
help: consider cloning the value if the performance cost is acceptable
|
LL | let x = foo(&a).clone();
| ++++++++
```
```
error[E0507]: cannot move out of `val`, a captured variable in an `FnMut` closure
--> $DIR/issue-87456-point-to-closure.rs:10:28
|
LL | let val = String::new();
| --- captured outer variable
LL |
LL | take_mut(|| {
| -- captured by this `FnMut` closure
LL |
LL | let _foo: String = val;
| ^^^ move occurs because `val` has type `String`, which does not implement the `Copy` trait
|
help: consider borrowing here
|
LL | let _foo: String = &val;
| +
help: consider cloning the value if the performance cost is acceptable
|
LL | let _foo: String = val.clone();
| ++++++++
```
```
error[E0507]: cannot move out of `*x` which is behind a shared reference
--> $DIR/borrowck-fn-in-const-a.rs:6:16
|
LL | return *x
| ^^ move occurs because `*x` has type `String`, which does not implement the `Copy` trait
|
help: consider cloning the value if the performance cost is acceptable
|
LL - return *x
LL + return x.clone()
|
```
Call lower_const_param instead of duplicating the code
Follow up of #123689
r? `@oli-obk`
I had this commit in my old branch that I had forgotten about, `@fmease` pointed about this in #123689
I've left the branches that are not `Range` as do nothing as that's what we are currently doing but maybe we want to err or something.
Make the computation of `coroutine_captures_by_ref_ty` more sophisticated
Currently, we treat all the by-(mut/)ref borrows of a coroutine-closure as having a "closure env" borrowed lifetime.
When we have the given code:
```rust
let x: &'a i32 = ...;
let c = async || {
let _x = *x;
};
```
Then when we call:
```rust
c()
// which, because `AsyncFn` takes a `&self`, we insert an autoref:
(&c /* &'env {coroutine-closure} */)()
```
We will return a future whose captures contain `&'env i32` instead of `&'a i32`, which is way more restrictive than necessary. We should be able to drop `c` while the future is alive since it's not actually borrowing any data *originating from within* the closure's captures, but since the capture has that `'env` lifetime, this is not possible.
This wouldn't be true, for example, if the closure captured `i32` instead of `&'a i32`, because the `'env` lifetime is actually *necessary* since the data (`i32`) is owned by the closure.
This PR identifies two criteria where we *need* to take the borrow with the closure env lifetime:
1. If the closure borrows data from inside the closure's captures. This is not true if the parent capture is by-ref, OR if the parent capture is by-move and the child capture begins with a deref projection. This is the example described above.
2. If we're dealing with mutable references, since we cannot reborrow `&'env mut &'a mut i32` into `&'a mut i32`, *only* `&'env mut i32`.
See the documentation on `should_reborrow_from_env_of_parent_coroutine_closure` for more info.
**important:** As disclaimer states on that function, luckily, if this heuristic is not correct, then the program is not unsound, since we still borrowck and validate the choices made from this function -- the only side-effect is that the user may receive unnecessary borrowck errors.
Fixes#123241
Disable Ctrl-C handling on WASM
WASM fundamentally doesn't support signals. If WASI ever gets support for notifying the guest process of a Ctrl-C that happened, this would have to be done through the guest process polling for the signal, which will require thread support in WASI too to be compatible with the api provided by the ctrlc crate.
WASM fundamentally doesn't support signals. If WASI ever gets support
for notifying the guest process of a Ctrl-C that happened, this would
have to be done through the guest process polling for the signal, which
will require thread support in WASI too to be compatible with the api
provided by the ctrlc crate.
Tweak value suggestions in `borrowck` and `hir_analysis`
Unify the output of `suggest_assign_value` and `ty_kind_suggestion`.
Ideally we'd make these a single function, but doing so would likely require modify the crate dependency tree.
Rework ptr-to-ref conversion suggestion for method calls
If we have a value `z` of type `*const u8` and try to call `z.to_string()`, the upstream compiler will show you a note suggesting to call `<*const u8>::as_ref` first.
This PR extends that:
- The note will only be shown when the method would exist on the corresponding reference type
- It can now suggest any of `<*const u8>::as_ref`, `<*mut u8>::as_ref` and `<*mut u8>::as_mut`, depending on what the method needs.
I didn't introduce a `help` message because that's not a good idea with `unsafe` functions (and you'd also need to unwrap the `Option<&_>` somehow).
People should check the safety requirements.
For the simplest case
```rust
fn main() {
let x = 8u8;
let z: *const u8 = &x;
// issue #21596
println!("{}", z.to_string()); //~ ERROR E0599
}
```
the output changes like this:
```diff
error[E0599]: `*const u8` doesn't implement `std::fmt::Display`
--> $DIR/suggest-convert-ptr-to-ref.rs:5:22
|
LL | println!("{}", z.to_string());
| ^^^^^^^^^ `*const u8` cannot be formatted with the default formatter
|
- = note: try using `<*const T>::as_ref()` to get a reference to the type behind the pointer: https://doc.rust-lang.org/std/primitive.pointer.html#method.as_ref
- = note: using `<*const T>::as_ref()` on a pointer which is unaligned or points to invalid or uninitialized memory is undefined behavior
+note: the method `to_string` exists on the type `&u8`
+ --> $SRC_DIR/alloc/src/string.rs:LL:COL
+ = note: try using the unsafe method `<*const T>::as_ref` to get an optional reference to the value behind the pointer: https://doc.rust-lang.org/std/primitive.pointer.html#method.as_ref
= note: the following trait bounds were not satisfied:
`*const u8: std::fmt::Display`
which is required by `*const u8: ToString`
```
I removed the separate note about the safety requirements because it was incomplete and the linked doc page already has the information you need.
Fixes#83695, but that's more of a side effect. The upstream compiler already suggests the right method name here.
Provide suggestion to dereference closure tail if appropriate
When encoutnering a case like
```rust
use std::collections::HashMap;
fn main() {
let vs = vec![0, 0, 1, 1, 3, 4, 5, 6, 3, 3, 3];
let mut counts = HashMap::new();
for num in vs {
let count = counts.entry(num).or_insert(0);
*count += 1;
}
let _ = counts.iter().max_by_key(|(_, v)| v);
```
produce the following suggestion
```
error: lifetime may not live long enough
--> $DIR/return-value-lifetime-error.rs:13:47
|
LL | let _ = counts.iter().max_by_key(|(_, v)| v);
| ------- ^ returning this value requires that `'1` must outlive `'2`
| | |
| | return type of closure is &'2 &i32
| has type `&'1 (&i32, &i32)`
|
help: dereference the return value
|
LL | let _ = counts.iter().max_by_key(|(_, v)| **v);
| ++
```
Fix#50195.
Use `suggest_impl_trait` in return type suggestion on type error
Discovered while doing other refactoring. Review with whitespace disabled.
r? estebank
Use `fn` ptr signature instead of `{closure@..}` in infer error
When suggesting a type on inference error, do not use `{closure@..}`. Instead, replace with an appropriate `fn` ptr.
On the error message, use `short_ty_string` and write long types to disk.
```
error[E0284]: type annotations needed for `Select<{closure@lib.rs:2782:13}, _, Expression<'_>, _>`
--> crates/lang/src/parser.rs:41:13
|
41 | let lit = select! {
| ^^^
42 | Token::Int(i) = e => Expression::new(Expr::Lit(ast::Lit::Int(i.parse().unwrap())), e.span()),
| ---- type must be known at this point
|
= note: the full type name has been written to '/home/gh-estebank/iowo/target/debug/deps/lang-e2d6e25819442273.long-type-4587393693885174369.txt'
= note: cannot satisfy `<_ as chumsky::input::Input<'_>>::Span == SimpleSpan`
help: consider giving `lit` an explicit type, where the type for type parameter `I` is specified
|
41 | let lit: Select<for<'a, 'b> fn(tokens::Token<'_>, &'a mut MapExtra<'_, 'b, _, _>) -> Option<Expression<'_>>, _, Expression<'_>, _> = select! {
| +++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
```
instead of
```
error[E0284]: type annotations needed for `Select<{closure@/home/gh-estebank/.cargo/registry/src/index.crates.io-6f17d22bba15001f/chumsky-1.0.0-alpha.6/src/lib.rs:2782:13: 2782:28}, _, Expression<'_>, _>`
--> crates/lang/src/parser.rs:41:13
|
41 | let lit = select! {
| ^^^
42 | Token::Int(i) = e => Expression::new(Expr::Lit(ast::Lit::Int(i.parse().unwrap())), e.span()),
| ---- type must be known at this point
|
= note: cannot satisfy `<_ as chumsky::input::Input<'_>>::Span == SimpleSpan`
help: consider giving `lit` an explicit type, where the type for type parameter `I` is specified
|
41 | let lit: Select<{closure@/home/gh-estebank/.cargo/registry/src/index.crates.io-6f17d22bba15001f/chumsky-1.0.0-alpha.6/src/lib.rs:2782:13: 2782:28}, _, Expression<'_>, _> = select! {
| ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
```
Address #123630 (test missing).
Skip `unused_parens` report for `Paren(Path(..))` in macro.
fixes#120642
In following code, `unused_parens` suggest change `<($($rest),*)>::bar()` to `<$rest>::bar()` which will cause another err: `error: variable 'rest' is still repeating at this depth`:
```rust
trait Foo {
fn bar();
}
macro_rules! problem {
($ty:ident) => {
impl<$ty: Foo> Foo for ($ty,) {
fn bar() { <$ty>::bar() }
}
};
($ty:ident $(, $rest:ident)*) => {
impl<$ty: Foo, $($rest: Foo),*> Foo for ($ty, $($rest),*) {
fn bar() {
<$ty>::bar();
<($($rest),*)>::bar()
}
}
problem!($($rest),*);
}
}
```
I think maybe we can handle this by avoid warning for `Paren(Path(..))` in the macro. Is this reasonable approach?
Do not accept the following
```rust
macro_rules! lexes {($($_:tt)*) => {}}
lexes!(🐛"foo");
```
Before, invalid emoji identifiers were gated during parsing instead of lexing in all cases, but this didn't account for macro expansion of literal prefixes.
Fix#123696.
Propagate temporary lifetime extension into if and match.
This PR makes this work:
```rust
let a = if true {
..;
&temp() // used to error, but now gets lifetime extended
} else {
..;
&temp() // used to error, but now gets lifetime extended
};
```
and
```rust
let a = match () {
_ => {
..;
&temp() // used to error, but now gets lifetime extended
}
};
```
to make it consistent with:
```rust
let a = {
..;
&temp() // lifetime is extended
};
```
This is one small part of [the temporary lifetimes work](https://github.com/rust-lang/lang-team/issues/253).
This part is backwards compatible (so doesn't need be edition-gated), because all code affected by this change previously resulted in a hard error.
Only assert for child/parent projection compatibility AFTER checking that theyre coming from the same place
This assertion doesn't make sense until we check that these captures are actually equivalent.
Fixes#123697
<sub>Some days I wonder how I even write code that works...</sub>
Add support to intrinsics fallback body
Before this fix, the call to `body()` would crash, since `has_body()` would return true, but we would try to retrieve the body of an intrinsic which is not allowed.
Instead, the `Instance::body()` function will now convert an Intrinsic into an Item before retrieving its body.
Note: I also changed how we monomorphize the instance body. Unfortunately, the call still ICE for some shims.
r? `@oli-obk`
Add `REDUNDANT_LIFETIMES` lint to detect lifetimes which are semantically redundant
There already is a `UNUSED_LIFETIMES` lint which is fired when we detect where clause bounds like `where 'a: 'static`, however, it doesn't use the full power of lexical region resolution to detect failures.
Right now `UNUSED_LIFETIMES` is an `Allow` lint, though presumably we could bump it to warn? I can (somewhat) easily implement a structured suggestion so this can be rustfix'd automatically, since we can just walk through the HIR body, replacing instances of the redundant lifetime.
