Update expect-test to 1.0
The only change is that `expect_file` now uses path relative to the
current file (same as `include!`). Before, it used paths relative to
the workspace root, which makes no sense.
The only change is that `expect_file` now uses path relative to the
current file (same as `include!`). Before, it used paths relative to
the workspace root, which makes no sense.
Rollup of 14 pull requests
Successful merges:
- #75832 (Move to intra-doc links for wasi/ext/fs.rs, os_str_bytes.rs…)
- #75852 (Switch to intra-doc links in `core::hash`)
- #75874 (Shorten liballoc doc intra link while readable)
- #75881 (Expand rustdoc theme chooser x padding)
- #75885 (Fix another clashing_extern_declarations false positive.)
- #75892 (Fix typo in TLS Model in Unstable Book)
- #75910 (Add test for issue #27130)
- #75917 (Move to intra doc links for core::ptr::non_null)
- #75975 (Allow --bess ing expect-tests in tools)
- #75990 (Add __fastfail for Windows on arm/aarch64)
- #76015 (Fix loading pretty-printers in rust-lldb script)
- #76022 (Clean up rustdoc front-end source code)
- #76029 (Move to intra-doc links for library/core/src/sync/atomic.rs)
- #76057 (Move retokenize hack to save_analysis)
Failed merges:
r? @ghost
Update compiler-builtins
Update the compiler-builtins dependency to include latest changes.
This allows for `aarch64-unknown-linux-musl` to pass all tests.
Fixes#57820 and fixes#46651
It's a unit-test in a sense that it only checks syntax highlighting.
However, the resulting HTML is written to disk and can be easily
inspected in the browser.
To update the test, run with `--bless` argument or set
`UPDATE_EXPEC=1` env var
Introduce expect snapshot testing library into rustc
Snapshot testing is a technique for writing maintainable unit tests.
Unlike usual `assert_eq!` tests, snapshot tests allow
to *automatically* upgrade expected values on test failure.
In a sense, snapshot tests are inline-version of our beloved
UI-tests.
Example:
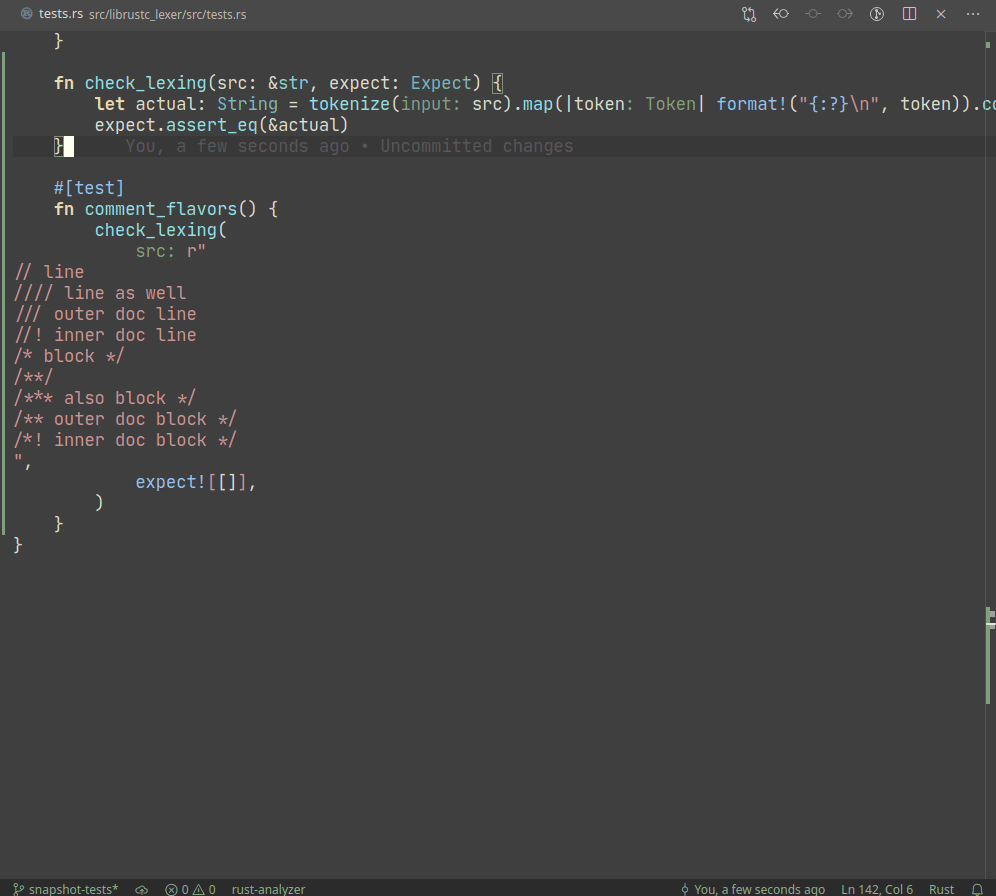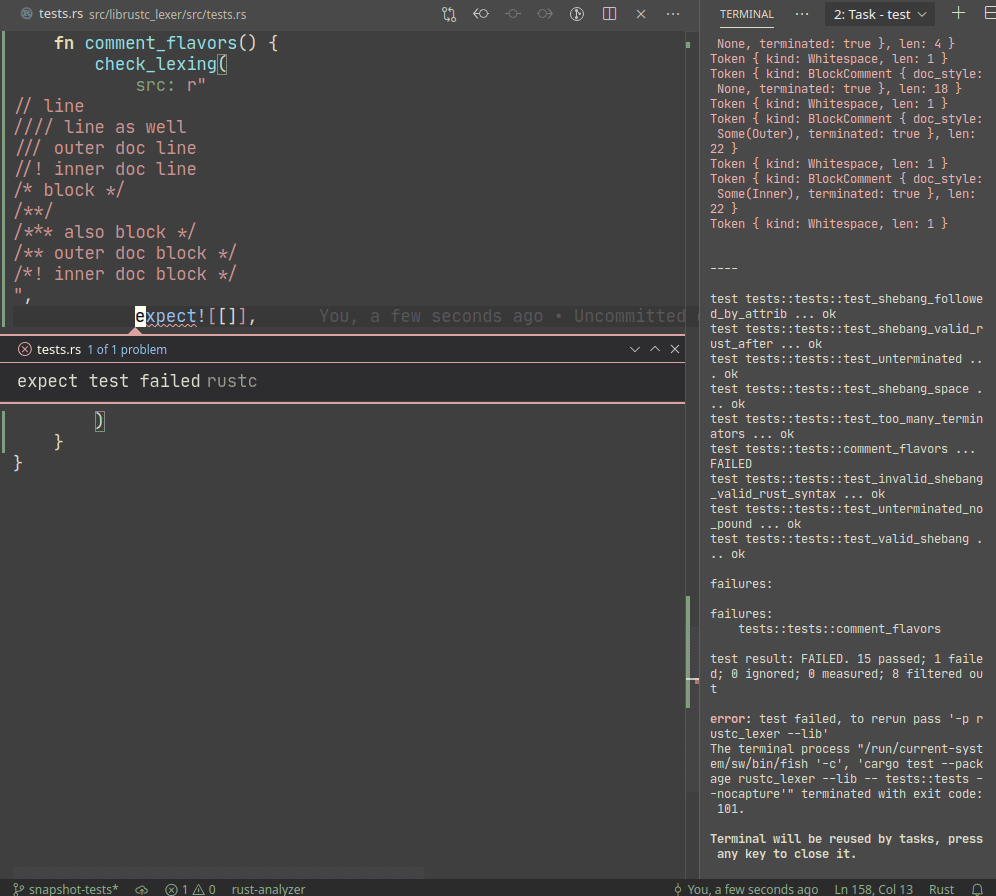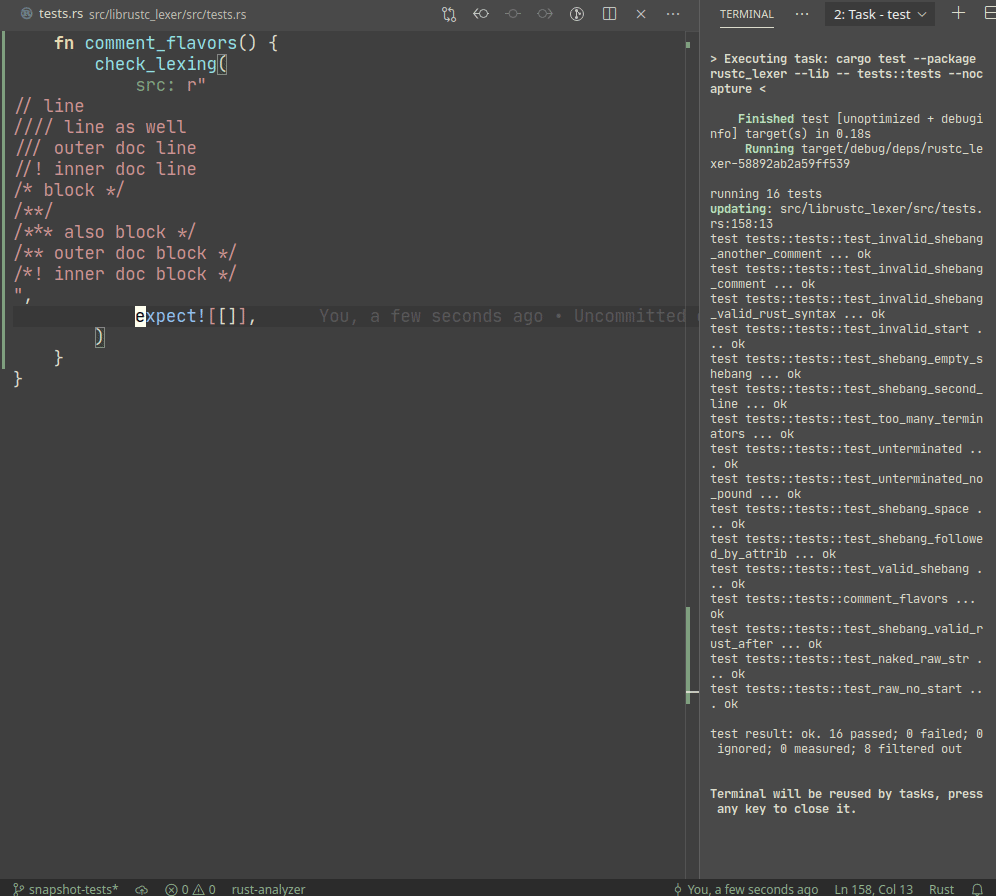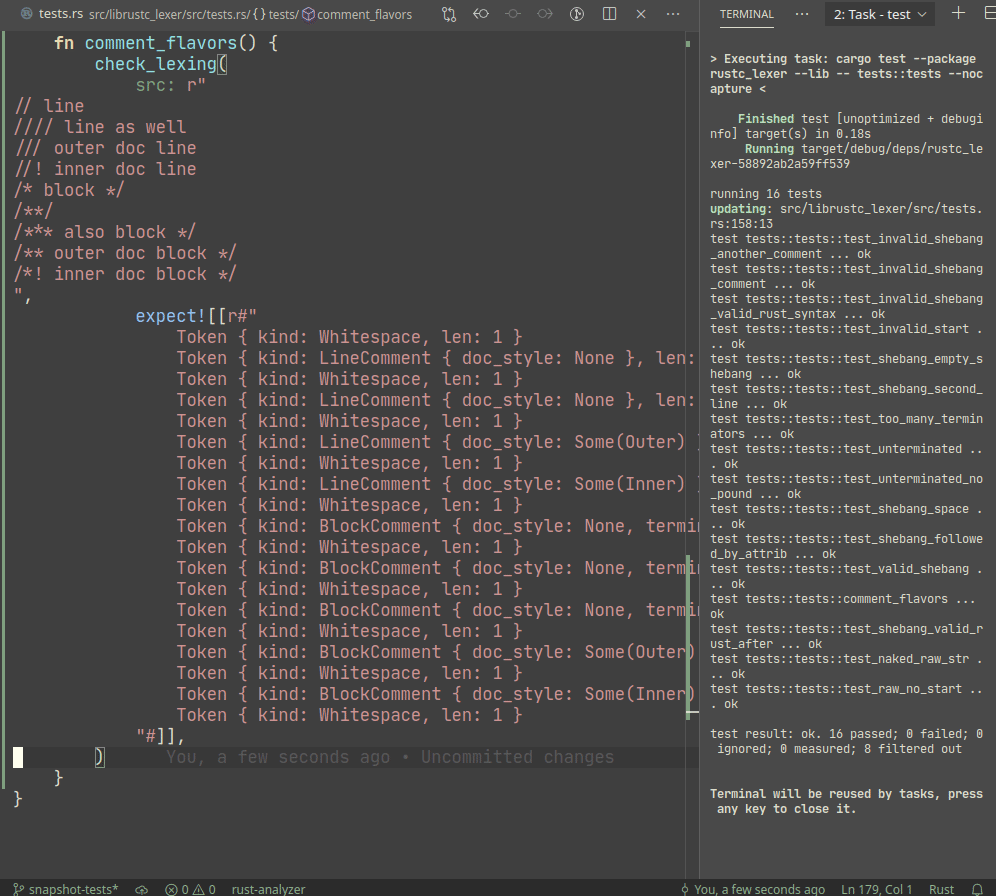
A particular library we use, `expect_test` provides an `expect!`
macro, which creates a sort of self-updating string literal (by using
`file!` macro). Self-update is triggered by setting `UPDATE_EXPECT`
environmental variable (this info is printed during the test failure).
This library was extracted from rust-analyzer, where we use it for
most of our tests.
There are some other, more popular snapshot testing libraries:
* https://github.com/mitsuhiko/insta
* https://github.com/aaronabramov/k9
The main differences of `expect` are:
* first-class snapshot objects (so, tests can be written as functions,
rather than as macros)
* focus on inline-snapshots (but file snapshots are also supported)
* restricted feature set (only `assert_eq` and `assert_debug_eq`)
* no extra runtime (ie, no `cargo insta`)
See rust-analyzer/rust-analyzer#5101 for a
an extended comparison.
It is unclear if this testing style will stick with rustc in the long
run. At the moment, rustc is mainly tested via integrated UI tests.
But in the library-ified world, unit-tests will become somewhat more
important (that's why use use `rustc_lexer` library-ified library as
an example in this PR). Given that the cost of removal shouldn't be
too high, it probably makes sense to just see if this flies!
Snapshot testing is a technique for writing maintainable unit tests.
Unlike usual `assert_eq!` tests, snapshot tests allow
to *automatically* upgrade expected values on test failure.
In a sense, snapshot tests are inline-version of our beloved
UI-tests.
Example:

A particular library we use, `expect_test` provides an `expect!`
macro, which creates a sort of self-updating string literal (by using
`file!` macro). Self-update is triggered by setting `UPDATE_EXPECT`
environmental variable (this info is printed during the test failure).
This library was extracted from rust-analyzer, where we use it for
most of our tests.
There are some other, more popular snapshot testing libraries:
* https://github.com/mitsuhiko/insta
* https://github.com/aaronabramov/k9
The main differences of `expect` are:
* first-class snapshot objects (so, tests can be written as functions,
rather than as macros)
* focus on inline-snapshots (but file snapshots are also supported)
* restricted feature set (only `assert_eq` and `assert_debug_eq`)
* no extra runtime (ie, no `cargo insta`)
See https://github.com/rust-analyzer/rust-analyzer/pull/5101 for a
an extended comparison.
It is unclear if this testing style will stick with rustc in the long
run. At the moment, rustc is mainly tested via integrated UI tests.
But in the library-ified world, unit-tests will become somewhat more
important (that's why use use `rustc_lexer` library-ified library as
an example in this PR). Given that the cost of removal shouldn't be
too high, it probably makes sense to just see if this flies!
- Move the type parameter from `encode` and `decode` methods to
the trait.
- Remove `UseSpecialized(En|De)codable` traits.
- Remove blanket impls for references.
- Add `RefDecodable` trait to allow deserializing to arena-allocated
references safely.
- Remove ability to (de)serialize HIR.
- Create proc-macros `(Ty)?(En|De)codable` to help implement these new
traits.
Move platform support to the rustc book.
