Reserve prefixed identifiers and literals (RFC 3101)
This PR denies any identifiers immediately followed by one of three tokens `"`, `'` or `#`, which is stricter than the requirements of RFC 3101 but may be necessary according to the discussion at [Zulip].
[Zulip]: https://rust-lang.zulipchat.com/#narrow/stream/268952-edition-2021/topic/reserved.20prefixes/near/238470099
The tracking issue #84599 says we'll add a feature gate named `reserved_prefixes`, but I don't think I can do this because it is impossible for the lexer to know whether a feature is enabled or not. I guess determining the behavior by the edition information should be enough.
Fixes#84599
2229: Capture box completely in move closures
Even if the content from box is used in a sharef-ref context,
we capture the box entirerly.
This is motivated by:
1) We only capture data that is on the stack.
2) Capturing data from within the box might end up moving more data than
the user anticipated.
Closes https://github.com/rust-lang/project-rfc-2229/issues/50
r? `@nikomatsakis`
Fix ICE with `-Zunpretty=hir,typed`
This PR fixes#82328. The `-Zunpretty=hir,typed` pretty-printer maintains an `Option` with type-checking results and sets the `Option` to `Some` when entering a body. However, this leads to an ICE if an expression occurs in a function signature (i.e. outside of a body), such as `128` in
```rust
fn foo(-128..=127: i8) {}
```
This PR fixes the ICE by checking (if necessary) whether the expression's owner has a body, and retrieving type-checking results for that on the fly.
Allow loading of llvm plugins on nightly
Based on a discussion in #82734 / with `@wsmoses.`
Mainly moves [this](0149bc4e7e) behind a -Z flag, so it can only be used on nightly,
as requested by `@nagisa` in https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/82734#issuecomment-835863940
This change allows loading of llvm plugins like Enzyme.
Right now it also requires a shared library LLVM build of rustc for symbol resolution.
```rust
// test.rs
extern { fn __enzyme_autodiff(_: usize, ...) -> f64; }
fn square(x : f64) -> f64 {
return x * x;
}
fn main() {
unsafe {
println!("Hello, world {} {}!", square(3.0), __enzyme_autodiff(square as usize, 3.0));
}
}
```
```
./rustc test.rs -Z llvm-plugins="./LLVMEnzyme-12.so" -C passes="enzyme"
./test
Hello, world 9 6!
```
I will try to figure out how to simplify the usage and get this into stable in a later iteration,
but having this on nightly will already help testing further steps.
Use HTTPS links where possible
While looking at #86583, I wondered how many other (insecure) HTTP links were in `rustc`. This changes most other `http` links to `https`. While most of the links are in comments or documentation, there are a few other HTTP links that are used by CI that are changed to HTTPS.
Notes:
- I didn't change any to or in licences
- Some links don't support HTTPS :(
- Some `http` links were dead, in those cases I upgraded them to their new places (all of which used HTTPS)
Check that `#[cmse_nonsecure_entry]` is applied to a function definition
This PR fixes#83475. The compiler currently neglects to check whether `#[cmse_nonsecure_entry]` is applied to a function (and not, say, a struct) definition, leading to an ICE later on when the type checker attempts to retrieve the function signature. I have fixed this problem by adding an appropriate check to the `check_attr` pass, so that an error is reported instead of an ICE.
Rollup of 5 pull requests
Successful merges:
- #86330 (Change how edition based future compatibility warnings are handled)
- #86513 (Rustdoc: Do not list impl when trait has doc(hidden))
- #86592 (Use `#[non_exhaustive]` where appropriate)
- #86608 (chore(rustdoc): remove unused members of RenderType)
- #86624 (Update compiler-builtins)
Failed merges:
r? `@ghost`
`@rustbot` modify labels: rollup
Use `#[non_exhaustive]` where appropriate
Due to the std/alloc split, it is not possible to make `alloc::collections::TryReserveError::AllocError` non-exhaustive without having an unstable, doc-hidden method to construct (which negates the benefits from `#[non_exhaustive]`).
`@rustbot` label +C-cleanup +T-libs +S-waiting-on-review
rustc_data_structures has a dependency on crossbeam-utils but never uses
it. It appears to have originally had this dependency in order to set
the "nightly" feature; however, its other dependencies use a different
version of crossbeam-utils, so this doesn't actually affect anything.
Furthermore, in current crossbeam-utils, the "nightly" feature has
become a no-op.
The sha-1 and md-5 packages contain crates named sha1 and md5,
respectively. This discrepancy makes it somewhat more challenging to
automate detection of unused crates. Explicitly rename the packages to
the names of the crates they contain, to simplify such detection.
Don't lint :pat when re-parsing a macro from another crate.
`compile_macro` is used both when compiling the original definition in the crate that defines it, and to compile the macro when loading it when compiling a crate that uses it. We should only emit lints in the first case.
This adds a `is_definition: bool` to pass this information in, so we don't warn about things that only concern the definition site.
Fixes#86567
Even if the content from box is used in a sharef-ref context,
we capture the box entirerly.
This is motivated by:
1) We only capture data that is on the stack.
2) Capturing data from within the box might end up moving more data than
the user anticipated.
Fix use placement for suggestions near main.
This fixes an edge case for the suggestion to add a `use`. When running with `--test`, the `main` function will be annotated with an `#[allow(dead_code)]` attribute. The `UsePlacementFinder` would end up using the dummy span of that synthetic attribute. If there are top-level inner attributes, this would place the `use` in the wrong position. The solution here is to ignore attributes with dummy spans.
In the process of working on this, I discovered that the `use_suggestion_placement` test was broken. `UsePlacementFinder` is unaware of active attributes. Attributes like `#[derive]` don't exist in the AST since they are removed. Fixing that is difficult, since the AST does not retain enough information. I considered trying to place the `use` towards the top of the module after any `extern crate` items, but I couldn't find a way to get a span for the start of a module block (the `mod` span starts at the `mod` keyword, and it seems tricky to find the spot just after the opening bracket and past inner attributes). For now, I just put some comments about the issue. This appears to have been a known issue in #44215 where the test for it was introduced, and the fix seemed to be deferred to later.
Due to the std/alloc split, it is not possible to make
`alloc::collections::TryReserveError::AllocError` non-exhaustive without
having an unstable, doc-hidden method to construct (which negates the
benefits from `#[non_exhaustive]`.
Permit zero non-zero-field on transparent types
Fixes#77841
This makes the transparent fields meet the below:
> * A `repr(transparent)` type `T` must meet the following rules:
> * It may have any number of 1-ZST fields
> * In addition, it may have at most one other field of type U
r? `@nikomatsakis`
Support lowercase error codes in `--explain`
This enables `rustc --explain` to accept a lowercase error code. Thus, for instance, `rustc --explain e0573` would be valid after this change, where before a user would have needed to do `rustc --explain E0573`. Although the upper case form of an error code is canonical, the user may prefer the easier-to-type lowercase form, and there's nothing to be gained by forcing them to type the upper case version.
Resolves#86518.
Error code cleanup and enforce checks
Fixes#86097.
It now checks if an error code is unused, and if so, will report an error if the error code wasn't commented out in the `error_codes.rs` file. It also checks that the constant used in the tidy check is up-to-date.
r? `@Mark-Simulacrum`
Check whether the closure's owner is an ADT in thir-unsafeck
This pull request fixes#85871. The code in `rustc_mir_build/src/check_unsafety.rs` incorrectly assumes that a closure's owner always has a body, but only functions, closures, and constants have bodies, whereas a closure can also appear inside a struct or enum:
```rust
struct S {
arr: [(); match || 1 { _ => 42 }]
}
enum E {
A([(); { || 1; 42 }])
}
```
This pull request fixes the resulting ICE by checking whether the closure's owner is an ADT and only deferring to `thir_check_unsafety(owner)` if it isn't.
Better errors for Debug and Display traits
Currently, if someone tries to pass value that does not implement `Debug` or `Display` to a formatting macro, they get a very verbose and confusing error message. This PR changes the error messages for missing `Debug` and `Display` impls to be less overwhelming in this case, as suggested by #85844. I was a little less aggressive in changing the error message than that issue proposed. Still, this implementation would be enough to reduce the number of messages to be much more manageable.
After this PR, information on the cause of an error involving a `Debug` or `Display` implementation would suppressed if the requirement originated within a standard library macro. My reasoning was that errors originating from within a macro are confusing when they mention details that the programmer can't see, and this is particularly problematic for `Debug` and `Display`, which are most often used via macros. It is possible that either a broader or a narrower criterion would be better. I'm quite open to any feedback.
Fixes#85844.