Fixes#118376
r? lcnr
async closure coroutine by move body MirPass refactoring
Unsure about the last commit, but I think the other changes help in simplifying the control flow
Don't use bytepos offsets when computing semicolon span for removal
Causes problems when we recover confusable characters w/ a different byte width
Fixes#123607
Unconditionally show update nightly hint on ICE
Instead of trying to guess if a update nightly hint should be shown (by checking for system time, querying version and channel info etc.), just show the update nightly hint for nightly compilers. This avoids breaking tests that match on ICE test outputs on nightly/dev channels.
> Another issue is that the outdated nightly hint triggers for ICE tests, causing a mismatch with the test expectation. There doesn't seem to be any env var to suppress this.
See <https://rust-lang.zulipchat.com/#narrow/stream/326414-t-infra.2Fbootstrap/topic/stage0.20compiletest.20broken/near/425543681> for context.
When suggesting a type on inference error, do not use `{closure@..}`.
Instead, replace with an appropriate `fn` ptr.
On the error message, use `short_ty_string` and write long types to
disk.
```
error[E0284]: type annotations needed for `Select<{closure@lib.rs:2782:13}, _, Expression<'_>, _>`
--> crates/lang/src/parser.rs:41:13
|
41 | let lit = select! {
| ^^^
42 | Token::Int(i) = e => Expression::new(Expr::Lit(ast::Lit::Int(i.parse().unwrap())), e.span()),
| ---- type must be known at this point
|
= note: the full type name has been written to '/home/gh-estebank/iowo/target/debug/deps/lang-e2d6e25819442273.long-type-4587393693885174369.txt'
= note: cannot satisfy `<_ as chumsky::input::Input<'_>>::Span == SimpleSpan`
help: consider giving `lit` an explicit type, where the type for type parameter `I` is specified
|
41 | let lit: Select<for<'a, 'b> fn(tokens::Token<'_>, &'a mut MapExtra<'_, 'b, _, _>) -> Option<Expression<'_>>, _, Expression<'_>, _> = select! {
| +++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
```
instead of
```
error[E0284]: type annotations needed for `Select<{closure@/home/gh-estebank/.cargo/registry/src/index.crates.io-6f17d22bba15001f/chumsky-1.0.0-alpha.6/src/lib.rs:2782:13: 2782:28}, _, Expression<'_>, _>`
--> crates/lang/src/parser.rs:41:13
|
41 | let lit = select! {
| ^^^
42 | Token::Int(i) = e => Expression::new(Expr::Lit(ast::Lit::Int(i.parse().unwrap())), e.span()),
| ---- type must be known at this point
|
= note: cannot satisfy `<_ as chumsky::input::Input<'_>>::Span == SimpleSpan`
help: consider giving `lit` an explicit type, where the type for type parameter `I` is specified
|
41 | let lit: Select<{closure@/home/gh-estebank/.cargo/registry/src/index.crates.io-6f17d22bba15001f/chumsky-1.0.0-alpha.6/src/lib.rs:2782:13: 2782:28}, _, Expression<'_>, _> = select! {
| ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
```
Fix#123630.
Unify the output of `suggest_assign_value` and `ty_kind_suggestion`.
Ideally we'd make these a single function, but doing so would likely require modify the crate dependency tree.
This adds a whole bunch of tests checking for any difference with llvm's
archive writer. It also fixes two mistakes in the porting from C++ to
Rust. The first one causes a divergence for Mach-O archives which may or
may not be harmless. The second will definitively cause issues, but only
applies to thin archives, which rustc currently doesn't create.
I added this back in 111999, but I no longer think it's a good idea
- It had to get scaled back to only power-of-two things to not break a bunch of targets
- LLVM seems to be getting better at memcpy removal anyway
- Introducing vector instructions has seemed to sometimes (115515) make autovectorization worse
So this removes it from the codegen crates entirely, and instead just tries to use <https://doc.rust-lang.org/nightly/nightly-rustc/rustc_codegen_ssa/traits/builder/trait.BuilderMethods.html#method.typed_place_copy> instead of direct `memcpy` so things will still use load/store for immediates.
Rollup of 8 pull requests
Successful merges:
- #123254 (Do not allocate for ZST ThinBox (attempt 2 using const_allocate))
- #123626 (Add MC/DC support to coverage test tools)
- #123638 (rustdoc: synthetic auto: filter out clauses from the implementor's ParamEnv)
- #123653 (Split `non_local_definitions` lint tests in separate test files)
- #123658 (Stop making any assumption about the projections applied to the upvars in the `ByMoveBody` pass)
- #123662 (Don't rely on upvars being assigned just because coroutine-closure kind is assigned)
- #123665 (Fix typo in `Future::poll()` docs)
- #123672 (compiletest: unset `RUSTC_LOG_COLOR`)
r? `@ghost`
`@rustbot` modify labels: rollup
Don't rely on upvars being assigned just because coroutine-closure kind is assigned
Previously, code relied on the implicit assumption that if a coroutine-closure's kind variable was constrained, then its upvars were also constrained. This is because we assign all of them at once at the end up upvar analysis.
However, there's another way that a coroutine-closure's kind can be constrained: from a signature hint in closure signature deduction. After #123350, we use these hints, which means the implicit assumption above no longer holds.
This PR adds the necessary checks so that we don't ICE.
r? oli-obk
Stop making any assumption about the projections applied to the upvars in the `ByMoveBody` pass
So it turns out that because of subtle optimizations like [`truncate_capture_for_optimization`](ab5bda1aa7/compiler/rustc_hir_typeck/src/upvar.rs (L2351)), we simply cannot make any assumptions about the shape of the projections applied to the upvar locals in a coroutine body.
So stop doing that -- the code is resilient to such projections, so the assertion really existed only to "protect against the unknown".
r? oli-obk
Fixes#123650
Ensure we do not accidentally insert new early aborts in the analysis passes
pulling the infallible part out into a separate function makes sure that someone needs to change the signature in order to regress this.
We only want to stop compilation in the presence of errors after all analyses are done, but before we start running lints.
per-item we can still stop doing work if previous queries returned errors, but that's a separate story.
KCFI: Use legal charset in shim encoding
To separate `ReifyReason::FnPtr` from `ReifyReason::VTable`, we hyphenated the shims. Hyphens are not actually legal, but underscores are, so use those instead.
r? `@compiler-errors`
sanitizers: Create the rustc_sanitizers crate
Create the `rustc_sanitizers` crate and move the source code for the CFI and KCFI sanitizers to it. The tracking issue for reviewing and moving sanitizers into a compiler crate is #123619. This is part of our work to organize and stabilize support for the sanitizers. (See our roadmap at https://hackmd.io/`@rcvalle/S1Ou9K6H6.)`
Replace some `CrateStore` trait methods with hooks.
Just like with the `CrateStore` trait, this avoids the cyclic definition issues with `CStore` being
defined after TyCtxt, but needing to be used in TyCtxt.
Re-enable the early otherwise branch optimization
Closes#95162. Fixes#119014.
This is the first part of #121397.
An invalid enum discriminant can come from anywhere. We have to check to see if all successors contain the discriminant statement. This should have a pass to hoist instructions.
r? cjgillot
Before this fix, the call to `body()` would crash, since `has_body()`
would return true, but we would try to retrieve the body of an intrinsic
which is not allowed.
Instead, the `Instance::body()` function will now convert an Intrinsic
into an Item before retrieving its body.
Pass list of defineable opaque types into canonical queries
This eliminates `DefiningAnchor::Bubble` for good and brings the old solver closer to the new one wrt cycles and nested obligations. At that point the difference between `DefiningAnchor::Bind([])` and `DefiningAnchor::Error` was academic. We only used the difference for some sanity checks, which actually had to be worked around in places, so I just removed `DefiningAnchor` entirely and just stored the list of opaques that may be defined.
fixes#108498
fixes https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/116877
* [x] run crater
- https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/122077#issuecomment-2013293931
To separate `ReifyReason::FnPtr` from `ReifyReason::VTable`, we
hyphenated the shims. Hyphens are not actually legal, but underscores
are, so use those instead.
CFI: Fix ICE in KCFI non-associated function pointers
We oddly weren't testing the more usual case of casting non-methods to function pointers. The KCFI shim insertion logic would ICE on these due to asking for an irrefutable associated item if we cast a function to a function pointer without needing a traditional shim.
r? `@compiler-errors`
parser: reduce visibility of unnecessary public `UnmatchedDelim`
`lexer::UnmatchedDelim` struct in `rustc_parse` is unnecessary public outside of the crate. This commit reduces the visibility to `pub(crate)`.
Beside, this removes unnecessary field `expected_delim` that causes warnings after changing the visibility.
Remove unnecessary cast from `LLVMRustGetInstrProfIncrementIntrinsic`
(Noticed while reviewing #123409.)
This particular cast appears to have been copied over from clang, but there are plenty of other call sites in clang that don't bother with a cast here, and it works fine without one.
For context, `llvm::Intrinsic::ID` is a typedef for `unsigned`, and `llvm::Intrinsic::instrprof_increment` is a member of `enum IndependentIntrinsics : unsigned`.
---
The formatting change in `unwrap(M)` is the result of manually running `clang-format` on this file, and then reverting all changes other than the ones affecting these lines.
Fix `ByMove` coroutine-closure shim (for 2021 precise closure capturing behavior)
This PR reworks the way that we perform the `ByMove` coroutine-closure shim to account for the fact that the upvars of the outer coroutine-closure and the inner coroutine might not line up due to edition-2021 closure capture rules changes.
Specifically, the number of upvars may differ *and/or* the inner coroutine may have additional projections applied to an upvar. This PR reworks the information we pass into the `ByMoveBody` MIR visitor to account for both of these facts.
I tried to leave comments explaining exactly what everything is doing, but let me know if you have questions.
r? oli-obk
Safe Transmute: Compute transmutability from `rustc_target::abi::Layout`
In its first step of computing transmutability, `rustc_transmutability` constructs a byte-level representation of type layout (`Tree`). Previously, this representation was computed for ADTs by inspecting the ADT definition and performing our own layout computations. This process was error-prone, verbose, and limited our ability to analyze many types (particularly default-repr types).
In this PR, we instead construct `Tree`s from `rustc_target::abi::Layout`s. This helps ensure that layout optimizations are reflected our analyses, and increases the kinds of types we can now analyze, including:
- default repr ADTs
- transparent unions
- `UnsafeCell`-containing types
Overall, this PR expands the expressvity of `rustc_transmutability` to be much closer to the transmutability analysis performed by miri. Future PRs will work to close the remaining gaps (e.g., support for `Box`, raw pointers, `NonZero*`, coroutines, etc.).
r? `@compiler-errors`
Fix argument ABI for overaligned structs on ppc64le
When passing a 16 (or higher) aligned struct by value on ppc64le, it needs to be passed as an array of `i128` rather than an array of `i64`. This will force the use of an even starting doubleword.
For the case of a 16 byte struct with alignment 16 it is important that `[1 x i128]` is used instead of `i128` -- apparently, the latter will get treated similarly to `[2 x i64]`, not exhibiting the correct ABI. Add a `force_array` flag to `Uniform` to support this.
The relevant clang code can be found here:
fe2119a7b0/clang/lib/CodeGen/Targets/PPC.cpp (L878-L884)fe2119a7b0/clang/lib/CodeGen/Targets/PPC.cpp (L780-L784)
I think the corresponding psABI wording is this:
> Fixed size aggregates and unions passed by value are mapped to as
> many doublewords of the parameter save area as the value uses in
> memory. Aggregrates and unions are aligned according to their
> alignment requirements. This may result in doublewords being
> skipped for alignment.
In particular the last sentence. Though I didn't find any wording for Clang's behavior of clamping the alignment to 16.
Fixes https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/122767.
r? `@cuviper`
Create the rustc_sanitizers crate and move the source code for the CFI
and KCFI sanitizers to it.