This moves the [Platform Support](https://forge.rust-lang.org/release/platform-support.html) page from the forge to the rustc book. There are several reasons for doing this:
* The forge is not really oriented towards end-users (it mostly contains infrastructure, governance and policy, internal team pages, etc.). This platform support page is useful to user to know which targets are supported.
* This page can now be updated in-sync with any PRs that add or remove a target, or change its status.
* This is now automatically checked on CI to verify the list does not get out of sync. Currently it only checks the presence/absence of an entry, but more sophisticated checks could be added in the future.
I'm not 100% certain this is the best location, but I think it fits. I'd like to see the rustc guide continue to grow, including things like linking information and more platform-specific details.
Avoid deleting temporary files on error
Previously if the compiler error'd, fatally, then temporary directories which
should be preserved by -Csave-temps would be deleted due to fatal compiler
errors being implemented as panics.
cc @infinity0
(Hopefully) fixes#75275, but I haven't tested
Previously if the compiler error'd, fatally, then temporary directories which
should be preserved by -Csave-temps would be deleted due to fatal compiler
errors being implemented as panics.
By moving `{known,used}_attrs` from `SessionGlobals` to `Session`. This
means they are accessed via the `Session`, rather than via TLS. A few
`Attr` methods and `librustc_ast` functions are now methods of
`Session`.
All of this required passing a `Session` to lots of functions that didn't
already have one. Some of these functions also had arguments removed, because
those arguments could be accessed directly via the `Session` argument.
`contains_feature_attr()` was dead, and is removed.
Some functions were moved from `librustc_ast` elsewhere because they now need
to access `Session`, which isn't available in that crate.
- `entry_point_type()` --> `librustc_builtin_macros`
- `global_allocator_spans()` --> `librustc_metadata`
- `is_proc_macro_attr()` --> `Session`
We store an `ImplicitCtxt` pointer in a thread-local value (TLV). This allows
implicit access to a `GlobalCtxt` and some other things.
We also store a `GlobalCtxt` pointer in `GCX_PTR`. This is always the same
`GlobalCtxt` as the one within the `ImplicitCtxt` pointer in TLV. `GCX_PTR`
is only used in the parallel compiler's `handle_deadlock()` function.
This commit does the following.
- It removes `GCX_PTR`.
- It also adds `ImplicitCtxt::new()`, which constructs an `ImplicitCtxt` from a
`GlobalCtxt`. `ImplicitCtxt::new()` + `tls::enter_context()` is now
equivalent to the old `tls::enter_global()`.
- Makes `tls::get_tlv()` public for the parallel compiler, because it's
now used in `handle_deadlock()`.
Update cargo
14 commits in aa6872140ab0fa10f641ab0b981d5330d419e927..974eb438da8ced6e3becda2bbf63d9b643eacdeb
2020-07-23 13:46:27 +0000 to 2020-07-29 16:15:05 +0000
- Fix O0 build scripts by default without `[profile.release]` (rust-lang/cargo#8560)
- Emphasize git dependency version locking behavior. (rust-lang/cargo#8561)
- Update lock file encodings on changes (rust-lang/cargo#8554)
- Fix sporadic lto test failures. (rust-lang/cargo#8559)
- build-std: Fix libraries paths following upstream (rust-lang/cargo#8558)
- Flag git http errors as maybe spurious (rust-lang/cargo#8553)
- Display builtin aliases with `cargo --list` (rust-lang/cargo#8542)
- Check manifest for requiring nonexistent features (rust-lang/cargo#7950)
- Clarify test name filter usage (rust-lang/cargo#8552)
- Revert Cargo Book changes for default edition (rust-lang/cargo#8551)
- Prepare for not defaulting to master branch for git deps (rust-lang/cargo#8522)
- Include `+` for crates.io feature requirements in the Cargo Book section on features (rust-lang/cargo#8547)
- Update termcolor and fwdansi versions (rust-lang/cargo#8540)
- Cargo book nitpick in Manifest section (rust-lang/cargo#8543)
This commit is a proof-of-concept for switching the standard library's
backtrace symbolication mechanism on most platforms from libbacktrace to
gimli. The standard library's support for `RUST_BACKTRACE=1` requires
in-process parsing of object files and DWARF debug information to
interpret it and print the filename/line number of stack frames as part
of a backtrace.
Historically this support in the standard library has come from a
library called "libbacktrace". The libbacktrace library seems to have
been extracted from gcc at some point and is written in C. We've had a
lot of issues with libbacktrace over time, unfortunately, though. The
library does not appear to be actively maintained since we've had
patches sit for months-to-years without comments. We have discovered a
good number of soundness issues with the library itself, both when
parsing valid DWARF as well as invalid DWARF. This is enough of an issue
that the libs team has previously decided that we cannot feed untrusted
inputs to libbacktrace. This also doesn't take into account the
portability of libbacktrace which has been difficult to manage and
maintain over time. While possible there are lots of exceptions and it's
the main C dependency of the standard library right now.
For years it's been the desire to switch over to a Rust-based solution
for symbolicating backtraces. It's been assumed that we'll be using the
Gimli family of crates for this purpose, which are targeted at safely
and efficiently parsing DWARF debug information. I've been working
recently to shore up the Gimli support in the `backtrace` crate. As of a
few weeks ago the `backtrace` crate, by default, uses Gimli when loaded
from crates.io. This transition has gone well enough that I figured it
was time to start talking seriously about this change to the standard
library.
This commit is a preview of what's probably the best way to integrate
the `backtrace` crate into the standard library with the Gimli feature
turned on. While today it's used as a crates.io dependency, this commit
switches the `backtrace` crate to a submodule of this repository which
will need to be updated manually. This is not done lightly, but is
thought to be the best solution. The primary reason for this is that the
`backtrace` crate needs to do some pretty nontrivial filesystem
interactions to locate debug information. Working without `std::fs` is
not an option, and while it might be possible to do some sort of
trait-based solution when prototyped it was found to be too unergonomic.
Using a submodule allows the `backtrace` crate to build as a submodule
of the `std` crate itself, enabling it to use `std::fs` and such.
Otherwise this adds new dependencies to the standard library. This step
requires extra attention because this means that these crates are now
going to be included with all Rust programs by default. It's important
to note, however, that we're already shipping libbacktrace with all Rust
programs by default and it has a bunch of C code implementing all of
this internally anyway, so we're basically already switching
already-shipping functionality to Rust from C.
* `object` - this crate is used to parse object file headers and
contents. Very low-level support is used from this crate and almost
all of it is disabled. Largely we're just using struct definitions as
well as convenience methods internally to read bytes and such.
* `addr2line` - this is the main meat of the implementation for
symbolication. This crate depends on `gimli` for DWARF parsing and
then provides interfaces needed by the `backtrace` crate to turn an
address into a filename / line number. This crate is actually pretty
small (fits in a single file almost!) and mirrors most of what
`dwarf.c` does for libbacktrace.
* `miniz_oxide` - the libbacktrace crate transparently handles
compressed debug information which is compressed with zlib. This crate
is used to decompress compressed debug sections.
* `gimli` - not actually used directly, but a dependency of `addr2line`.
* `adler32`- not used directly either, but a dependency of
`miniz_oxide`.
The goal of this change is to improve the safety of backtrace
symbolication in the standard library, especially in the face of
possibly malformed DWARF debug information. Even to this day we're still
seeing segfaults in libbacktrace which could possibly become security
vulnerabilities. This change should almost entirely eliminate this
possibility whilc also paving the way forward to adding more features
like split debug information.
Some references for those interested are:
* Original addition of libbacktrace - #12602
* OOM with libbacktrace - #24231
* Backtrace failure due to use of uninitialized value - #28447
* Possibility to feed untrusted data to libbacktrace - #21889
* Soundness fix for libbacktrace - #33729
* Crash in libbacktrace - #39468
* Support for macOS, never merged - ianlancetaylor/libbacktrace#2
* Performance issues with libbacktrace - #29293, #37477
* Update procedure is quite complicated due to how many patches we
need to carry - #50955
* Libbacktrace doesn't work on MinGW with dynamic libs - #71060
* Segfault in libbacktrace on macOS - #71397
Switching to Rust will not make us immune to all of these issues. The
crashes are expected to go away, but correctness and performance may
still have bugs arise. The gimli and `backtrace` crates, however, are
actively maintained unlike libbacktrace, so this should enable us to at
least efficiently apply fixes as situations come up.
revise RwLock for HermitCore
- current version is derived from the wasm implementation
- increasing the readability of `Condvar`
- simplify the interface to the libos
Revert libbacktrace -> gimli
This reverts 4cbd265c11028f8d7b8513db3cc1e8d7a36d8964 (and technically 79673d3009 but it's made empty by previous reverts).
