Remove edition umbrella features.
In the 2018 edition, there was an "umbrella" feature `#[feature(rust_2018_preview)]` which was used to enable several other features at once. This umbrella mechanism was not used in the 2021 edition and likely will not be used in 2024 either. During 2018 users reported that setting the feature was awkward, especially since they already needed to opt-in via the edition mechanism.
This PR removes this mechanism because I believe it will not be used (and will clean up and simplify the code). I believe that there are better ways to handle features and editions. In short:
- For highly experimental features, that may or may not be involved in an edition, they can implement regular feature gates like `tcx.features().my_feature`.
- For experimental features that *might* be involved in an edition, they should implement gates with `tcx.features().my_feature && span.at_least_rust_20xx()`. This requires the user to still specify `#![feature(my_feature)]`, to avoid disrupting testing of other edition features which are ready and have been accepted within the edition.
- For experimental features that have graduated to definitely be part of an edition, they should implement gates with `tcx.features().my_feature || span.at_least_rust_20xx()`, or just remove the feature check altogether and just check `span.at_least_rust_20xx()`.
- For relatively simple changes, they can skip the whole feature gating thing and just check `span.at_least_rust_20xx()`, and rely on the instability of the edition itself (which requires `-Zunstable-options`) to gate it.
I am working on documenting all of this in the rustc-dev-guide.
Implement repr(packed) for repr(simd)
This allows creating vectors with non-power-of-2 lengths that do not have padding. See rust-lang/portable-simd#319
Rearrange `default_configuration` and `CheckCfg::fill_well_known`.
There are comments saying these two functions should be kept in sync, but they have very different structures, process symbols in different orders, and there are some inconsistencies.
This commit reorders them so they're both mostly processing symbols in alphabetical order, which makes cross-checking them a lot easier. The commit also adds some macros to factor out repetitive code patterns.
The commit also moves the handling of `sym::test` out of `build_configuration` into `default_configuration`, where all the other symbols are handled.
r? `@bjorn3`
guarantee that char and u32 are ABI-compatible
In https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/116894 we added a guarantee that `char` has the same alignment as `u32`, but there is still one axis where these types could differ: function call ABI. So let's nail that down as well: in a function signature, `char` and `u32` are completely equivalent.
This is a new stable guarantee, so it will need t-lang approval.
There are comments saying these two functions should be kept in sync,
but they have very different structures, process symbols in different
orders, and there are some inconsistencies.
This commit reorders them so they're both mostly processing symbols in
alphabetical order, which makes cross-checking them a lot easier. The
commit also adds some macros to factor out repetitive code patterns.
Plus it adds `sanitizer_cfi_normalize_{integers,pointers}` to
`fill_well_known`, which were missing.
The commit also moves the handling of `sym::test` out of
`build_configuration` into `default_configuration`, where all the other
symbols are handled.
This is an extension of the previous commit. It means the output of
something like this:
```
stringify!(let a: Vec<u32> = vec![];)
```
goes from this:
```
let a: Vec<u32> = vec![] ;
```
With this PR, it now produces this string:
```
let a: Vec<u32> = vec![];
```
`tokenstream::Spacing` appears on all `TokenTree::Token` instances,
both punct and non-punct. Its current usage:
- `Joint` means "can join with the next token *and* that token is a
punct".
- `Alone` means "cannot join with the next token *or* can join with the
next token but that token is not a punct".
The fact that `Alone` is used for two different cases is awkward.
This commit augments `tokenstream::Spacing` with a new variant
`JointHidden`, resulting in:
- `Joint` means "can join with the next token *and* that token is a
punct".
- `JointHidden` means "can join with the next token *and* that token is a
not a punct".
- `Alone` means "cannot join with the next token".
This *drastically* improves the output of `print_tts`. For example,
this:
```
stringify!(let a: Vec<u32> = vec![];)
```
currently produces this string:
```
let a : Vec < u32 > = vec! [] ;
```
With this PR, it now produces this string:
```
let a: Vec<u32> = vec![] ;
```
(The space after the `]` is because `TokenTree::Delimited` currently
doesn't have spacing information. The subsequent commit fixes this.)
The new `print_tts` doesn't replicate original code perfectly. E.g.
multiple space characters will be condensed into a single space
character. But it's much improved.
`print_tts` still produces the old, uglier output for code produced by
proc macros. Because we have to translate the generated code from
`proc_macro::Spacing` to the more expressive `token::Spacing`, which
results in too much `proc_macro::Along` usage and no
`proc_macro::JointHidden` usage. So `space_between` still exists and
is used by `print_tts` in conjunction with the `Spacing` field.
This change will also help with the removal of `Token::Interpolated`.
Currently interpolated tokens are pretty-printed nicely via AST pretty
printing. `Token::Interpolated` removal will mean they get printed with
`print_tts`. Without this change, that would result in much uglier
output for code produced by decl macro expansions. With this change, AST
pretty printing and `print_tts` produce similar results.
The commit also tweaks the comments on `proc_macro::Spacing`. In
particular, it refers to "compound tokens" rather than "multi-char
operators" because lifetimes aren't operators.
Implement `--env` compiler flag (without `tracked_env` support)
Part of https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/80792.
Implementation of https://github.com/rust-lang/compiler-team/issues/653.
Not an implementation of https://github.com/rust-lang/rfcs/pull/2794.
It adds the `--env` compiler flag option which allows to set environment values used by `env!` and `option_env!`.
Important to note: When trying to retrieve an environment variable value, it will first look into the ones defined with `--env`, and if there isn't one, then only it will look into the environment variables. So if you use `--env PATH=a`, then `env!("PATH")` will return `"a"` and not the actual `PATH` value.
As mentioned in the title, `tracked_env` support is not added here. I'll do it in a follow-up PR.
r? rust-lang/compiler
remove redundant imports
detects redundant imports that can be eliminated.
for #117772 :
In order to facilitate review and modification, split the checking code and removing redundant imports code into two PR.
r? `@petrochenkov`
Don't print host effect param in pretty `path_generic_args`
Make `own_args_no_defaults` pass back the `GenericParamDef`, so that we can pass both the args *and* param definitions into `path_generic_args`. That allows us to use the `GenericParamDef` to filter out effect params.
This allows us to filter out the host param regardless of whether it's `sym::host` or `true`/`false`.
This also renames a couple of `const_effect_param` -> `host_effect_param`, and restores `~const` pretty printing to `TraitPredPrintModifiersAndPath`.
cc #118785
r? `@fee1-dead` cc `@oli-obk`
detects redundant imports that can be eliminated.
for #117772 :
In order to facilitate review and modification, split the checking code and
removing redundant imports code into two PR.
Rollup of 5 pull requests
Successful merges:
- #117966 (add safe compilation options)
- #118747 (Remove extra check cfg handled by libc directly)
- #118774 (add test for inductive cycle hangs)
- #118775 (chore: add test case for type with generic)
- #118782 (use `&` instead of start-process in x.ps1)
r? `@ghost`
`@rustbot` modify labels: rollup
Don't warn an empty pattern unreachable if we're not sure the data is valid
Exhaustiveness checking used to be naive about the possibility of a place containing invalid data. This could cause it to emit an "unreachable pattern" lint on an arm that was in fact reachable, as in https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/117119.
This PR fixes that. We now track whether a place that is matched on may hold invalid data. This also forced me to be extra precise about how exhaustiveness manages empty types.
Note that this now errs in the opposite direction: the following arm is truly unreachable (because the binding causes a read of the value) but not linted as such. I'd rather not recommend writing a `match ... {}` that has the implicit side-effect of loading the value. [Never patterns](https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/118155) will solve this cleanly.
```rust
match union.value {
_x => unreachable!(),
}
```
I recommend reviewing commit by commit. I went all-in on the test suite because this went through a lot of iterations and I kept everything. The bit I'm least confident in is `is_known_valid_scrutinee` in `check_match.rs`.
Fixes https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/117119.
add test for inductive cycle hangs
the same pattern is already tested for coinductive cycles, but I now understand the underlying issue and want to make sure we also test it for inductive ones
r? `@compiler-errors`
Strengthen well known check-cfg names and values test
https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/118494 is changing the implementation of how we expect well known check-cfg names and values, but we currently don't have a test that checks every well known only some of them.
This PR therefore strengthen our well known names/values test to include all of the configs to at least avoid unintended regressions and validate new entry.
*this PR also contains some drive-by consolidation of unexpected `target_os`, `target_arch` into a single file*
r? `@nnethercote` (maybe? feel free to re-assign)
Add more SIMD platform-intrinsics
- [x] simd_masked_load
- [x] LLVM codegen - llvm.masked.load
- [x] cranelift codegen - implemented but untested
- [ ] simd_masked_store
- [x] LLVM codegen - llvm.masked.store
- [ ] cranelift codegen
Also added a run-pass test to test both intrinsics, and additional build-fail & check-fail to cover validation for both intrinsics
as they unnecessarily clutter the diagnostic output and make the
experience of adding a new target to the compiler more painful than
it should be.
target_os and target_arch are still being tested in the
well-known-values.rs test, but in one place.
Make async generators fused by default
I actually changed my mind about this since the implementation PR landed. I think it's beneficial for `async gen` blocks to be "fused" by default -- i.e., for them to repeatedly return `Poll::Ready(None)` -- rather than panic.
We have [`FusedStream`](https://docs.rs/futures/latest/futures/stream/trait.FusedStream.html) in futures-rs to represent streams with this capability already anyways.
r? eholk
cc ```@rust-lang/wg-async,``` would like to know if anyone else has opinions about this.
coverage: Simplify the heuristic for ignoring `async fn` return spans
The code for extracting coverage spans from MIR has a special heuristic for dealing with `async fn`, so that the function's closing brace does not have a confusing double count.
The code implementing that heuristic is currently mixed in with the code for flushing remaining spans after the main refinement loop, making the refinement code harder to understand.
We can solve that by hoisting the heuristic to an earlier stage, after the spans have been extracted and sorted but before they have been processed by the refinement loop.
The coverage tests verify that the heuristic is still effective, so coverage mappings/reports for `async fn` have not changed.
---
This PR also has the side-effect of fixing the `None some_prev` panic that started appearing after #118525.
The old code assumed that `prev` would always be present after the refinement loop. That was only true if the list of collected spans was non-empty, but prior to #118525 that didn't seem to come up in practice. After that change, the list of collected spans could be empty in some specific circumstances, leading to panics.
The new code uses an `if let` to inspect `prev`, which correctly does nothing if there is no span present.
update target feature following LLVM API change
LLVM commit e817966718 renamed* the `unaligned-scalar-mem` target feature to `fast-unaligned-access`.
(*) technically the commit folded two previous features into one, but there are no references to the other one in rust.
Add tests related to normalization in implied bounds
Getting ```@aliemjay's``` tests from #109763, so we can better track what's going on in every different example.
r? ```@jackh726```
coverage: Use `SpanMarker` to improve coverage spans for `if !` expressions
Coverage instrumentation works by extracting source code spans from MIR. However, some kinds of syntax are effectively erased during MIR building, so their spans don't necessarily exist anywhere in MIR, making them invisible to the coverage instrumentor (unless we resort to various heuristics and hacks to recover them).
This PR introduces `CoverageKind::SpanMarker`, which is a new variant of `StatementKind::Coverage`. Its sole purpose is to represent spans that would otherwise not appear in MIR, so that the coverage instrumentor can extract them.
When coverage is enabled, the MIR builder can insert these dummy statements as needed, to improve the accuracy of spans used by coverage mappings.
Fixes#115468.
---
```@rustbot``` label +A-code-coverage
temporarily revert "ice on ambguity in mir typeck"
Reverts #116530 as a temporary measure to fix#117577. That issue should be ultimately fixed by checking WF of type annotations prior to normalization, which is implemented in #104098 but this PR is intended to be backported to beta.
r? ``@compiler-errors`` (the reviewer of the reverted PR)
recurse into refs when comparing tys for diagnostics
before:

after:
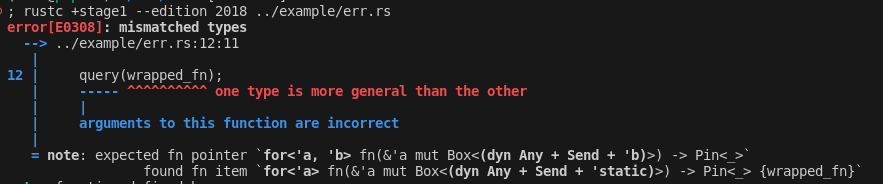
this diff from the test suite is also quite nice imo:
```diff
`@@` -4,8 +4,8 `@@` error[E0308]: mismatched types
LL | debug_assert_eq!(iter.next(), Some(value));
| ^^^^^^^^^^^ expected `Option<<I as Iterator>::Item>`, found `Option<&<I as Iterator>::Item>`
|
- = note: expected enum `Option<<I as Iterator>::Item>`
- found enum `Option<&<I as Iterator>::Item>`
+ = note: expected enum `Option<_>`
+ found enum `Option<&_>`
```
privacy: visit trait def id of projections
Fixes#117997.