Co-authored-by: David Wood <agile.lion3441@fuligin.ink>
We oddly weren't testing the more usual case of casting non-methods to
function pointers. The KCFI shim insertion logic would ICE on these due
to asking for an irrefutable associated item if we cast a function to a
function pointer without needing a traditional shim.
Implement minimal, internal-only pattern types in the type system
rebase of https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/107606
You can create pattern types with `std::pat::pattern_type!(ty is pat)`. The feature is incomplete and will panic on you if you use any pattern other than integral range patterns. The only way to create or deconstruct a pattern type is via `transmute`.
This PR's implementation differs from the MCP's text. Specifically
> This means you could implement different traits for different pattern types with the same base type. Thus, we just forbid implementing any traits for pattern types.
is violated in this PR. The reason is that we do need impls after all in order to make them usable as fields. constants of type `std::time::Nanoseconds` struct are used in patterns, so the type must be structural-eq, which it only can be if you derive several traits on it. It doesn't need to be structural-eq recursively, so we can just manually implement the relevant traits on the pattern type and use the pattern type as a private field.
Waiting on:
* [x] move all unrelated commits into their own PRs.
* [x] fix niche computation (see 2db07f94f44f078daffe5823680d07d4fded883f)
* [x] add lots more tests
* [x] T-types MCP https://github.com/rust-lang/types-team/issues/126 to finish
* [x] some commit cleanup
* [x] full self-review
* [x] remove 61bd325da19a918cc3e02bbbdce97281a389c648, it's not necessary anymore I think.
* [ ] ~~make sure we never accidentally leak pattern types to user code (add stability checks or feature gate checks and appopriate tests)~~ we don't even do this for the new float primitives
* [x] get approval that [the scope expansion to trait impls](https://rust-lang.zulipchat.com/#narrow/stream/326866-t-types.2Fnominated/topic/Pattern.20types.20types-team.23126/near/427670099) is ok
r? `@BoxyUwU`
In its first step of computing transmutability, `rustc_transmutability`
constructs a byte-level representation of type layout (`Tree`). Previously, this
representation was computed for ADTs by inspecting the ADT definition and
performing our own layout computations. This process was error-prone, verbose,
and limited our ability to analyze many types (particularly default-repr types).
In this PR, we instead construct `Tree`s from `rustc_target::abi::Layout`s. This
helps ensure that layout optimizations are reflected our analyses, and increases
the kinds of types we can now analyze, including:
- default repr ADTs
- transparent unions
- `UnsafeCell`-containing types
Overall, this PR expands the expressvity of `rustc_transmutability` to be much
closer to the transmutability analysis performed by miri. Future PRs will work
to close the remaining gaps (e.g., support for `Box`, raw pointers, `NonZero*`,
coroutines, etc.).
`lexer::UnmatchedDelim` struct in `rustc_parse` is unnecessary public
outside of the crate. This commit reduces the visibility to
`pub(crate)`.
Beside, this removes unnecessary field `expected_delim` that causes
warnings after changing the visibility.
Stop exporting `TypeckRootCtxt` and `FnCtxt`.
While they have many convenient APIs, it is better to expose dedicated functions for them
noticed in #122213
Add consistency with phrases "meantime" and "mean time"
"mean time" is used in a few places while "meantime" is used everywhere else; this would make usage consistent throughout the codebase.
The actual ABI implication here is that in some cases the values
are required to be "consecutive", i.e. must either all be passed
in registers or all on stack (without padding).
Adjust the code to either use Uniform::new() or Uniform::consecutive()
depending on which behavior is needed.
Then, when lowering this in LLVM, skip the [1 x i128] to i128
simplification if is_consecutive is set. i128 is the only case
I'm aware of where this is problematic right now. If we find
other cases, we can extend this (either based on target information
or possibly just by not simplifying for is_consecutive entirely).
When passing a 16 (or higher) aligned struct by value on ppc64le,
it needs to be passed as an array of `i128` rather than an array
of `i64`. This will force the use of an even starting register.
For the case of a 16 byte struct with alignment 16 it is important
that `[1 x i128]` is used instead of `i128` -- apparently, the
latter will get treated similarly to `[2 x i64]`, not exhibiting
the correct ABI. Add a `force_array` flag to `Uniform` to support
this.
The relevant clang code can be found here:
fe2119a7b0/clang/lib/CodeGen/Targets/PPC.cpp (L878-L884)fe2119a7b0/clang/lib/CodeGen/Targets/PPC.cpp (L780-L784)
I think the corresponding psABI wording is this:
> Fixed size aggregates and unions passed by value are mapped to as
> many doublewords of the parameter save area as the value uses in
> memory. Aggregrates and unions are aligned according to their
> alignment requirements. This may result in doublewords being
> skipped for alignment.
In particular the last sentence.
Fixes https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/122767.
This particular cast appears to have been copied over from clang, but there are
plenty of other call sites in clang that don't bother with a cast here, and it
works fine without one.
For context, `llvm::Intrinsic::ID` is a typedef for `unsigned`, and
`llvm::Intrinsic::instrprof_increment` is a member of
`enum IndependentIntrinsics : unsigned`.
Save/restore more items in cache with incremental compilation
Right now they don't play very well together, consider a simple example:
```
$ export RUSTFLAGS="--emit asm"
$ cargo new --lib foo
Created library `foo` package
$ cargo build -q
$ touch src/lib.rs
$ cargo build
error: could not copy
"/path/to/foo/target/debug/deps/foo-e307cc7fa7b6d64f.4qbzn9k8mosu50a5.rcgu.s"
to "/path/to/foo/target/debug/deps/foo-e307cc7fa7b6d64f.s":
No such file or directory (os error 2)
```
Touch triggers the rebuild, incremental compilation detects no changes (yay) and everything explodes while trying to copy files were they should go.
This pull request fixes it by copying and restoring more files in the incremental compilation cache
Fixes https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/89149
Fixes https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/88829
Related: https://internals.rust-lang.org/t/interaction-between-incremental-compilation-and-emit/20551
Fix incorrect 'llvm_target' value used on watchOS target
## Issue
`xcodebuild -create-xcframework` command doesn't recognize static libraries that are built on "arm64_32-apple-watchos" target.
Here are steps to reproduce the issue on a Mac:
1. Install nightly toolchain `nightly-2024-03-27`. Needs this specific version, because newer nightly versions are broken on watchos target.
1. Create an empty library: `mkdir watchos-lib && cd watchos-lib && cargo init --lib`.
1. Add configuration `lib.crate-type=["staticlib"]` to Cargo.toml.
1. Build the library: `cargo +nightly-2024-03-27 build --release -Zbuild-std --target arm64_32-apple-watchos`
1. Run `xcodebuild -create-xcframework` to put the static library into a xcframework, which results in an error:
```
$ xcodebuild -create-xcframework -library target/arm64_32-apple-watchos/release/libwatchos_lib.a -output test.xcframework
error: unable to determine the platform for the given binary '.../watchos-lib/target/arm64_32-apple-watchos/release/libwatchos_lib.a'; check your deployment version settings
```
## Fix
The root cause of this error is `xcodebuild` couldn't read `LC_BUILD_VERSION` from the static library to determine the library's target platform. And the reason it's missing is that an incorrect `llvm_target` value is used in `arm64_32-apple-watchos` target. The expected value is `<arch>-apple-watchos<major>.<minor>.0`, i.e. "arm64_32-apple-watchos8.0.0".
The [.../apple/mod.rs](43f4f2a3b1/compiler/rustc_target/src/spec/base/apple/mod.rs (L321)) file contains functions that construct such string. There is an existing function `watchos_sim_llvm_target` which returns llvm target value for watchOS simulator. But there is none for watchOS device. This PR adds that missing function to align watchOS with other Apple platform targets.
To verify the fix, you can simply build a toolchain on this PR branch and repeat the steps above using the built local toolchain to verify the `xcodebuild -create-xcframework` command can create a xcframework successfully.
Furthermore, you can verify `LC_BUILD_VERSION` contains correct info by using the simple shell script below to print `LC_BUILD_VERSION` of the static library that's built on watchos target:
```shell
bin=target/arm64_32-apple-watchos/release/libwatchos_lib.a
file=$(ar -t "$bin" | grep -E '\.o$' | head -n 1)
ar -x "$bin" "$file"
vtool -show-build-version "$file"
```
Here is an example output from my machine:
```
watchos_rust-495d6aaf3bccc08d.watchos_rust.35ba42bf9255ca9d-cgu.0.rcgu.o:
Load command 1
cmd LC_BUILD_VERSION
cmdsize 24
platform WATCHOS
minos 8.0
sdk n/a
ntools 0
```
Remove sharding for VecCache
This sharding is never used (per the comment in code). If we re-add sharding at some point in the future this is cheap to restore, but for now no need for the extra complexity.
Add a debug asserts call to match_projection_projections to ensure invariant
Small nit as follow up of #123471.
r? `@compiler-errors`
`@bors` rollup=always
Do not ICE when encountering a lifetime error involving an argument with
an immutable reference of a method that differs from the trait definition.
Fix#123414.
This sharding is never used (per the comment in code). If we re-add
sharding at some point in the future this is cheap to restore, but for
now no need for the extra complexity.
Rollup of 7 pull requests
Successful merges:
- #123294 (Require LLVM_CONFIG to be set in rustc_llvm/build.rs)
- #123467 (MSVC targets should use COFF as their archive format)
- #123498 (explaining `DefKind::Field`)
- #123519 (Improve cfg and check-cfg configuration)
- #123525 (CFI: Don't rewrite ty::Dynamic directly)
- #123526 (Do not ICE when calling incorrectly defined `transmute` intrinsic)
- #123528 (Hide async_gen_internals from standard library documentation)
r? `@ghost`
`@rustbot` modify labels: rollup
CFI: Don't rewrite ty::Dynamic directly
Now that we're using a type folder, the arguments in predicates are processed automatically - we don't need to descend manually.
We also want to keep projection clauses around, and this does so.
r? `@compiler-errors`
Improve cfg and check-cfg configuration
This PR improves cfg and check-cfg configuration by:
1. Extracting both logic under a common module (to improve the connection between the two)
2. Adding more documentation, in particular some steps when adding a new cfg
I also added my-self as mention in our triagebot conf for the new module.
Inspired by https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/123411#discussion_r1554056681
MSVC targets should use COFF as their archive format
While adding support for Arm64EC I ran into an issue where the standard library's rlib was missing the "EC Symbol Table" which is required for the MSVC linker to find import library symbols (generated by Rust's `raw-dylib` feature) when building for EC.
The root cause of the issue is that LLVM only generated symbol tables (including the EC Symbol Table) if the `ArchiveKind` is `COFF`, but the MSVC targets didn't set their archive format, so it was defaulting to GNU.
Require LLVM_CONFIG to be set in rustc_llvm/build.rs
This environment variable should always be set by bootstrap in `rustc_llvm_env`. The fallback is quite ugly and complicated, so removing it is nice.
bf71daedc2/src/bootstrap/src/core/build_steps/compile.rs (L1166)
I tried finding when this was added in git history, but it pointed all the way to "add build scripts" at which point I stopped digging more. This has always been here.
cc `@nikic` `@cuviper` in case you happen to be aware of a deeper reason behind this
r? bootstrap
Check def id before calling `match_projection_projections`
When I "inlined" `assemble_candidates_from_predicates` into `for_each_item_bound` in #120584, I forgot to copy over the check that actually made sure the def id of the candidate was equal to the def id of the obligation. This means that we normalize goal a bit too often even if it's not productive to do so.
This PR adds that def id check back.
Fixes#123448
Now that we're using a type folder, the arguments in predicates are
processed automatically - we don't need to descend manually.
We also want to keep projection clauses around, and this does so.
