macros: `LintDiagnostic` derive
- Move `LintDiagnosticBuilder` into `rustc_errors` so that a diagnostic derive can refer to it.
- Introduce a `DecorateLint` trait, which is equivalent to `SessionDiagnostic` or `AddToDiagnostic` but for lints. Necessary without making more changes to the lint infrastructure as `DecorateLint` takes a `LintDiagnosticBuilder` and re-uses all of the existing logic for determining what type of diagnostic a lint should be emitted as (e.g. error/warning).
- Various refactorings of the diagnostic derive machinery (extracting `build_field_mapping` helper and moving `sess` field out of the `DiagnosticDeriveBuilder`).
- Introduce a `LintDiagnostic` derive macro that works almost exactly like the `SessionDiagnostic` derive macro except that it derives a `DecorateLint` implementation instead. A new derive is necessary for this because `SessionDiagnostic` is intended for when the generated code creates the diagnostic. `AddToDiagnostic` could have been used but it would have required more changes to the lint machinery.
~~At time of opening this pull request, ignore all of the commits from #98624, it's just the last few commits that are new.~~
r? `@oli-obk`
Fix repr(align) enum handling
`enum`, for better or worse, supports `repr(align)`. That has already caused a bug in https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/92464, which was "fixed" in https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/92932, but it turns out that that fix is wrong and caused https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/96185.
So this reverts #92932 (which fixes#96185), and attempts another strategy for fixing #92464: special-case enums when doing a cast, re-using the code to load the discriminant rather than assuming that the enum has scalar layout. This works fine for the interpreter.
However, #92464 contained another testcase that was previously not in the test suite -- and after adding it, it ICEs again. This is not surprising; codegen needs the same patch that I did in the interpreter. Probably this has to happen [around here](d32ce37a17/compiler/rustc_codegen_ssa/src/mir/rvalue.rs (L276)). Unfortunately I don't know how to do that -- the interpreter can load a discriminant from an operand, but codegen can only do that from a place. `@oli-obk` `@eddyb` `@bjorn3` any idea?
lints: mostly translatable diagnostics
As lints are created slightly differently than other diagnostics, intended to try make them translatable first and then look into the applicability of diagnostic structs but ended up just making most of the diagnostics in the crate translatable (which will still be useful if I do make a lot of them structs later anyway).
r? ``@compiler-errors``
Change enum->int casts to not go through MIR casts.
follow-up to https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/96814
this simplifies all backends and even gives LLVM more information about the return value of `Rvalue::Discriminant`, enabling optimizations in more cases.
Interpret: AllocRange Debug impl, and use it more consistently
The two commits are pretty independent but it did not seem worth having two PRs for them.
r? ``@oli-obk``
Add method to mutate MIR body without invalidating CFG caches.
In addition to adding this method, a handful of passes are updated to use it. There's still quite a few passes that could in principle make use of this as well, but do not at the moment because they use `VisitorMut` or `MirPatch`, which needs additional support for this.
The method name is slightly unwieldy, but I don't expect anyone to be writing it a lot, and at least it says what it does. If anyone has a suggestion for a better name though, would be happy to rename.
r? rust-lang/mir-opt
CTFE interning: don't walk allocations that don't need it
The interning of const allocations visits the mplace looking for references to intern. Walking big aggregates like big static arrays can be costly, so we only do it if the allocation we're interning contains references or interior mutability.
Walking ZSTs was avoided before, and this optimization is now applied to cases where there are no references/relocations either.
---
While initially looking at this in the context of #93215, I've been testing with smaller allocations than the 16GB one in that issue, and with different init/uninit patterns (esp. via padding).
In that example, by default, `eval_to_allocation_raw` is the heaviest query followed by `incr_comp_serialize_result_cache`. So I'll show numbers when incremental compilation is disabled, to focus on the const allocations themselves at 95% of the compilation time, at bigger array sizes on these minimal examples like `static ARRAY: [u64; LEN] = [0; LEN];`.
That is a close construction to parts of the `ctfe-stress-test-5` benchmark, which has const allocations in the megabytes, while most crates usually have way smaller ones. This PR will have the most impact in these situations, as the walk during the interning starts to dominate the runtime.
Unicode crates (some of which are present in our benchmarks) like `ucd`, `encoding_rs`, etc come to mind as having bigger than usual allocations as well, because of big tables of code points (in the hundreds of KB, so still an order of magnitude or 2 less than the stress test).