Rollup of 6 pull requests
Successful merges:
- #86223 (Specify the kind of the item for E0121)
- #86521 (Add comments around code where ordering is important due for panic-safety)
- #86523 (Improvements to intra-doc link macro disambiguators)
- #86542 (Line numbers aligned with content)
- #86549 (Add destructuring example of E0508)
- #86557 (Update books)
Failed merges:
- #86548 (Fix crate filter search reset)
r? `@ghost`
`@rustbot` modify labels: rollup
Re-add support for parsing (and pretty-printing) inner-attributes in match body
Re-add support for parsing (and pretty-printing) inner-attributes within body of a `match`.
In other words, we can do `match EXPR { #![inner_attr] ARM_1 ARM_2 ... }` again.
I believe this unbreaks the only four crates that crater flagged as broken by PR #83312.
(I am putting this up so that the lang-team can check it out and decide whether it changes their mind about what to do regarding PR #83312.)
Fix emit path hashing
With `--emit KIND=PATH`, the PATH should not affect hashes used for dependency tracking. It does not with other ways of specifying output paths (`-o` or `--out-dir`).
Also updates `rustc -Zls` to print more info about crates, which is used here to implement a `run-make` test.
It seems there was already a test explicitly checking that `OutputTypes` hash *is* affected by the path. I think this behaviour is wrong, so I updated the test.
Disambiguate between SourceFiles from different crates even if they have the same path
This PR fixes an ICE that can occur when the compiler encounters a source file that is part of both the local crate and an upstream crate:
1. While importing source files from an upstream crate the compiler creates a `SourceFile` entry for `foo.rs` in the `SourceMap`. Since this is an imported source file its `src` field is `None`.
2. At a later point the parser encounters `foo.rs` again. It tells the `SourceMap` to load the file but because we already have an entry for `foo.rs` the `SourceMap` will return the existing version with `src == None`.
3. The parser proceeds under the assumption that `src.is_some()` and panics when actually trying to use the file's contents.
This PR fixes the issue by adding the source file's associated `CrateNum` to the `SourceMap`'s interning key. As a consequence the two instances of the file will each have a separate entry in the `SourceMap`. They just happen to share the same file path. This approach seemed less problematic to me than trying to mutate the `SourceFile` after it had already been created.
Another, more involved, approach might be to merge the `src` and the `external_src` field.
Fixes#85955
Fix `unused_unsafe` around `await`
Enables `unused_unsafe` lint for `unsafe { future.await }`.
The existing test for this is `unsafe { println!() }`, so I assume that `println!` used to contain compiler-generated unsafe but this is no longer true, and so the existing test is broken. I replaced the test with `unsafe { ...await }`. I believe `await` is currently the only instance of compiler-generated unsafe.
Reverts some parts of #85421, but the issue predates that PR.
Add `future_prelude_collision` lint
Implements #84594. (RFC rust-lang/rfcs#3114 ([rendered](https://github.com/rust-lang/rfcs/blob/master/text/3114-prelude-2021.md))) Not entirely complete but wanted to have my progress decently available while I finish off the last little bits.
Things left to implement:
* [x] UI tests for lints
* [x] Only emit lint for 2015 and 2018 editions
* [ ] Lint name/message bikeshedding
* [x] Implement for `FromIterator` (from best I can tell, the current approach as mentioned from [this comment](https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/84594#issuecomment-847288288) won't work due to `FromIterator` instances not using dot-call syntax, but if I'm correct about this then that would also need to be fixed for `TryFrom`/`TryInto`)*
* [x] Add to `rust-2021-migration` group? (See #85512) (added to `rust-2021-compatibility` group)
* [ ] Link to edition guide in lint docs
*edit: looked into it, `lookup_method` will also not be hit for `TryFrom`/`TryInto` for non-dotcall syntax. If anyone who is more familiar with typecheck knows the equivalent for looking up associated functions, feel free to chime in.
Rollup of 11 pull requests
Successful merges:
- #85054 (Revert SGX inline asm syntax)
- #85182 (Move `available_concurrency` implementation to `sys`)
- #86037 (Add `io::Cursor::{remaining, remaining_slice, is_empty}`)
- #86114 (Reopen#79692 (Format symbols under shared frames))
- #86297 (Allow to pass arguments to rustdoc-gui tool)
- #86334 (Resolve type aliases to the type they point to in intra-doc links)
- #86367 (Fix comment about rustc_inherit_overflow_checks in abs().)
- #86381 (Add regression test for issue #39161)
- #86387 (Remove `#[allow(unused_lifetimes)]` which is now unnecessary)
- #86398 (Add regression test for issue #54685)
- #86493 (Say "this enum variant takes"/"this struct takes" instead of "this function takes")
Failed merges:
r? `@ghost`
`@rustbot` modify labels: rollup
Say "this enum variant takes"/"this struct takes" instead of "this function takes"
This makes error messages for functions with incorrect argument counts adapt if they refer to a struct or enum variant:
```
error[E0061]: this enum variant takes 1 argument but 0 arguments were supplied
--> $DIR/struct-enum-wrong-args.rs:7:13
|
LL | let _ = Ok();
| ^^-- supplied 0 arguments
| |
| expected 1 argument
error[E0061]: this struct takes 1 argument but 0 arguments were supplied
--> $DIR/struct-enum-wrong-args.rs:8:13
|
LL | let _ = Wrapper();
| ^^^^^^^-- supplied 0 arguments
| |
| expected 1 argument
```
Fixes#86481.
Add MIR pass to lower call to `core::slice::len` into `Len` operand
During some larger experiment with range analysis I've found that code like `let l = slice.len()` produces different MIR then one found in bound checks. This optimization pass replaces terminators that are calls to `core::slice::len` with just a MIR operand and Goto terminator.
It uses some heuristics to remove the outer borrow that is made to call `core::slice::len`, but I assume it can be eliminated, just didn't find how.
Would like to express my gratitude to `@oli-obk` who helped me a lot on Zullip
Emit warnings for unused fields in custom targets.
Add a warning which lists any fields in a custom target `json` file that aren't used. Currently unrecognized fields are ignored so, for example, a typo in the `json` will silently produce a target which isn't the one intended.
Do not emit alloca for ZST locals with multiple assignments
This extends 35566bfd7d to additionally stop emitting unnecessary allocas for zero sized locals that are assigned multiple times.
When rebuilding the standard library with `-Zbuild-std` this reduces the number of locals that require an allocation from 62315 to 61767.
Replace some `std::iter::repeat` with `str::repeat`
I noticed that there were some instances where `std::iter::repeat` would be used to repeat a string or a char to take a specific count of it and then collect it into a `String` when `str::repeat` is actually much faster and better for that.
See also: https://github.com/rust-lang/rust-clippy/issues/7260.
Add pattern walking support to THIR walker
Suggested in https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/85263#issuecomment-861906730, this splits off the support for pattern walking in THIR from #85263. This has no observable effect on THIR unsafety checking, since it is not currently possible to trigger unsafety from the THIR checker using the additional patterns or constants that are now walked. THIR patterns are walked in source code order.
r? `@LeSeulArtichaut`
Fix ICE with `#[repr(simd)]` on enum
This pull request fixes#83505. `#[repr(simd)]` may only be applied to structs, which correctly causes `E0517` for the example given in #83505, but the compiler attempts to recover from this error, which leads to an ICE later, when `.non_enum_variant()` is called on the `AdtDef`. I have added a check that prevents this from happening.
make UB during CTFE a hard error
This is a next step for https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/71800. `const_err` has been a future-incompatibility lint for 4 months now since https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/80394 (and err-by-default for many years before that), so I think we could try making it a proper hard error at least in some situations.
I didn't yet adjust the tests, since I first want to gauge the fall-out via crater.
Cc `@rust-lang/wg-const-eval`
Remove some last remants of {push,pop}_unsafe!
These macros have already been removed, but there was still some code handling these macros. That code is now removed.
Provide option for specifying the profiler runtime
Currently, if `-Zinstrument-coverage` is enabled, the target is linked
against the `library/profiler_builtins` crate (which pulls in LLVM's
compiler-rt runtime).
This option enables backends to specify an alternative runtime crate for
handling injected instrumentation calls.
Use `AttrVec` for `Arm`, `FieldDef`, and `Variant`
Uses `AttrVec` for `Arm`, `FieldDef`, and `Variant`, i.e., where the size of the vector can be empty often.
Skips `Crate` and `Item` because I think they may have the attributes on common cases and need more work outside of `rustc_ast` (e.g. rustc_expand needs a lot of tweaks). But if it's reasonable to change, I'm happy to do so.