CFI: Restore typeid_for_instance default behavior
Restore typeid_for_instance default behavior of performing self type erasure, since it's the most common case and what it does most of the time. Using concrete self (or not performing self type erasure) is for assigning a secondary type id, and secondary type ids are only assigned when they're unique and to methods, and also are only tested for when methods are used as function pointers.
Fix target-cpu fpu features on Arm R/M-profile
This is achieved by converting `+<fpu>,-d32,{,-fp64}` to `+<fpu>d16{,sp}`.
By using a single additive feature that captures `d16` vs `d32` and `sp` vs
`dp`, we prevent `-<feature>` from overriding `-C target-cpu` at build time.
Remove extraneous `-fp16` from `armv7r` targets, as this is not included in
`vfp3` anyway, but was preventing `fp16` from being enabled by e.g.,
`-C target-cpu=cortex-r7`, which does support `fp16`.
Add aarch64-apple-visionos and aarch64-apple-visionos-sim tier 3 targets
Introduces `aarch64-apple-visionos` and `aarch64-apple-visionos-sim` as tier 3 targets. This allows native development for the Apple Vision Pro's visionOS platform.
This work has been tracked in https://github.com/rust-lang/compiler-team/issues/642. There is a corresponding `libc` change https://github.com/rust-lang/libc/pull/3568 that is not required for merge.
Ideally we would be able to incorporate [this change](https://github.com/gimli-rs/object/pull/626) to the `object` crate, but the author has stated that a release will not be cut for quite a while. Therefore, the two locations that would reference the xrOS constant from `object` are hardcoded to their MachO values of 11 and 12, accompanied by TODOs to mark the code as needing change. I am open to suggestions on what to do here to get this checked in.
# Tier 3 Target Policy
At this tier, the Rust project provides no official support for a target, so we place minimal requirements on the introduction of targets.
> A tier 3 target must have a designated developer or developers (the "target maintainers") on record to be CCed when issues arise regarding the target. (The mechanism to track and CC such developers may evolve over time.)
See [src/doc/rustc/src/platform-support/apple-visionos.md](e88379034a/src/doc/rustc/src/platform-support/apple-visionos.md)
> Targets must use naming consistent with any existing targets; for instance, a target for the same CPU or OS as an existing Rust target should use the same name for that CPU or OS. Targets should normally use the same names and naming conventions as used elsewhere in the broader ecosystem beyond Rust (such as in other toolchains), unless they have a very good reason to diverge. Changing the name of a target can be highly disruptive, especially once the target reaches a higher tier, so getting the name right is important even for a tier 3 target.
> * Target names should not introduce undue confusion or ambiguity unless absolutely necessary to maintain ecosystem compatibility. For example, if the name of the target makes people extremely likely to form incorrect beliefs about what it targets, the name should be changed or augmented to disambiguate it.
> * If possible, use only letters, numbers, dashes and underscores for the name. Periods (.) are known to cause issues in Cargo.
This naming scheme matches `$ARCH-$VENDOR-$OS-$ABI` which is matches the iOS Apple Silicon simulator (`aarch64-apple-ios-sim`) and other Apple targets.
> Tier 3 targets may have unusual requirements to build or use, but must not
create legal issues or impose onerous legal terms for the Rust project or for
Rust developers or users.
> - The target must not introduce license incompatibilities.
> - Anything added to the Rust repository must be under the standard Rust license (`MIT OR Apache-2.0`).
> - The target must not cause the Rust tools or libraries built for any other host (even when supporting cross-compilation to the target) to depend on any new dependency less permissive than the Rust licensing policy. This applies whether the dependency is a Rust crate that would require adding new license exceptions (as specified by the `tidy` tool in the rust-lang/rust repository), or whether the dependency is a native library or binary. In other words, the introduction of the target must not cause a user installing or running a version of Rust or the Rust tools to besubject to any new license requirements.
> - Compiling, linking, and emitting functional binaries, libraries, or other code for the target (whether hosted on the target itself or cross-compiling from another target) must not depend on proprietary (non-FOSS) libraries. Host tools built for the target itself may depend on the ordinary runtime libraries supplied by the platform and commonly used by other applications built for the target, but those libraries must not be required for code generation for the target; cross-compilation to the target must not require such libraries at all. For instance, `rustc` built for the target may depend on a common proprietary C runtime library or console output library, but must not depend on a proprietary code generation library or code optimization library. Rust's license permits such combinations, but the Rust project has no interest in maintaining such combinations within the scope of Rust itself, even at tier 3.
> - "onerous" here is an intentionally subjective term. At a minimum, "onerous" legal/licensing terms include but are *not* limited to: non-disclosure requirements, non-compete requirements, contributor license agreements (CLAs) or equivalent, "non-commercial"/"research-only"/etc terms, requirements conditional on the employer or employment of any particular Rust developers, revocable terms, any requirements that create liability for the Rust project or its developers or users, or any requirements that adversely affect the livelihood or prospects of the Rust project or its developers or users.
This contribution is fully available under the standard Rust license with no additional legal restrictions whatsoever. This PR does not introduce any new dependency less permissive than the Rust license policy.
The new targets do not depend on proprietary libraries.
> Tier 3 targets should attempt to implement as much of the standard libraries as possible and appropriate (core for most targets, alloc for targets that can support dynamic memory allocation, std for targets with an operating system or equivalent layer of system-provided functionality), but may leave some code unimplemented (either unavailable or stubbed out as appropriate), whether because the target makes it impossible to implement or challenging to implement. The authors of pull requests are not obligated to avoid calling any portions of the standard library on the basis of a tier 3 target not implementing those portions.
This new target mirrors the standard library for watchOS and iOS, with minor divergences.
> The target must provide documentation for the Rust community explaining how to build for the target, using cross-compilation if possible. If the target supports running binaries, or running tests (even if they do not pass), the documentation must explain how to run such binaries or tests for the target, using emulation if possible or dedicated hardware if necessary.
Documentation is provided in [src/doc/rustc/src/platform-support/apple-visionos.md](e88379034a/src/doc/rustc/src/platform-support/apple-visionos.md)
> Neither this policy nor any decisions made regarding targets shall create any binding agreement or estoppel by any party. If any member of an approving Rust team serves as one of the maintainers of a target, or has any legal or employment requirement (explicit or implicit) that might affect their decisions regarding a target, they must recuse themselves from any approval decisions regarding the target's tier status, though they may otherwise participate in discussions.
> * This requirement does not prevent part or all of this policy from being cited in an explicit contract or work agreement (e.g. to implement or maintain support for a target). This requirement exists to ensure that a developer or team responsible for reviewing and approving a target does not face any legal threats or obligations that would prevent them from freely exercising their judgment in such approval, even if such judgment involves subjective matters or goes beyond the letter of these requirements.
> Tier 3 targets must not impose burden on the authors of pull requests, or other developers in the community, to maintain the target. In particular, do not post comments (automated or manual) on a PR that derail or suggest a block on the PR based on a tier 3 target. Do not send automated messages or notifications (via any medium, including via `@)` to a PR author or others involved with a PR regarding a tier 3 target, unless they have opted into such messages.
> * Backlinks such as those generated by the issue/PR tracker when linking to an issue or PR are not considered a violation of this policy, within reason. However, such messages (even on a separate repository) must not generate notifications to anyone involved with a PR who has not requested such notifications.
> Patches adding or updating tier 3 targets must not break any existing tier 2 or tier 1 target, and must not knowingly break another tier 3 target without approval of either the compiler team or the maintainers of the other tier 3 target.
> * In particular, this may come up when working on closely related targets, such as variations of the same architecture with different features. Avoid introducing unconditional uses of features that another variation of the target may not have; use conditional compilation or runtime detection, as appropriate, to let each target run code supported by that target.
I acknowledge these requirements and intend to ensure that they are met.
This target does not touch any existing tier 2 or tier 1 targets and should not break any other targets.
When encoutnering a case like
```rust
//@ run-rustfix
use std::collections::HashMap;
fn main() {
let vs = vec![0, 0, 1, 1, 3, 4, 5, 6, 3, 3, 3];
let mut counts = HashMap::new();
for num in vs {
let count = counts.entry(num).or_insert(0);
*count += 1;
}
let _ = counts.iter().max_by_key(|(_, v)| v);
```
produce the following suggestion
```
error: lifetime may not live long enough
--> $DIR/return-value-lifetime-error.rs:13:47
|
LL | let _ = counts.iter().max_by_key(|(_, v)| v);
| ------- ^ returning this value requires that `'1` must outlive `'2`
| | |
| | return type of closure is &'2 &i32
| has type `&'1 (&i32, &i32)`
|
help: dereference the return value
|
LL | let _ = counts.iter().max_by_key(|(_, v)| **v);
| ++
```
Fix#50195.
Subtree sync for rustc_codegen_cranelift
This fixes an ICE when compiling unchecked_shl/unchecked_shr.
r? `@ghost`
`@rustbot` label +A-codegen +A-cranelift +T-compiler
Actually use the inferred `ClosureKind` from signature inference in coroutine-closures
A follow-up to https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/123349, which fixes another subtle bug: We were not taking into account the async closure kind we infer during closure signature inference.
When I pass a closure directly to an arg like `fn(x: impl async FnOnce())`, that should have the side-effect of artificially restricting the kind of the async closure to `ClosureKind::FnOnce`. We weren't doing this -- that's a quick fix; however, it uncovers a second, more subtle bug with the way that `move`, async closures, and `FnOnce` interact.
Specifically, when we have an async closure like:
```
let x = Struct;
let c = infer_as_fnonce(async move || {
println!("{x:?}");
}
```
The outer closure captures `x` by move, but the inner coroutine still immutably borrows `x` from the outer closure. Since we've forced the closure to by `async FnOnce()`, we can't actually *do* a self borrow, since the signature of `AsyncFnOnce::call_once` doesn't have a borrowed lifetime. This means that all `async move` closures that are constrained to `FnOnce` will fail borrowck.
We can fix that by detecting this case specifically, and making the *inner* async closure `move` as well. This is always beneficial to closure analysis, since if we have an `async FnOnce()` that's `move`, there's no reason to ever borrow anything, so `move` isn't artificially restrictive.
Match ergonomics: implement "`&`pat everywhere"
Implements the eat-two-layers (feature gate `and_pat_everywhere`, all editions) ~and the eat-one-layer (feature gate `and_eat_one_layer_2024`, edition 2024 only, takes priority on that edition when both feature gates are active)~ (EDIT: will be done in later PR) semantics.
cc #123076
r? ``@Nadrieril``
``@rustbot`` label A-patterns A-edition-2024
This is achieved by converting `+<fpu>,-d32,{,-fp64}` to `+<fpu>d16{,sp}`.
By using a single additive feature that captures `d16` vs `d32` and `sp` vs
`dp`, we prevent `-<feature>` from overriding `-C target-cpu` at build time.
Remove extraneous `-fp16` from `armv7r` targets, as this is not included in
`vfp3` anyway, but was preventing `fp16` from being enabled by e.g.,
`-C target-cpu=cortex-r7`, which does support `fp16`.
Restore typeid_for_instance default behavior of performing self type
erasure, since it's the most common case and what it does most of the
time. Using concrete self (or not performing self type erasure) is for
assigning a secondary type id, and secondary type ids are only assigned
when they're unique and to methods, and also are only tested for when
methods are used as function pointers.
do not ICE in `fn forced_ambiguity` if we get an error
see the comment. currently causing an ICE in typenum which we've been unable to minimize.
r? `@compiler-errors`
Cleanup: Rename `HAS_PROJECTIONS` to `HAS_ALIASES` etc.
The name of the bitflag `HAS_PROJECTIONS` and of its corresponding method `has_projections` is quite historical dating back to a time when projections were the only kind of alias type.
I think it's time to update it to clear up any potential confusion for newcomers and to reduce unnecessary friction during contributor onboarding.
r? types
Manually run `clang-format` on `CoverageMappingWrapper.cpp`
In the current version of #123409, there are several unrelated changes to `CoverageMappingWrapper.cpp` that seem to be the result of running `clang-format` on that file.