The current plan is to land this PR as a temporary change, so that we can get a better handle on the regressions introduced by it. Trying to fix/examine them in master is difficult, and we want to be better able to evaluate them without impact to other PRs being landed in the mean time.
That said, it is currently *my* belief that gimli, in one form or another, will need to land sometime soon. I think it's quite likely that it may slip a week or two, but I would personally push for re-landing it then "regardless" of the regressions. We should try to focus efforts on understanding and removing as much of the performance impact as possible, as everyone pretty much agrees that it should be quite minimal (and entirely in the linker, basically).
r? @nnethercote
Generating the coverage map
@tmandry @wesleywiser
rustc now generates the coverage map and can support (limited)
coverage report generation, at the function level.
Example commands to generate a coverage report:
```shell
$ BUILD=$HOME/rust/build/x86_64-unknown-linux-gnu
$ $BUILD/stage1/bin/rustc -Zinstrument-coverage \
$HOME/rust/src/test/run-make-fulldeps/instrument-coverage/main.rs
$ LLVM_PROFILE_FILE="main.profraw" ./main
called
$ $BUILD/llvm/bin/llvm-profdata merge -sparse main.profraw -o main.profdata
$ $BUILD/llvm/bin/llvm-cov show --instr-profile=main.profdata main
```
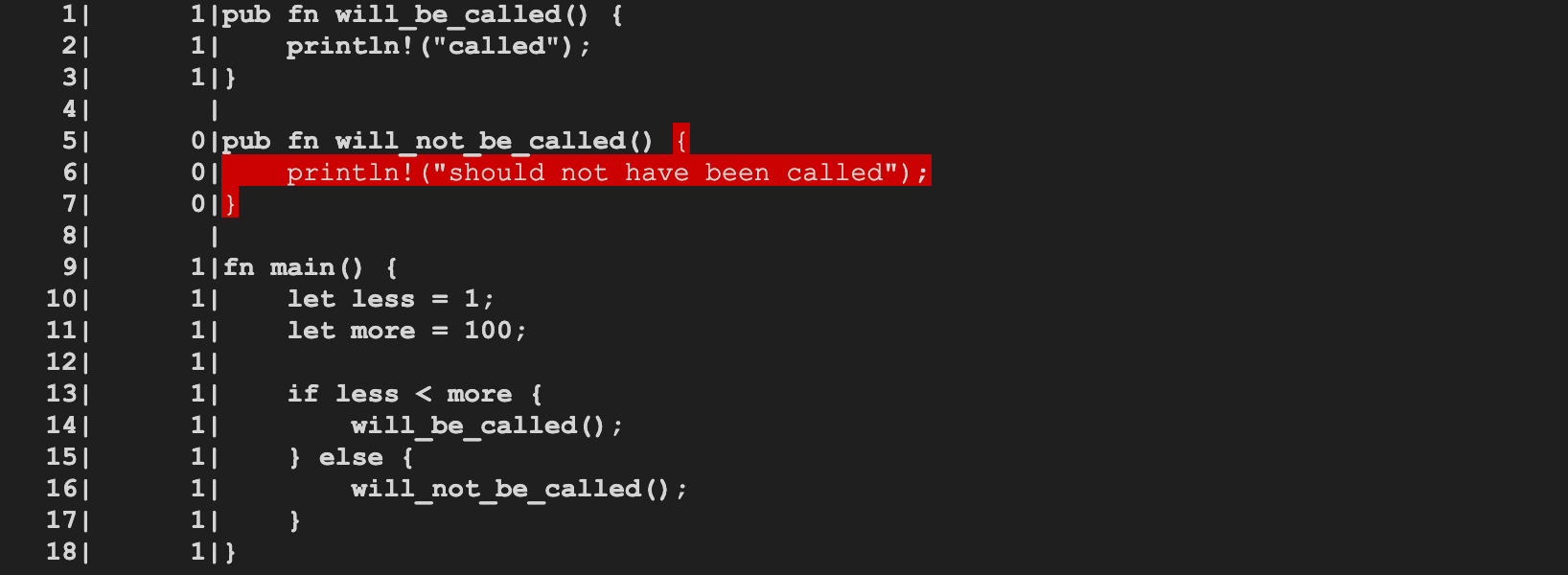
r? @wesleywiser
Rust compiler MCP rust-lang/compiler-team#278
Relevant issue: #34701 - Implement support for LLVMs code coverage instrumentation
std: Switch from libbacktrace to gimli
This commit is a proof-of-concept for switching the standard library's
backtrace symbolication mechanism on most platforms from libbacktrace to
gimli. The standard library's support for `RUST_BACKTRACE=1` requires
in-process parsing of object files and DWARF debug information to
interpret it and print the filename/line number of stack frames as part
of a backtrace.
Historically this support in the standard library has come from a
library called "libbacktrace". The libbacktrace library seems to have
been extracted from gcc at some point and is written in C. We've had a
lot of issues with libbacktrace over time, unfortunately, though. The
library does not appear to be actively maintained since we've had
patches sit for months-to-years without comments. We have discovered a
good number of soundness issues with the library itself, both when
parsing valid DWARF as well as invalid DWARF. This is enough of an issue
that the libs team has previously decided that we cannot feed untrusted
inputs to libbacktrace. This also doesn't take into account the
portability of libbacktrace which has been difficult to manage and
maintain over time. While possible there are lots of exceptions and it's
the main C dependency of the standard library right now.
For years it's been the desire to switch over to a Rust-based solution
for symbolicating backtraces. It's been assumed that we'll be using the
Gimli family of crates for this purpose, which are targeted at safely
and efficiently parsing DWARF debug information. I've been working
recently to shore up the Gimli support in the `backtrace` crate. As of a
few weeks ago the `backtrace` crate, by default, uses Gimli when loaded
from crates.io. This transition has gone well enough that I figured it
was time to start talking seriously about this change to the standard
library.
This commit is a preview of what's probably the best way to integrate
the `backtrace` crate into the standard library with the Gimli feature
turned on. While today it's used as a crates.io dependency, this commit
switches the `backtrace` crate to a submodule of this repository which
will need to be updated manually. This is not done lightly, but is
thought to be the best solution. The primary reason for this is that the
`backtrace` crate needs to do some pretty nontrivial filesystem
interactions to locate debug information. Working without `std::fs` is
not an option, and while it might be possible to do some sort of
trait-based solution when prototyped it was found to be too unergonomic.
Using a submodule allows the `backtrace` crate to build as a submodule
of the `std` crate itself, enabling it to use `std::fs` and such.
Otherwise this adds new dependencies to the standard library. This step
requires extra attention because this means that these crates are now
going to be included with all Rust programs by default. It's important
to note, however, that we're already shipping libbacktrace with all Rust
programs by default and it has a bunch of C code implementing all of
this internally anyway, so we're basically already switching
already-shipping functionality to Rust from C.
* `object` - this crate is used to parse object file headers and
contents. Very low-level support is used from this crate and almost
all of it is disabled. Largely we're just using struct definitions as
well as convenience methods internally to read bytes and such.
* `addr2line` - this is the main meat of the implementation for
symbolication. This crate depends on `gimli` for DWARF parsing and
then provides interfaces needed by the `backtrace` crate to turn an
address into a filename / line number. This crate is actually pretty
small (fits in a single file almost!) and mirrors most of what
`dwarf.c` does for libbacktrace.
* `miniz_oxide` - the libbacktrace crate transparently handles
compressed debug information which is compressed with zlib. This crate
is used to decompress compressed debug sections.
* `gimli` - not actually used directly, but a dependency of `addr2line`.
* `adler32`- not used directly either, but a dependency of
`miniz_oxide`.
The goal of this change is to improve the safety of backtrace
symbolication in the standard library, especially in the face of
possibly malformed DWARF debug information. Even to this day we're still
seeing segfaults in libbacktrace which could possibly become security
vulnerabilities. This change should almost entirely eliminate this
possibility whilc also paving the way forward to adding more features
like split debug information.
