When encountering trait bound errors that satisfy some heuristics that
tell us that the relevant trait for the user comes from the root
obligation and not the current obligation, we use the root predicate for
the main message.
This allows to talk about "X doesn't implement Pattern<'_>" over the
most specific case that just happened to fail, like "char doesn't
implement Fn(&mut char)" in
`tests/ui/traits/suggest-dereferences/root-obligation.rs`
The heuristics are:
- the type of the leaf predicate is (roughly) the same as the type
from the root predicate, as a proxy for "we care about the root"
- the leaf trait and the root trait are different, so as to avoid
talking about `&mut T: Trait` and instead remain talking about
`T: Trait` instead
- the root trait is not `Unsize`, as to avoid talking about it in
`tests/ui/coercion/coerce-issue-49593-box-never.rs`.
```
error[E0277]: the trait bound `&char: Pattern<'_>` is not satisfied
--> $DIR/root-obligation.rs:6:38
|
LL | .filter(|c| "aeiou".contains(c))
| -------- ^ the trait `Fn<(char,)>` is not implemented for `&char`, which is required by `&char: Pattern<'_>`
| |
| required by a bound introduced by this call
|
= note: required for `&char` to implement `FnOnce<(char,)>`
= note: required for `&char` to implement `Pattern<'_>`
note: required by a bound in `core::str::<impl str>::contains`
--> $SRC_DIR/core/src/str/mod.rs:LL:COL
help: consider dereferencing here
|
LL | .filter(|c| "aeiou".contains(*c))
| +
```
Fix#79359, fix#119983, fix#118779, cc #118415 (the suggestion needs
to change).
Support async trait bounds in macros
r? fmease
This is similar to your work on const trait bounds. This theoretically regresses `impl async $ident:ident` in macros, but I doubt this is occurring in practice.
When encountering a tail expression in the then arm of an `if` expression
without an `else` arm, account for `async fn` and `async` blocks to
suggest `return`ing the value and pointing at the return type of the
`async fn`.
We now also account for AFIT when looking for the return type to point at.
Fix#115405.
Encode `coroutine_for_closure` for foreign crates
Async closures (and "coroutine closures" in general) need to have their child coroutine encoded. This PR does that.
r? oli-obk
Harmonize `AsyncFn` implementations, make async closures conditionally impl `Fn*` traits
This PR implements several changes to the built-in and libcore-provided implementations of `Fn*` and `AsyncFn*` to address two problems:
1. async closures do not implement the `Fn*` family traits, leading to breakage: https://crater-reports.s3.amazonaws.com/pr-120361/index.html
2. *references* to async closures do not implement `AsyncFn*`, as a consequence of the existing blanket impls of the shape `AsyncFn for F where F: Fn, F::Output: Future`.
In order to fix (1.), we implement `Fn` traits appropriately for async closures. It turns out that async closures can:
* always implement `FnOnce`, meaning that they're drop-in compatible with `FnOnce`-bound combinators like `Option::map`.
* conditionally implement `Fn`/`FnMut` if they have no captures, which means that existing usages of async closures should *probably* work without breakage (crater checking this: https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/120712#issuecomment-1930587805).
In order to fix (2.), we make all of the built-in callables implement `AsyncFn*` via built-in impls, and instead adjust the blanket impls for `AsyncFn*` provided by libcore to match the blanket impls for `Fn*`.
For a rigid projection, recursively look at the self type's item bounds to fix the `associated_type_bounds` feature
Given a deeply nested rigid projection like `<<<T as Trait1>::Assoc1 as Trait2>::Assoc2 as Trait3>::Assoc3`, this PR adjusts both trait solvers to look at the item bounds for all of `Assoc3`, `Assoc2`, and `Assoc1` in order to satisfy a goal. We do this because the item bounds for projections may contain relevant bounds for *other* nested projections when the `associated_type_bounds` (ATB) feature is enabled. For example:
```rust
#![feature(associated_type_bounds)]
trait Trait1 {
type Assoc1: Trait2<Assoc2: Foo>;
// Item bounds for `Assoc1` are:
// `<Self as Trait1>::Assoc1: Trait2`
// `<<Self as Trait1>::Assoc1 as Trait2>::Assoc2: Foo`
}
trait Trait2 {
type Assoc2;
}
trait Foo {}
fn hello<T: Trait1>(x: <<T as Trait1>::Assoc1 as Trait2>::Assoc2) {
fn is_foo(_: impl Foo) {}
is_foo(x);
// Currently fails with:
// ERROR the trait bound `<<Self as Trait1>::Assoc1 as Trait2>::Assoc2: Foo` is not satisfied
}
```
This has been a long-standing place of brokenness for ATBs, and is also part of the reason why ATBs currently desugar so differently in various positions (i.e. sometimes desugaring to param-env bounds, sometimes desugaring to RPITs, etc). For example, in RPIT and TAIT position, `impl Foo<Bar: Baz>` currently desugars to `impl Foo<Bar = impl Baz>` because we do not currently take advantage of these nested item bounds if we desugared them into a single set of item bounds on the opaque. This is obviously both strange and unnecessary if we just take advantage of these bounds as we should.