Instead of asking for those changes to be undone, I figure it's easier to just make them myself as a separate PR, since I was vaguely intending to do that at some point anyway.
In a few cases I've strategically added comments to make the grouping of parameters a little nicer, but mostly it doesn't matter much.
change `NormalizesTo` to fully structurally normalize
notes in https://hackmd.io/wZ016dE4QKGIhrOnHLlThQ
need to also update the dev-guide once this PR lands. in short, the setup is now as follows:
`normalizes-to` internally implements one step normalization, applying that normalization to the `goal.predicate.term` causes the projected term to get recursively normalized. With this `normalizes-to` normalizes until the projected term is rigid, meaning that we normalize as many steps necessary, but at least 1.
To handle rigid aliases, we add another candidate only if the 1 to inf step normalization failed. With this `normalizes-to` is now full structural normalization. We can now change `AliasRelate` to simply emit `normalizes-to` goals for the rhs and lhs.
This avoids the concerns from https://github.com/rust-lang/trait-system-refactor-initiative/issues/103 and generally feels cleaner
Try using a `dyn Debug` trait object instead of a closure
These closures were introduced in https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/93098
let's see if we can't use fmt::Arguments instead
cc `@Aaron1011`
some smaller DefiningOpaqueTypes::No -> Yes switches
r? `@compiler-errors`
These are some easy cases, so let's get them out of the way first.
I added tests exercising the specialization code paths that I believe weren't tested so far.
follow-up to https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/117348
Only inspect user-written predicates for privacy concerns
fixes#123288
Previously we looked at the elaborated predicates, which, due to adding various bounds on fields, end up requiring trivially true bounds. But these bounds can contain private types, which the privacy visitor then found and errored about.
Rollup of 9 pull requests
Successful merges:
- #121546 (Error out of layout calculation if a non-last struct field is unsized)
- #122448 (Port hir-tree run-make test to ui test)
- #123212 (CFI: Change type transformation to use TypeFolder)
- #123218 (Add test for getting parent HIR for synthetic HIR node)
- #123324 (match lowering: make false edges more precise)
- #123389 (Avoid panicking unnecessarily on startup)
- #123397 (Fix diagnostic for qualifier in extern block)
- #123431 (Stabilize `proc_macro_byte_character` and `proc_macro_c_str_literals`)
- #123439 (coverage: Remove useless constants)
r? `@ghost`
`@rustbot` modify labels: rollup
coverage: Remove useless constants
After #122972 and #123419, these constants don't serve any useful purpose, so get rid of them.
`@rustbot` label +A-code-coverage
match lowering: make false edges more precise
When lowering match expressions, we add false edges to hide details of the lowering from borrowck. Morally we pretend we're testing the patterns (and guards) one after the other in order. See the tests for examples. Problem is, the way we implement this today is too coarse for deref patterns.
In deref patterns, a pattern like `deref [1, x]` matches on a `Vec` by creating a temporary to store the output of the call to `deref()` and then uses that to continue matching. Here the pattern has a binding, which we set up after the pre-binding block. Problem is, currently the false edges tell borrowck that the pre-binding block can be reached from a previous arm as well, so the `deref()` temporary may not be initialized. This triggers an error when we try to use the binding `x`.
We could call `deref()` a second time, but this opens the door to soundness issues if the deref impl is weird. Instead in this PR I rework false edges a little bit.
What we need from false edges is a (fake) path from each candidate to the next, specifically from candidate C's pre-binding block to next candidate D's pre-binding block. Today, we link the pre-binding blocks directly. In this PR, I link them indirectly by choosing an earlier node on D's success path. Specifically, I choose the earliest block on D's success path that doesn't make a loop (if I chose e.g. the start block of the whole match (which is on the success path of all candidates), that would make a loop). This turns out to be rather straightforward to implement.
r? `@matthewjasper` if you have the bandwidth, otherwise let me know
coverage: Correctly report and check LLVM's coverage mapping version
I was puzzled by the fact that the LLVM 18 update (#120055) didn't need to modify this version check, despite the fact that LLVM 18 uses a newer version of the coverage mapping format.
This turned out to be because we were inappropriately hard-coding a specific version (`Version6`) in the C++ wrapper, instead of using `CovMapVersion::CurrentVersion` to reflect the version actually used by LLVM on our behalf.
This PR fixes that, and also changes the Rust-side version check to accept the new coverage mapping version used by LLVM 18, since the necessary compatibility work has already been done.
---
### Quick history of `LLVMRustCoverageMappingVersion`:
- Originally it returned LLVM's `coverage::CovMapVersion::CurrentVersion`, as intended. The Rust-side code would verify it, and also embed it as the actual coverage version number in the output binary.
- At some point it was changed to a hard-coded value, to work around a (now-irrelevant) compatibility issue. This was incorrect (but mostly benign), because the override should have been performed on the Rust side instead, after verifying LLVM's value.
- Later contributors dutifully updated the hard-coded value, because they didn't have enough context to identify the problem.
- With this PR, it once again returns LLVM's current coverage version number, and the Rust-side code checks it against an expected range. We don't override the result, but we do indicate where that override should occur if it ever becomes necessary.
The reason is that in specialization graph computation we use `DefiningAnchor::Error`, so there's no difference anyway. And in the other use cases, we
* already errored in the specialization_graph computation, or
* already errored in coherence, or
* are comparing opaque types with inference variables already, or
* there are no opaque types involved
check `FnDef` return type for WF
better version of #106807, fixes#84533 (mostly). It's not perfect given that we still ignore WF requirements involving bound regions but I wasn't able to quickly write an example, so even if theoretically exploitable, it should be far harder to trigger.
This is strictly more restrictive than checking the return type for WF as part of the builtin `FnDef: FnOnce` impl (#106807) and moving to this approach in the future will not break any code.
~~It also agrees with my theoretical view of how this should behave~~
r? types
CFI: Support function pointers for trait methods
Adds support for both CFI and KCFI for function pointers to trait methods by attaching both concrete and abstract types to functions.
KCFI does this through generation of a `ReifyShim` on any function pointer for a method that could go into a vtable, and keeping this separate from `ReifyShim`s that are *intended* for vtable us by setting a `ReifyReason` on them.
CFI does this by setting both the concrete and abstract type on every instance.
This should land after #123024 or a similar PR, as it diverges the implementation of CFI vs KCFI.
r? `@compiler-errors`
The expected value is "<arch>-apple-watchos<major>.<minor>.0", i.e.
"arm64_32-apple-watchos8.0.0".
compiler/rustc_target/src/spec/base/apple/mod.rs contains functions that
construct such string. There is an existing function
`watchos_sim_llvm_target` which returns llvm target value for watchOS
simulator. But there is none for watchOS device. This commit adds that
missing function to align watchOS with other Apple platform targets.
instantiate higher ranked goals outside of candidate selection
This PR modifies `evaluate` to more eagerly instantiate higher-ranked goals, preventing the `leak_check` during candidate selection from detecting placeholder errors involving that binder.
For a general background regarding higher-ranked region solving and the leak check, see https://hackmd.io/qd9Wp03cQVy06yOLnro2Kg.
> The first is something called the **leak check**. You can think of it as a "quick and dirty" approximation for the region check, which will come later. The leak check detects some kinds of errors early, essentially deciding between "this set of outlives constraints are guaranteed to result in an error eventually" or "this set of outlives constraints may be solvable".
## The ideal future
We would like to end up with the following idealized design to handle universal binders:
```rust
fn enter_forall<'tcx, T, R>(
forall: Binder<'tcx, T>,
f: impl FnOnce(T) -> R,
) -> R {
let new_universe = infcx.increment_universe_index();
let value = instantiate_binder_with_placeholders_in(new_universe, forall);
let result = f(value);
eagerly_handle_higher_ranked_region_constraints_in(new_universe);
infcx.decrement_universe_index();
assert!(!result.has_placeholders_in_or_above(new_universe));
result
}
```
That is, when universally instantiating a binder, anything using the placeholders has to happen inside of a limited scope (the closure `f`). After this closure has completed, all constraints involving placeholders are known.
We then handle any *external constraints* which name these placeholders. We destructure `TypeOutlives` constraints involving placeholders and eagerly handle any region constraints involving these placeholders. We do not return anything mentioning the placeholders created inside of this function to the caller.
Being able to eagerly handle *all* region constraints involving placeholders will be difficult due to complex `TypeOutlives` constraints, involving inference variables or alias types, and higher ranked implied bounds. The exact issues and possible solutions are out of scope of this FCP.
#### How does the leak check fit into this
The `leak_check` is an underapproximation of `eagerly_handle_higher_ranked_region_constraints_in`. It detects some kinds of errors involving placeholders from `new_universe`, but not all of them.
It only looks at region outlives constraints, ignoring `TypeOutlives`, and checks whether one of the following two conditions are met for **placeholders in or above `new_universe`**, in which case it results in an error:
- `'!p1: '!p2` a placeholder `'!p2` outlives a different placeholder `'!p1`
- `'!p1: '?2` an inference variable `'?2` outlives a placeholder `'!p1` *which it cannot name*
It does not handle all higher ranked region constraints, so we still return constraints involving placeholders from `new_universe` which are then (re)checked by `lexical_region_resolve` or MIR borrowck.
As we check higher ranked constraints in the full regionck anyways, the `leak_check` is not soundness critical. It's current only purpose is to move some higher ranked region errors earlier, enabling it to guide type inference and trait solving. Adding additional uses of the `leak_check` in the future would only strengthen inference and is therefore not breaking.
## Where do we use currently use the leak check
The `leak_check` is currently used in two places:
Coherence does not use a proper regionck, only relying on the `leak_check` called [at the end of the implicit negative overlap check](8b94152af6/compiler/rustc_trait_selection/src/traits/coherence.rs (L235-L238)). During coherence all parameters are instantiated with inference variables, so the only possible region errors are higher-ranked. We currently also sometimes make guesses when destructuring `TypeOutlives` constraints which can theoretically result in incorrect errors. This could result in overlapping impls.
We also use the `leak_check` [at the end of `fn evaluation_probe`](8b94152af6/compiler/rustc_trait_selection/src/traits/select/mod.rs (L607-L610)). This function is used during candidate assembly for `Trait` goals. Most notably we use [inside of `evaluate_candidate` during winnowing](0e4243538b/compiler/rustc_trait_selection/src/traits/select/mod.rs (L491-L502)). Conceptionally, it is as if we compute each candidate in a separate `enter_forall`.
## The current use in `fn evaluation_probe` is undesirable
Because we only instantiate a higher-ranked goal once inside of `fn evaluation_probe`, errors involving placeholders from that binder can impact selection. This results in inconsistent behavior ([playground](
*[playground](https://play.rust-lang.org/?version=stable&mode=debug&edition=2021&gist=dac60ebdd517201788899ffa77364831)*)):
```rust
trait Leak<'a> {}
impl Leak<'_> for Box<u32> {}
impl Leak<'static> for Box<u16> {}
fn impls_leak<T: for<'a> Leak<'a>>() {}
trait IndirectLeak<'a> {}
impl<'a, T: Leak<'a>> IndirectLeak<'a> for T {}
fn impls_indirect_leak<T: for<'a> IndirectLeak<'a>>() {}
fn main() {
// ok
//
// The `Box<u16>` impls fails the leak check,
// meaning that we apply the `Box<u32>` impl.
impls_leak::<Box<_>>();
// error: type annotations needed
//
// While the `Box<u16>` impl would fail the leak check
// we have already instantiated the binder while applying
// the generic `IndirectLeak` impl, so during candidate
// selection of `Leak` we do not detect the placeholder error.