Some references for those interested are:
* Original addition of libbacktrace - #12602
* OOM with libbacktrace - #24231
* Backtrace failure due to use of uninitialized value - #28447
* Possibility to feed untrusted data to libbacktrace - #21889
* Soundness fix for libbacktrace - #33729
* Crash in libbacktrace - #39468
* Support for macOS, never merged - ianlancetaylor/libbacktrace#2
* Performance issues with libbacktrace - #29293, #37477
* Update procedure is quite complicated due to how many patches we
need to carry - #50955
* Libbacktrace doesn't work on MinGW with dynamic libs - #71060
* Segfault in libbacktrace on macOS - #71397
Switching to Rust will not make us immune to all of these issues. The
crashes are expected to go away, but correctness and performance may
still have bugs arise. The gimli and `backtrace` crates, however, are
actively maintained unlike libbacktrace, so this should enable us to at
least efficiently apply fixes as situations come up.
---
I want to note that my purpose for creating a PR here is to start a conversation about this. I think that all the various pieces are in place that this is compelling enough that I think this transition should be talked about seriously. There are a number of items which still need to be addressed before actually merging this PR, however:
* [ ] `gimli` needs to be published to crates.io
* [ ] `addr2line` needs a publish
* [ ] `miniz_oxide` needs a publish
* [ ] Tests probably shouldn't recommend the `gimli` crate's traits for implementing
* [ ] The `backtrace` crate's branch changes need to be merged to the master branch (https://github.com/rust-lang/backtrace-rs/pull/349)
* [ ] The support for `libbacktrace` on some platforms needs to be audited to see if we should support more strategies in the gimli implementation - https://github.com/rust-lang/backtrace-rs/issues/325, https://github.com/rust-lang/backtrace-rs/issues/326, https://github.com/rust-lang/backtrace-rs/issues/350, https://github.com/rust-lang/backtrace-rs/issues/351
Most of the merging/publishing I'm not actively pushing on right now. It's a bit wonky for crates to support libstd so I'm holding off on pulling the trigger everywhere until there's a bit more discussion about how to go through with this. Namely https://github.com/rust-lang/backtrace-rs/pull/349 I'm going to hold off merging until we decide to go through with the submodule strategy.
In any case this is a pretty major change, so I suspect that the compiler team is likely going to be interested in this. I don't mean to force changes by dumping a bunch of code by any means. Integration of external crates into the standard library is so difficult I wanted to have a proof-of-concept to review while talking about whether to do this at all (hence the PR), but I'm more than happy to follow any processes needed to merge this. I must admit though that I'm not entirely sure myself at this time what the process would be to decide to merge this, so I'm hoping others can help me figure that out!
This commit is a proof-of-concept for switching the standard library's
backtrace symbolication mechanism on most platforms from libbacktrace to
gimli. The standard library's support for `RUST_BACKTRACE=1` requires
in-process parsing of object files and DWARF debug information to
interpret it and print the filename/line number of stack frames as part
of a backtrace.
Historically this support in the standard library has come from a
library called "libbacktrace". The libbacktrace library seems to have
been extracted from gcc at some point and is written in C. We've had a
lot of issues with libbacktrace over time, unfortunately, though. The
library does not appear to be actively maintained since we've had
patches sit for months-to-years without comments. We have discovered a
good number of soundness issues with the library itself, both when
parsing valid DWARF as well as invalid DWARF. This is enough of an issue
that the libs team has previously decided that we cannot feed untrusted
inputs to libbacktrace. This also doesn't take into account the
portability of libbacktrace which has been difficult to manage and
maintain over time. While possible there are lots of exceptions and it's
the main C dependency of the standard library right now.
For years it's been the desire to switch over to a Rust-based solution
for symbolicating backtraces. It's been assumed that we'll be using the
Gimli family of crates for this purpose, which are targeted at safely
and efficiently parsing DWARF debug information. I've been working
recently to shore up the Gimli support in the `backtrace` crate. As of a
few weeks ago the `backtrace` crate, by default, uses Gimli when loaded
from crates.io. This transition has gone well enough that I figured it
was time to start talking seriously about this change to the standard
library.
This commit is a preview of what's probably the best way to integrate
the `backtrace` crate into the standard library with the Gimli feature
turned on. While today it's used as a crates.io dependency, this commit
switches the `backtrace` crate to a submodule of this repository which
will need to be updated manually. This is not done lightly, but is
thought to be the best solution. The primary reason for this is that the
`backtrace` crate needs to do some pretty nontrivial filesystem
interactions to locate debug information. Working without `std::fs` is
not an option, and while it might be possible to do some sort of
trait-based solution when prototyped it was found to be too unergonomic.
Using a submodule allows the `backtrace` crate to build as a submodule
of the `std` crate itself, enabling it to use `std::fs` and such.
Otherwise this adds new dependencies to the standard library. This step
requires extra attention because this means that these crates are now
going to be included with all Rust programs by default. It's important
to note, however, that we're already shipping libbacktrace with all Rust
programs by default and it has a bunch of C code implementing all of
this internally anyway, so we're basically already switching
already-shipping functionality to Rust from C.
* `object` - this crate is used to parse object file headers and
contents. Very low-level support is used from this crate and almost
all of it is disabled. Largely we're just using struct definitions as
well as convenience methods internally to read bytes and such.
* `addr2line` - this is the main meat of the implementation for
symbolication. This crate depends on `gimli` for DWARF parsing and
then provides interfaces needed by the `backtrace` crate to turn an
address into a filename / line number. This crate is actually pretty
small (fits in a single file almost!) and mirrors most of what
`dwarf.c` does for libbacktrace.
* `miniz_oxide` - the libbacktrace crate transparently handles
compressed debug information which is compressed with zlib. This crate
is used to decompress compressed debug sections.
* `gimli` - not actually used directly, but a dependency of `addr2line`.
* `adler32`- not used directly either, but a dependency of
`miniz_oxide`.
The goal of this change is to improve the safety of backtrace
symbolication in the standard library, especially in the face of
possibly malformed DWARF debug information. Even to this day we're still
seeing segfaults in libbacktrace which could possibly become security
vulnerabilities. This change should almost entirely eliminate this
possibility whilc also paving the way forward to adding more features
like split debug information.
Some references for those interested are:
* Original addition of libbacktrace - #12602
* OOM with libbacktrace - #24231
* Backtrace failure due to use of uninitialized value - #28447
* Possibility to feed untrusted data to libbacktrace - #21889
* Soundness fix for libbacktrace - #33729
* Crash in libbacktrace - #39468
* Support for macOS, never merged - ianlancetaylor/libbacktrace#2
* Performance issues with libbacktrace - #29293, #37477
* Update procedure is quite complicated due to how many patches we
need to carry - #50955
* Libbacktrace doesn't work on MinGW with dynamic libs - #71060
* Segfault in libbacktrace on macOS - #71397
Switching to Rust will not make us immune to all of these issues. The
crashes are expected to go away, but correctness and performance may
still have bugs arise. The gimli and `backtrace` crates, however, are
actively maintained unlike libbacktrace, so this should enable us to at
least efficiently apply fixes as situations come up.
Fix cross compilation of LLVM to aarch64 Windows targets
When cross-compiling, the LLVM build system recurses to build tools that need to run on the host system. However, since we pass cmake defines to set the compiler and target, LLVM still compiles these tools for the target system, rather than the host. The tools then fail to execute during the LLVM build.
This change sets defines for the tools that need to run on the host (llvm-nm, llvm-tablegen, and llvm-config), so that the LLVM build does not attempt to build them, and instead relies on the tools already built.
If compiling with clang-cl, adds the `--target` option to specify the target triple. MSVC compilers do not require this, since there is a separate compiler binary for each cross-compilation target.
Related issue: #72881
Requires LLVM change: rust-lang/llvm-project#67
When cross-compiling, the LLVM build system recurses to build tools
that need to run on the host system. However, since we pass cmake defines
to set the compiler and target, LLVM still compiles these tools for the
target system, rather than the host. The tools then fail to execute
during the LLVM build.
This change sets defines for the tools that need to run on the
host (llvm-nm, llvm-tablegen, and llvm-config), so that the LLVM build
does not attempt to build them, and instead relies on the tools already built.