Fixes#77662
Fix ICE when using `#[doc(keyword = "...")]` on non-items
This pull request fixes#83512. The code for checking attributes calls `expect_item()` when it shouldn't, thus causing an ICE. I have implemented a proper check for the node kind, so that an error is reported instead of the ICE.
Make `s` pre-interned
Now we should be able to pre-intern `s` as the test `ui/lint/rfc-2457-non-ascii-idents/lint-confusable-idents.rs` no longer fails.
Prefer `partition_point` to look up assoc items
Since we now have `partition_point` (instead of `equal_range`), I think it's worth trying to use it instead of manually finding it.
`partition_point` uses `binary_search_by` internally (#85406) and its performance has been improved (#74024), so I guess this will make a performance difference.
Use better error message for hard errors in CTFE
I noticed this while working on #86255: currently the same message is used for hard errors and soft errors in CTFE. This changes the error messages to make hard errors use a message that indicates the reality of the situation correctly, since usage of the constant is never allowed when there was a hard error evaluating it. This doesn't affect the behaviour of these error messages, only the content.
This changes the error logic to check if the error should be hard or soft where it is generated, instead of where it is emitted, to allow this distinction in error messages.
Replace parent substs of associated types with inference vars in borrow checker
Fixes https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/83190
Fixes https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/78450
When we normalize an associated type that refers to an opaque type, it can happen that the substs of the associated type do not occur in the projection (they are parent substs). We previously didn't replace those substs with inference vars, which left a concrete region after all regions should have already been replaced with inference vars and triggered a `delay_span_bug`. After we normalize the opaque type, we now try to replace any remaining concrete regions with inference vars.
Handle C-variadic arguments properly when reporting region errors
This pull request fixes#86053. The issue is that for a C-variadic function
```rust
#![feature(c_variadic)]
unsafe extern "C" fn foo(_: (), ...) {}
```
`foo`'s signature will contain only the first parameter (and have `c_variadic` set to `true`), whereas its body has a second argument (a `hir::Pat` for the `...`).
The code for reporting region errors iterates over the body's parameters and tries to fetch the corresponding parameter from the signature; this causes an out-of-bounds ICE for the `...` (though not in the example above, because there are no region errors to report).
I have simply restricted the iteration over the body parameters to exclude `...`, which is fine because `...` cannot cause a region error.
Stop returning a value from `report_assert_as_lint`
This function only ever returns `None`. Make that explicity by not returning a value at all.
`@rustbot` modify labels +C-cleanup +T-compiler
Fix span calculation in format strings
This pull request fixes#86085. The ICE described there is due to an error in the span calculation inside format strings, if the format string is the result of a macro invocation:
```rust
fn main() {
format!(concat!("abc}"));
}
```
currently produces:
```
error: invalid format string: unmatched `}` found
--> test.rs:2:17
|
2 | format!(concat!("abc}"));
| ^ unmatched `}` in format string
```
which is obviously incorrect. This happens because the span of the entire `concat!()` is combined with the _relative_ location of the unmatched `` `}` `` in the _result_ of the macro invocation (i.e. 4).
In #86085, this has led to a span that starts or ends in the middle of a multibyte character, but the root cause was the same. This pull request fixes the problem.
Box `thir::ExprKind::Adt` for performance
`Adt` is the biggest variant in the enum and probably isn't used very often compared to the other expr kinds, so boxing it should be beneficial for performance. We need a perf test to be sure.
Refactor vtable codegen
This refactor the codegen of vtables of miri interpreter, llvm, cranelift codegen backends.
This is preparation for the implementation of trait upcasting feature. cc #65991
Note that aside from code reorganization, there's an internal behavior change here that now InstanceDef::Virtual's index now include the three metadata slots, and now the first method is with index 3.
cc `@RalfJung` `@bjorn3`
Currently the same message is used for hard errors and soft errors. This
makes hard errors use a message that indicates the reality of the
situation correctly, since usage of the constant is never allowed when
there was a hard error evaluating it.
Improve CTFE UB validation error messages
As mentioned in https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/86245#discussion_r650494012 this PR slightly improves the formatting of validation errors, to move the path to the error prefix.
From:
`type validation failed: encountered invalid vtable: size is bigger than largest supported object at .0`
To:
`type validation failed at .0: encountered invalid vtable: size is bigger than largest supported object`.
Fix force-warns to allow dashes.
The `--force-warns` flag was not allowing lint names with dashes, only supporting underscores. This changes it to allow dashes to match the behavior of the A/W/D/F flags.
Fix ICEs on invalid vtable size/alignment const UB errors
The invalid vtable size/alignment errors from `InterpCx::read_size_and_align_from_vtable` were "freeform const UB errors", causing ICEs when reaching validation. This PR turns them into const UB hard errors to catch them during validation and avoid that.
Fixes#86193
r? `@RalfJung`
(It seemed cleaner to have 2 variants but they can be merged into one variant with a message payload if you prefer that ?)
Do not suggest to add type annotations for unnameable types
Consider this example:
```rust
const A = || 42;
struct S<T> { t: T }
const B: _ = S { t: || 42 };
```
This currently produces the following output:
```
error: missing type for `const` item
--> src/lib.rs:1:7
|
1 | const A = || 42;
| ^ help: provide a type for the item: `A: [closure@src/lib.rs:1:11: 1:16]`
error[E0121]: the type placeholder `_` is not allowed within types on item signatures
--> src/lib.rs:4:10
|
4 | const B: _ = S { t: || 42 };
| ^
| |
| not allowed in type signatures
| help: replace `_` with the correct type: `S<[closure@src/lib.rs:4:21: 4:26]>`
error: aborting due to 2 previous errors
```
However, these suggestions are obviously useless, because the suggested types cannot be written down. With my changes, the suggestion is replaced with a note, because there is no simple fix:
```
error: missing type for `const` item
--> test.rs:1:7
|
1 | const A = || 42;
| ^
|
note: however, the inferred type `[closure@test.rs:1:11: 1:16]` cannot be named
--> test.rs:1:11
|
1 | const A = || 42;
| ^^^^^
error[E0121]: the type placeholder `_` is not allowed within types on item signatures
--> test.rs:4:10
|
4 | const B: _ = S { t: || 42 };
| ^ not allowed in type signatures
|
note: however, the inferred type `S<[closure@test.rs:4:21: 4:26]>` cannot be named
--> test.rs:4:14
|
4 | const B: _ = S { t: || 42 };
| ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
error: aborting due to 2 previous errors
```
Hash DefId in rustc_span.
This is mostly just moving code around. Changes are simplifications of unneeded callbacks from rustc_span to rustc_middle.
r? `@petrochenkov`
Make `relate_type_and_mut` public
#85343 improved diagnostics around `Relate` impls but made `relate_type_and_mut` private, which was accessible as `relate` previously. This makes it public so that we can use it on rust-semverver.
r? ```@Aaron1011```
Detect incorrect vtable alignment during const eval
This PR fixes#86132 by detecting invalid alignment values for trait objects in the interpreter, and emitting an error about this conversion failure, to avoid the ICE.
I've noticed that the error emitted at a50d72158e/compiler/rustc_mir/src/interpret/traits.rs (L163-L166) doesn't seem to be present in the const-ub tests, so I've tried adding a test that triggers both of these cases: one for the invalid size, and another for the invalid alignment that #86132 tracks (I have found different magic values triggering different `Align::from_bytes` errors than the "power of 2" one, if need be).
However, when doing that, I *cannot* for the life of me figure out the correct incantation to make these 2 errors trigger with the "it is undefined behavior to use this value" message rather than the "any use of this value will cause an error" lint.
I've tried Oli's suggestions of different values, tuples and arrays, using the transparent wrapper trick from the other tests and I was only able to trigger the regular const-ub errors about the size of the vtable, or that the drop pointer was invalid. Maybe these "type validation failed" errors happen before this part of the interpreter is reached and there just needs some magic incorrect values to bypass them, I don't know.
Since this fixes an ICE, and if the constants are indeed used, these 2 tests will turn into a hard error, I thought I'd open the PR anyways. And if ```@RalfJung``` you know of a way I could manage that (if you think that these tests are worth checking that the `throw_ub_format!` does indeed create const-ub errors as we expect) I'd be grateful.
For that reason, r? ```@RalfJung``` and cc ```@oli-obk.```
Do not suggest ampmut if rhs is already mutable
Removes invalid suggestion in #85765, although it should highlight the user type instead of the local variable.
Looking at the comments of this line:
84b1005bfd/compiler/rustc_mir_build/src/build/matches/mod.rs (L2107)
It was intentionally set to `None`, causing it to highlight the local variable instead. I am not sure if I will be able to fix it.