// Evaluation of `Box<_>: Leak<'!a>` is therefore ambiguous,
// resulting in `for<'a> Box<_>: Leak<'a>` also being ambiguous.
impls_indirect_leak::<Box<_>>();
}
```
We generally prefer `where`-bounds over implementations during candidate selection, both for [trait goals](11f32b73e0/compiler/rustc_trait_selection/src/traits/select/mod.rs (L1863-L1887)) and during [normalization](11f32b73e0/compiler/rustc_trait_selection/src/traits/project.rs (L184-L198)). However, we currently **do not** use the `leak_check` during candidate assembly in normalizing. This can result in inconsistent behavior:
```rust
trait Trait<'a> {
type Assoc;
}
impl<'a, T> Trait<'a> for T {
type Assoc = usize;
}
fn trait_bound<T: for<'a> Trait<'a>>() {}
fn projection_bound<T: for<'a> Trait<'a, Assoc = usize>>() {}
// A function with a trivial where-bound which is more
// restrictive than the impl.
fn function<T: Trait<'static, Assoc = usize>>() {
// ok
//
// Proving `for<'a> T: Trait<'a>` using the where-bound results
// in a leak check failure, so we use the more general impl,
// causing this to succeed.
trait_bound::<T>();
// error
//
// Proving the `Projection` goal `for<'a> T: Trait<'a, Assoc = usize>`
// does not use the leak check when trying the where-bound, causing us
// to prefer it over the impl, resulting in a placeholder error.
projection_bound::<T>();
// error
//
// Trying to normalize the type `for<'a> fn(<T as Trait<'a>>::Assoc)`
// only gets to `<T as Trait<'a>>::Assoc` once `'a` has been already
// instantiated, causing us to prefer the where-bound over the impl
// resulting in a placeholder error. Even if were were to also use the
// leak check during candidate selection for normalization, this
// case would still not compile.
let _higher_ranked_norm: for<'a> fn(<T as Trait<'a>>::Assoc) = |_| ();
}
```
This is also likely to be more performant. It enables more caching in the new trait solver by simply [recursively calling the canonical query][new solver] after instantiating the higher-ranked goal.
It is also unclear how to add the leak check to normalization in the new solver. To handle https://github.com/rust-lang/trait-system-refactor-initiative/issues/1 `Projection` goals are implemented via `AliasRelate`. This again means that we instantiate the binder before ever normalizing any alias. Even if we were to avoid this, we lose the ability to [cache normalization by itself, ignoring the expected `term`](5bd5d214ef/compiler/rustc_trait_selection/src/solve/normalizes_to/mod.rs (L34-L49)). We cannot replace the `term` with an inference variable before instantiating the binder, as otherwise `for<'a> T: Trait<Assoc<'a> = &'a ()>` breaks. If we only replace the term after instantiating the binder, we cannot easily evaluate the goal in a separate context, as [we'd then lose the information necessary for the leak check](11f32b73e0/compiler/rustc_next_trait_solver/src/canonicalizer.rs (L230-L232)). Adding this information to the canonical input also seems non-trivial.
## Proposed solution
I propose to instantiate the binder outside of candidate assembly, causing placeholders from higher-ranked goals to get ignored while selecting their candidate. This mostly[^1] matches the [current behavior of the new solver][new solver]. The impact of this change is therefore as follows:
```rust
trait Leak<'a> {}
impl Leak<'_> for Box<u32> {}
impl Leak<'static> for Box<u16> {}
fn impls_leak<T: for<'a> Leak<'a>>() {}
trait IndirectLeak<'a> {}
impl<'a, T: Leak<'a>> IndirectLeak<'a> for T {}
fn impls_indirect_leak<T: for<'a> IndirectLeak<'a>>() {}
fn guide_selection() {
// ok -> ambiguous
impls_leak::<Box<_>>();
// ambiguous
impls_indirect_leak::<Box<_>>();
}
trait Trait<'a> {
type Assoc;
}
impl<'a, T> Trait<'a> for T {
type Assoc = usize;
}
fn trait_bound<T: for<'a> Trait<'a>>() {}
fn projection_bound<T: for<'a> Trait<'a, Assoc = usize>>() {}
// A function which a trivial where-bound which is more
// restrictive than the impl.
fn function<T: Trait<'static, Assoc = usize>>() {
// ok -> error
trait_bound::<T>();
// error
projection_bound::<T>();
// error
let _higher_ranked_norm: for<'a> fn(<T as Trait<'a>>::Assoc) = |_| ();
}
```
This does not change the behavior if candidates have higher ranked nested goals, as in this case the `leak_check` causes the nested goal to result in an error ([playground](https://play.rust-lang.org/?version=stable&mode=debug&edition=2021&gist=a74c25300b23db9022226de99d8a2fa6)):
```rust
trait LeakCheckFailure<'a> {}
impl LeakCheckFailure<'static> for () {}
trait Trait<T> {}
impl Trait<u32> for () where for<'a> (): LeakCheckFailure<'a> {}
impl Trait<u16> for () {}
fn impls_trait<T: Trait<U>, U>() {}
fn main() {
// ok
//
// It does not matter whether candidate assembly
// considers the placeholders from higher-ranked goal.
//
// Either `for<'a> (): LeakCheckFailure<'a>` has no
// applicable candidate or it has a single applicable candidate
// when then later results in an error. This allows us to
// infer `U` to `u16`.
impls_trait::<(), _>()
}
```
## Impact on existing crates
This is a **breaking change**. [A crater run](https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/119820#issuecomment-1926862174) found 17 regressed crates with 7 root causes.
For a full analysis of all affected crates, see https://gist.github.com/lcnr/7c1c652f30567048ea240554a36ed95c.
---
I believe this breakage to be acceptable and would merge this change. I am confident that the new position of the leak check matches our idealized future and cannot envision any other consistent alternative. Where possible, I intend to open PRs fixing/avoiding the regressions before landing this PR.
I originally intended to remove the `coherence_leak_check` lint in the same PR. However, while I am confident in the *position* of the leak check, deciding on its exact behavior is left as future work, cc #112999. This PR therefore only moves the leak check while keeping the lint when relying on it in coherence.
[new solver]: https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/blob/master/compiler/rustc_trait_selection/src/solve/eval_ctxt/mod.rs#L479-L484
[^1]: the new solver has a separate cause of inconsistent behavior rn https://github.com/rust-lang/trait-system-refactor-initiative/issues/53#issuecomment-1914310171
r? `@nikomatsakis`
Check `x86_64` size assertions on `aarch64`, too
(Context: https://rust-lang.zulipchat.com/#narrow/stream/131828-t-compiler/topic/Checking.20size.20assertions.20on.20aarch64.3F)
Currently the compiler has around 30 sets of `static_assert_size!` for various size-critical data structures (e.g. various IR nodes), guarded by `#[cfg(all(target_arch = "x86_64", target_pointer_width = "64"))]`.
(Presumably this cfg avoids having to maintain separate size values for 32-bit targets and unusual 64-bit targets. Apparently it may have been necessary before the i128/u128 alignment changes, too.)
This is slightly incovenient for people on aarch64 workstations (e.g. Macs), because the assertions normally aren't checked until we push to a PR. So this PR adds `aarch64` to the `#[cfg(..)]` guarding all of those assertions in the compiler.
---
Implemented with a simple find/replace. Verified by manually inspecting each `static_assert_size!` in `compiler/`, and checking that either the replacement succeeded, or adding aarch64 wouldn't have been appropriate.
Assert that args are actually compatible with their generics, rather than just their count
Right now we just check that the number of args is right, rather than actually checking the kinds. Uplift a helper fn that I wrote from trait selection to do just that. Found a couple bugs along the way.
r? `@lcnr` or `@fmease` (or anyone really lol)
More postfix match fixes
These affect diagnostics only, as far as I can tell. I'm too lazy to come up with UI tests, but I could be convinced otherwise.
Specifically, I think changing the precedence computation actually doesn't change anything, but tweaking `contains_exterior_struct_lit` does mean that some diagnostics will begin parenthesizing `S {}.match {}`.
pattern analysis: fix union handling
Little known fact: rust supports union patterns. Exhaustiveness handles them soundly but reports nonsensical missing patterns. This PR fixes the reported patterns and documents what we're doing.
r? `@compiler-errors`
Rename `expose_addr` to `expose_provenance`
`expose_addr` is a bad name, an address is just a number and cannot be exposed. The operation is actually about the provenance of the pointer.
This PR thus changes the name of the method to `expose_provenance` without changing its return type. There is sufficient precedence for returning a useful value from an operation that does something else without the name indicating such, e.g. [`Option::insert`](https://doc.rust-lang.org/nightly/std/option/enum.Option.html#method.insert) and [`MaybeUninit::write`](https://doc.rust-lang.org/nightly/std/mem/union.MaybeUninit.html#method.write).
Returning the address is merely convenient, not a fundamental part of the operation. This is implied by the fact that integers do not have provenance since
```rust
let addr = ptr.addr();
ptr.expose_provenance();
let new = ptr::with_exposed_provenance(addr);
```
must behave exactly like
```rust
let addr = ptr.expose_provenance();
let new = ptr::with_exposed_provenance(addr);
```
as the result of `ptr.expose_provenance()` and `ptr.addr()` is the same integer. Therefore, this PR removes the `#[must_use]` annotation on the function and updates the documentation to reflect the important part.
~~An alternative name would be `expose_provenance`. I'm not at all opposed to that, but it makes a stronger implication than we might want that the provenance of the pointer returned by `ptr::with_exposed_provenance`[^1] is the same as that what was exposed, which is not yet specified as such IIUC. IMHO `expose` does not make that connection.~~
A previous version of this PR suggested `expose` as name, libs-api [decided on](https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/122964#issuecomment-2033194319) `expose_provenance` to keep the symmetry with `with_exposed_provenance`.
CC `@RalfJung`
r? libs-api
[^1]: I'm using the new name for `from_exposed_addr` suggested by #122935 here.
Better reporting on generic argument mismatchs
This allows better reporting as per issue #116615 .
If you have a function:
```
fn foo(a: T, b: T) {}
```
and call it like so:
```
foo(1, 2.)
```
it'll give improved error reported similar to the following:
```
error[E0308]: mismatched types
--> generic-mismatch-reporting-issue-116615.rs:6:12
|
6 | foo(1, 2.);
| --- - ^^ expected integer, found floating-point number
| | |
| | expected argument `b` to be an integer because that argument needs to match the type of this parameter
| arguments to this function are incorrect
|
note: function defined here
--> generic-mismatch-reporting-issue-116615.rs:1:4
|
1 | fn foo<T>(a: T, b: T) {}
| ^^^ - ---- ----
| | | |
| | | this parameter needs to match the integer type of `a`
| | `b` needs to match the type of this parameter
| `a` and `b` all reference this parameter T
```
Open question, do we need to worry about error message translation into other languages? Not sure what the status of that is in Rust.
NB: Needs some checking over and some tests have altered that need sanity checking, but overall this is starting to get somewhere now. Will take out of draft PR status when this has been done, raising now to allow feedback at this stage, probably 90% ready.
Assert `FnDef` kind
Only found one bug, where we were using the variant def id rather than its ctor def id to make the `FnDef` for a `type_of`
r? fmease
Remove MIR unsafe check
Now that THIR unsafeck is enabled by default in stable I think we can remove MIR unsafeck entirely. This PR also removes safety information from MIR.
Rollup of 4 pull requests
Successful merges:
- #122411 ( Provide cabi_realloc on wasm32-wasip2 by default )
- #123349 (Fix capture analysis for by-move closure bodies)
- #123359 (Link against libc++abi and libunwind as well when building LLVM wrappers on AIX)
- #123388 (use a consistent style for links)
r? `@ghost`
`@rustbot` modify labels: rollup
Link against libc++abi and libunwind as well when building LLVM wrappers on AIX
Unlike `libc++.so` on Linux which is a linker script
```ld
INPUT(libc++.so.1 -lc++abi -lunwind)
```
AIX linker doesn't support such script, so `c++abi` and `unwind` have to be specified explicitly.