If compiling with clang-cl, this change also adds the `--target` option
to specify the target triple. MSVC compilers do not require this, since there
is a separate compiler binary for cross-compilation.
This pulls in a fix for the install script on some tr(1) implementations,
as well as an update to use `anyhow` instead of `failure` for error
handling.
Update cargo, rls
## cargo
14 commits in c26576f9adddd254b3dd63aecba176434290a9f6..fede83ccf973457de319ba6fa0e36ead454d2e20
2020-06-23 16:21:21 +0000 to 2020-07-02 21:51:34 +0000
- Fix overflow error on 32-bit. (rust-lang/cargo#8446)
- Exclude the target directory from backups using CACHEDIR.TAG (rust-lang/cargo#8378)
- CONTRIBUTING.md: Link to Zulip rather than Discord (rust-lang/cargo#8436)
- Update built-in help for features (rust-lang/cargo#8433)
- Update core-foundation requirement from 0.7.0 to 0.9.0 (rust-lang/cargo#8432)
- Parse `# env-dep` directives in dep-info files (rust-lang/cargo#8421)
- Move string interning to util (rust-lang/cargo#8419)
- Expose built cdylib artifacts in the Compilation structure (rust-lang/cargo#8418)
- Remove unused serde_derive dependency from the crates.io crate (rust-lang/cargo#8416)
- Remove unused remove_dir_all dependency (rust-lang/cargo#8412)
- Improve git error messages a bit (rust-lang/cargo#8409)
- Improve the description of Config.home_path (rust-lang/cargo#8408)
- Improve support for non-`master` main branches (rust-lang/cargo#8364)
- Document that OUT_DIR in JSON messages is an absolute path (rust-lang/cargo#8403)
## rls
2020-06-19 15:36:00 +0200 to 2020-06-30 23:34:52 +0200
- Update cargo (rust-lang-nursery/rls#1686)
Update Chalk to 0.14
Not a ton here. Notable changes:
- Update to `0.14.0`
- New dependency on `tracing`, in `librustc_traits` only
- `FnAbi` from Chalk is `rustc_target::spec::abi::Abi`
- `Dynamic` actually lowers region
- Actually lower closures, with some tests. This doesn't 100% work, but can't confirm that's *only* because of closure lowering.
- Use `FxIndexSet` instead of `FxHashSet` in `chalk_fulfill`, which seems to have fixed the non-deterministic test error ordering. Guess we'll see on CI
- Actually implement `opaque_ty_data`, though I don't think this is sufficient for tests for them (I haven't added any)
- Uncomment some of the chalk tests that now work
r? @nikomatsakis
Implement mixed script confusable lint.
This implements the mixed script confusable lint defined in RFC 2457.
This is blocked on #72069 and https://github.com/unicode-rs/unicode-security/pull/13, and will need a Cargo.toml version bump after those are resolved.
The lint message warning is sub-optimal for now. We'll need a mechanism to properly output `AugmentScriptSet` to screen, this is to be added in `unicode-security` crate.
r? @Manishearth
Move remaining `NodeId` APIs from `Definitions` to `Resolver`
Implements https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/73291#issuecomment-643515557
TL;DR: it moves all fields that are only needed during name resolution passes into the `Resolver` and keep the rest in `Definitions`. This effectively enforces that all references to `NodeId`s are gone once HIR lowering is completed.
After this, the only remaining work for #50928 should be to adjust the dev guide.
r? @petrochenkov
None of the tools seem to need syn 0.15.35, so we can just build syn
1.0.
This was causing an issue with clippy's `compile-test` program: since
multiple versions of `syn` would exist in the build directory, we would
non-deterministically pick one based on filesystem iteration order. If
the pre-1.0 version of `syn` was picked, a strange build error would
occur (see
https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/73594#issuecomment-647671463)
To prevent this kind of issue from happening again, we now panic if we
find multiple versions of a crate in the build directly, instead of
silently picking the first version we find.
Upgrade Chalk
Things done in this PR:
- Upgrade Chalk to `0.11.0`
- Added compare-mode=chalk
- Bump rustc-hash in `librustc_data_structures` to `1.1.0` to match Chalk
- Removed `RustDefId` since the builtin type support is there
- Add a few more `FIXME(chalk)`s for problem spots I hit when running all tests with chalk
- Added some more implementation code for some newer builtin Chalk types (e.g. `FnDef`, `Array`)
- Lower `RegionOutlives` and `ObjectSafe` predicates
- Lower `Dyn` without the region
- Handle `Int`/`Float` `CanonicalVarKind`s
- Uncomment some Chalk tests that actually work now
- Remove the revisions in `src/test/ui/coherence/coherence-subtyping.rs` since they aren't doing anything different
r? @nikomatsakis
Diagnose use of incompatible sanitizers
Emit an error when incompatible sanitizer are configured through command
line options. Previously the last one configured prevailed and others
were silently ignored.
Additionally use a set to represent configured sanitizers, making it
possible to enable multiple sanitizers at once. At least in principle,
since currently all of them are considered to be incompatible with
others.
Emit an error when incompatible sanitizer are configured through command
line options. Previously the last one configured prevailed and others
were silently ignored.
Additionally use a set to represent configured sanitizers, making it
possible to enable multiple sanitizers at once. At least in principle,
since currently all of them are considered to be incompatible with
others.
Enable LVI hardening for x86_64-fortanix-unknown-sgx
This implements mitigations for the Load Value Injection vulnerability (CVE-2020-0551) for the `x86_64-fortanix-unknown-sgx` target by enabling new LLVM passes. More information about LVI and mitigations may be found at https://software.intel.com/security-software-guidance/insights/deep-dive-load-value-injection.
This PR unconditionally enables the mitigations for `x86_64-fortanix-unknown-sgx` since there is no available hardware that doesn't require the mitigations. This may be reconsidered in the future.
* [x] This depends on https://github.com/rust-lang/compiler-builtins/pull/359/
Update annotate-snippets-rs to 0.8.0
#59346
I made major changes to this library. In the previous version we worked with owned while in the current one with borrowed.
I have adapted it without changing the behavior.
I have modified the coverage since the previous one did not return correctly the index of the character in the line.
Recursively expand `TokenKind::Interpolated` in `probably_equal_for_proc_macro`
Fixes#68430
When comparing the captured and re-parsed `TokenStream` for a `TokenKind::Interpolated`, we currently treat any nested `TokenKind::Interpolated` tokens as unequal. If a `TokenKind::Interpolated` token shows up in the captured `TokenStream` due to a `macro_rules!` expansion, we will throw away the captured `TokenStream`, losing span information.
This PR recursively invokes `nt_to_tokenstream` on nested `TokenKind::Interpolated` tokens, effectively flattening the stream into a sequence of non-interpolated tokens. This allows it to compare equal with the re-parsed stream, allowing us to keep the original captured `TokenStream` (with span information).
This requires all of the `probably_equal_for_proc_macro` methods to be moved from `librustc_ast` to `librustc_parse` so that they can call `nt_to_tokenstream`.
Rollup of 7 pull requests
Successful merges:
- #71289 (Allow using `Self::` in doc)
- #72375 (Improve E0599 explanation)
- #72385 (Add some teams to prioritization exclude_labels)
- #72395 (Allow rust-highfive to label issues it creates.)
- #72453 (Add flag to open docs: x.py doc --open)
- #72459 (Add core::future::IntoFuture)
- #72461 (Clean up E0600 explanation)
Failed merges:
r? @ghost
Update cargo
9 commits in cb06cb2696df2567ce06d1a39b1b40612a29f853..500b2bd01c958f5a33b6aa3f080bea015877b83c
2020-05-08 21:57:44 +0000 to 2020-05-18 17:12:54 +0000
- Handle LTO with an rlib/cdylib crate type (rust-lang/cargo#8254)
- Gracefully handle errors during a build. (rust-lang/cargo#8247)
- Update `im-rc` to 15.0.0 (rust-lang/cargo#8255)
- Fix `cargo update` with unused patch. (rust-lang/cargo#8243)
- Rephrased error message for disallowed sections in virtual workspace (rust-lang/cargo#8200)
- Ignore broken console output in some situations. (rust-lang/cargo#8236)
- Expand error message to explain that a string was found (rust-lang/cargo#8235)
- Add context to some fs errors. (rust-lang/cargo#8232)
- Move SipHasher to an isolated module. (rust-lang/cargo#8233)
update stacker to 0.1.9 to unbreak build on OpenBSD
the version 0.1.8 of stacker (what is currently pinned in Cargo.lock) doesn't build on OpenBSD (see https://github.com/rust-lang/stacker/pull/34).
update the version to 0.1.9
Prevent compiler stack overflow for deeply recursive code
I was unable to write a test that
1. runs in under 1s
2. overflows on my machine without this patch
The following reproduces the issue, but I don't think it's sensible to include a test that takes 30s to compile. We can now easily squash newly appearing overflows by the strategic insertion of calls to `ensure_sufficient_stack`.