## Approach
This PR repeatedly peels off each projection of a given goal's self type and tries to match its item bounds against a goal, repeating with the self type of the projection. This is pretty straightforward to implement in the new solver, only requiring us to loop on the self type of a rigid projection to discover inner rigid projections, and we also need to introduce an extra probe so we can normalize them.
In the old solver, we can do essentially the same thing, however we rely on the fact that projections *should* be normalized already. This is obviously not always the case -- however, in the case that they are not fully normalized, such as a projection which has both infer vars and, we bail out with ambiguity if we hit an infer var for the self type.
## Caveats
⚠️ In the old solver, this has the side-effect of actually stalling some higher-ranked trait goals of the form `for<'a> <?0 as Tr<'a>>: Tr2`. Because we stall them, they no longer are eagerly treated as error -- this cause some existing `known-bug` tests to go from fail -> pass.
I'm pretty unconvinced that this is a problem since we make code that we expect to pass in the *new* solver also pass in the *old* solver, though this obviously doesn't solve the *full* problem.
## And then also...
We also adjust the desugaring of ATB to always desugar to a regular associated bound, rather than sometimes to an impl Trait **except** for when the ATB is present in a `dyn Trait`. We need to lower `dyn Trait<Assoc: Bar>` to `dyn Trait<Assoc = impl Bar>` because object types need all of their associated types specified.
I would also be in favor of splitting out the ATB feature and/or removing support for object types in order to stabilize just the set of positions for which the ATB feature is consistent (i.e. always elaborates to a bound).
Build DebugInfo for async closures
The test is pretty bare, because I don't really know how to write debuginfo tests. I'd like to land this first, and then flesh it out correctly one it's no longer ICEing on master (which breaks people's ability to test using async closures).
r? oli-obk cc `@rust-lang/wg-debugging` (if any of y'all want to help me write a more fleshed out async closures test)
Rollup of 9 pull requests
Successful merges:
- #119592 (resolve: Unload speculatively resolved crates before freezing cstore)
- #120103 (Make it so that async-fn-in-trait is compatible with a concrete future in implementation)
- #120206 (hir: Make sure all `HirId`s have corresponding HIR `Node`s)
- #120214 (match lowering: consistently lower bindings deepest-first)
- #120688 (GVN: also turn moves into copies with projections)
- #120702 (docs: also check the inline stmt during redundant link check)
- #120727 (exhaustiveness: Prefer "`0..MAX` not covered" to "`_` not covered")
- #120734 (Add `SubdiagnosticMessageOp` as a trait alias.)
- #120739 (improve pretty printing for associated items in trait objects)
r? `@ghost`
`@rustbot` modify labels: rollup
Make it so that async-fn-in-trait is compatible with a concrete future in implementation
There's no technical reason why an AFIT like `async fn foo()` cannot be satisfied with an implementation signature like `fn foo() -> Pin<Box<dyn Future<Output = ()> + 'static>>`.
We rejected this previously because we were uncertain about how AFITs worked with refinement, but I don't believe this needs to be a restriction any longer.
r? oli-obk
Stop bailing out from compilation just because there were incoherent traits
fixes#120343
but also has a lot of "type annotations needed" fallout. Some are fixed in the second commit.
Don't expect early-bound region to be local when reporting errors in RPITIT well-formedness
The implicit lifetime in the example code gets replaced with `ReError`, which fails a `sub_regions` check in the lexical region solver. Error reporting ends up calling `is_suitable_region` on an early bound region in the *trait* definition. This causes an ICE because we `expect_local()`.
This is kind of a bad explanation, but this code just makes diagnostics reporting a bit more gracefully fallible. If the reviewer wants a thorough investigation of exactly where we get this region outlives obligation, I can write one up. Doesn't really seem worth it, though, imo.