Fix capture analysis for by-move closure bodies
The check we were doing to figure out if a coroutine was borrowing from its parent coroutine-closure was flat-out wrong -- a misunderstanding of mine of the way that `tcx.closure_captures` represents its captures.
Fixes#123251 (the miri/ui test I added should more than cover that issue)
r? `@oli-obk` -- I recognize that this PR may be underdocumented, so please ask me what I should explain further.
Rename `UninhabitedEnumBranching` to `UnreachableEnumBranching`
Per [#120268](https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/120268#discussion_r1517492060), I rename `UninhabitedEnumBranching` to `UnreachableEnumBranching` .
I solved some nits to add some comments.
I adjusted the workaround restrictions. This should be useful for `a <= b` and `if let Some/Ok(v)`. For enum with few variants, `early-tailduplication` should not cause compile time overhead.
r? RalfJung
Avoid expanding to unstable internal method
Fixes#123156
Rather than expanding to `std::rt::begin_panic`, the expansion is now to `unreachable!()`. The resulting behavior is identical. A test that previously triggered the same error as #123156 has been added to ensure it does not regress.
r? compiler
rename ptr::from_exposed_addr -> ptr::with_exposed_provenance
As discussed on [Zulip](https://rust-lang.zulipchat.com/#narrow/stream/136281-t-opsem/topic/To.20expose.20or.20not.20to.20expose/near/427757066).
The old name, `from_exposed_addr`, makes little sense as it's not the address that is exposed, it's the provenance. (`ptr.expose_addr()` stays unchanged as we haven't found a better option yet. The intended interpretation is "expose the provenance and return the address".)
The new name nicely matches `ptr::without_provenance`.
Make inductive cycles always ambiguous
This makes inductive cycles always result in ambiguity rather than be treated like a stack-dependent error.
This has some interactions with specialization, and so breaks a few UI tests that I don't agree should've ever worked in the first place, and also breaks a handful of crates in a way that I don't believe is a problem.
On the bright side, it puts us in a better spot when it comes to eventually enabling coinduction everywhere.
## Results
This was cratered in https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/116494#issuecomment-2008657494, which boils down to two regressions:
* `lu_packets` - This code should have never compiled in the first place. More below.
* **ALL** other regressions are due to `commit_verify@0.11.0-beta.1` (edit: and `commit_verify@0.10.x`) - This actually seems to be fixed in version `0.11.0-beta.5`, which is the *most* up to date version, but it's still prerelease on crates.io so I don't think cargo ends up picking `beta.5` when building dependent crates.
### `lu_packets`
Firstly, this crate uses specialization, so I think it's automatically worth breaking. However, I've minimized [the regression](https://crater-reports.s3.amazonaws.com/pr-116494-3/try%23d614ed876e31a5f3ad1d0fbf848fcdab3a29d1d8/gh/lcdr.lu_packets/log.txt) to:
```rust
// Upstream crate
pub trait Serialize {}
impl Serialize for &() {}
impl<S> Serialize for &[S] where for<'a> &'a S: Serialize {}
// ----------------------------------------------------------------------- //
// Downstream crate
#![feature(specialization)]
#![allow(incomplete_features, unused)]
use upstream::Serialize;
trait Replica {
fn serialize();
}
impl<T> Replica for T {
default fn serialize() {}
}
impl<T> Replica for Option<T>
where
for<'a> &'a T: Serialize,
{
fn serialize() {}
}
```
Specifically this fails when computing the specialization graph for the `downstream` crate.
The code ends up cycling on `&[?0]: Serialize` when we equate `&?0 = &[?1]` during impl matching, which ends up needing to prove `&[?1]: Serialize`, which since cycles are treated like ambiguity, ends up in a **fatal overflow**. For some reason this requires two crates, squashing them into one crate doesn't work.
Side-note: This code is subtly order dependent. When minimizing, I ended up having the code start failing on `nightly` very easily after removing and reordering impls. This seems to me all the more reason to remove this behavior altogether.
## Side-note: Item Bounds (edit: this was fixed independently in #121123)
Due to the changes in #120584 where we now consider an alias's item bounds *and* all the item bounds of the alias's nested self type aliases, I've had to add e6b64c6194 which is a hack to make sure we're not eagerly normalizing bounds that have nothing to do with the predicate we're trying to solve, and which result in.
This is fixed in a more principled way in #121123.
---
r? lcnr for an initial review
CFI: Support non-general coroutines
Previously, we assumed all `ty::Coroutine` were general coroutines and attempted to generalize them through the `Coroutine` trait. Select appropriate traits for each kind of coroutine.
I have this marked as a draft because it currently only fixes async coroutines, and I think it make sense to try to fix gen/async gen coroutines before this is merged.
If the issue [mentioned](https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/123106#issuecomment-2030794213) in the original PR is actually affecting someone, we can land this as is to remedy it.
Check that nested statics in thread locals are duplicated per thread.
follow-up to #123310
cc ``@compiler-errors`` ``@RalfJung``
fwiw: I have no idea how thread local statics make that work under LLVM, and miri fails on this example, which I would have expected to be the correct behaviour.
Since the `#[thread_local]` attribute is just an internal implementation detail, I'm just going to start hard erroring on nested mutable statics in thread locals.
Make sure to insert `Sized` bound first into clauses list
#120323 made it so that we don't insert an implicit `Sized` bound whenever we see an *explicit* `Sized` bound. However, since the code that inserts implicit sized bounds puts the bound as the *first* in the list, that means that it had the **side-effect** of possibly meaning we check `Sized` *after* checking other trait bounds.
If those trait bounds result in ambiguity or overflow or something, it may change how we winnow candidates. (**edit: SEE** #123303) This is likely the cause for the regression in https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/123279#issuecomment-2028899598, since the impl...
```rust
impl<T: Job + Sized> AsJob for T { // <----- changing this to `Sized + Job` or just `Job` (which turns into `Sized + Job`) will FIX the issue.
}
```
...looks incredibly suspicious.
Fixes [after beta-backport] #123279.
Alternative is to revert #120323. I don't have a strong opinion about this, but think it may be nice to keep the diagnostic changes around.
De-LLVM the unchecked shifts [MCP#693]
This is just one part of the MCP (https://github.com/rust-lang/compiler-team/issues/693), but it's the one that IMHO removes the most noise from the standard library code.
Seems net simpler this way, since MIR already supported heterogeneous shifts anyway, and thus it's not more work for backends than before.
r? WaffleLapkin
Add `Ord::cmp` for primitives as a `BinOp` in MIR
Update: most of this OP was written months ago. See https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/118310#issuecomment-2016940014 below for where we got to recently that made it ready for review.
---
There are dozens of reasonable ways to implement `Ord::cmp` for integers using comparison, bit-ops, and branches. Those differences are irrelevant at the rust level, however, so we can make things better by adding `BinOp::Cmp` at the MIR level:
1. Exactly how to implement it is left up to the backends, so LLVM can use whatever pattern its optimizer best recognizes and cranelift can use whichever pattern codegens the fastest.
2. By not inlining those details for every use of `cmp`, we drastically reduce the amount of MIR generated for `derive`d `PartialOrd`, while also making it more amenable to MIR-level optimizations.
Having extremely careful `if` ordering to μoptimize resource usage on broadwell (#63767) is great, but it really feels to me like libcore is the wrong place to put that logic. Similarly, using subtraction [tricks](https://graphics.stanford.edu/~seander/bithacks.html#CopyIntegerSign) (#105840) is arguably even nicer, but depends on the optimizer understanding it (https://github.com/llvm/llvm-project/issues/73417) to be practical. Or maybe [bitor is better than add](https://discourse.llvm.org/t/representing-in-ir/67369/2?u=scottmcm)? But maybe only on a future version that [has `or disjoint` support](https://discourse.llvm.org/t/rfc-add-or-disjoint-flag/75036?u=scottmcm)? And just because one of those forms happens to be good for LLVM, there's no guarantee that it'd be the same form that GCC or Cranelift would rather see -- especially given their very different optimizers. Not to mention that if LLVM gets a spaceship intrinsic -- [which it should](https://rust-lang.zulipchat.com/#narrow/stream/131828-t-compiler/topic/Suboptimal.20inlining.20in.20std.20function.20.60binary_search.60/near/404250586) -- we'll need at least a rustc intrinsic to be able to call it.
As for simplifying it in Rust, we now regularly inline `{integer}::partial_cmp`, but it's quite a large amount of IR. The best way to see that is with 8811efa88b (diff-d134c32d028fbe2bf835fef2df9aca9d13332dd82284ff21ee7ebf717bfa4765R113) -- I added a new pre-codegen MIR test for a simple 3-tuple struct, and this PR change it from 36 locals and 26 basic blocks down to 24 locals and 8 basic blocks. Even better, as soon as the construct-`Some`-then-match-it-in-same-BB noise is cleaned up, this'll expose the `Cmp == 0` branches clearly in MIR, so that an InstCombine (#105808) can simplify that to just a `BinOp::Eq` and thus fix some of our generated code perf issues. (Tracking that through today's `if a < b { Less } else if a == b { Equal } else { Greater }` would be *much* harder.)
---
r? `@ghost`
But first I should check that perf is ok with this
~~...and my true nemesis, tidy.~~
Adds support for both CFI and KCFI for attaching concrete and abstract
types to functions. KCFI does this through generation of `ReifyShim` on
any function pointer that could go in a vtable, and checking the
`ReifyReason` when emitting the instance. CFI does this by attaching
both the concrete and abstract type to every instance.
TypeID codegen tests are switched to be anchored on the left rather than
the right in order to allow emission of additional type attachments.
Fixes#115953
KCFI needs to be able to tell which kind of `ReifyShim` it is examining
in order to decide whether to use a concrete type (`FnPtr` case) or an
abstract case (`Vtable` case). You can *almost* tell this from context,
but there is one case where you can't - if a trait has a method which is
*not* `#[track_caller]`, with an impl that *is* `#[track_caller]`, both
the vtable and a function pointer created from that method will be
`ReifyShim(def_id)`.
Currently, the reason is optional to ensure no additional unique
`ReifyShim`s are added without KCFI on. However, the case in which an
extra `ReifyShim` is created is sufficiently rare that this may be worth
revisiting to reduce complexity.
Previously, we assumed all `ty::Coroutine` were general coroutines and
attempted to generalize them through the `Coroutine` trait. Select
appropriate traits for each kind of coroutine.
rustdoc: heavily simplify the synthesis of auto trait impls
`gd --numstat HEAD~2 HEAD src/librustdoc/clean/auto_trait.rs`
**+315 -705** 🟩🟥🟥🟥⬛
---
As outlined in issue #113015, there are currently 3[^1] large separate routines that “clean” `rustc_middle::ty` data types related to generics & predicates to rustdoc data types. Every single one has their own kinds of bugs. While I've patched a lot of bugs in each of the routines in the past, it's about time to unify them. This PR is only the first in a series. It completely **yanks** the custom “bounds cleaning” of mod `auto_trait` and reuses the routines found in mod `simplify`. As alluded to, `simplify` is also flawed but it's still more complete than `auto_trait`'s routines. [See also my review comment over at `tests/rustdoc/synthetic_auto/bounds.rs`](https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/123340#discussion_r1546900539).
This is preparatory work for rewriting “bounds cleaning” from scratch in follow-up PRs in order to finally [fix] #113015.
Apart from that, I've eliminated all potential sources of *instability* in the rendered output.
See also #119597. I'm pretty sure this fixes#119597.
This PR does not attempt to fix [any other issues related to synthetic auto trait impls](https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues?q=is%3Aissue+is%3Aopen+label%3AA-synthetic-impls%20label%3AA-auto-traits).
However, it's definitely meant to be a *stepping stone* by making `auto_trait` more contributor-friendly.