A refactoring in #117076 changed the `DefIdVisitorSkeleton` to avoid calling `visit_projection_ty` for `ty::Projection` aliases, and instead just iterate over the args - this makes sense, as `visit_projection_ty` will indirectly visit all of the same args, but in doing so, will also create a `TraitRef` containing the trait's `DefId`, which also gets visited. The trait's `DefId` isn't visited when we only visit the arguments without separating them into `TraitRef` and own args first.
Eventually this influences the reachability set and whether a function is encoded into the metadata.
Add instance evaluation and methods to read an allocation in StableMIR
The instance evaluation is needed to handle intrinsics such as `type_id` and `type_name`.
Since we now use Allocation to represent all evaluated constants, provide a few methods to help process the data inside an allocation.
I've also started to add a structured way to get information about the compilation target machine. For now, I've only added information needed to process an allocation.
r? ``````@ouz-a``````
according to a poll of gay people in my phone, purple is the most popular color to use for highlighting
| color | percentage |
| ---------- | ---------- |
| bold white | 6% |
| blue | 14% |
| cyan | 26% |
| purple | 37% |
| magenta | 17% |
unfortunately, purple is not supported by 16-color terminals, which rustc apparently wants to support for some reason.
until we require support for full 256-color terms (e.g. by doing the same feature detection as we currently do for urls), we can't use it.
instead, i have collapsed the purple votes into magenta on the theory that they're close, and also because magenta is pretty.
Introduce support for `async gen` blocks
I'm delighted to demonstrate that `async gen` block are not very difficult to support. They're simply coroutines that yield `Poll<Option<T>>` and return `()`.
**This PR is WIP and in draft mode for now** -- I'm mostly putting it up to show folks that it's possible. This PR needs a lang-team experiment associated with it or possible an RFC, since I don't think it falls under the jurisdiction of the `gen` RFC that was recently authored by oli (https://github.com/rust-lang/rfcs/pull/3513, https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/117078).
### Technical note on the pre-generator-transform yield type:
The reason that the underlying coroutines yield `Poll<Option<T>>` and not `Poll<T>` (which would make more sense, IMO, for the pre-transformed coroutine), is because the `TransformVisitor` that is used to turn coroutines into built-in state machine functions would have to destructure and reconstruct the latter into the former, which requires at least inserting a new basic block (for a `switchInt` terminator, to match on the `Poll` discriminant).
This does mean that the desugaring (at the `rustc_ast_lowering` level) of `async gen` blocks is a bit more involved. However, since we already need to intercept both `.await` and `yield` operators, I don't consider it much of a technical burden.
r? `@ghost`
never_patterns: Parse match arms with no body
Never patterns are meant to signal unreachable cases, and thus don't take bodies:
```rust
let ptr: *const Option<!> = ...;
match *ptr {
None => { foo(); }
Some(!),
}
```
This PR makes rustc accept the above, and enforces that an arm has a body xor is a never pattern. This affects parsing of match arms even with the feature off, so this is delicate. (Plus this is my first non-trivial change to the parser).
~~The last commit is optional; it introduces a bit of churn to allow the new suggestions to be machine-applicable. There may be a better solution? I'm not sure.~~ EDIT: I removed that commit
r? `@compiler-errors`
A refactoring in #117076 changed the `DefIdVisitorSkeleton` to avoid
calling `visit_projection_ty` for `ty::Projection` aliases, and instead
just iterate over the args - this makes sense, as `visit_projection_ty`
will indirectly visit all of the same args, but in doing so, will also
create a `TraitRef` containing the trait's `DefId`, which also gets
visited. The trait's `DefId` isn't visited when we only visit the
arguments without separating them into `TraitRef` and own args first.
Signed-off-by: David Wood <david@davidtw.co>
When MIR is built for an if-not expression, the `!` part of the condition
doesn't correspond to any MIR statement, so coverage instrumentation normally
can't see it.
We can fix that by deliberately injecting a dummy statement whose sole purpose
is to associate that span with its enclosing block.
Resolve associated item bindings by namespace
This is the 3rd commit split off from #118360 with tests reblessed (they no longer contain duplicated diags which were caused by 4c0addc80a) & slightly adapted (removed supertraits from a UI test, cc #118040).
> * Resolve all assoc item bindings (type, const, fn (feature `return_type_notation`)) by namespace instead of trying to resolve a type first (in the non-RTN case) and falling back to consts afterwards. This is consistent with RTN. E.g., for `Tr<K = {…}>` we now always try to look up assoc consts (this extends to supertrait bounds). This gets rid of assoc tys shadowing assoc consts in assoc item bindings which is undesirable & inconsistent (types and consts live in different namespaces after all)
> * Consolidate the resolution of assoc {ty, const} bindings and RTN (dedup, better diags for RTN)
> * Fix assoc consts being labeled as assoc *types* in several diagnostics
> * Make a bunch of diagnostics translatable
Fixes#112560 (error → pass).
As discussed
r? `@compiler-errors`
---
**Addendum**: What I call “associated item bindings” are commonly referred to as “type bindings” for historical reasons. Nowadays, “type bindings” include assoc type bindings, assoc const bindings and RTN (return type notation) which is why I prefer not to use this outdated term.
Rollup of 6 pull requests
Successful merges:
- #116420 (discard invalid spans in external blocks)
- #118686 (Only check principal trait ref for object safety)
- #118688 (Add method to get type of an Rvalue in StableMIR)
- #118707 (Ping GuillaumeGomez for changes in rustc_codegen_gcc)
- #118712 (targets: remove not-added {i386,i486}-unknown-linux-gnu)
- #118719 (CFI: Add char to CFI integer normalization)
Failed merges:
- #117586 (Uplift the (new solver) canonicalizer into `rustc_next_trait_solver`)
r? `@ghost`
`@rustbot` modify labels: rollup
discard invalid spans in external blocks
Fixes#116203
This PR has discarded the invalid `const_span`, thereby making the format more neat.
r? ``@Nilstrieb``
Avoid adding builtin functions to `symbols.o`
We found performance regressions in #113923. The problem seems to be that `--gc-sections` does not remove these symbols. I tested that lld removes these symbols, but ld and gold do not.
I found that `used` adds symbols to `symbols.o` at 3e202ead60/compiler/rustc_codegen_ssa/src/back/linker.rs (L1786-L1791).
The PR removes builtin functions.
Note that under LTO, ld still preserves these symbols. (lld will still remove them.)
The first commit also fixes#118559. But I think the second commit also makes sense.
compile-time evaluation: detect writes through immutable pointers
This has two motivations:
- it unblocks https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/116745 (and therefore takes a big step towards `const_mut_refs` stabilization), because we can now detect if the memory that we find in `const` can be interned as "immutable"
- it would detect the UB that was uncovered in https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/117905, which was caused by accidental stabilization of `copy` functions in `const` that can only be called with UB
When UB is detected, we emit a future-compat warn-by-default lint. This is not a breaking change, so completely in line with [the const-UB RFC](https://rust-lang.github.io/rfcs/3016-const-ub.html), meaning we don't need t-lang FCP here. I made the lint immediately show up for dependencies since it is nearly impossible to even trigger this lint without `const_mut_refs` -- the accidentally stabilized `copy` functions are the only way this can happen, so the crates that popped up in #117905 are the only causes of such UB (in the code that crater covers), and the three cases of UB that we know about have all been fixed in their respective crates already.
The way this is implemented is by making use of the fact that our interpreter is already generic over the notion of provenance. For CTFE we now use the new `CtfeProvenance` type which is conceptually an `AllocId` plus a boolean `immutable` flag (but packed for a more efficient representation). This means we can mark a pointer as immutable when it is created as a shared reference. The flag will be propagated to all pointers derived from this one. We can then check the immutable flag on each write to reject writes through immutable pointers.
I just hope perf works out.
Fix is_foreign_item for StableMIR instance
Change the implementation of `Instance::is_foreign_item` to directly query the compiler for the instance `def_id` instead of incorrectly relying on the conversion to `CrateItem`. I also added a method to check if the instance has body, since the function already existed and it just wasn't exposed via public APIs. This makes it much cheaper for the user to check if the instance has body.
## Background:
- In pull https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/118524, I fixed the conversion from Instance to CrateItem to avoid the conversion if the instance didn't have a body available. This broke the `is_foreign_item`.
r? `@ouz-a`
Enforce `must_use` on associated types and RPITITs that have a must-use trait in bounds
Warn when an RPITIT or (un-normalized) associated type with a `#[must_use]` trait in its bounds is unused.
This is pending T-lang approval, since it changes the semantics of the `#[must_use]` attribute slightly, but I think it strictly catches more strange errors.
I could also limit this to just RPITITs, but that seems less useful.
Fixes#118444
tip for define macro name after `macro_rules!`
Fixes#118295
~Note that there are some bad case such as `macro_rules![]` or `macro_rules!()`. However, I think these are acceptable as they are likely to be seldom used (feel free to close this if you think its shortcomings outweigh its benefits)~
Edit: this problem was resolved by utilizing the `source_map.span_to_next_source`.
r? `@petrochenkov`
Use the glob binding in resolve_rustdoc_path process
Fixes#117920
Returning `None` seems enough.
I reproduces and tests this locally by `cargo +stage1 build`, but I cannot reproduce this ICE by putting [the following code](https://play.rust-lang.org/?version=nightly&mode=debug&edition=2021&gist=8b3ca8f4a7676eb90baf30437ba041a2) into `tests/ui/...` and then compiling it using `rustc +stage1 /path/to/test.rs` or `x.py test`:
```rust
#![crate_type = "lib"]
use super::Hasher;
/// [`Hasher`]
pub use core:#️⃣:*;
```
r? `@petrochenkov`
Change the implementation of `Instance::is_foreign_item` to directly
query the compiler for the instance `def_id` instead of incorrectly
relying on the conversion to `CrateItem`.
Background:
- In pull https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/118524, I fixed the
conversion from Instance to CrateItem to avoid the conversion if the
instance didn't have a body available. This broke the `is_foreign_item`.
Add ADT variant infomation to StableMIR and finish implementing TyKind::internal()
Introduce a `VariantDef` type and a mechanism to retrieve the definition from an `AdtDef`.
The `VariantDef` representation itself is just a combination of `AdtDef` and `VariantIdx`, which allow us to retrieve further information of a variant. I don't think we need to cache extra information for now, and we can translate on an on demand manner. I am leaving the fields public today due to https://github.com/rust-lang/project-stable-mir/issues/56, but they shouldn't. For this PR, I've only added a method to retrieve the variant name, and its fields. I also added an implementation of `RustcInternal` that allow users to retrieve more information using Rust internal APIs.
I have also finished the implementation of `RustcInternal` for `TyKind` which fixes https://github.com/rust-lang/project-stable-mir/issues/46.
## Motivation
Both of these changes are needed in order to properly interpret things like projections. For example,
- The variant definition is used to find out which variant we are downcasting to.
- Being able to create `Ty` from `TyKind` helps for example processing each stage of a projection, like the code in `place.ty()`.
Provide context when `?` can't be called because of `Result<_, E>`
When a method chain ending in `?` causes an E0277 because the expression's `Result::Err` variant doesn't have a type that can be converted to the `Result<_, E>` type parameter in the return type, provide additional context of which parts of the chain can and can't support the `?` operator.
```
error[E0277]: `?` couldn't convert the error to `String`
--> $DIR/question-mark-result-err-mismatch.rs:27:25
|
LL | fn bar() -> Result<(), String> {
| ------------------ expected `String` because of this
LL | let x = foo();
| ----- this has type `Result<_, String>`
...