Fixes#85765
Fix some diagnostic issues with const_generics_defaults feature gate
This PR makes a few changes:
- print out const param defaults in "lifetime ordering" errors rather than discarding them
- update `is_simple_text` to account for const params when checking if a type has no generics, this was causing a note to be failed to add to an error message
- fixes some diagnostic wording that incorrectly said there was ordering restrictions between type/const params despite the `const_generics_defaults` feature gate is active
Don't use a generator for BoxedResolver
The generator is non-trivial and requires unsafe code anyway. Using regular unsafe code without a generator is much easier to follow.
Based on #85810 as it touches rustc_interface too.
Suggest a trailing comma if a 1-tuple is expected and a parenthesized expression is found
This pull request fixes#86100. The following code:
```rust
fn main() {
let t: (i32,) = (1);
}
```
currently produces:
```
warning: unnecessary parentheses around assigned value
--> test.rs:2:21
|
2 | let t: (i32,) = (1);
| ^^^ help: remove these parentheses
|
= note: `#[warn(unused_parens)]` on by default
error[E0308]: mismatched types
--> test.rs:2:21
|
2 | let t: (i32,) = (1);
| ------ ^^^ expected tuple, found integer
| |
| expected due to this
|
= note: expected tuple `(i32,)`
found type `{integer}`
error: aborting due to previous error; 1 warning emitted
```
With my changes, I get the same warning and the following error:
```
error[E0308]: mismatched types
--> test.rs:2:21
|
2 | let t: (i32,) = (1);
| ------ ^^^ expected tuple, found integer
| |
| expected due to this
|
= note: expected tuple `(i32,)`
found type `{integer}`
help: use a trailing comma to create a tuple with one element
|
2 | let t: (i32,) = (1,);
| ^^^^
```
i.e. I have added a suggestion to add a trailing comma to create a 1-tuple. This suggestion is only issued if a 1-tuple is expected and the expression (`(1)` in the example above) is surrounded by parentheses and does not already have a tuple type. In this situation, I'd say that it is pretty likely that the user meant to create a tuple.
std: Stabilize wasm simd intrinsics
This commit performs two changes to stabilize Rust support for
WebAssembly simd intrinsics:
* The stdarch submodule is updated to pull in rust-lang/stdarch#1179.
* The `wasm_target_feature` feature gate requirement for the `simd128`
feature has been removed, stabilizing the name `simd128`.
This should conclude the FCP started on #74372 and...
Closes#74372
This commit performs two changes to stabilize Rust support for
WebAssembly simd intrinsics:
* The stdarch submodule is updated to pull in rust-lang/stdarch#1179.
* The `wasm_target_feature` feature gate requirement for the `simd128`
feature has been removed, stabilizing the name `simd128`.
This should conclude the FCP started on #74372 and...
Closes#74372
MVP for using rust-lld as part of cc
Will fix#71519. I need to figure out how to write a test showing that lld is used instead of whatever linker cc normally uses. When I manually run rustc using `echo 'fn main() {}' | RUSTC_LOG=rustc_codegen_ssa:🔙:link=debug ./rustc -Clinker-flavor=gcc-lld --crate-type bin -Clink-arg=-Wl,-v` (thanks to bjorn3 on Zulip), I can see that lld is used, but I'm not sure how to inspect that output in a test.
Disable the machine outliner by default
This addresses a codegen-issue that needs to be fixed upstream in LLVM.
While we wait for the fix, we can disable it.
Verified manually that the outliner is no longer run when
`-Copt-level=z` is specified, and also that you can override this with
`-Cllvm-args=-enable-machine-outliner` if you need it anyway.
A regression test is not really feasible in this instance, given that we
do not have any minimal reproducers.
Fixes#85351
cc `@pnkfelix`
Use preorder traversal when checking for SSA locals
Traverse blocks in topological sort of dominance partial order, to ensure that
local analyzer correctly identifies locals that are already in static single
assignment form, while avoiding dependency on implicit numeric order of blocks.
When rebuilding the standard library, this change reduces the number of locals
that require an alloca from 62452 to 62348.
ignore test if rust-lld not found
create ld -> rust-lld symlink at build time instead of run time
for testing in ci
copy instead of symlinking
remove linux check
test for linker, suggestions from bjorn3
fix overly restrictive lld matcher
use -Zgcc-ld flag instead of -Clinker-flavor
refactor code adding lld to gcc path
revert ci changes
suggestions from petrochenkov
rename gcc_ld to gcc-ld in dirs
Rollup of 7 pull requests
Successful merges:
- #82037 (Make symbols stripping work on MacOS X)
- #84687 (Multiple improvements to RwLocks)
- #85997 (rustdoc: Print a warning if the diff when comparing to old nightlies is empty)
- #86051 (Updated code examples and wording in move keyword documentation )
- #86111 (fix off by one in `std::iter::Iterator` documentation)
- #86113 (build doctests with lld if use-lld = true)
- #86175 (update Miri)
Failed merges:
r? `@ghost`
`@rustbot` modify labels: rollup
As reported in the stabilization issue, MacOS' linker doesn't support the `-s` and `-S` flags to strip symbols anymore. However, the os ships a separated tool to perform these operations.
This change allows the compiler to use that tool after a target has been compiled to strip symbols.
For rationale, see: https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/72110#issuecomment-641169818
For option selection, see: https://www.unix.com/man-page/osx/1/strip/
Signed-off-by: David Calavera <david.calavera@gmail.com>
Peephole optimize `x == false` and `x != true`
This adds peephole optimizations to make `x == false`, `false == x`, `x != true`, and `true != x` get optimized to `!x` in the `instcombine` MIR pass. That pass currently handles `x == true` -> `x` already.
Include macro name in 'local ambiguity' error
Currently, we only point at the span of the macro argument. When the
macro call is itself generated by another macro, this can make it
difficult or impossible to determine which macro is responsible for
producing the error.
Enable rustdoc to document safe wasm intrinsics
This commit fixes an issue not found during #84988 where rustdoc is used
to document cross-platform intrinsics but it was requiring that
functions which use `#[target_feature]` are `unsafe` erroneously, even
if they're WebAssembly specific. Rustdoc today, for example, already has
a special case where it enables annotations like
`#[target_feature(enable = "simd128")]` on platforms other than
WebAssembly. The purpose of this commit is to relax the "require all
`#[target_feature]` functions are `unsafe`" requirement for all targets
whenever rustdoc is running, enabling all targets to fully document
other targets, such as WebAssembly, where intrinsics functions aren't
always `unsafe`.
Comment out unused error codes and add description for E0316
I have added an extended description of `E0316` and commented out a bunch of unused error codes to make clear the fact that they are no longer in use. You can check for yourself with
```shell
for ec in \
E0314 E0315 E0473 E0474 E0475 E0479 E0480 E0481 \
E0483 E0484 E0485 E0486 E0487 E0488 E0489
do
if [ ! -z "`grep -r $ec compiler/* --exclude-dir=rustc_error_codes`" ]
then
echo $ec
false
fi
done
```
i.e. these error codes appear nowhere in the compiler code and thus cannot be emitted.
r? ```@GuillaumeGomez```
Currently, we only point at the span of the macro argument. When the
macro call is itself generated by another macro, this can make it
difficult or impossible to determine which macro is responsible for
producing the error.
This commit fixes an issue not found during #84988 where rustdoc is used
to document cross-platform intrinsics but it was requiring that
functions which use `#[target_feature]` are `unsafe` erroneously, even
if they're WebAssembly specific. Rustdoc today, for example, already has
a special case where it enables annotations like
`#[target_feature(enable = "simd128")]` on platforms other than
WebAssembly. The purpose of this commit is to relax the "require all
`#[target_feature]` functions are `unsafe`" requirement for all targets
whenever rustdoc is running, enabling all targets to fully document
other targets, such as WebAssembly, where intrinsics functions aren't
always `unsafe`.
Remove the install prefix from the rpath set when using -Crpath
It was broken anyway for rustup installs and nobody seems to have noticed.
Fixes https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/82392
Unify duplicate linker_and_flavor methods in rustc_codegen_{cranelift,ssa}.
The two methods were exactly the same so this removes the cranelift copy. This will help make sure both they don't get out of sync.
Fix ICE during type layout when there's a `[type error]`
Fixes#84108.
Based on estebank's [comment], except I used `delay_span_bug` because it
should work in more cases, and I think it expresses its intent more
clearly.
r? `@estebank`
[comment]: https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/84108#issuecomment-818916848
Driver improvements
This PR contains a couple of cleanups for the driver and a few small improvements for the custom codegen backend interface. It also implements `--version` and `-Cpasses=list` support for custom codegen backends.