---
* Replace `FxHash{Map,Set}` with `FxIndex{Map,Set}` to guarantee a stable iteration order
* Or as a perf opt, `UnordSet` (a thin wrapper around `FxHashSet`) in cases where we never iterate over the set.
* Yes, we do make use of `swap_remove` but that shouldn't matter since all the callers are deterministic. It does make the output less “predictable” but it's still better than before. Ofc, I rely on `rustc_infer` being deterministic. I hope that holds.
* Utilizing `clean::simplify` over the custom “bounds cleaning” routines wipes out the last reference to `collect_referenced_late_bound_regions` in rustdoc (`simplify` uses `bound_vars`) which was a source of instability / unpredictability (cc #116388)
* Remove the types `RegionTarget` and `RegionDeps` from `librustdoc`. They were duplicates of the identical types found in `rustc`. Just import them from `rustc`. For some reason, they were duplicated when splitting `auto_trait` in two in #49711.
* Get rid of the useless “type namespace” `AutoTraitFinder` in `librustdoc`
* The struct only held a `DocContext`, it was over-engineered
* Turn the associated functions into free ones
* Eliminates rightward drift; increases legibility
* `rustc` also contains a useless `AutoTraitFinder` struct but I plan on removing that in a follow-up PR
* Rename a bunch of methods to be way more descriptive
* Eliminate `use super::*;`
* Lead to `clean/mod.rs` accumulating a lot of unnecessary imports
* Made `auto_traits` less modular
* Eliminate a custom `TypeFolder`: We can just use the rustc helper `fold_regions` which does that for us
I plan on adding extensive documentation to `librustdoc`'s `auto_trait` in follow-up PRs.
I don't want to do that in this PR because further refactoring & bug fix PRs may alter the overall structure of `librustdoc`'s & `rustc`'s `auto_trait` modules to a great degree. I'm slowly digging into the dark details of `rustc`'s `auto_trait` module again and once I have the full picture I will be able to provide proper docs.
---
While this PR does indeed touch `rustc`'s `auto_trait` — mostly tiny refactorings — I argue this PR doesn't need any compiler reviewers next to rustdoc ones since that module falls under the purview of rustdoc — it used to be part of `librustdoc` after all (#49711).
Sorry for not having split this into more commits. If you'd like me to I can try to split it into more atomic commits retroactively. However, I don't know if that would actually make reviewing easier. I think the best way to review this might just be to place the master version of `auto_trait` on the left of your screen and the patched one on the right, not joking.
r? `@GuillaumeGomez`
[^1]: Or even 4 depending on the way you're counting.
Only allow compiler_builtins to call LLVM intrinsics, not any link_name function
This is another case of accidental reliance on `inline(never)` like I rooted out in https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/118770. Without this PR, attempting to build some large programs with `-Zcross-crate-inline-threshold=yes` with a sysroot also compiled with that flag will result in linker errors like this:
```
= note: /usr/bin/ld: /tmp/cargo-installNrfN4T/x86_64-unknown-linux-gnu/release/deps/libcompiler_builtins-d2a9b69f4e45b883.rlib(compiler_builtins-d2a9b69f4e45b883.compiler_builtins.dbbc6c2ca970faa4-cgu.0.rcgu.o): in function `core::panicking::panic_fmt':
/home/ben/.rustup/toolchains/nightly-x86_64-unknown-linux-gnu/lib/rustlib/src/rust/library/core/src/panicking.rs:72:(.text.unlikely._ZN4core9panicking9panic_fmt17ha407cc99e97c942fE+0x31): undefined reference to `rust_begin_unwind'
```
With `-Zcross-crate-inline-threshold=yes` we can inline `panic_fmt` into `compiler_builtins`. Then we end up with a call to an upstream monomorphization, but one that has a `link_name` set. But unlike LLVM's magic intrinsic names, this link name is going to make it to the linker, and then we have a problem.
This logic looks scuffed, but also we're doing this in 4 other places. Don't know if that means it's good or bad.
1684a753db/compiler/rustc_codegen_cranelift/src/abi/mod.rs (L386)1684a753db/compiler/rustc_ast_passes/src/feature_gate.rs (L306)1684a753db/compiler/rustc_codegen_ssa/src/codegen_attrs.rs (L609)1684a753db/compiler/rustc_codegen_gcc/src/declare.rs (L170)
Update `ParamEnv` docs
There is now a wealth of information in the dev guide about `ParamEnv` so we should explicitly link to it from the doc comments. I also added a caution against using `ParamEnv` and removed the comment about it being "suitable for type checking" as you should practically never use `ParamEnv::empty` for type checking
r? `@compiler-errors`
match lowering: handle or-patterns one layer at a time
`create_or_subcandidates` and `merge_trivial_subcandidates` both call themselves recursively to handle nested or-patterns, which is hard to follow. In this PR I avoid the need for that; we now process a single "layer" of or-patterns at a time.
By calling back into `match_candidates`, we only need to expand one layer at a time. Conversely, since we always try to simplify a layer that we just expanded (thanks to https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/123067), we only have to merge one layer at a time.
r? `@matthewjasper`
Don't inherit codegen attrs from parent static
Putting this up partly for discussion and partly for review. Specifically, in #121644, `@oli-obk` designed a system that creates new static items for representing nested allocations in statics. However, in that PR, oli made it so that these statics inherited the codegen attrs from the parent.
This causes problems such as colliding symbols with `#[export_name]` and ICEs with `#[no_mangle]` since these synthetic statics have no `tcx.item_name(..)`.
So the question is, is there any case where we *do* want to inherit codegen attrs from the parent? The only one that seems a bit suspicious is the thread-local attribute. And there may be some interesting interactions with the coverage attributes as well...
Fixes (after backport) #123274. Fixes#123243. cc #121644.
r? `@oli-obk` cc `@nnethercote` `@RalfJung` (reviewers on that pr)
Fix error message for `env!` when env var is not valid Unicode
Currently (without this PR) the `env!` macro emits an ```environment variable `name` not defined at compile time``` error when the environment variable is defined, but not a valid Unicode string. This PR introduces a separate more accurate error message, and a test to verify this behaviour.
For reference, before this PR, the new test would have outputted:
```
error: environment variable `NON_UNICODE_VAR` not defined at compile time
--> non_unicode_env.rs:2:13
|
2 | let _ = env!("NON_UNICODE_VAR");
| ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
|
= help: use `std::env::var("NON_UNICODE_VAR")` to read the variable at run time
= note: this error originates in the macro `env` (in Nightly builds, run with -Z macro-backtrace for more info)
error: aborting due to 1 previous error
```
whereas with this PR, the test ouputs:
```
error: environment variable `NON_UNICODE_VAR` is not a valid Unicode string
--> non_unicode_env.rs:2:13
|
2 | let _ = env!("NON_UNICODE_VAR");
| ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
|
= note: this error originates in the macro `env` (in Nightly builds, run with -Z macro-backtrace for more info)
error: aborting due to 1 previous error
```
Use the `Align` type when parsing alignment attributes
Use the `Align` type in `rustc_attr::parse_alignment`, removing the need to call `Align::from_bytes(...).unwrap()` later in the compilation process.
pattern analysis: Require enum indices to be contiguous
We had a cfg-hack to allow rust-analyzer to use non-contiguous indices for its enum variants. Unfortunately this no longer works if r-a uses the in-tree version of the crate.
This PR removes the hack, and on the r-a side we'll have to use contiguous indices but that's not too hard.
r? `@compiler-errors`
Stop calling visitors `V`
Renames some visitors which currently have the unhelpful name of `V`. It's not self-documenting, and there is no situation where saving a few bytes in source code helps anyone.
Stacked on top of #123202 due to conflict.
match lowering: sort `Eq` candidates in the failure case too
This is a slight tweak to MIR gen of matches. Take a match like:
```rust
match (s, flag) {
("a", _) if foo() => 1,
("b", true) => 2,
("a", false) => 3,
(_, true) => 4,
_ => 5,
}
```
If we switch on `s == "a"`, the first candidate matches, and we learn almost nothing about the second candidate. So there's a choice:
1. (what we do today) stop sorting candidates, keep the "b" case grouped with everything below. This could allow us to be clever here and test on `flag == true` next.
2. (what this PR does) sort "b" into the failure case. The "b" will be alone (fewer opportunities for picking a good test), but that means the two "a" cases require a single test.
Today, we aren't clever in which tests we pick, so this is an unambiguous win. In a future where we pick tests better, idk. Grouping tests as much as possible feels like a generally good strategy.
This was proposed in https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/29623 (9 years ago :D)
The original proposal allows reference patterns
with "compatible" mutability, however it's not clear
what that means so for now we require an exact match.
I don't know the type system code well, so if something
seems to not make sense it's probably because I made a
mistake
CFI: Abstract Closures and Coroutines
This will abstract coroutines in a moment, it's just abstracting closures for now to show `@rcvalle`
This uses the same principal as the methods on traits - figure out the `dyn` type representing the fn trait, instantiate it, and attach that alias set. We're essentially just computing how we would be called in a dynamic context, and attaching that.
Similar to methods on a trait object, the most common way to indirectly
call a closure or coroutine is through the vtable on the appropriate
trait. This uses the same approach as we use for trait methods, after
backing out the trait arguments from the type.
Add support for `NonNull`s in the `ambiguous_wide_ptr_comparisions` lint
This PR add support for `NonNull` pointers in the `ambiguous_wide_ptr_comparisions` lint.
Fixes https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/121264
r? `@Nadrieril` (since you just reviewed #121268, feel free to reassign)
KCFI: Require -C panic=abort
While the KCFI scheme is not incompatible with unwinding, LLVM's `invoke` instruction does not currently support KCFI bundles. While it likely will in the near future, we won't be able to assume that in Rust for a while.
We encountered this problem while [turning on closure support](https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/123106#issuecomment-2027436640).
r? ``@workingjubilee``
Replace regions in const canonical vars' types with `'static` in next-solver canonicalizer
We shouldn't ever have non-static regions in consts on stable (or really any regions at all, lol).
The test I committed is less minimal than, e.g., https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/123155?notification_referrer_id=NT_kwDOADgQyrMxMDAzNDU4MDI0OTozNjc0MzE0#issuecomment-2025472029 -- however, I believe that it actually portrays the underlying issue here a bit better than that one.
In the linked issue, we end up emitting a normalizes-to predicate for a const placeholder because we don't actually unify `false` and `""`. In the test I committed, we emit a normalizes-to predicate as a part of actually solving a negative coherence goal.
Fixes#123155Fixes#118783
r? lcnr
This is just one part of the MCP, but it's the one that IMHO removes the most noise from the standard library code.
Seems net simpler this way, since MIR already supported heterogeneous shifts anyway, and thus it's not more work for backends than before.
CFI: Support calling methods on supertraits
Automatically adjust `Virtual` calls to supertrait functions to use the supertrait's trait object type as the receiver rather than the child trait.
cc `@compiler-errors` - this is the next usage of `trait_object_ty` I intend to have, so I thought it might be relevant while reviewing the existing one.
Add detection of [Partial]Ord methods in the `ambiguous_wide_pointer_comparisons` lint
Partially addresses https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/121264 by adding diagnostics items for PartialOrd and Ord methods, detecting such diagnostics items as "binary operation" and suggesting the correct replacement.
I also took the opportunity to change the suggestion to use new methods `.cast()` on `*mut T` an d `*const T`.
While the KCFI scheme is not incompatible with unwinding, LLVM's
`invoke` instruction does not currently support KCFI bundles. While it
likely will in the near future, we won't be able to assume that in Rust
for a while.
Rollup of 4 pull requests
Successful merges:
- #123176 (Normalize the result of `Fields::ty_with_args`)
- #123186 (copy any file from stage0/lib to stage0-sysroot/lib)
- #123187 (Forward port 1.77.1 release notes)
- #123188 (compiler: fix few unused_peekable and needless_pass_by_ref_mut clippy lints)
r? `@ghost`
`@rustbot` modify labels: rollup