LL | .map_err(|_| ())?;
| ---------------^ the trait `From<()>` is not implemented for `String`
| |
| this can't be annotated with `?` because it has type `Result<_, ()>`
|
= note: the question mark operation (`?`) implicitly performs a conversion on the error value using the `From` trait
= help: the following other types implement trait `From<T>`:
<String as From<char>>
<String as From<Box<str>>>
<String as From<Cow<'a, str>>>
<String as From<&str>>
<String as From<&mut str>>
<String as From<&String>>
= note: required for `Result<(), String>` to implement `FromResidual<Result<Infallible, ()>>`
```
Fix#72124.
Remove `#[rustc_host]`, use internal desugaring
Also removed a way for users to explicitly specify the host param since that isn't particularly useful. This should eliminate any pain with encoding attributes across crates and etc.
r? `@compiler-errors`
Added shadowed hint for overlapping associated types
Previously, when you tried to set an associated type that is shadowed by an associated type in a subtrait, like this:
```rust
trait A {
type X;
}
trait B: A {
type X; // note: this is legal
}
impl<Y> Clone for Box<dyn B<X=Y, X=Y>> {
fn clone(&self) -> Self {
todo!()
}
}
you got a confusing error message, that says nothing about the shadowing:
error[E0719]: the value of the associated type `X` (from trait `B`) is already specified
--> test.rs:9:34
|
9 | impl<Y> Clone for Box<dyn B<X=Y, X=Y>> {
| --- ^^^ re-bound here
| |
| `X` bound here first
error[E0191]: the value of the associated type `X` (from trait `A`) must be specified
--> test.rs:9:27
|
2 | type X;
| ------ `X` defined here
...
9 | impl<Y> Clone for Box<dyn B<X=Y, X=Y>> {
| ^^^^^^^^^^^ help: specify the associated type: `B<X=Y, X=Y, X = Type>`
error: aborting due to 2 previous errors
Some errors have detailed explanations: E0191, E0719.
For more information about an error, try `rustc --explain E0191`.
```
Now instead, the error shows that the associated type is shadowed, and suggests renaming as a potential fix.
```rust
error[E0719]: the value of the associated type `X` in trait `B` is already specified
--> test.rs:9:34
|
9 | impl<Y> Clone for Box<dyn B<X=Y, X=Y>> {
| --- ^^^ re-bound here
| |
| `X` bound here first
error[E0191]: the value of the associated type `X` in `A` must be specified
--> test.rs:9:27
|
2 | type X;
| ------ `A::X` defined here
...
6 | type X; // note: this is legal
| ------ `A::X` shadowed here
...
9 | impl<Y> Clone for Box<dyn B<X=Y, X=Y>> {
| ^^^^^^^^^^^ associated type `X` must be specified
|
help: consider renaming this associated type
--> test.rs:2:5
|
2 | type X;
| ^^^^^^
help: consider renaming this associated type
--> test.rs:6:5
|
6 | type X; // note: this is legal
| ^^^^^^
```
error: aborting due to 2 previous errors
Some errors have detailed explanations: E0191, E0719.
For more information about an error, try `rustc --explain E0191`.
The rename help message is only emitted when the trait is local. This is true both for the supertrait as for the subtrait.
There might be cases where you can use the fully qualified path (for instance, in a where clause), but this PR currently does not deal with that.
fixes#100109
(continues from #117642, because I didn't know renaming the branch would close the PR)
Shadowing the associated type of a supertrait is allowed.
This however makes it impossible to set the associated type
of the supertrait in a dyn object.
This PR makes the error message for that case clearer, like
adding a note that shadowing is happening, as well as suggesting
renaming of one of the associated types.
r=petrochenckov
When a method chain ending in `?` causes an E0277 because the
expression's `Result::Err` variant doesn't have a type that can be
converted to the `Result<_, E>` type parameter in the return type,
provide additional context of which parts of the chain can and can't
support the `?` operator.
```
error[E0277]: `?` couldn't convert the error to `String`
--> $DIR/question-mark-result-err-mismatch.rs:28:25
|
LL | fn bar() -> Result<(), String> {
| ------------------ expected `String` because of this
LL | let x = foo();
| ----- this can be annotated with `?` because it has type `Result<String, String>`
LL | let one = x
LL | .map(|s| ())
| ----------- this can be annotated with `?` because it has type `Result<(), String>`
LL | .map_err(|_| ())?;
| ---------------^ the trait `From<()>` is not implemented for `String`
| |
| this can't be annotated with `?` because it has type `Result<(), ()>`
|
= note: the question mark operation (`?`) implicitly performs a conversion on the error value using the `From` trait
= help: the following other types implement trait `From<T>`:
<String as From<char>>
<String as From<Box<str>>>
<String as From<Cow<'a, str>>>
<String as From<&str>>
<String as From<&mut str>>
<String as From<&String>>
= note: required for `Result<(), String>` to implement `FromResidual<Result<Infallible, ()>>`
```
Fix#72124.
`build_session` is passed an `EarlyErrorHandler` and then constructs a
`Handler`. But the `EarlyErrorHandler` is still used for some time after
that.
This commit changes `build_session` so it consumes the passed
`EarlyErrorHandler`, and also drops it as soon as the `Handler` is
built. As a result, `parse_cfg` and `parse_check_cfg` now take a
`Handler` instead of an `EarlyErrorHandler`.
Although, we would like to avoid crashes whenever
possible, and that's why I wanted to make this API fallible. It's
looking pretty hard to do proper validation.
I think many of our APIs will unfortunately depend on the user doing
the correct thing since at the MIR level we are working on,
we expect types to have been checked already.
Add `deeply_normalize_for_diagnostics`, use it in coherence
r? lcnr
Normalize trait refs used for coherence error reporting with `-Ztrait-solver=next-coherence`.
Two things:
1. I said before that we can't add this to `TyErrCtxt` because we compute `OverlapResult`s even if there are no diagnostics being emitted, e.g. for a reservation impl.
2. I didn't want to add this to an `InferCtxtExt` trait because I felt it was unnecessary. I don't particularly care about the API though.
Pretty print `Fn<(..., ...)>` trait refs with parentheses (almost) always
It's almost always better, at least in diagnostics, to print `Fn(i32, u32)` instead of `Fn<(i32, u32)>`.
Related to but doesn't fix#118225. That needs a separate fix.
Add support for making lib features internal
We have the notion of an "internal" lang feature: a feature that is never intended to be stabilized, and using which can cause ICEs and other issues without that being considered a bug.
This extends that idea to lib features as well. It is an alternative to https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/115623: instead of using an attribute to declare lib features internal, we simply do this based on the name. Everything ending in `_internals` or `_internal` is considered internal.
Then we rename `core_intrinsics` to `core_intrinsics_internal`, which fixes https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/115597.
Make the following API stable:
// in core::any
pub fn type_name_of_val<T: ?Sized>(_val: &T) -> &'static str
Const stability is not added because this relies on `type_name` which is also
not const. That has a blocking issue.
Fixes#66359
Add support for `gen fn`
This builds on #116447 to add support for `gen fn` functions. For the most part we follow the same approach as desugaring `async fn`, but replacing `Future` with `Iterator` and `async {}` with `gen {}` for the body.
The version implemented here uses the return type of a `gen fn` as the yield type. For example:
```rust
gen fn count_to_three() -> i32 {
yield 1;
yield 2;
yield 3;
}
```
In the future, I think we should experiment with a syntax like `gen fn count_to_three() yield i32 { ... }`, but that can go in another PR.
cc `@oli-obk` `@compiler-errors`
Remove the `precise_pointer_size_matching` feature gate
`usize` and `isize` are special for pattern matching because their range might depend on the platform. To make code portable across platforms, the following is never considered exhaustive:
```rust
let x: usize = ...;
match x {
0..=18446744073709551615 => {}
}
```
Because of how rust handles constants, this also unfortunately counts `0..=usize::MAX` as non-exhaustive. The [`precise_pointer_size_matching`](https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/56354) feature gate was introduced both for this convenience and for the possibility that the lang team could decide to allow the above.
Since then, [half-open range patterns](https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/67264) have been implemented, and since #116692 they correctly support `usize`/`isize`:
```rust
match 0usize { // exhaustive!
0..5 => {}
5.. => {}
}
```
I believe this subsumes all the use cases of the feature gate. Moreover no attempt has been made to stabilize it in the 5 years of its existence. I therefore propose we retire this feature gate.
Closes https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/56354
Remove mention of rust to make the error message generic.
The deprecation notice is used when in crates as well. This applies to versions Rust or Crates.
Relates #118148
Tweak unclosed generics errors
Remove unnecessary span label for parse errors that already have a suggestion.
Provide structured suggestion to close generics in more cases.
The deprecation notice is used when in crates as well. This applies to versions Rust or Crates.
Fixes#118148
Signed-off-by: Harold Dost <h.dost@criteo.com>
Tweak `.clone()` suggestion to work in more cases
When going through auto-deref, the `<T as Clone>` impl sometimes needs to be specified for rustc to actually clone the value and not the reference.
```
error[E0507]: cannot move out of dereference of `S`
--> $DIR/needs-clone-through-deref.rs:15:18
|
LL | for _ in self.clone().into_iter() {}
| ^^^^^^^^^^^^ ----------- value moved due to this method call
| |
| move occurs because value has type `Vec<usize>`, which does not implement the `Copy` trait
|
note: `into_iter` takes ownership of the receiver `self`, which moves value
--> $SRC_DIR/core/src/iter/traits/collect.rs:LL:COL
help: you can `clone` the value and consume it, but this might not be your desired behavior
|
LL | for _ in <Vec<usize> as Clone>::clone(&self.clone()).into_iter() {}
| ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ +
```
When encountering a move error, look for implementations of `Clone` for the moved type. If there is one, check if all its obligations are met. If they are, we suggest cloning without caveats. If they aren't, we suggest cloning while mentioning the unmet obligations, potentially suggesting `#[derive(Clone)]` when appropriate.
```
error[E0507]: cannot move out of a shared reference
--> $DIR/suggest-clone-when-some-obligation-is-unmet.rs:20:28
|
LL | let mut copy: Vec<U> = map.clone().into_values().collect();
| ^^^^^^^^^^^ ------------- value moved due to this method call
| |
| move occurs because value has type `HashMap<T, U, Hash128_1>`, which does not implement the `Copy` trait
|
note: `HashMap::<K, V, S>::into_values` takes ownership of the receiver `self`, which moves value
--> $SRC_DIR/std/src/collections/hash/map.rs:LL:COL
help: you could `clone` the value and consume it, if the `Hash128_1: Clone` trait bound could be satisfied
|
LL | let mut copy: Vec<U> = <HashMap<T, U, Hash128_1> as Clone>::clone(&map.clone()).into_values().collect();
| ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ +
help: consider annotating `Hash128_1` with `#[derive(Clone)]`
|
LL + #[derive(Clone)]
LL | pub struct Hash128_1;
|
```
Fix#109429.
When encountering multiple mutable borrows, suggest cloning and adding
derive annotations as needed.
```
error[E0596]: cannot borrow `sm.x` as mutable, as it is behind a `&` reference
--> $DIR/accidentally-cloning-ref-borrow-error.rs:32:9
|
LL | foo(&mut sm.x);
| ^^^^^^^^^ `sm` is a `&` reference, so the data it refers to cannot be borrowed as mutable
|
help: `Str` doesn't implement `Clone`, so this call clones the reference `&Str`
--> $DIR/accidentally-cloning-ref-borrow-error.rs:31:21
|
LL | let mut sm = sr.clone();
| ^^^^^^^
help: consider annotating `Str` with `#[derive(Clone)]`
|
LL + #[derive(Clone)]
LL | struct Str {
|
help: consider specifying this binding's type
|
LL | let mut sm: &mut Str = sr.clone();
| ++++++++++
```
Fix#34629. Fix#76643. Fix#91532.
Structured `use` suggestion on privacy error
When encoutering a privacy error on an item through a re-export that is accessible in an alternative path, provide a structured suggestion with that path.
```
error[E0603]: module import `mem` is private
--> $DIR/private-std-reexport-suggest-public.rs:4:14
|
LL | use foo::mem;
| ^^^ private module import
|
note: the module import `mem` is defined here...