```rust
// compile-pass
#![recursion_limit="1000000"]
macro_rules! chain {
(EE $e:expr) => {$e.sin()};
(RECURSE $i:ident $e:expr) => {chain!($i chain!($i chain!($i chain!($i $e))))};
(Z $e:expr) => {chain!(RECURSE EE $e)};
(Y $e:expr) => {chain!(RECURSE Z $e)};
(X $e:expr) => {chain!(RECURSE Y $e)};
(A $e:expr) => {chain!(RECURSE X $e)};
(B $e:expr) => {chain!(RECURSE A $e)};
(C $e:expr) => {chain!(RECURSE B $e)};
// causes overflow on x86_64 linux
// less than 1 second until overflow on test machine
// after overflow has been fixed, takes 30s to compile :/
(D $e:expr) => {chain!(RECURSE C $e)};
(E $e:expr) => {chain!(RECURSE D $e)};
(F $e:expr) => {chain!(RECURSE E $e)};
// more than 10 seconds
(G $e:expr) => {chain!(RECURSE F $e)};
(H $e:expr) => {chain!(RECURSE G $e)};
(I $e:expr) => {chain!(RECURSE H $e)};
(J $e:expr) => {chain!(RECURSE I $e)};
(K $e:expr) => {chain!(RECURSE J $e)};
(L $e:expr) => {chain!(RECURSE L $e)};
}
fn main() {
let x = chain!(D 42.0_f32);
}
```
fixes#55471fixes#41884fixes#40161fixes#34844fixes#32594
cc @alexcrichton @rust-lang/compiler
I looked at all code that checks the recursion limit and inserted stack growth calls where appropriate.
perf: Unify the undo log of all snapshot types
Extracted from #69218 and extended to all the current snapshot types.
Since snapshotting is such a frequent action in the compiler and many of the scopes execute so little work, the act of creating the snapshot and rolling back empty/small snapshots end up showing in perf. By unifying all the logs into one the creation of snapshots becomes significantly cheaper at the cost of some complexity when combining the log with the specific data structures that are being mutated.
Depends on https://github.com/rust-lang-nursery/ena/pull/29
In addition to fixing the toolstate, this also changes the default
compilation model to the out-of-process one, which should hopefully
target considerable memory usage for long-running instances of the RLS.
By merging the undo_log of all structures part of the snapshot the cost
of creating a snapshot becomes much cheaper. Since snapshots with no or
few changes are so frequent this ends up mattering more than the slight
overhead of dispatching on the variants that map to each field.
Implement `confusable_idents` lint.
This collects all identifier symbols into `ParseSession` and examines them within the non-ascii-idents lint.
The skeleton generation part needs to be added to `unicode-security` crate. Will update this PR when the crate is updated.
r? @petrochenkov
EDIT: also included the `concat_idents` part.
We anticipate this to have uses in all sorts of crates and keeping it in
`rustc_data_structures` enables access to it from more locations without
necessarily pulling in the large `librustc` crate.
Miri: port error backtraces to std::backtrace
No need to pull in an external dependency if libstd already includes this feature (using the same dependency internally, but... still).
r? @oli-obk
Have the per-query caches store the results on arenas
This PR leverages the cache for each query to serve as storage area for the query results.
It introduces a new cache `ArenaCache`, which moves the result to an arena,
and only stores the reference in the hash map.
This allows to remove a sizeable part of the usage of the global `TyCtxt` arena.
I only migrated queries that already used arenas before.
Update backtrace-sys
Diff:
- Don't look for old RUSTC_DEBUGINFO vars (rust-lang/backtrace-rs#313)
This fixes an issue of libbacktrace never being built with debuginfo.
r? @Mark-Simulacrum
cc @alexcrichton
Move `{Free,}RegionRelations` and `FreeRegionMap` to `rustc_infer`
...and out of `rustc_middle`. This is to further #65031, albeit in a very minor way
r? @Mark-Simulacrum
Detect mistyped associated consts in `Instance::resolve`.
*Based on #71049 to prevent redundant/misleading downstream errors.*
Fixes#70942 by refusing to resolve an associated `const` if it doesn't have the same type in the `impl` that it does in the `trait` (which we assume had errored, and `delay_span_bug` guards against bugs).
Deprecate the asm! macro in favor of llvm_asm!
Since we will be changing the syntax of `asm!` soon, deprecate it and encourage people to use `llvm_asm!` instead (which preserves the old syntax). This will avoid breakage when `asm!` is changed.
RFC: https://github.com/rust-lang/rfcs/pull/2843
Rollup of 6 pull requests
Successful merges:
- #69903 (Do not ICE in the face of invalid enum discriminant)
- #70354 (Update RELEASES.md for 1.43.0)
- #70774 (End cleanup on rustdoc-js tools)
- #70990 (Improve rustdoc source code a bit)
- #71145 (Add illumos triple)
- #71166 (Clean up E0518 explanation)
Failed merges:
r? @ghost
submodules: update clippy from af5940b7 to d236b30a
Changes:
````
rustup https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/70643
Explain panic on `E0463` in integration tests
Temporarily disable rustfmt integration test
Cleanup: Use rustc's is_proc_macro_attr
Cleanup: Use our `sym!` macro more
Fixes#5405: redundant clone false positive with arrays
update lints
verbose_bit_mask: fix bit mask used in docs
Update documentation for new_ret_no_self
````
Fixes#71114
Changes:
````
Rename dummy_hir_id -> parent_hir_id
rustup https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/71116
Change default many single char names threshold
Better precedence case management + more tests
Use only check_expr with parent expr and precedence
Check for Deref trait impl + add fixed version
Report using stmts and expr + tests
Global rework + fix imports
Working basic dereference clip
Add test for zero single char names
Make the single char threshold strict inequality
large_enum_variant: Report sizes of variants
Refactor: Use rustc's `match_def_path`
deps: bump compiletest-rs from 0.4 to 0.5
rustup https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/70643
Explain panic on `E0463` in integration tests
Temporarily disable rustfmt integration test
result_map_unit_fn: Fix incorrect UI tests
Cleanup: Use rustc's is_proc_macro_attr
Cleanup: Use our `sym!` macro more
Fixes#5405: redundant clone false positive with arrays
Disallow bit-shifting in `integer_arithmetic` lint
update lints
cargo dev fmt
Make use of Option/Result diagnostic items
Make use of some existing diagnostic items
Say that diagnostic items are preferred over paths
verbose_bit_mask: fix bit mask used in docs
Update documentation for new_ret_no_self
Update doc generation script
Add lint on large const arrays
Make the epsilon note spanless
Split check_fn function
Indicate when arrays are compared in error message
Make epsilon note spanless when comparing arrays
Add float cmp const tests for arrays
Add float cmp tests for arrays
Handle constant arrays with single value
Don't show comparison suggestion for arrays
Allow for const arrays of zeros
Handle evaluating constant index expression
Add handling of float arrays to miri_to_const
Update stderr of float_cmp test
Update field names in is_float
Add tests for float in array comparison
Add lint when comparing floats in an array
````
Fixes#71114
update openssl-src to 111.8.1+1.1.1f
This update includes a fix for alexcrichton/openssl-src-rs#52 which allows Cargo to build correctly on Solaris/illumos.