Fix corrected example in E0759.md
This pull request fixes#86061, which was probably caused by a copy-paste error, where the supposedly corrected code example was also marked with `compile_fail`. Thus, the fact that the "correct" example actually _isn't_ correct was not caught by the doc-tests. This pull request removes the incorrect `compile_fail` annotation and fixes the example.
r? ``@GuillaumeGomez``
Fix two ICEs in the parser
This pull request fixes#84104 and fixes#84148. The latter is caused by an invalid `assert_ne!()` in the parser, which I have simply removed because the error is then caught in another part of the parser.
#84104 is somewhat more subtle and has to do with a suggestion to remove extraneous `<` characters; for instance:
```rust
fn main() {
foo::<Ty<<<i32>();
}
```
currently leads to
```
error: unmatched angle brackets
--> unmatched-langle.rs:2:10
|
2 | foo::<Ty<<<i32>();
| ^^^ help: remove extra angle brackets
```
which is obviously wrong and stems from the fact that the code for issuing the above suggestion does not consider the possibility that there might be other tokens in between the opening angle brackets. In #84104, this has led to a span being generated that ends in the middle of a multi-byte character (because the code issuing the suggestion thought that it was only skipping over `<`, which are single-byte), causing an ICE.
Add variance-related information to lifetime error messages
This PR adds a basic framework for displaying variance-related information in error messages. For example:
```
error: lifetime may not live long enough
--> $DIR/type-check-pointer-comparisons.rs:12:5
|
LL | fn compare_mut<'a, 'b>(x: *mut &'a i32, y: *mut &'b i32) {
| -- -- lifetime `'b` defined here
| |
| lifetime `'a` defined here
LL | x == y;
| ^ requires that `'a` must outlive `'b`
|
= help: consider adding the following bound: `'a: 'b`
= note: requirement occurs because of a mutable pointer to &i32
= note: mutable pointers are invariant over their type parameter
= help: see <https://doc.rust-lang.org/nomicon/subtyping.html> for more information about variance
```
The last three lines are new.
This is accomplished by adding a new struct `VarianceDiagInfo`, and passing it along through the various relation methods. When relating types that change the variance (e.g. `&mut T` or `*mut T`), we pass a more specific `VarianceDiagInfo` storing information about the cause of the variance change. When an error, we use the `VarianceDiagInfo` to add additional information to the error message.
This PR doesn't change any variance-related computation or behavior - only diagnostic messages. Therefore, the implementation is quite incomplete - more detailed error messages can be filled in in subsequent PRs.
Limitations:
* We only attempt to deal with invariance - since it's at the bottom of the 'variance lattice', our variance will never change again after it becomes invariant. Handling contravariance would be trickier, since we can change between contravariance and covariance multiple times (e.g. `fn(fn(&'static u8))`). Since contravariance (AFAIK) is only used for function arguments, we can probably get away without a very fancy message for cases involving contravariance.
* `VarianceDiagInfo` currently only handles mutable pointers/references. However, user-defined types (structs, enums, and unions) have the variance of their type parameters inferred, so it would be good to eventually display information about that. We'll want to try to find a balance between displaying too much and too little information about how the variance was inferred.
* The improved error messages are only displayed when `#![feature(nll)]` / `-Z borrowck=mir` is enabled. If issue https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/58781 is not resolved relatively soon, then we might want to duplicate some of this logic in the 'current' (non-NLL) region/outlives handling code.
linker: Reorder linker arguments
- Split arguments into order-independent and order-dependent, to define more precisely what (pre-,post-,late-,)link-args mean.
- Add some comments.
- Combine all native library arguments together, to simplify potential support for library deduplication and similar things
- Split arguments into order-independent and order-dependent, to define more precisely what (pre,post,late)-link-args mean
parser: Ensure that all nonterminals have tokens after parsing
`parse_nonterminal` should always result in something with tokens.
This requirement wasn't satisfied in two cases:
- `stmt` nonterminal with expression statements (e.g. `0`, or `{}`, or `path + 1`) because `fn parse_stmt_without_recovery` forgot to propagate `force_collect` in some cases.
- `expr` nonterminal with expressions with built-in attributes (e.g. `#[allow(warnings)] 0`) due to an incorrect optimization in `fn parse_expr_force_collect`, it assumed that all expressions starting with `#` have their tokens collected during parsing, but that's not true if all the attributes on that expression are built-in and inert.
(Discovered when trying to implement eager `cfg` expansion for all attributes https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/83824#issuecomment-817317170.)
r? `@Aaron1011`
Drop an `if let` that will always succeed
We've already checked that `proj_base == []` in the line above and renaming
`place_local` to `local` doesn't gain us anything.
``@rustbot`` modify labels +C-cleanup +T-compiler
Tweak wasm_base target spec to indicate linker is not GNU and update linker inferring logic for wasm-ld.
Reported via [Zulip](https://rust-lang.zulipchat.com/#narrow/stream/131828-t-compiler/topic/wasi.20linker.20unknown.20argument.3A.20--as-needed): we try passing `--as-needed` to the linker if it's GNU ld which `wasm-ld` is not. Usually this isn't an issue for wasm as we would use the WasmLd linker driver but because the linker in question (`wasm32-unknown-wasi-wasm-ld`) ended with `-ld` our linker inferring [logic](f64503eb55/compiler/rustc_codegen_ssa/src/back/link.rs (L957-L1040)) used the `GccLinker` implementations. (UPD: The linker inferring logic actually didn't apply in this case because the linker is actually invoked through gcc in the reported issue. But it's still worth updating the logic I think.)
This change then has 2 parts:
1. Update wasm_base target spec to indicate `linker_is_gnu: false` plus a few additions of `target.is_like_wasm` to handle flags `wasm-ld` does in fact support.
2. Improve the linker detection logic to properly determine the correct flavor of wasm linker we're using when we can.
We need to add the new `target.is_like_wasm` branches to handle the case where the "linker" used could be something like clang which would then under the hood call wasm-ld.
Preserve metadata w/ Solaris-like linkers.
#84468 moved the `-zignore` linker flag from the `gc_sections` method to `add_as_needed` which is more accurate but Solaris-style linkers will also end up removing an unreferenced ELF sections [1]. This had the unfortunate side effect of causing the `.rustc` section (which has the metada) to be removed which could cause issues when trying to link against the resulting crates or use proc macros.
Since the `-zignore` is positional, we fix this by moving the metadata objects to before the flag.
[1] Specifically a section is considered unreferenced if:
* The section is allocatable
* No other sections bind to (relocate) to this section
* The section provides no global symbols
https://docs.oracle.com/cd/E19683-01/817-3677/6mj8mbtbs/index.html#chapter4-19
Show test type during prints
Test output can sometimes be confusing. For example doctest with the no_run argument are displayed the same way than test that are run.
During #83857 I got the feedback that test output can be confusing.
For the moment test output is
```
test $DIR/test-type.rs - f (line 12) ... ignored
test $DIR/test-type.rs - f (line 15) ... ok
test $DIR/test-type.rs - f (line 21) ... ok
test $DIR/test-type.rs - f (line 6) ... ok
```
I propose to change output by indicating the test type as
```
test $DIR/test-type.rs - f (line 12) ... ignored
test $DIR/test-type.rs - f (line 15) - compile ... ok
test $DIR/test-type.rs - f (line 21) - compile fail ... ok
test $DIR/test-type.rs - f (line 6) ... ok
```
by indicating the test type after the test name (and in the case of doctest after the function name and line) and before the "...".
------------
Note: this is a proof of concept, the implementation is probably not optimal as the properties added in `TestDesc` are only use in the display and does not represent actual change of behavior, maybe `TestType::DocTest` could have fields
Partial support for raw-dylib linkage
First cut of functionality for issue #58713: add support for `#[link(kind = "raw-dylib")]` on `extern` blocks in lib crates compiled to .rlib files. Does not yet support `#[link_name]` attributes on functions, or the `#[link_ordinal]` attribute, or `#[link(kind = "raw-dylib")]` on `extern` blocks in bin crates; I intend to publish subsequent PRs to fill those gaps. It's also not yet clear whether this works for functions in `extern "stdcall"` blocks; I also intend to investigate that shortly and make any necessary changes as a follow-on PR.
This implementation calls out to an LLVM function to construct the actual `.idata` sections as temporary `.lib` files on disk and then links those into the generated .rlib.
BPF target support
This adds `bpfel-unknown-none` and `bpfeb-unknown-none`, two new no_std targets that generate little and big endian BPF. The approach taken is very similar to the cuda target, where `TargetOptions::obj_is_bitcode` is enabled and code generation is done by the linker.