--> $DIR/private-std-reexport-suggest-public.rs:8:9
|
LL | use std::mem;
| ^^^^^^^^
note: ...and refers to the module `mem` which is defined here
--> $SRC_DIR/std/src/lib.rs:LL:COL
|
= note: you could import this
help: import `mem` through the re-export
|
LL | use std::mem;
| ~~~~~~~~
```
Fix#42909.
When encoutering a privacy error on an item through a re-export that is
accessible in an alternative path, provide a structured suggestion with
that path.
```
error[E0603]: module import `mem` is private
--> $DIR/private-std-reexport-suggest-public.rs:4:14
|
LL | use foo::mem;
| ^^^ private module import
|
note: the module import `mem` is defined here...
--> $DIR/private-std-reexport-suggest-public.rs:8:9
|
LL | use std::mem;
| ^^^^^^^^
note: ...and refers to the module `mem` which is defined here
--> $SRC_DIR/std/src/lib.rs:LL:COL
|
= note: you could import this
help: import `mem` through the re-export
|
LL | use std::mem;
| ~~~~~~~~
```
Fix#42909.
When encountering multiple mutable borrows, suggest cloning and adding
derive annotations as needed.
```
error[E0596]: cannot borrow `sm.x` as mutable, as it is behind a `&` reference
--> $DIR/accidentally-cloning-ref-borrow-error.rs:32:9
|
LL | foo(&mut sm.x);
| ^^^^^^^^^ `sm` is a `&` reference, so the data it refers to cannot be borrowed as mutable
|
help: `Str` doesn't implement `Clone`, so this call clones the reference `&Str`
--> $DIR/accidentally-cloning-ref-borrow-error.rs:31:21
|
LL | let mut sm = sr.clone();
| ^^^^^^^
help: consider annotating `Str` with `#[derive(Clone)]`
|
LL + #[derive(Clone)]
LL | struct Str {
|
help: consider specifying this binding's type
|
LL | let mut sm: &mut Str = sr.clone();
| ++++++++++
```
```
error[E0596]: cannot borrow `*inner` as mutable, as it is behind a `&` reference
--> $DIR/issue-91206.rs:14:5
|
LL | inner.clear();
| ^^^^^ `inner` is a `&` reference, so the data it refers to cannot be borrowed as mutable
|
help: you can `clone` the `Vec<usize>` value and consume it, but this might not be your desired behavior
--> $DIR/issue-91206.rs:11:17
|
LL | let inner = client.get_inner_ref();
| ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
help: consider specifying this binding's type
|
LL | let inner: &mut Vec<usize> = client.get_inner_ref();
| +++++++++++++++++
```
When encountering a case where `let x: T = (val: &T).clone();` and
`T: !Clone`, already mention that the reference is being cloned. We now
also suggest `#[derive(Clone)]` not only on `T` but also on type
parameters to satisfy blanket implementations.
```
error[E0308]: mismatched types
--> $DIR/assignment-of-clone-call-on-ref-due-to-missing-bound.rs:17:39
|
LL | let mut x: HashSet<Day> = v.clone();
| ------------ ^^^^^^^^^ expected `HashSet<Day>`, found `&HashSet<Day>`
| |
| expected due to this
|
= note: expected struct `HashSet<Day>`
found reference `&HashSet<Day>`
note: `HashSet<Day>` does not implement `Clone`, so `&HashSet<Day>` was cloned instead
--> $DIR/assignment-of-clone-call-on-ref-due-to-missing-bound.rs:17:39
|
LL | let mut x: HashSet<Day> = v.clone();
| ^
= help: `Clone` is not implemented because the trait bound `Day: Clone` is not satisfied
help: consider annotating `Day` with `#[derive(Clone)]`
|
LL + #[derive(Clone)]
LL | enum Day {
|
```
Case taken from # #41825.
When encountering a move error, look for implementations of `Clone` for
the moved type. If there is one, check if all its obligations are met.
If they are, we suggest cloning without caveats. If they aren't, we
suggest cloning while mentioning the unmet obligations, potentially
suggesting `#[derive(Clone)]` when appropriate.
```
error[E0507]: cannot move out of a shared reference
--> $DIR/suggest-clone-when-some-obligation-is-unmet.rs:20:28
|
LL | let mut copy: Vec<U> = map.clone().into_values().collect();
| ^^^^^^^^^^^ ------------- value moved due to this method call
| |
| move occurs because value has type `HashMap<T, U, Hash128_1>`, which does not implement the `Copy` trait
|
note: `HashMap::<K, V, S>::into_values` takes ownership of the receiver `self`, which moves value
--> $SRC_DIR/std/src/collections/hash/map.rs:LL:COL
help: you could `clone` the value and consume it, if the `Hash128_1: Clone` trait bound could be satisfied
|
LL | let mut copy: Vec<U> = <HashMap<T, U, Hash128_1> as Clone>::clone(&map.clone()).into_values().collect();
| ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ +
help: consider annotating `Hash128_1` with `#[derive(Clone)]`
|
LL + #[derive(Clone)]
LL | pub struct Hash128_1;
|
```
Fix#109429.
When going through auto-deref, the `<T as Clone>` impl sometimes needs
to be specified for rustc to actually clone the value and not the
reference.
```
error[E0507]: cannot move out of dereference of `S`
--> $DIR/needs-clone-through-deref.rs:15:18
|
LL | for _ in self.clone().into_iter() {}
| ^^^^^^^^^^^^ ----------- value moved due to this method call
| |
| move occurs because value has type `Vec<usize>`, which does not implement the `Copy` trait
|
note: `into_iter` takes ownership of the receiver `self`, which moves value
--> $SRC_DIR/core/src/iter/traits/collect.rs:LL:COL
help: you can `clone` the value and consume it, but this might not be your desired behavior
|
LL | for _ in <Vec<usize> as Clone>::clone(&self.clone()).into_iter() {}
| ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ +
```
CC #109429.
[rustdoc] Don't generate the "Fields" heading if there is no field displayed
Fixes https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/118195.
If no field is displayed, we should not generate the `Fields` heading in enum struct variants.
r? ``@notriddle``
Restrict what symbols can be used in `#[diagnostic::on_unimplemented]` format strings
This commit restricts what symbols can be used in a format string for any option of the `diagnostic::on_unimplemented` attribute. We previously allowed all the ad-hoc options supported by the internal `#[rustc_on_unimplemented]` attribute. For the stable attribute we only want to support generic parameter names and `{Self}` as parameters. For any other parameter an warning is emitted and the parameter is replaced by the literal parameter string, so for example `{integer}` turns into `{integer}`. This follows the general design of attributes in the `#[diagnostic]` attribute namespace, that any syntax "error" is treated as warning and subsequently ignored.
r? `@compiler-errors`
This commit restricts what symbols can be used in a format string for
any option of the `diagnostic::on_unimplemented` attribute. We
previously allowed all the ad-hoc options supported by the internal
`#[rustc_on_unimplemented]` attribute. For the stable attribute we only
want to support generic parameter names and `{Self}` as parameters. For
any other parameter an warning is emitted and the parameter is replaced
by the literal parameter string, so for example `{integer}` turns into
`{integer}`. This follows the general design of attributes in the
`#[diagnostic]` attribute namespace, that any syntax "error" is treated
as warning and subsequently ignored.
Rollup of 3 pull requests
Successful merges:
- #117869 ([rustdoc] Add highlighting for comments in items declaration)
- #118525 (coverage: Skip spans that can't be un-expanded back to the function body)
- #118574 (rustc_session: Address all `rustc::potential_query_instability` lints)
r? `@ghost`
`@rustbot` modify labels: rollup
coverage: Skip spans that can't be un-expanded back to the function body
When we extract coverage spans from MIR, we try to "un-expand" them back to spans that are inside the function's body span.
In cases where that doesn't succeed, the current code just swaps in the entire body span instead. But that tends to result in coverage spans that are completely unrelated to the control flow of the affected code, so it's better to just discard those spans.
---
Extracted from #118305, since this is a general improvement that isn't specific to branch coverage.
---
`@rustbot` label +A-code-coverage
[rustdoc] Add highlighting for comments in items declaration
Fixes#117555.
So after the discussion in https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/117643, the outcome was that having the comments in the item declaration at the same level (in term of color) as the rest of the code was actually a bit distracting and could be improved.
The current highlighting color for comments is "lighter" than the rest and I think it fits perfectly to improve the current situation. With this, we now have different "levels" which makes it easier to read and filter out what we want when reading the items declaration.
Here's a screenshot:

r? `@notriddle`
Provide structured suggestion for type mismatch in loop
We currently provide only a `help` message, this PR introduces the last two structured suggestions instead:
```
error[E0308]: mismatched types
--> $DIR/issue-98982.rs:2:5
|
LL | fn foo() -> i32 {
| --- expected `i32` because of return type
LL | / for i in 0..0 {
LL | | return i;
LL | | }
| |_____^ expected `i32`, found `()`
|
note: the function expects a value to always be returned, but loops might run zero times
--> $DIR/issue-98982.rs:2:5
|
LL | for i in 0..0 {
| ^^^^^^^^^^^^^ this might have zero elements to iterate on
LL | return i;
| -------- if the loop doesn't execute, this value would never get returned
help: return a value for the case when the loop has zero elements to iterate on
|
LL ~ }
LL ~ /* `i32` value */
|
help: otherwise consider changing the return type to account for that possibility
|
LL ~ fn foo() -> Option<i32> {
LL | for i in 0..0 {
LL ~ return Some(i);
LL ~ }
LL ~ None
|
```
Fix#98982.
Report errors in jobserver inherited through environment variables
This pr attempts to catch situations, when jobserver exists, but is not being inherited.
r? `@petrochenkov`
Because a macro invocation can expand to a never pattern, we can't rule
out a `arm!(),` arm at parse time. Instead we detect that case at
expansion time, if the macro tries to output a pattern followed by `=>`.
When we extract coverage spans from MIR, we try to "un-expand" them back to
spans that are inside the function's body span.
In cases where that doesn't succeed, the current code just swaps in the entire
body span instead. But that tends to result in coverage spans that are
completely unrelated to the control flow of the affected code, so it's better
to just discard those spans.
move packed-struct tests into packed/ folder
We already have a bunch of other tests named `packed/packed-struct*`, no reason to have these two tests be separate.
Add more information to StableMIR Instance
Allow stable MIR users to retrieve an instance function signature, the index for a VTable instance and more information about its underlying definition.
These are needed to properly interpret function calls, either via VTable or direct calls. The `CrateDef` implementation will also allow users to emit diagnostic messages.
I also fixed a few issues that we had identified before with how we were retrieving body of things that may not have a body available.
Handle recursion limit for subtype and well-formed predicates
Adds a recursion limit check for subtype predicates and well-formed predicates.
`-Ztrait-solver=next` currently panics with unimplemented for these cases.
These cases are arguably bugs in the occurs check but:
- I could not find a simple way to fix the occurs check
- There should still be a recursion limit check to prevent hangs anyway.
closes#117151
r? types
Centralize live loans maintenance to fix scope differences due to liveness
As found in the recent [polonius crater run](https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/117593#issuecomment-1801398892), NLLs and the location-insensitive polonius computed different scopes on some specific CFG shapes, e.g. the following.

I had missed that liveness data was pushed from different sources than just the liveness computation: there are a few places that do this -- and some of them may be unneeded or at the very least untested, as no tests changed when I tried removing some of them.
Here, `_6` is e.g. dead on entry to `bb2[0]` during `liveness::trace`, but its regions will be marked as live later during "constraint generation" (which I plan to refactor away and put in the liveness module soon). This should cause the inflowing loans to be marked live, but they were only computed in `liveness::trace`.
Therefore, this PR moves live loan maintenance to `LivenessValues`, so that the various places pushing liveness data will all also update live loans at the same time -- except for promoteds which I don't believe need them, and their liveness handling is already interesting/peculiar.
All the regressions I saw in the initial crater run were related to this kind of shapes, and this change did fix all of them on the [next run](https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/117593#issuecomment-1826132145).
r? `@matthewjasper`
(This will conflict with #117880 but whichever lands first is fine by me, the end goal is the same for both)
Restore `#![no_builtins]` crates participation in LTO.
After #113716, we can make `#![no_builtins]` crates participate in LTO again.
`#![no_builtins]` with LTO does not result in undefined references to the error. I believe this type of issue won't happen again.