add basic IP support in HermitCore
- add initial version to support sockets
- use TcpStream as test case
- HermitCore uses smoltcp as IP stack for pure Rust applications
- further functionalities (e.g. UDP support) will be added step by step
- in principle, the current PR is a revision of #69404
Polonius: update to 0.12.1, fix more move errors false positives, update test expectations
This PR:
- updates `polonius-engine` to version 0.12.1 to fix some move errors false positives
- fixes a fact generation mistake creating the other move errors false positives
- updates the test expectations for the polonius compare-mode so that all (minus the 2 OOMs) ui tests pass again (matching the [analysis doc](https://hackmd.io/CjYB0fs4Q9CweyeTdKWyEg?view) starting at case 34)
In my opinion, this is safe to rollup.
r? @nikomatsakis
submodules: update clippy from 1ff81c1b to 70b93aab
Changes:
````
remove redundant import
rustup https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/68404
rustup https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/69644
rustup https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/70344
Move verbose_file_reads to restriction
move redundant_pub_crate to nursery
readme: explain how to run only a single lint on a codebase
Remove dependency on `matches` crate
Move useless_transmute to nursery
nursery group -> style
Update for PR feedback
Auto merge of #5314 - ehuss:remove-git2, r=flip1995
Lint for `pub(crate)` items that are not crate visible due to the visibility of the module that contains them
````
Fixes#70456
Changes:
````
remove redundant import
rustup https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/68404
rustup https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/69644
rustup https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/70344
Move verbose_file_reads to restriction
move redundant_pub_crate to nursery
readme: explain how to run only a single lint on a codebase
Remove dependency on `matches` crate
Move useless_transmute to nursery
nursery group -> style
Update for PR feedback
Auto merge of #5314 - ehuss:remove-git2, r=flip1995
Lint for `pub(crate)` items that are not crate visible due to the visibility of the module that contains them
````
Fixes#70456
Move the query system to a dedicated crate
The query system `rustc::ty::query` is split out into the `rustc_query_system` crate.
Some commits are unformatted, to ease rebasing.
Based on #67761 and #69910.
r? @Zoxc
Decouple `rustc_hir::print` into `rustc_hir_pretty`
High level summary:
- The HIR pretty printer, `rustc_hir::print` is moved into a new crate `rustc_hir_pretty`.
- `rustc_ast_pretty` and `rustc_errors` are dropped as `rustc_hir` dependencies.
- The dependence on HIR pretty is generally reduced, leaving `rustc_save_analysis`, `rustdoc`, `rustc_metadata`, and `rustc_driver` as the remaining clients.
The main goal here is to reduce `rustc_hir`'s dependencies and its size such that it can start and finish earlier, thereby working towards https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/65031.
r? @Zoxc
Update backtrace crate to 0.3.46
* Support line-tables-only when using libbacktrace
* Update libbacktrace to latest master
* Define HAVE_KERN_PROC on FreeBSD to fixrust-lang/rust#54434
- add initial version to support sockets
- use TcpStream as test case
- HermitCore uses smoltcp as IP stack for pure Rust applications
- further functionalities (e.g. UDP support) will be added step by step
tidy: Better license checks.
This implements some improvements to the license checks in tidy:
* Use `cargo_metadata` instead of parsing vendored crates. This allows license checks to run without vendoring enabled, and allows the checks to run on PR builds.
* Check for stale entries.
* Check that the licenses for exceptions are what we think they are.
* Verify exceptions do not leak into the runtime.
Closes#62618Closes#62619Closes#63238 (I think)
There are some substantive changes here. The follow licenses have changed from the original comments:
* openssl BSD+advertising clause to Apache-2.0
* pest MPL2 to MIT/Apache-2.0
* smallvec MPL2 to MIT/Apache-2.0
* clippy lints MPL2 to MIT OR Apache-2.0
Remove some imports to the rustc crate
- When we have `NestedVisitorMap::None`, we use `type Map = dyn intravisit::Map<'v>;` instead of the actual map. This doesn't actually result in dynamic dispatch (in the future we may want to use an associated type default to simplify the code).
- Use `rustc_session::` imports instead of `rustc::{session, lint}`.
r? @Zoxc
Changes:
````
rustup https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/69738
rustup https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/68944
Make use of `or_patterns` feature
rustup https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/69589/
Rustup to rust-lang/rust#69076
Don't convert Path to lossy str
Use `into_path`
Use pattern matching instead of manually checking condition
Fix typo
Remove git2 dependency.
Document that wildcard_imports doesn't warn about `use ...::prelude::*;`
Change changelog formatting
Update changelog_update doc to reflect the actual ordering of the changelog
Update CHANGELOG.md
````
Fixes#70007
Changes:
````
Rustup to rust-lang/rust#69674
Use visit_place
Check for mutation
Only fires on temporaries
Extend `redundant_clone` to the case that cloned value is not consumed
add CR feedback
Improve documentation
Use `edition:2018` flag more widely
Update tests/ui/needless_doc_main.rs
Move links to the end of each chapter on adding_lints
Move links to the end of each chapter on CONTRIBUTING
Clean-up adding_lints.md
Clean-up CONTRIBUTING.md
needless_doc_main: only check rust code
Use `node_type_opt` over `node_type`
Fix doc
Fix ICE with trivial_bounds feature
clippy_lints: readme: don't mention crates.io since it is no longer used to publish clippy.
update rust-lang.github.io to rustc-dev-guide.rust-lang.org
Improve placeholder in map_unit_fn
Fix match single binding when in a let stmt
Improve error messages for {option,result}_map_unit_fn
Mention the setup instructions in CONTRIBUTING
redundant_pattern: take binding (ref, ref mut) into account in suggestion.
check_pat: delay creation of the "normal" vec until we reach the branch where is is actually needed
deps: bump itertools 0.8 -> 0.9
add lint on File::read_to_string and File::read_to_end
transition rustc-guide to rustc-dev-guide
Rename macro_use_import -> macro_use_imports
warn on macro_use attr
Fix deploy script for tag deploys
````
Fixes#69957
Polonius: update `polonius-engine` to 0.12.0
Since @albins won't have the time to finish up #68993 for a while, I'll take care of the trivial remaining tasks (rebasing, taking care of tidy/rustfmt).
I'll r? @nikomatsakis since they're assigned to #68993, but have actually [already reviewed it pre-rebase](https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/68993#issuecomment-586413089).
When CI passes: I'll notify bors and close#68993, since this PR supersedes it.
Remove experimental chalk option
As suggested by @nikomatsakis [here](https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/68807#issuecomment-583339932).
The current version of chalk used by the experimental `-Zchalk` flag is [v0.9.0, which is over a year old](https://crates.io/crates/chalk-engine). Since v0.9.0, chalk has seen [a lot of further development](https://github.com/rust-lang/chalk/compare/41dfe13...master), and the intent is to eventually upgrade rustc to use a more recent chalk.
However, it will take a decent chunk of effort to upgrade the current experimental chalk support, and it is currently [blocking at least some PRs](https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/68807) due to chalk:0.9.0's use of unstable features. So for the interim until the next chalk release and experimental rustc integration, we remove the chalk-specific code from rustc.
[experiment] Support linking from a .rlink file
Flag `-Z no-link` was previously introduced, which allows creating an `.rlink` file to perform compilation without linking. This change enables linking from an `.rlink` file.
Part of Issue #64191
Flag `-Z no-link` was previously introduced, which allows creating
an `.rlink` file to perform compilation without linking.
This change enables linking from an `.rlink` file.
Changes:
````
Update jobserver.
Update tar.
Emit report on error with Ztimings.
Do not run `formats_source` if `rustfmt` is not available
Fix rebuild_sub_package_then_while_package on HFS.
Remove likely brittle test.
Install rustfmt for testing in CI
Fix build-std collisions.
Fix BuildScriptOutput when a build script is run multiple times.
Fix required-features using renamed dependencies.
Fix using global options before an alias.
Update changelog for 1.42.
Bump to 0.44.0.
Log rustfmt output if it fails; also do not check that rustfmt exists
Update pretty_env_logger requirement from 0.3 to 0.4
Swap std::sync::mpsc channel with crossbeam_channel
Fix tests on Linux/MacOS
Fix typo.
Add tests
Deduplicate warnings about missing rustfmt
Log entry 2: first implementation
Refactor code
Stabilize config-profile.
Log entry 1
Format code
Remove tempdir after install
Keep existing package with git install
Use non-ephemeral workspace
Test that git install reads virtual manifest
Fix failing test
Search for root manifest with ephemeral workspaces
Support out-dir in build section of Cargo configuration file
````