I added the targets to `dist-various-2`. There are [some tests](https://github.com/alessandrod/bpf-linker/tree/main/tests/assembly) in bpf-linker and I'm planning to add more. Those are currently not ran as part of rust CI.
Remove special handling of `box_free` from `LocalAnalyzer`
The special casing of `box_free` predates the use of dominators in
analyzer. It is no longer necessary now that analyzer verifies that
the first assignment dominates all uses.
This addresses a codegen-issue that needs to be fixed upstream in LLVM.
While we wait for the fix, we can disable it.
Verified manually that the outliner is no longer run when
`-Copt-level=z` is specified, and also that you can override this with
`-Cllvm-args=-enable-machine-outliner` if you need it anyway.
A regression test is not really feasible in this instance, given that we
do not have any minimal reproducers.
Fixes#85351
Allow raw pointers in SIMD types
Closes#85915 by loosening the strictness in typechecking and adding a test to guarantee it passes.
This still might be too strict, as references currently do pass monomorphization, but my understanding is that they are not guaranteed to be "scalar" in the same way.
Remove `doc(include)`
This nightly feature is redundant now that `extended_key_value_attributes` is stable (https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/83366). `@rust-lang/rustdoc` not sure if you think this needs FCP; there was already an FCP in #82539, but technically it was for deprecating, not removing the feature altogether.
This should not be merged before #83366.
cc `@petrochenkov`
Implement DepTrackingHash for `Option` through blanket impls instead of macros
This avoids having to add a new macro call for both the `Option` and the type itself.
Noticed this while working on https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/84233.
r? `@Aaron1011`
This does not yet support #[link_name] attributes on functions, the #[link_ordinal]
attribute, #[link(kind = "raw-dylib")] on extern blocks in bin crates, or
stdcall functions on 32-bit x86.
don't suggest unsized indirection in where-clauses
Skip where-clauses when suggesting using indirection in combination with
`?Sized` bounds on type parameters.
Fixes#85943.
`@estebank` I think this doesn't conflict with your work in #85947; please let me know if you'd like me to cherry pick it to a new branch based on yours instead.
wasm: Make simd types passed via indirection again
This commit updates wasm target specs to use `simd_types_indirect: true`
again. Long ago this was added since wasm simd types were always
translated to `v128` under-the-hood in LLVM, meaning that it didn't
matter whether that target feature was enabled or not. Now, however,
`v128` is conditionally used in codegen depending on target features
enabled, meaning that it's possible to get linker errors about different
signatures in code that correctly uses simd types. The fix is the same
as for all other platforms, which is to pass the type indirectly.
rustc: Store metadata-in-rlibs in object files
This commit updates how rustc compiler metadata is stored in rlibs.
Previously metadata was stored as a raw file that has the same format as
`--emit metadata`. After this commit, however, the metadata is encoded
into a small object file which has one section which is the contents of
the metadata.
The motivation for this commit is to fix a common case where #83730
arises. The problem is that when rustc crates a `dylib` crate type it
needs to include entire rlib files into the dylib, so it passes
`--whole-archive` (or the equivalent) to the linker. The problem with
this, though, is that the linker will attempt to read all files in the
archive. If the metadata file were left as-is (today) then the linker
would generate an error saying it can't read the file. The previous
solution was to alter the rlib just before linking, creating a new
archive in a temporary directory which has the metadata file removed.
This problem from before this commit is now removed if the metadata file
is stored in an object file that the linker can read. The only caveat we
have to take care of is to ensure that the linker never actually
includes the contents of the object file into the final output. We apply
similar tricks as the `.llvmbc` bytecode sections to do this.
This involved changing the metadata loading code a bit, namely updating
some of the LLVM C APIs used to use non-deprecated ones and fiddling
with the lifetimes a bit to get everything to work out. Otherwise though
this isn't intended to be a functional change really, only that metadata
is stored differently in archives now.
This should end up fixing #83730 because by default dylibs will no
longer have their rlib dependencies "altered" meaning that
split-debuginfo will continue to have valid paths pointing at the
original rlibs. (note that we still "alter" rlibs if LTO is enabled to
remove Rust object files and we also "alter" for the #[link(cfg)]
feature, but that's rarely used).
Closes#83730
Since PR #69251, the `#[track_caller]` attribute has been supported on
traits. However, it only has an effect on direct (monomorphized) method
calls. Calling a `#[track_caller]` method on a trait object will *not*
propagate caller location information - instead, `Location::caller()` will
return the location of the method definition.
This PR forwards caller location information when `#[track_caller]` is
present on the method definition in the trait. This is possible because
`#[track_caller]` in this position is 'inherited' by any impls of that
trait, so all implementations will have the same ABI.
This PR does *not* change the behavior in the case where
`#[track_caller]` is present only on the impl of a trait.
While all implementations of the method might have an explicit
`#[track_caller]`, we cannot know this at codegen time, since other
crates may have impls of the trait. Therefore, we keep the current
behavior of not forwarding the caller location, ensuring that all
implementations of the trait will have the correct ABI.
See the modified test for examples of how this works
This commit updates how rustc compiler metadata is stored in rlibs.
Previously metadata was stored as a raw file that has the same format as
`--emit metadata`. After this commit, however, the metadata is encoded
into a small object file which has one section which is the contents of
the metadata.
The motivation for this commit is to fix a common case where #83730
arises. The problem is that when rustc crates a `dylib` crate type it
needs to include entire rlib files into the dylib, so it passes
`--whole-archive` (or the equivalent) to the linker. The problem with
this, though, is that the linker will attempt to read all files in the
archive. If the metadata file were left as-is (today) then the linker
would generate an error saying it can't read the file. The previous
solution was to alter the rlib just before linking, creating a new
archive in a temporary directory which has the metadata file removed.
This problem from before this commit is now removed if the metadata file
is stored in an object file that the linker can read. The only caveat we
have to take care of is to ensure that the linker never actually
includes the contents of the object file into the final output. We apply
similar tricks as the `.llvmbc` bytecode sections to do this.
This involved changing the metadata loading code a bit, namely updating
some of the LLVM C APIs used to use non-deprecated ones and fiddling
with the lifetimes a bit to get everything to work out. Otherwise though
this isn't intended to be a functional change really, only that metadata
is stored differently in archives now.
This should end up fixing #83730 because by default dylibs will no
longer have their rlib dependencies "altered" meaning that
split-debuginfo will continue to have valid paths pointing at the
original rlibs. (note that we still "alter" rlibs if LTO is enabled to
remove Rust object files and we also "alter" for the #[link(cfg)]
feature, but that's rarely used).
Closes#83730
Support for force-warns
Implements https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/85512.
This PR adds a new command line option `force-warns` which will force the provided lints to warn even if they are allowed by some other mechanism such as `#![allow(warnings)]`.
Some remaining issues:
* https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/85512 mentions that `force-warns` should also be capable of taking lint groups instead of individual lints. This is not implemented.
* If a lint has a higher warning level than `warn`, this will cause that lint to warn instead. We probably want to allow the lint to error if it is set to a higher lint and is not allowed somewhere else.
* One test is currently ignored because it's not working - when a deny-by-default lint is allowed, it does not currently warn under `force-warns`. I'm not sure why, but I wanted to get this in before the weekend.
r? `@nikomatsakis`
For extern providers, both provide and provide_extern are called.
wasm_import_module_map is already provided in provide, so it doesn't
need to be provided in provide_extern.
Reland - Report coverage `0` of dead blocks
Fixes: #84018
With `-Z instrument-coverage`, coverage reporting of dead blocks
(for example, blocks dropped because a conditional branch is dropped,
based on const evaluation) is now supported.
Note, this PR relands an earlier, reverted PR that failed when compiling
generators. The prior issues with generators has been resolved and a new
test was added to prevent future regressions.
Check out the resulting changes to test coverage of dead blocks in the
test coverage reports in this PR.
r? `@tmandry`
fyi: `@wesleywiser`
Restoring the `num_def_ids` function in the CStore API
## The context
I am the maintainer of https://github.com/hacspec/hacspec, an embedded Rust DSL aimed at cryptographic specifications. As it is normal for an embedded DSL, Hacspec's compiler relies on being plugged to the internal API of the Rust compiler, which is unstable and subject to changes.
## The problem
The Hacspec compiler features its own typechecker, that performs an additional, more restrictive typechecking pass over the Rust code of a crate. To complete this typechecking, the Hacspec compiler needs to retrieve the signature of functions defined in non-local imported crates. Rather than retrieving these signatures on-demand, the Hacspec compiler pre-populates its typechecking context with all the Hacspec-compatible symbols defined in non-local crates first. This requires having a way to iterate over all the definitions in a non-local crate.