Fixes#72140. Fixes#112245. Fixes#110606. Fixes#105734. Fixes#96486. Fixes#108853. Fixes#108893. Fixes#78744. Fixes#91158. Fixes https://github.com/rust-lang/cargo/issues/10118. Fixes https://github.com/rust-lang/compiler-builtins/issues/347.
The `nightly-2023-07-20` version does not always reproduce problems due to changes in compiler-builtins, core, and user code. That's why this issue recurs and disappears.
Some issues were not tested due to the difficulty of reproducing them.
r? pnkfelix
cc `@bjorn3` `@japaric` `@alexcrichton` `@Amanieu`
Stabilize C string literals
RFC: https://rust-lang.github.io/rfcs/3348-c-str-literal.html
Tracking issue: https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/105723
Documentation PR (reference manual): https://github.com/rust-lang/reference/pull/1423
# Stabilization report
Stabilizes C string and raw C string literals (`c"..."` and `cr#"..."#`), which are expressions of type [`&CStr`](https://doc.rust-lang.org/stable/core/ffi/struct.CStr.html). Both new literals require Rust edition 2021 or later.
```rust
const HELLO: &core::ffi::CStr = c"Hello, world!";
```
C strings may contain any byte other than `NUL` (`b'\x00'`), and their in-memory representation is guaranteed to end with `NUL`.
## Implementation
Originally implemented by PR https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/108801, which was reverted due to unintentional changes to lexer behavior in Rust editions < 2021.
The current implementation landed in PR https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/113476, which restricts C string literals to Rust edition >= 2021.
## Resolutions to open questions from the RFC
* Adding C character literals (`c'.'`) of type `c_char` is not part of this feature.
* Support for `c"..."` literals does not prevent `c'.'` literals from being added in the future.
* C string literals should not be blocked on making `&CStr` a thin pointer.
* It's possible to declare constant expressions of type `&'static CStr` in stable Rust (as of v1.59), so C string literals are not adding additional coupling on the internal representation of `CStr`.
* The unstable `concat_bytes!` macro should not accept `c"..."` literals.
* C strings have two equally valid `&[u8]` representations (with or without terminal `NUL`), so allowing them to be used in `concat_bytes!` would be ambiguous.
* Adding a type to represent C strings containing valid UTF-8 is not part of this feature.
* Support for a hypothetical `&Utf8CStr` may be explored in the future, should such a type be added to Rust.
generic_const_exprs: suggest to add the feature, not use it
Usually our missing feature messages look something like
```
= help: add `#![feature(inline_const)]` to the crate attributes to enable
```
However `generic_const_exprs` used a different verb. That's inconsistent and it also means playground won't add that nice hyperlink to add the feature automatically. So let's use the same verb as everywhere else.
rustdoc: `div.where` instead of fmt-newline class
This is about equally readable, a lot more terse, and stops special-casing functions and methods.
```console
$ du -hs doc-old/ doc-new/
671M doc-old/
670M doc-new/
```
Add `-Zfunction-return={keep,thunk-extern}` option
This is intended to be used for Linux kernel RETHUNK builds.
With this commit (optionally backported to Rust 1.73.0), plus a patched Linux kernel to pass the flag, I get a RETHUNK build with Rust enabled that is `objtool`-warning-free and is able to boot in QEMU and load a sample Rust kernel module.
Issue: https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/116853.
On Fn arg mismatch for a fn path, suggest a closure
When encountering a fn call that has a path to another fn being passed in, where an `Fn` impl is expected, and the arguments differ, suggest wrapping the argument with a closure with the appropriate arguments.
The last `help` is new:
```
error[E0631]: type mismatch in function arguments
--> $DIR/E0631.rs:9:9
|
LL | fn f(_: u64) {}
| ------------ found signature defined here
...
LL | foo(f);
| --- ^ expected due to this
| |
| required by a bound introduced by this call
|
= note: expected function signature `fn(usize) -> _`
found function signature `fn(u64) -> _`
note: required by a bound in `foo`
--> $DIR/E0631.rs:3:11
|
LL | fn foo<F: Fn(usize)>(_: F) {}
| ^^^^^^^^^ required by this bound in `foo`
help: consider wrapping the function in a closure
|
LL | foo(|arg0: usize| f(/* u64 */));
| +++++++++++++ +++++++++++
```
This is intended to be used for Linux kernel RETHUNK builds.
With this commit (optionally backported to Rust 1.73.0), plus a
patched Linux kernel to pass the flag, I get a RETHUNK build with
Rust enabled that is `objtool`-warning-free and is able to boot in
QEMU and load a sample Rust kernel module.
Signed-off-by: Miguel Ojeda <ojeda@kernel.org>
This is about equally readable, a lot more terse, and stops
special-casing functions and methods.
```console
$ du -hs doc-old/ doc-new/
671M doc-old/
670M doc-new/
```
Add thinlto support to codegen, assembly and coverage tests
Using `--emit=llvm-ir` with thinlto usually result in multiple IR files.
Resolve test case failure issue reported in #113923.
Tweak message on ADT with private fields building
When trying to create an inaccessible ADT due to private fields, handle the case when no fields were passed.
```
error: cannot construct `Foo` with struct literal syntax due to private fields
--> $DIR/issue-76077.rs:8:5
|
LL | foo::Foo {};
| ^^^^^^^^
|
= note: private field `you_cant_use_this_field` that was not provided
```
rustdoc-search: allow spaces around `::` in path query
This restriction made sense back when spaces separated function parameters, but now that they separate path components, there's no real ambiguity any more.
Additionally, the Rust language allows it.
The other two commits are misc code cleanup.
Fix `PartialEq` args when `#[const_trait]` is enabled
This is based off of your PR that enforces effects on all methods, so just see the last commits.
r? fee1-dead
When encountering a fn call that has a path to another fn being passed
in, where an `Fn` impl is expected, and the arguments differ, suggest
wrapping the argument with a closure with the appropriate arguments.
When trying to create an inaccessible ADT due to private fields, handle
the case when no fields were passed.
```
error: cannot construct `Foo` with struct literal syntax due to private fields
--> $DIR/issue-76077.rs:8:5
|
LL | foo::Foo {};
| ^^^^^^^^
|
= note: private field `you_cant_use_this_field` that was not provided
```
This restriction made sense back when spaces separated function
parameters, but now that they separate path components, there's
no real ambiguity any more.
Additionally, the Rust language allows it.
ConstProp: Correctly remove const if unknown value assigned to it.
Closes#118328
The problematic sequence of MIR is:
```rust
_1 = const 0_usize;
_1 = const _; // This is an associated constant we can't know before monomorphization.
_0 = _1;
```
1. When `ConstProp::visit_assign` happens on `_1 = const 0_usize;`, it records that `0x0usize` is the value for `_1`.
2. Next `visit_assign` happens on `_1 = const _;`. Because the rvalue `.has_param()`, it can't be const evaled.
3. Finaly, `visit_assign` happens on `_0 = _1;`. Here it would think the value of `_1` was `0x0usize` from step 1.
The solution is to remove consts when checking the RValue fails, as they may have contained values that should now be invalidated, as that local was overwritten.
This should probably be back-ported to beta. Stable is more iffy, as it's gone unidentified since 1.70, so I only think it's worthwhile if there's another reason for a 1.74.1 release anyway.
Suggest `let` or `==` on typo'd let-chain
When encountering a bare assignment in a let-chain, suggest turning the
assignment into a `let` expression or an equality check.
```
error: expected expression, found `let` statement
--> $DIR/bad-if-let-suggestion.rs:5:8
|
LL | if let x = 1 && i = 2 {}
| ^^^^^^^^^
|
= note: only supported directly in conditions of `if` and `while` expressions
help: you might have meant to continue the let-chain
|
LL | if let x = 1 && let i = 2 {}
| +++
help: you might have meant to compare for equality
|
LL | if let x = 1 && i == 2 {}
| +
```
Add `never_patterns` feature gate
This PR adds the feature gate and most basic parsing for the experimental `never_patterns` feature. See the tracking issue (https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/118155) for details on the experiment.
`@scottmcm` has agreed to be my lang-team liaison for this experiment.
Fix coroutine validation for mixed panic strategy
Validation introduced in #113124 allows `UnwindAction::Continue` and `TerminatorKind::Resume` to occur only in functions with ABI that can unwind. The function ABI depends on the panic strategy, which can vary across crates.
Usually MIR is built and validated in the same crate. The coroutine drop glue thus far was an exception. As a result validation could fail when mixing different panic strategies.
Avoid the problem by executing `AbortUnwindingCalls` along with the validation.
Fixes#116953.
Eagerly return `ExprKind::Err` on `yield`/`await` in wrong coroutine context
This PR does 2 things:
1. Refuses to lower `.await` or `yield` when we are outside of the right coroutine context for the operator. Instead, we lower to `hir::ExprKind::Err`, to silence subsequent redundant errors.
2. Reworks a bit of the span tracking in `LoweringContext` to fix a bad span when we have something like `let x = [0; async_fn().await]` where the `await` is inside of an anon const. The span for the "item" still kinda sucks, since it overlaps with the `await` span, but at least it's accurate.
Rollup of 6 pull requests
Successful merges:
- #118193 (Add missing period in `std::process::Command` docs)
- #118222 (unify read_to_end and io::copy impls for reading into a Vec)
- #118323 (give dev-friendly error message for incorrect config profiles)
- #118378 (Perform LTO optimisations with wasm-ld + -Clinker-plugin-lto)
- #118399 (Clean dead codes in miri)
- #118410 (update test for new LLVM 18 codegen)
r? `@ghost`
`@rustbot` modify labels: rollup
Validation introduced in #113124 allows UnwindAction::Continue and
TerminatorKind::Resume to occur only in functions with ABI that can
unwind. The function ABI depends on the panic strategy, which can vary
across crates.
Usually MIR is built and validated in the same crate. The coroutine drop
glue thus far was an exception. As a result validation could fail when
mixing different panic strategies.
Avoid the problem by executing AbortUnwindingCalls along with the
validation.
When encountering a bare assignment in a let-chain, suggest turning the
assignment into a `let` expression or an equality check.
```
error: expected expression, found `let` statement
--> $DIR/bad-if-let-suggestion.rs:5:8
|
LL | if let x = 1 && i = 2 {}
| ^^^^^^^^^
|
= note: only supported directly in conditions of `if` and `while` expressions
help: you might have meant to continue the let-chain
|
LL | if let x = 1 && let i = 2 {}
| +++
help: you might have meant to compare for equality
|
LL | if let x = 1 && i == 2 {}
| +
```
effects: Run `enforce_context_effects` for all method calls
So that we also perform checks when overloaded `PartialEq`s are called.
r? `@compiler-errors`
rustc_span: Use correct edit distance start length for suggestions
Otherwise the suggestions can be off-base for non-ASCII identifiers. For example suggesting that `Ok` is a name similar to `读文`.
Closes https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/72553.
Added linker_arg(s) Linker trait methods for link-arg to be prefixed "-Wl," for cc-like linker args and not verbatim
https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/99427#issuecomment-1234443468
> here's one possible improvement to -l link-arg making it more portable between linkers and useful - befriending it with the verbatim modifier (https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/99425).
>
> -l link-arg:-verbatim=-foo would add -Wl,-foo (or equivalent) when C compiler is used as a linker, and just -foo when bare linker is used.
> -l link-arg:+verbatim=-bar on the other hand would always pass just -bar.
Account for `!` arm in tail `match` expr
On functions with a default return type that influences the coerced type of `match` arms, check if the failing arm is actually of type `!`. If so, suggest changing the return type so the coercion against the prior arms is successful.
```
error[E0308]: `match` arms have incompatible types
--> $DIR/match-tail-expr-never-type-error.rs:9:13
|
LL | fn bar(a: bool) {
| - help: try adding a return type: `-> i32`
LL | / match a {
LL | | true => 1,
| | - this is found to be of type `{integer}`
LL | | false => {
LL | | never()
| | ^^^^^^^
| | |
| | expected integer, found `()`
| | this expression is of type `!`, but it get's coerced to `()` due to its surrounding expression
LL | | }
LL | | }
| |_____- `match` arms have incompatible types
```
Fix#24157.
Do not erase late bound regions when selecting inherent associated types
In the fix for #97156 we would want the following code:
```rust
#![feature(inherent_associated_types)]
#![allow(incomplete_features)]
struct Foo<T>(T);
impl Foo<fn(&'static ())> {
type Assoc = u32;
}
trait Other {}
impl Other for u32 {}
// FIXME(inherent_associated_types): Avoid emitting two diagnostics (they only differ in span).