In a check build, for a single static array shown above, from 100 to 10^9 u64s (for lengths in powers of ten), the constant factors are lowered:
(log scales for easier comparisons)
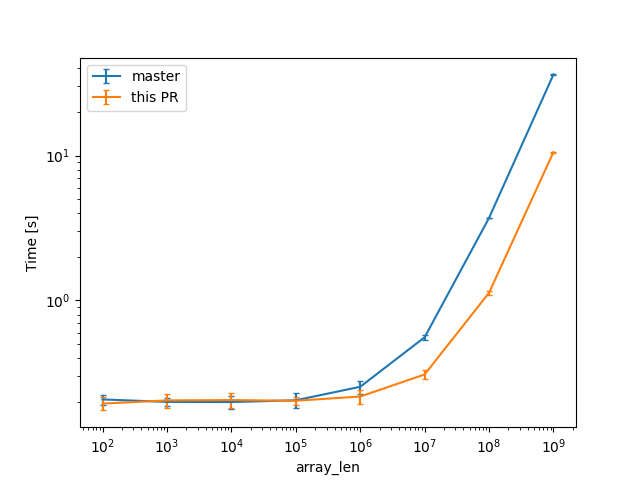
(linear scale for absolute diff at higher Ns)
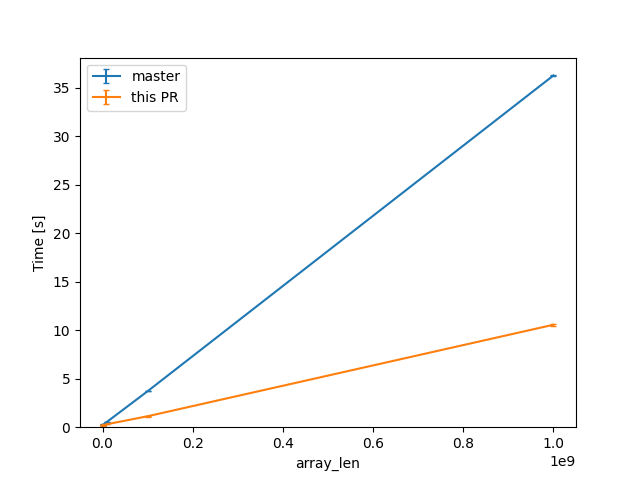
For one of the alternatives of that issue
```rust
const ROWS: usize = 100_000;
const COLS: usize = 10_000;
static TWODARRAY: [[u128; COLS]; ROWS] = [[0; COLS]; ROWS];
```
we can see a similar reduction of around 3x (from 38s to 12s or so).
For the same size, the slowest case IIRC is when there are uninitialized bytes e.g. via padding
```rust
const ROWS: usize = 100_000;
const COLS: usize = 10_000;
static TWODARRAY: [[(u64, u8); COLS]; ROWS] = [[(0, 0); COLS]; ROWS];
```
then interning/walking does not dominate anymore (but means there is likely still some interesting work left to do here).
Compile times in this case rise up quite a bit, and avoiding interning walks has less impact: around 23%, from 730s on master to 568s with this PR.
Fix FFI-unwind unsoundness with mixed panic mode
UB maybe introduced when an FFI exception happens in a `C-unwind` foreign function and it propagates through a crate compiled with `-C panic=unwind` into a crate compiled with `-C panic=abort` (#96926).
To prevent this unsoundness from happening, we will disallow a crate compiled with `-C panic=unwind` to be linked into `panic-abort` *if* it contains a call to `C-unwind` foreign function or function pointer. If no such call exists, then we continue to allow such mixed panic mode linking because it's sound (and stable). In fact we still need the ability to do mixed panic mode linking for std, because we only compile std once with `-C panic=unwind` and link it regardless panic strategy.
For libraries that wish to remain compile-once-and-linkable-to-both-panic-runtimes, a `ffi_unwind_calls` lint is added (gated under `c_unwind` feature gate) to flag any FFI unwind calls that will cause the linkable panic runtime be restricted.
In summary:
```rust
#![warn(ffi_unwind_calls)]
mod foo {
#[no_mangle]
pub extern "C-unwind" fn foo() {}
}
extern "C-unwind" {
fn foo();
}
fn main() {
// Call to Rust function is fine regardless ABI.
foo::foo();
// Call to foreign function, will cause the crate to be unlinkable to panic-abort if compiled with `-Cpanic=unwind`.
unsafe { foo(); }
//~^ WARNING call to foreign function with FFI-unwind ABI
let ptr: extern "C-unwind" fn() = foo::foo;
// Call to function pointer, will cause the crate to be unlinkable to panic-abort if compiled with `-Cpanic=unwind`.
ptr();
//~^ WARNING call to function pointer with FFI-unwind ABI
}
```
Fix#96926
`@rustbot` label: T-compiler F-c_unwind
Enable MIR inlining
Continuation of https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/82280 by `@wesleywiser.`
#82280 has shown nice compile time wins could be obtained by enabling MIR inlining.
Most of the issues in https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/81567 are now fixed,
except the interaction with polymorphization which is worked around specifically.
I believe we can proceed with enabling MIR inlining in the near future
(preferably just after beta branching, in case we discover new issues).
Steps before merging:
- [x] figure out the interaction with polymorphization;
- [x] figure out how miri should deal with extern types;
- [x] silence the extra arithmetic overflow warnings;
- [x] remove the codegen fulfilment ICE;
- [x] remove the type normalization ICEs while compiling nalgebra;
- [ ] tweak the inlining threshold.
cleanup mir visitor for `rustc::pass_by_value`
by changing `& $($mutability)?` to `$(& $mutability)?`
I also did some formatting changes because I started doing them for the visit methods I changed and then couldn't get myself to stop xx, I hope that's still fairly easy to review.
Accept `DiagnosticMessage` in `LintDiagnosticBuilder::build` so that
lints can be built with translatable diagnostic messages.
Signed-off-by: David Wood <david.wood@huawei.com>
move MIR syntax into a dedicated file and ping some people whenever it changes
Adding or changing MIR operations/statements/whatever should be under significant scrutiny wrt their wider impact, specified semantics, and so on. So let's start by putting all that into a dedicated file and pinging some people whenever that file changes.
This PR only moves definitions around, and then fiddles with imports until it all works again.