I used to do this with `CrateMetadata::all_def_path_hashes_and_def_ids`, but this function was deleted in 908bf5a310. Then, I fellback on `CStore::num_def_ids`, exploiting the fact that all the `DefIds` for a crate have the same `krate_num` and range from `0` to `num_def_ids(krate_num)`. But `num_def_ids` was deleted in b6120bfb35.
I looked to the `Cstore::item_children_untracked` function to replicate the feature of traversing through all the `DefId` for a crate, using `CRATE_DEF_INDEX` as the root, but this does not work as recursive `Cstore::item_children_untracked` calls do not reach all the symbols I was able to reach using the two previous methods.
## Description of this PR
This PR simply restores in the public API of `CStore` the `num_def_ids` function, giving the size of the definition table for a given crate.
Remove unused feature gates
The first commit removes a usage of a feature gate, but I don't expect it to be controversial as the feature gate was only used to workaround a limitation of rust in the past. (closures never being `Clone`)
The second commit uses `#[allow_internal_unstable]` to avoid leaking the `trusted_step` feature gate usage from inside the index newtype macro. It didn't work for the `min_specialization` feature gate though.
The third commit removes (almost) all feature gates from the compiler that weren't used anyway.
This commit updates wasm target specs to use `simd_types_indirect: true`
again. Long ago this was added since wasm simd types were always
translated to `v128` under-the-hood in LLVM, meaning that it didn't
matter whether that target feature was enabled or not. Now, however,
`v128` is conditionally used in codegen depending on target features
enabled, meaning that it's possible to get linker errors about different
signatures in code that correctly uses simd types. The fix is the same
as for all other platforms, which is to pass the type indirectly.
Improve debugging experience for enums on windows-msvc
This PR makes significant improvements over the status quo of debugging enums on the windows-msvc platform with either WinDbg or Visual Studio in three ways:
1. Improves the debugger experience for directly tagged enums.
2. Fixes a bug which caused the debugger to sometimes show the wrong debug info for niche layout enums. For example, `Option<&u32>` could sometimes use the debug info for `Option<&f64>` instead leading to nonsensical variable values in the debugger.
3. Significantly improves the debugger experience for niche-layout enums.
Let's look at a few examples:
```rust
pub enum CStyleEnum {
Base = 2,
Exponent = 16,
}
pub enum NicheLayoutEnum {
Tag1,
Data { my_data: CStyleEnum },
Tag2,
Tag3,
Tag4,
}
pub enum OtherEnum<T> {
Case1(T),
Case2(T),
}
fn main() {
let a = Some(CStyleEnum::Base);
let b = Option::<CStyleEnum>::None;
let c = NicheLayoutEnum::Tag1;
let d = NicheLayoutEnum::Data { my_data: CStyleEnum::Exponent };
let e = NicheLayoutEnum::Tag2;
let f = Some(&1u32);
let g = Option::<&'static u32>::None;
let h = Some(&2u64);
let i = Option::<&'static u64>::None;
let j = Some(12u32);
let k = Option::<u32>::None;
let l = Some(12.34f64);
let m = Option::<f64>::None;
let n = CStyleEnum::Base;
let o = CStyleEnum::Exponent;
let p = Some("IAMA optional string!".to_string());
let q = OtherEnum::Case1(42u32);
}
```
This is what WinDbg Preview shows using the latest rustc nightly:
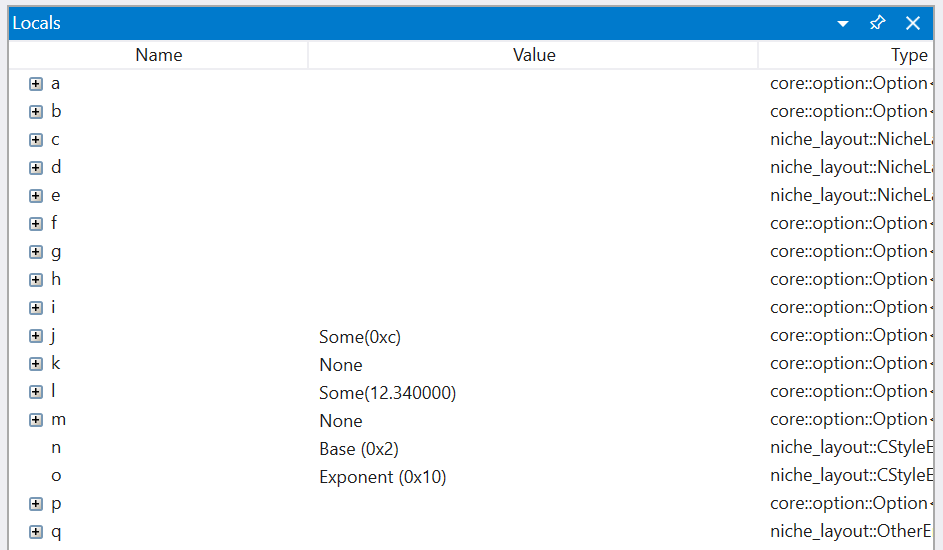
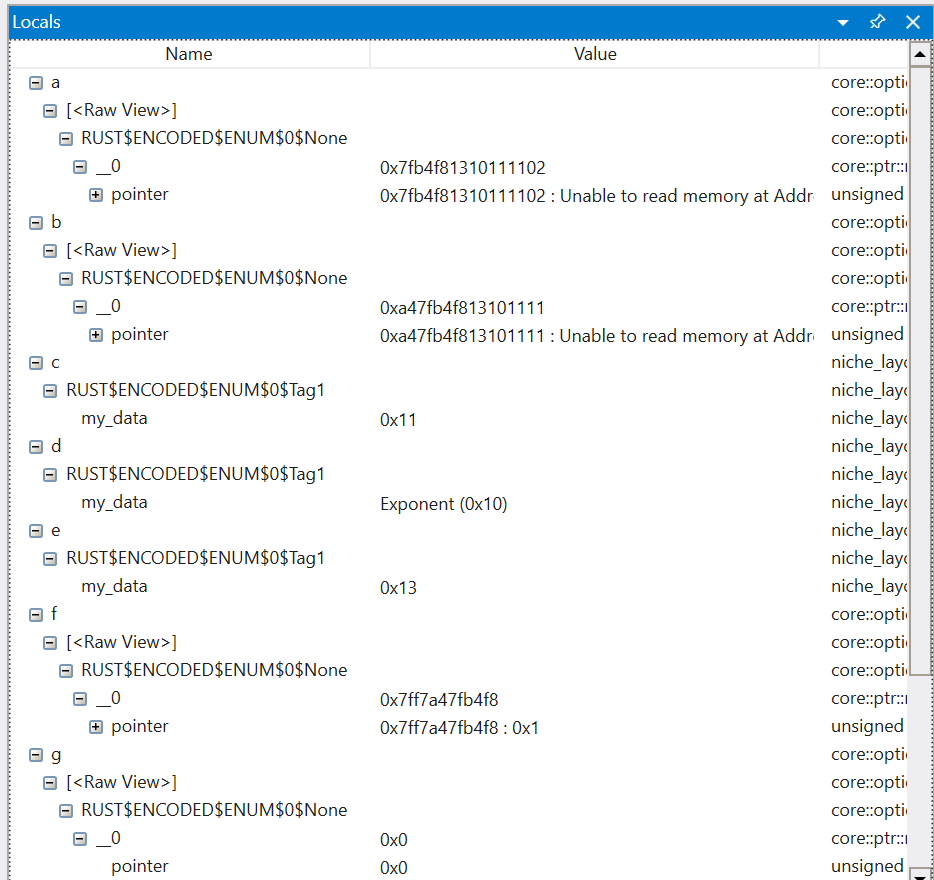
Most of the variables don't show a meaningful value expect for a few cases that we have targeted natvis definitions covering. Even worse, drilling into many of these variables shows information that can be difficult to interpret without an understanding of the layout of Rust types:
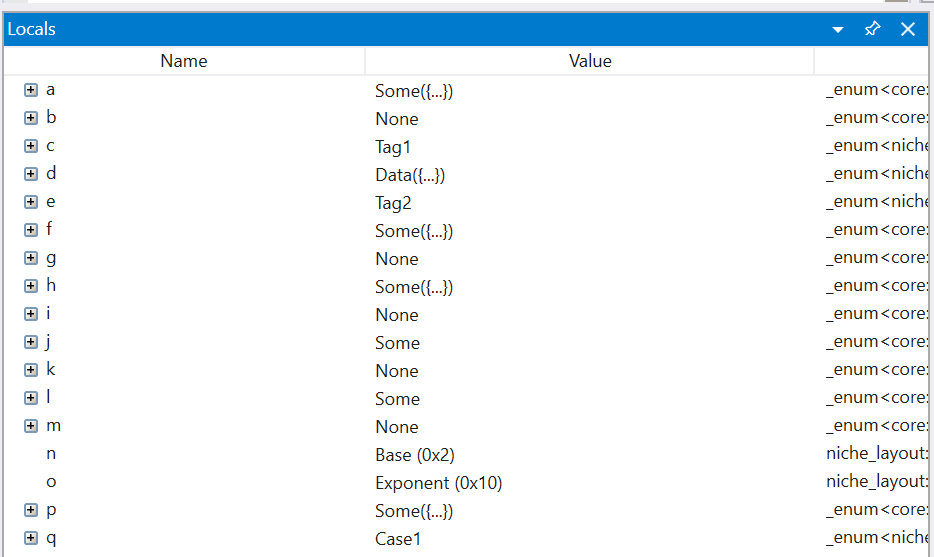
With the changes in this PR, we're able to write two natvis definitions that cover all enum cases generally. After building with these changes, WinDbg now shows this instead:
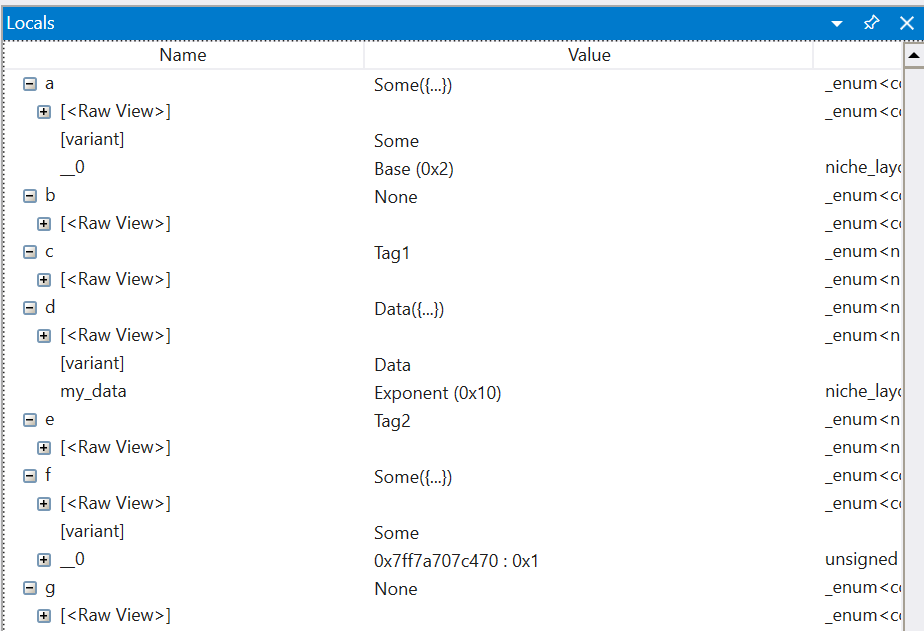
Drilling into the same variables, we can see much more useful information:
Fixes#84670Fixes#84671
Restored underlying num_def_ids_method
Update compiler/rustc_metadata/src/rmeta/decoder/cstore_impl.rs
Changed name to fit with naming convention
Co-authored-by: bjorn3 <bjorn3@users.noreply.github.com>
Update compiler/rustc_metadata/src/rmeta/decoder/cstore_impl.rs
Replace regular doc with Rustdoc comment
Co-authored-by: Joshua Nelson <jyn514@gmail.com>
Clarifies third-party use of num_def_ids_untracked
Use pattern matching instead of checking lengths explicitly
This piece of code checks that there are exaclty two variants, one having
exactly one field, the other having exactly zero fields. If any of these
conditions is violated, it returns `None`. Otherwise it assigns that one
field's ty to `field_ty`.
Instead of fiddling with indices and length checks explicitly, use pattern
matching to simplify this.
`@rustbot` modify labels +C-cleanup +T-compiler
Turn off frame pointer elimination on all Apple platforms.
This ends up disabling frame pointer elimination on aarch64_apple_darwin
which matches what clang does by default along with the
aarch64_apple_ios and x86_64_apple_darwin targets.
Further, the Apple docs "Writing ARM64 Code for Apple Platforms" has a section
called "Respect the Purpose of Specific CPU Registers" which
specifically calls out the frame pointer register (x29):