// FIXME(inherent_associated_types): Enhancement: Spruce up the diagnostic by saying something like
// "implementation is not general enough" as is done for traits via
// `try_report_trait_placeholder_mismatch`.
fn bar(_: Foo<for<'a> fn(&'a ())>::Assoc) {}
//~^ ERROR mismatched types
//~| ERROR mismatched types
fn main() {}
```
to fail with ...
```
error[E0220]: associated type `Assoc` not found for `Foo<for<'a> fn(&'a ())>` in the current scope
--> tests/ui/associated-inherent-types/issue-109789.rs:18:36
|
4 | struct Foo<T>(T);
| ------------- associated item `Assoc` not found for this struct
...
18 | fn bar(_: Foo<for<'a> fn(&'a ())>::Assoc) {}
| ^^^^^ associated item not found in `Foo<for<'a> fn(&'a ())>`
|
= note: the associated type was found for
- `Foo<fn(&'static ())>`
error: aborting due to previous error
For more information about this error, try `rustc --explain E0220`.
```
This PR fixes the ICE we are currently getting "was a subtype of Foo<Binder(fn(&ReStatic ()), [])> during selection but now it is not"
Also fixes#112631
r? `@lcnr`
On functions with a default return type that influences the coerced type
of `match` arms, check if the failing arm is actually of type `!`. If
so, suggest changing the return type so the coercion against the prior
arms is successful.
```
error[E0308]: `match` arms have incompatible types
--> $DIR/match-tail-expr-never-type-error.rs:9:13
|
LL | fn bar(a: bool) {
| - help: try adding a return type: `-> i32`
LL | / match a {
LL | | true => 1,
| | - this is found to be of type `{integer}`
LL | | false => {
LL | | never()
| | ^^^^^^^
| | |
| | expected integer, found `()`
| | this expression is of type `!`, but it get's coerced to `()` due to its surrounding expression
LL | | }
LL | | }
| |_____- `match` arms have incompatible types
```
Fix#24157.
Suggest swapping the order of `ref` and `box`
It is not valid grammar to write `ref box <ident>` in patterns, but `box ref <ident>` is.
This patch adds a diagnostic to suggest swapping them, analogous to what we do for `mut let`.
Add `debug_assert_nounwind` and convert `assert_unsafe_precondition`
`assert_unsafe_precondition` checks non-CTFE-evaluable conditions in runtime and performs no-op in compile time, while many of its current usage can be checked during const eval.
Rewrite exhaustiveness in one pass
This is at least my 4th attempt at this in as many years x) Previous attempts were all too complicated or too slow. But we're finally here!
The previous version of the exhaustiveness algorithm computed reachability for each arm then exhaustiveness of the whole match. Since each of these steps does roughly the same things, this rewrites the algorithm to do them all in one go. I also think this makes things much simpler.
I also rewrote the documentation of the algorithm in depth. Hopefully it's up-to-date and easier to follow now. Plz comment if anything's unclear.
r? `@oli-obk` I think you're one of the rare other people to understand the exhaustiveness algorithm?
cc `@varkor` I know you're not active anymore, but if you feel like having a look you might enjoy this :D
Fixes https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/79307
Don't ICE when encountering placeholders in implied bounds computation
I *could* fix this the right way, though I don't really want to think about the implications of the change. This should have minimal side-effects.
r? `@aliemjay`
Fixes#118286
coverage: Simplify building coverage expressions based on sums
This is a combination of some interlinked changes to the code that creates coverage counters/expressions for nodes and edges in the coverage graph:
- Some preparatory cleanups in `MakeBcbCounters::make_branch_counters`
- Use `BcbCounter` (instead of `CovTerm`) when building coverage expressions
- This makes it easier to introduce a fold for building sums
- Simplify the creation of coverage expressions based on sums, by having `Iterator::fold` do much of the work
- Get rid of the awkward `BcbBranch` enum, and replace it with graph edges represented as `(from_bcb, to_bcb)`
- This further simplifies the body of the fold
Currently we always do this:
```
use rustc_fluent_macro::fluent_messages;
...
fluent_messages! { "./example.ftl" }
```
But there is no need, we can just do this everywhere:
```
rustc_fluent_macro::fluent_messages! { "./example.ftl" }
```
which is shorter.
The `fluent_messages!` macro produces uses of
`crate::{D,Subd}iagnosticMessage`, which means that every crate using
the macro must have this import:
```
use rustc_errors::{DiagnosticMessage, SubdiagnosticMessage};
```
This commit changes the macro to instead use
`rustc_errors::{D,Subd}iagnosticMessage`, which avoids the need for the
imports.
In some cases we need to prepare a coverage expression that is the sum of an
arbitrary number of other terms. This patch simplifies the code paths that
build those sums.
This causes some churn in the mappings, because the previous code was building
its sums in a somewhat idiosyncratic order.
Fixes error count display is different when there's only one error left
Supersedes #114759
### What did I do?
I did the small change in `rustc_errors` by hand. Then I did the other changes in `/compiler` by hand, those were just find replace on `*.rs` in the workspace. The changes in run-make are find replace for `run-make` in the workspace.
All other changes are blessed using `x test TEST --bless`. I blessed the tests that were blessed in #114759.
### how to review this nightmare
ping bors with an `r+`. You should check that my logic is sound and maybe quickly scroll through the diff, but fully verifying it seems fairly hard to impossible. I did my best to do this correctly.
Thank you `@adrianEffe` for bringing this up and your initial implementation.
cc `@flip1995,` you said you want to do a subtree sync asap
cc `@RalfJung` maybe you want to do a quick subtree sync afterwards as well for Miri
r? `@WaffleLapkin`
Add `Span` to `TraitBoundModifier`
This improves diagnostics for the message "`~const` is not allowed here", and also fixes the span that we use when desugaring `~const Tr` into `Tr<host>` in effects desugaring.
Add common trait for crate definitions
In stable mir, we specialize DefId, however some functionality is the same for every definition, such as def paths, and getting their crate. Use a trait to implement those.
feat: make `let_binding_suggestion` more reasonable
This is my first PR for rustc, which trying to fix https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/117894, I am not familiar with some internal api so maybe some modification here isn't the way to go, appreciated for any review suggestion.
Don't print "private fields" on empty tuple structs
Closes#118180.
While working on this I also noticed that empty struct variants are also rendered rather awkwardly. I'll make another issue for that, since I don't know what the correct rendering would be.
Rework supertrait lint once again
I accidentally pushed the wrong commits because I totally didn't check I was on the right computer when updating #118026.
Sorry, this should address all the nits in #118026.
r? lcnr
improve tool-only help for multiple `#[default]` variants
When defining an enum with multiple `#[default]` variants, we emit a tool-only suggestion for every `#[default]`ed variant to remove all other `#[default]`s. This PR improves the suggestion to correctly handle the cases where one variant has multiple `#[default]`s and where different `#[default]`s have the same span due to macro expansions.
fixes https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/118119
We currently provide only a `help` message, this PR introduces the last
two structured suggestions instead:
```
error[E0308]: mismatched types
--> $DIR/issue-98982.rs:2:5
|
LL | fn foo() -> i32 {
| --- expected `i32` because of return type
LL | / for i in 0..0 {
LL | | return i;
LL | | }
| |_____^ expected `i32`, found `()`
|
note: the function expects a value to always be returned, but loops might run zero times
--> $DIR/issue-98982.rs:2:5
|
LL | for i in 0..0 {
| ^^^^^^^^^^^^^ this might have zero elements to iterate on
LL | return i;
| -------- if the loop doesn't execute, this value would never get returned
help: return a value for the case when the loop has zero elements to iterate on
|
LL ~ }
LL ~ /* `i32` value */
|
help: otherwise consider changing the return type to account for that possibility
|
LL ~ fn foo() -> Option<i32> {
LL | for i in 0..0 {
LL ~ return Some(i);
LL ~ }
LL ~ None
|
```
Fix#98982.
Rollup of 6 pull requests
Successful merges:
- #118012 (Add support for global allocation in smir)
- #118013 (Enable Rust to use the EHCont security feature of Windows)
- #118100 (Enable profiler in dist-powerpc64-linux)
- #118142 (Tighten up link attributes for llvm-wrapper bindings)
- #118147 (Fix some unnecessary casts)
- #118161 (Allow defining opaques in `check_coroutine_obligations`)
r? `@ghost`
`@rustbot` modify labels: rollup
Allow defining opaques in `check_coroutine_obligations`
In the new trait solver, when an obligation stalls on an unresolved coroutine witness, we will stash away the *root* obligation, even if the stalled obligation is only a distant descendent of the root obligation, since the new solver is purely recursive.
This means that we may need to reprocess alias-relate obligations (and others) which may define opaque types in the new solver. Currently, we use the coroutine's def id as the defining anchor in `check_coroutine_obligations`, which will allow defining no opaque types, resulting in errors like:
```
error[E0271]: type mismatch resolving `{coroutine@<source>:6:5: 6:17} <: impl Clone`
--> <source>:6:5
|
6 | / move |_: ()| {
7 | | let () = yield ();
8 | | }
| |_____^ types differ
```
So this PR fixes the defining anchor and does the same trick as `check_opaque_well_formed`, where we manually compare opaques that were defined against their hidden types to make sure they weren't defined differently when processing these stalled coroutine obligations.
r? `@lcnr` cc `@cjgillot`
Enable Rust to use the EHCont security feature of Windows
In the future Windows will enable Control-flow Enforcement Technology (CET aka Shadow Stacks). To protect the path where the context is updated during exception handling, the binary is required to enumerate valid unwind entrypoints in a dedicated section which is validated when the context is being set during exception handling.
The required support for EHCONT Guard has already been merged into LLVM, long ago. This change simply adds the Rust codegen option to enable it.
Relevant LLVM change: https://reviews.llvm.org/D40223
This also adds a new `ehcont-guard` option to the bootstrap config which enables EHCont Guard when building std.
We at Microsoft have been using this feature for a significant period of time; we are confident that the LLVM feature, when enabled, generates well-formed code.
We currently enable EHCONT using a codegen feature, but I'm certainly open to refactoring this to be a target feature instead, or to use any appropriate mechanism to enable it.
Add support for global allocation in smir
Add APIs to StableMir to support global allocation. Before this change, StableMir users had no API available to retrieve Allocation provenance information. They had to resource to internal APIs instead.
One example is retrieving the Allocation of an `&str`. See test for an example on how the API can be used.
Add allow-by-default lint for unit bindings
### Example
```rust
#![warn(unit_bindings)]
macro_rules! owo {
() => {
let whats_this = ();
}
}
fn main() {
// No warning if user explicitly wrote `()` on either side.
let expr = ();
let () = expr;
let _ = ();
let _ = expr; //~ WARN binding has unit type
let pat = expr; //~ WARN binding has unit type
let _pat = expr; //~ WARN binding has unit type
// No warning for let bindings with unit type in macro expansions.
owo!();
// No warning if user explicitly annotates the unit type on the binding.
let pat: () = expr;
}
```
outputs
```
warning: binding has unit type `()`
--> $DIR/unit-bindings.rs:17:5
|
LL | let _ = expr;
| ^^^^-^^^^^^^^
| |
| this pattern is inferred to be the unit type `()`
|
note: the lint level is defined here
--> $DIR/unit-bindings.rs:3:9
|
LL | #![warn(unit_bindings)]
| ^^^^^^^^^^^^^
warning: binding has unit type `()`
--> $DIR/unit-bindings.rs:18:5
|
LL | let pat = expr;
| ^^^^---^^^^^^^^
| |
| this pattern is inferred to be the unit type `()`
warning: binding has unit type `()`
--> $DIR/unit-bindings.rs:19:5
|
LL | let _pat = expr;
| ^^^^----^^^^^^^^
| |
| this pattern is inferred to be the unit type `()`
warning: 3 warnings emitted
```
This lint is not triggered if any of the following conditions are met:
- The user explicitly annotates the binding with the `()` type.
- The binding is from a macro expansion.
- The user explicitly wrote `let () = init;`
- The user explicitly wrote `let pat = ();`. This is allowed for local lifetimes.