The frame pointer register (x29) must always address a valid frame
record. Some functions — such as leaf functions or tail calls — may
opt not to create an entry in this list As a result, stack traces
are always meaningful, even without debug information.
Other platforms are updated to not override the default.
rustc: Allow safe #[target_feature] on wasm
This commit updates the compiler's handling of the `#[target_feature]`
attribute when applied to functions on WebAssembly-based targets. The
compiler in general requires that any functions with `#[target_feature]`
are marked as `unsafe` as well, but this commit relaxes the restriction
for WebAssembly targets where the attribute can be applied to safe
functions as well.
The reason this is done is that the motivation for this feature of the
compiler is not applicable for WebAssembly targets. In general the
`#[target_feature]` attribute is used to enhance target CPU features
enabled beyond the basic level for the rest of the compilation. If done
improperly this means that your program could execute an instruction
that the CPU you happen to be running on does not understand. This is
considered undefined behavior where it is unknown what will happen (e.g.
it's not a deterministic `SIGILL`).
For WebAssembly, however, the target is different. It is not possible
for a running WebAssembly program to execute an instruction that the
engine does not understand. If this were the case then the program would
not have validated in the first place and would not run at all. Even if
this were allowed in some hypothetical future where engines have some
form of runtime feature detection (which they do not right now) any
implementation of such a feature would generate a trap if a module
attempts to execute an instruction the module does not understand. This
deterministic trap behavior would still not fall into the category of
undefined behavior because the trap is deterministic.
For these reasons the `#[target_feature]` attribute is now allowed on
safe functions, but only for WebAssembly targets. This notably enables
the wasm-SIMD intrinsics proposed for stabilization in #74372 to be
marked as safe generally instead of today where they're all `unsafe` due
to the historical implementation of `#[target_feature]` in the compiler.
This ends up disabling frame pointer elimination on aarch64_apple_darwin
which matches what clang does by default along with the
aarch64_apple_ios and x86_64_apple_darwin targets.
Further, the Apple docs "Writing ARM64 Code for Apple Platforms" has a section
called "Respect the Purpose of Specific CPU Registers" which
specifically calls out the frame pointer register (x29):
The frame pointer register (x29) must always address a valid frame
record. Some functions — such as leaf functions or tail calls — may
opt not to create an entry in this list As a result, stack traces
are always meaningful, even without debug information.
Other platforms are updated to not override the default.
Previously, we would generate a single struct with the layout of the
dataful variant plus an extra field whose name contained the value of
the niche (this would only really work for things like `Option<&_>`
where we can determine that the `None` case maps to `0` but for enums
that have multiple tag only variants, this doesn't work).
Now, we generate a union of two structs, one which is the layout of the
dataful variant and one which just has a way of reading the
discriminant. We also generate an enum which maps the discriminant value
to the tag only variants.
We also encode information about the range of values which correspond to
the dataful variant in the type name and then use natvis to determine
which union field we should display to the user.
As a result of this change, all niche-layout enums render correctly in
WinDbg and Visual Studio!
This wasn't necessary for msvc and caused issues where different types
with the same name such as different instantiations of `Option<T>` would
have colliding debuginfo. This confused the debugger which would pick
one of the type definitions and use for all types with that name even
though they had different layout.
Avoid creating anonymous nodes with zero or one dependency.
Anonymous nodes are only useful to encode dependencies, and cannot be replayed from one compilation session to another.
As such, anonymous nodes without dependency are always green.
Anonymous nodes with only one dependency are equivalent to this dependency.
cc #45408
cc `@michaelwoerister`
This piece of code checks that there are exaclty two variants, one having
exactly one field, the other having exactly zero fields. If any of these
conditions is violated, it returns `None`. Otherwise it assigns that one
field's ty to `field_ty`.
Instead of fiddling with indices and length checks explicitly, use pattern
matching to simplify this.
Fixes: #84018
With `-Z instrument-coverage`, coverage reporting of dead blocks
(for example, blocks dropped because a conditional branch is dropped,
based on const evaluation) is now supported.
Note, this PR relands an earlier, reverted PR that failed when compiling
generators. The prior issues with generators has been resolved and a new
test was added to prevent future regressions.
Check out the resulting changes to test coverage of dead blocks in the
test coverage reports in this PR.