### Known Issue
It is known that this lint can trigger on some proc-macro generated code whose span returns false for `Span::from_expansion` because e.g. the proc-macro simply forwards user code spans, and otherwise don't have distinguishing syntax context compared to non-macro-generated code. For those kind of proc-macros, I believe the correct way to fix them is to instead emit identifers with span like `Span::mixed_site().located_at(user_span)`.
Closes#71432.
Remove `feature` from the list of well known check-cfg name
This PR removes `feature` from the list of well known check-cfg.
This is done for multiple reasons:
- Cargo is the source of truth, rustc shouldn't have any knowledge of it
- It creates a conflict between Cargo and rustc when there are no features defined.
In this case Cargo won't pass any `--check-cfg` for `feature` since no feature will ever be passed, but rustc by having in it's list adds a implicit `cfg(feature, values(any()))` which is completely wrong. Having any cfg `feature` is unexpected not allow any `feature` value.
While doing this, I took the opportunity to specialise the diagnostic a bit for the case above.
r? `@petrochenkov`
Don't ICE when ambiguity is found when selecting `Index` implementation in typeck
Fixes#118111
The problem here is when we're manually "selecting" an impl for `base_ty: Index<?0>`, we don't consider placeholder region errors (leak check) or ambiguous predicates. Those can lead to us not actually emitting any fulfillment errors on line 3131.
In the future Windows will enable Control-flow Enforcement Technology
(CET aka Shadow Stacks). To protect the path where the context is
updated during exception handling, the binary is required to enumerate
valid unwind entrypoints in a dedicated section which is validated when
the context is being set during exception handling.
The required support for EHCONT has already been merged into LLVM,
long ago. This change adds the Rust codegen option to enable it.
Reference:
* https://reviews.llvm.org/D40223
This also adds a new `ehcont-guard` option to the bootstrap config which
enables EHCont Guard when building std.
The search sorting code already sorts by item type discriminant,
putting things with smaller discriminants first. There was
also a special case for sorting keywords and primitives earlier,
and this commit removes it by giving them lower discriminants.
The sorting code has another criteria where items with descriptions
appear earlier than items without, and that criteria has higher
priority than the item type. This shouldn't matter, though,
because primitives and keywords normally only appear in the
standard library, and it always gives them descriptions.
Fix early param lifetimes in generic_const_exprs
In cases like below, we never actually be able to capture region name for two reasons, first `'static` becomes anonymous lifetime and second we never capture region if it doesn't have a name so this results in ICE.
```
struct DataWrapper<'static> {
data: &'a [u8; Self::SIZE],
}
impl DataWrapper<'a> {
```
Fixes https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/118021
Remove `--check-cfg` checking of command line `--cfg` args
Back in https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/100574 we added to the `unexpected_cfgs` lint the checking of `--cfg` CLI arguments and emitted unexpected names and values for them.
The implementation works as expected, but it's usability in particular when using it in combination with Cargo+`RUSTFLAGS` as people who set `RUSTFLAGS=--cfg=tokio_unstable` (or whatever) have `unexpected_cfgs` warnings on all of their crates is debatable. ~~To fix this issue this PR proposes that we split the CLI argument checking into it's own separate allow-by-default lint: `unexpected_cli_cfgs`.~~
~~This has the advantage of letting people who want CLI warnings have them (although not by default anymore), while still linting on every unexpected cfg name and values in the code.~~
After some discussion with the Cargo team ([Zulip thread](https://rust-lang.zulipchat.com/#narrow/stream/246057-t-cargo/topic/check-cfg.20and.20RUSTFLAGS.20interaction)) and member of the compiler team (see below), I propose that we follow the suggestion from `@epage:` never check `--cfg` arguments, but still reserve us the possibility to do it later.
We would still lint on unexpected cfgs found in the source code no matter the `--cfg` args passed. This mean reverting https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/100574 but NOT https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/99519.
r? `@petrochenkov`
rustdoc-search: add support for traits and associated types
# Summary
Trait associated type queries work in rustdoc's type driven search. The data is included in the search-index.js file, and the queries are designed to "do what I mean" when users type them in, so, for example, `Iterator<Item=T> -> Option<T>` includes `Iterator::next` in the SERP[^SERP], and `Iterator<T> -> Option<T>` also includes `Iterator::next` in the SERP.
[^SERP]: search engine results page
## Sample searches
* [`iterator<Item=T>, fnmut -> T`][iterreduce]
* [`iterator<T>, fnmut -> T`][iterreduceterse]
[iterreduce]: http://notriddle.com/rustdoc-html-demo-5/associated-types/std/index.html?search=iterator%3CItem%3DT%3E%2C%20fnmut%20-%3E%20T&filter-crate=std
[iterreduceterse]: http://notriddle.com/rustdoc-html-demo-5/associated-types/std/index.html?search=iterator%3CT%3E%2C%20fnmut%20-%3E%20T&filter-crate=std
# Motivation
My primary motivation for working on search.js at all is to make it easier to use highly generic APIs, like the Iterator API. The type signature describes these functions pretty well, while the names are almost arbitrary.
Before this PR, type bindings were not consistently included in search-index.js at all (you couldn't find Iterator::next by typing in its function signature) and you couldn't explicitly search for them. This PR fixes both of these problems.
# Guide-level explanation
*Excerpt from [the Rustdoc book](http://notriddle.com/rustdoc-html-demo-5/associated-types/rustdoc/read-documentation/search.html), included in this PR.*
> Function signature searches can query generics, wrapped in angle brackets, and traits will be normalized like types in the search engine if no type parameters match them. For example, a function with the signature `fn my_function<I: Iterator<Item=u32>>(input: I) -> usize` can be matched with the following queries:
>
> * `Iterator<Item=u32> -> usize`
> * `Iterator<u32> -> usize` (you can leave out the `Item=` part)
> * `Iterator -> usize` (you can leave out iterator's generic entirely)
> * `T -> usize` (you can match with a generic parameter)
>
> Each of the above queries is progressively looser, except the last one would not match `dyn Iterator`, since that's not a type parameter.
# Reference-level explanation
Inside the angle brackets, you can choose whether to write a name before the parameter and the equal sign. This syntax is called [`GenericArgsBinding`](https://doc.rust-lang.org/reference/paths.html#paths-in-expressions) in the Rust Reference, and it allows you to constrain a trait's associated type.
As a convenience, you don't actually have to put the name in (Rust requires it, but Rustdoc Search doesn't). This works about the same way unboxing already works in Search: the terse `Iterator<u32>` is a match for `Iterator<Item=u32>`, but the opposite is not true, just like `u32` is a match for `Iterator<u32>`.
When converting a trait method for the search index, the trait is substituted for `Self`, and all associated types are bound to generics. This way, if you have the following trait definition:
```rust
pub trait MyTrait {
type Output;
fn method(self) -> Self::Output;
}
```
The following queries will match its method:
* `MyTrait<Output=T> -> T`
* `MyTrait<T> -> T`
* `MyTrait -> T`
But these queries will not match it:
* <i>`MyTrait<Output=u32> -> u32`</i>
* <i>`MyTrait<Output> -> Output`</i>
* <i>`MyTrait -> MyTrait::Output`</i>
# Drawbacks
It's a little bit bigger:
```console
$ du before/search-index1.74.0.js after/search-index1.74.0.js
4020 before/search-index1.74.0.js
4068 after/search-index1.74.0.js
```
# Rationale and alternatives
I don't want to just not do this. On it's own, it's not terribly useful, but in addition to searching by normal traits, this is also intended as a desugaring target for closures. That's why it needs to actually distinguish the two: it allows the future desugaring to distinguish function output and input.
The other alternative would be to not allow users to leave out the name, so `iterator<u32>` doesn't work. That would be unfortunate, because mixing up which ones have out params and which ones are plain generics is an easy enough mistake that the Rust compiler itself helps people out with it.
# Prior art
* <http://neilmitchell.blogspot.com/2020/06/hoogle-searching-overview.html>
The current Rustdoc algorithm, both before this PR and after it, has a fairly expensive matching algorithm over a fairly simple file format. Luckily, we aren't trying to scale to all of crates.io, so it's usable, but it's not great when I throw it at docs.servo.org
# Unresolved questions
Okay, but *how do we want to handle closures?* I know the system will desugar `FnOnce(T) -> U` into `trait:FnOnce<Output=U, primitive:tuple<T>>`, but what if I don't know what trait I'm looking for? This PR can merge with nothing, but it'd be nice to have a plan.
Specifically, how should the special form used to handle all varieties of basic callable: primitive:fn (function pointers), and trait:Fn, trait:FnOnce, and trait:FnMut should all be searchable using a single syntax, because I'm always forgetting which one is used in the function I'm looking for.
The essential question is how closely we want to copy Rust's own syntax. The tersest way to expression Option::map might be:
Option<T>, (T -> U) -> Option<U>
That's the approach I would prefer, but nobody's going to attempt it without being told, so maybe this would be better?
Option<T>, (fn(T) -> U) -> Option<U>
It does require double parens, but at least it's mostly unambiguous. Unfortunately, it looks like the syntax you'd use for function pointers, implying that if you specifically wanted to limit your search to function pointers, you'd need to use `primitive:fn(T) -> U`. Then again, searching is normally case-insensitive, so you'd want that anyway to disambiguate from `trait:Fn(T) -> U`.
# Future possibilities
## This thing really needs a ranking algorithm
That is, this PR increases the number of matches for some type-based queries. They're usually pretty good matches, but there's still more of them, and it's evident that if you have two functions, `foo(MyTrait<u8>)` and `bar(MyTrait<Item=u8>)`, if the user typed `MyTrait<u8>` then `foo` should show up first.
A design choice that these PRs have followed is that adding more stuff to the search query always reduces the number of functions that get matched. The advantage of doing it that way is that you can rank them by just counting how many atoms are in the function's signature (lowest score goes on top). Since it's impossible for a matching function to have fewer atoms than the search query, if there's a function with exactly the same set of atoms in it, then that'll be on top.
More complicated ranking algos tend to penalize long documents anyway, if the [distance metrics](https://www.benfrederickson.com/distance-metrics/?utm_source=flipboard&utm_content=other) I found through [Flipboard](https://flipboard.com/`@arnie0426/building-recommender-systems-nvue3iqtgrn10t45)` (and postgresql's `ts_rank_cd`) are anything to go by. Real-world data sets tend to have weird outliers, like they have God Functions with zillions of arguments of all sorts of types, and Rustdoc ought to put such a function at the bottom.
The other natural choice would be interleaving with `unifyFunctionTypes` to count the number of unboxings and reorderings. This would compute a distance function, and would do a fine job of ranking the results, as [described here](https://ndmitchell.com/downloads/slides-hoogle_finding_functions_from_types-16_may_2011.pdf) by the Hoogle dev, but is more complicated than it sounds. The current algorithm returns when it finds a result that *exists at all*, but a distance function should find an *optimal solution* to find the smallest sequence of edits.
## This could also use a benchmark suite and some optimization
This approach also lends itself to layering a bloom filter in front of the backtracking unification engine.
* At load time, hash the typeNameIdMap ID for each atom and set the matching entry in a fixed-size byte array for each function to 1. Call it `fnType.bloomFilter`
* At search time, do the same for the atoms in the query (excluding special forms like `[]` that can match more than one thing). Call it `parsedQuery.bloomFilter`
* For each function, `if (fnType.bloomFilter | (~parsedQuery.bloomFilter) !== ~0) { return false; }`
There's also room to optimize the unification engine itself, by using stacks and persistent data structures instead of copying arrays around, or by using hashing instead of linear scans (the current algorithm was rewritten from one that tried to do that, but was too much to fit in my head and had a bunch of bugs). The advantage of Just Backtracking Better over the bloom filter is that it doesn't require the engine to retain any special algebraic properties.
But, first, we need a set of benchmarks to be able to judge if such a thing will actually help.
## Referring to associated types by path
*I don't want to implement this one, but if I did, this is how I'd do it.*
In Rust, this is represented by a structure called a qualified path, or QPath. They look like this:
<Self as Iterator>::Item
<F as FnOnce>::Output
They can also, if it's unambiguous, use a plain path and just let the system figure it out:
Self::Item
F::Output
In Rustdoc Type-Driven Search, we don't want to force people to be unambiguous. Instead, we should try *all reasonable interpretations*, return results whenever any of them match, and let users make their query more specific if too many results are matches.
To enable associated type path searches in Rustdoc, we need to:
1. When lowering a trait method to a search-index.js function signature, Self should be explicitly represented as a generic argument. It should always be assigned `-1`, so that if the user uses `Self` in their search query, we can ensure it always matches the real Self and not something else. Any functions that don't *have* a Self should drop a `0` into the first position of the where clause, to express that there isn't one and reserve the `-1` position.
* Reminder: generics are negative, concrete types are positive, and zero is a reserved sentinel.
* Right now, `Iterator::next` is lowered as if it were `fn next<T>(self: Iterator<Item=T>) -> Option<T>`.
It should become `fn next<Self, T>(self: Self) -> Option<T> where Self: Iterator<Item=T>` instead.
3. Add another backtracking edge to the unification engine, so that when the user writes something like `some::thing`, the interpretation where `some` is a module and `thing` is a standalone item becomes one possible match candidate, while the interpretation where `some` is a trait and `thing` is an associated type is a separate match candidate. The backtracking engine is basically powerful enough to do this already, since unboxing generic type parameters into their traits already requires the ability to do this kind of thing.
* When interpreting `some::thing` where `some` is a trait and `thing` is an associated type, it should be treated equivalently to `<self as some>::thing`. If you want to bind it to some generic parameter other than `Self`, you need to explicitly say so.
* If no trait called `some` actually exists, treat it as a generic type parameter instead. Track every trait mentioned in the current working function signature, and add a match candidate for each one.
* A user that explicitly wants the trait-associated-type interpretation could write a qpath (like `<self as trait>::type`), and a user that explicitly wants the module-item interpretation should use an item type filter (like `struct:module::type`).
4. To actually do the matching, maintain a `Map<(QueryGenericParamId, TraitId), FnGenericParamId>` alongside the existing `Map<QueryGenericParamId, FnGenericParamId>` that is already used to handle plain generic parameters. This works, because, when a trait function signature is lowered to search-index.js, the `rustdoc` backend always generates an FnGenericParamId for every trait associated type it sees mentioned in the function's signature.
5. Parse QPaths. Specifically,
* QueryElem adds three new fields. `isQPath` is a boolean flag, and `traitNameId` contains an entry for `typeNameIdMap` corresponding to the trait part of a qpath, and `parentId` may contain either a concrete type ID or a negative number referring to a generic type parameter. The actual `id` of the query elem will always be a negative number, because this is essentially a funny way to add a generic type constraint.
* If it's a QPath, then both of those IDs get filled in with the respective parts of the map. The unification engine will check the where clause to ensure the trait actually applies to the generic parameter in question, will check the type parameter constraint, and will add a mapping to `mgens` recording this as a solution.
* If it's just a regular path, then `isQPath` is false, and the parser will fill in both `traitNameId` and `parentId` based on the same path. The unification engine, seeing isQPath is false and that these IDs were filled in, will try all three solutions: the path might be part of a concrete type name, or it might be referring to a trait, or it might be referring to a generic type parameter.
### Why not implement QPath searches?
I'm not sure if anybody really wants to write such complicated queries. You can do a pretty good job of describing the generic functions in the standard library without resorting to FQPs.
These two queries, for example, would both match the Iterator::map function if we added support for higher order function queries and a rule that allows a type to match its *notable traits*.
// I like this version, because it's identical to how `Option::map` would be written.
// There's a reason why Iterator::map and Option::map have the same name.
Iterator<T>, (T -> U) -> Iterator<U>
// This version explicitly uses the type parameter constraints.
Iterator<Item=T>, (T -> U) -> Iterator<Item=U>
If I try to write this one using FQP, however, the results seem worse:
// This one is less expressive than the versions that don't use associated type paths.
// It matches `Iterator::filter`, while the above two example queries don't.
Iterator, (Iterator::Item -> Iterator::Item) -> Iterator
// This doesn't work, because the return type of `Iterator::map` is not a generic
// parameter with an `Iterator` trait bound. It's a concrete type that
// implements `Iterator`. Return-Position-Impl-Trait is the same way.
//
// There's a difference between something like `map`, whose return value
// implements Iterator, and something like `collect`, where the caller
// gets to decide what the concrete type is going to be.
//Self, (Self::Item -> I::Item) -> I where Self: Iterator, I: Iterator
// This works, but it seems subjectively ugly, complex, and counterintuitive to me.
Self, (<Self as Iterator>::Item -> T) -> Iterator<Item=T>
Add `$message_type` field to distinguish json diagnostic outputs
Currently the json-formatted outputs have no way to unambiguously determine which kind of message is being output. A consumer can look for specific fields in the json object (eg "message"), but there's no guarantee that in future some other kind of output will have a field of the same name.
This PR adds a `"type"` field to add json outputs which can be used to unambiguously determine which kind of output it is. The mapping is:
`diagnostic`: regular compiler diagnostics
`artifact`: artifact notifications
`future_incompat`: Future incompatibility report
`unused_extern`: Unused crate warnings/errors
This matches the "internally tagged" representation for serde enums.
Add place.ty() and Ty build from a kind to smir
Add a method to retrieve the type of a place and a few utility functions needed to build the projection type. I decided to return a result to avoid panicking if the user passes invalid inputs, such as wrong list of locals.
r? `@spastorino`
When we encounter a function with a return type that has an anonymous
lifetime with no argument to borrow from, besides suggesting the
`'static` lifetime we now also suggest changing the arguments to be
borrows or changing the return type to be an owned type.
```
error[E0106]: missing lifetime specifier
--> $DIR/variadic-ffi-6.rs:7:6
|
LL | ) -> &usize {
| ^ expected named lifetime parameter
|
= help: this function's return type contains a borrowed value, but there is no value for it to be borrowed from
help: consider using the `'static` lifetime, but this is uncommon unless you're returning a borrowed value from a `const` or a `static`
|
LL | ) -> &'static usize {
| +++++++
help: instead, you are more likely to want to change one of the arguments to be borrowed...
|
LL | x: &usize,
| +
help: ...or alternatively, to want to return an owned value
|
LL - ) -> &usize {
LL + ) -> usize {
|
```
Fix#85843.
Don't consider regions in `deref_into_dyn_supertrait` lint
I actually wonder if we should just warn on *any* deref impl with a target type that matches a supertrait by *def-id*.
cc #89460
r? types
Typeck break expr even if break is illegal
Fixes#117821
We were returning immediately when encountering an illegal break. However, this caused problems later when the expr that the break was returning was evaluated during writeback. So now we don't return and instead simply set tainted by error. This lets typeck of break expr to occur even though we've encountered an illegal break.
Don't require intercrate mode for negative coherence
Negative coherence needs to be *sound*, but does not need to be *complete*, since it's looking for the *existence* of a negative goal, not the non-existence of a positive goal.
This removes some trivial and annoying ambiguities when a negative impl has region constraints.
r? lcnr idk if this needs an fcp but if it does, pls kick it off
Note about object lifetime defaults in does not live long enough error
This is a aspect of Rust that frequently trips up people who are not aware of it yet. This diagnostic attempts to explain what's happening and why the lifetime constraint, that was never mentioned in the source, arose.
The implementation feels a bit questionable, I'm not sure whether there are better ways to do this. There probably are.
fixes#117835
r? types
Add a test to ensure issue #89699 does not show up again. This test
emits an `async move` closure in a proc macro, which is used in a
test program compiled with edition 2015. We make sure the error message
is nice and shows up properly.
Rollup of 8 pull requests
Successful merges:
- #117828 (Avoid iterating over hashmaps in astconv)
- #117832 (interpret: simplify handling of shifts by no longer trying to handle signed and unsigned shift amounts in the same branch)
- #117891 (Recover `dyn` and `impl` after `for<...>`)
- #117957 (if available use a Child's pidfd for kill/wait)
- #117988 (Handle attempts to have multiple `cfg`d tail expressions)
- #117994 (Ignore but do not assume region obligations from unifying headers in negative coherence)
- #118000 (Make regionck care about placeholders in outlives components)
- #118068 (subtree update cg_gcc 2023/11/17)
r? `@ghost`
`@rustbot` modify labels: rollup
We were earlier returning immediately when encountering an illegal break. However, this caused problems later
when the expr that the break was returning was evaluated during writeback. So now we don't return and instead
simply set tainted by error. This lets typeck of break expr to occur even though we've encountered an illegal break.
Fix insertion of statements to be executed along return edge in inlining
Inlining creates additional statements to be executed along the return
edge: an assignment to the destination, storage end for temporaries.
Previously those statements where inserted directly into a call target,
but this is incorrect when the target has other predecessors.
Avoid the issue by creating a new dedicated block for those statements.
When the block happens to be redundant it will be removed by CFG
simplification that follows inlining.
Fixes#117355
Inlining creates additional statements to be executed along the return
edge: an assignment to the destination, storage end for temporaries.
Previously those statements where inserted directly into a call target,
but this is incorrect when the target has other predecessors.
Avoid the issue by creating a new dedicated block for those statements.
When the block happens to be redundant it will be removed by CFG
simplification that follows inlining.
Fixes#117355
This lint is not triggered if any of the following conditions are met:
- The user explicitly annotates the binding with the `()` type.
- The binding is from a macro expansion.
- The user explicitly wrote `let () = init;`
- The user explicitly wrote `let pat = ();`. This is allowed for local
lifetimes.
Make regionck care about placeholders in outlives components
Currently, we don't consider a placeholder type `!T` to be a type component when it comes to processing type-outlives obligations. This means that they are essentially treated like unit values with no sub-components, and always outlive any region. This is problematic for `non_lifetime_binders`, and even more problematic for `with_negative_coherence`, since negative coherence uses placeholders as universals.
This PR adds `Component::Placeholder` which acts much like `Component::Param`. This currently causes a regression in some non-lifetime-binders tests because `for<T> T: 'static` doesn't imply itself when processing outlives obligations, so code like this will fail:
```
fn foo() where for<T> T: 'static {
foo() //~ fails
}
```
Since the where clause doesn't imply itself. This requires making the `MatchAgainstHigherRankedOutlives` relation smarter when it comes to binders.
r? types
Ignore but do not assume region obligations from unifying headers in negative coherence
Partly addresses a FIXME that was added in #112875. Just as we can throw away the nested trait/projection obligations from unifying two impl headers, we can also just throw away the region obligations too.
I removed part of the FIXME that was incorrect, namely:
> Given that the only region constraints we get are involving inference regions in the root, it shouldn't matter, but still sus.
This is not true when unifying `fn(A)` and `for<'b> fn(&'b B)` which ends up with placeholder region outlives from non-root universes. I'm pretty sure this is okay, though it would be nice if we were to use them as assumptions. See the `explicit` revision of the test I committed, which still fails.
Fixes#117986
r? lcnr, feel free to reassign tho.
Recover `dyn` and `impl` after `for<...>`
Recover `dyn` and `impl` after `for<...>` in types. Reuses the logic for parsing bare trait objects, so it doesn't fix cases like `for<'a> dyn Trait + dyn Trait` or anything, but that seems somewhat of a different issue.
Parsing recovery logic is a bit involved, but I couldn't find a way to simplify it.
Fixes#117882
interpret: simplify handling of shifts by no longer trying to handle signed and unsigned shift amounts in the same branch
While we're at it, also update comments in codegen and MIR building related to shifts, and fix the overflow error printed by Miri on negative shift amounts.
When encountering struct fn call literal with private fields, suggest all builders
When encountering code like `Box(42)`, suggest `Box::new(42)` and *all* other associated functions that return `-> Box<T>`.
Add a way to give pre-sorted suggestions.
Ensure sanity of all computed ABIs
This moves the ABI sanity assertions from the codegen backend to the ABI computation logic. Sadly, due to past mistakes, we [have to](https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/117351#issuecomment-1788495503) be able to compute a sane ABI for nonsensical function types like `extern "C" fn(str) -> str`. So to make the sanity check pass we first need to make all ABI adjustment deal with unsized types... and we have no shared infrastructure for those adjustments, so that's a bunch of copy-paste. At least we have assertions failing loudly when one accidentally sets a different mode for an unsized argument.
To achieve this, this re-lands the parts of https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/80594 that got reverted in https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/81388. To avoid breaking wasm ABI again, that ABI now explicitly opts-in to the (wrong, broken) ABI that we currently keep for backwards compatibility. That's still better than having *every* ABI use the wrong broken default!
Cc `@bjorn3`
Fixes https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/115845