Fixes#120638Fixes#120648
Rework support for async closures; allow them to return futures that borrow from the closure's captures
This PR implements a new lowering for async closures via `TyKind::CoroutineClosure` which handles the curious relationship between the closure and the coroutine that it returns.
I wrote up a bunch in [this hackmd](https://hackmd.io/`@compiler-errors/S1HvqQxca)` which will be copied to the dev guide after this PR lands, and hopefully left sufficient comments in the source code explaining why this change is as large as it is.
This also necessitates that they begin implementing the `AsyncFn`-family of traits, rather than the `Fn`-family of traits -- if you need `Fn` implementations, you should probably use the non-sugar `|| async {}` syntax instead.
Notably this PR does not yet implement `async Fn()` syntax sugar for bounds, but I expect to add those soon (**edit:** #120392). For now, users must use `AsyncFn()` traits directly, which necessitates adding the `async_fn_traits` feature gate as well. I will add this as a follow-up very soon.
r? oli-obk
This is based on top of #120322, but that PR is minimal.
Introduce support for `async` bound modifier on `Fn*` traits
Adds `async` to the list of `TraitBoundModifiers`, which instructs AST lowering to map the trait to an async flavor of the trait. For now, this is only supported for `Fn*` to `AsyncFn*`, and I expect that this manual mapping via lang items will be replaced with a better system in the future.
The motivation for adding these bounds is to separate the users of async closures from the exact trait desugaring of their callable bounds. Instead of users needing to be concerned with the `AsyncFn` trait, they should be able to write `async Fn()` and it will desugar to whatever underlying trait we decide is best for the lowering of async closures.
Note: rustfmt support can be done in the rustfmt repo after a subtree sync.
Expand the primary span of E0277 when the immediate unmet bound is not what the user wrote:
```
error[E0277]: the trait bound `i32: Bar` is not satisfied
--> f100.rs:6:6
|
6 | <i32 as Foo>::foo();
| ^^^ the trait `Bar` is not implemented for `i32`, which is required by `i32: Foo`
|
help: this trait has no implementations, consider adding one
--> f100.rs:2:1
|
2 | trait Bar {}
| ^^^^^^^^^
note: required for `i32` to implement `Foo`
--> f100.rs:3:14
|
3 | impl<T: Bar> Foo for T {}
| --- ^^^ ^
| |
| unsatisfied trait bound introduced here
```
Fix#40120.
Deduplicate more sized errors on call exprs
Change the implicit `Sized` `Obligation` `Span` for call expressions to include the whole expression. This aids the existing deduplication machinery to reduce the number of errors caused by a single unsized expression.
Don't fire `OPAQUE_HIDDEN_INFERRED_BOUND` on sized return of AFIT
Conceptually, we should probably not fire `OPAQUE_HIDDEN_INFERRED_BOUND` for methods like:
```
trait Foo { async fn bar() -> Self; }
```
Even though we technically cannot prove that `Self: Sized`, which is one of the item bounds of the `Output` type in the `-> impl Future<Output = Sized>` from the async desugaring.
This is somewhat justifiable along the same lines as how we allow regular methods to return `-> Self` even though `Self` isn't sized.
Fixes#113538
(side-note: some days i wonder if we should just remove the `OPAQUE_HIDDEN_INFERRED_BOUND` lint... it does make me sad that we have non-well-formed types in signatures, though.)
Don't manually resolve async closures in `rustc_resolve`
There's a comment here that talks about doing this "[so] closure [args] are detected as upvars rather than normal closure arg usages", but we do upvar analysis on the HIR now:
cd6d8f2a04/compiler/rustc_passes/src/upvars.rs (L21-L29)
Removing this ad-hoc logic makes it so that `async |x: &str|` now introduces an implicit binder, like regular closures.
r? ```@oli-obk```
Add `AsyncFn` family of traits
I'm proposing to add a new family of `async`hronous `Fn`-like traits to the standard library for experimentation purposes.
## Why do we need new traits?
On the user side, it is useful to be able to express `AsyncFn` trait bounds natively via the parenthesized sugar syntax, i.e. `x: impl AsyncFn(&str) -> String` when experimenting with async-closure code.
This also does not preclude `AsyncFn` becoming something else like a trait alias if a more fundamental desugaring (which can take many[^1] different[^2] forms) comes around. I think we should be able to play around with `AsyncFn` well before that, though.
I'm also not proposing stabilization of these trait names any time soon (we may even want to instead express them via new syntax, like `async Fn() -> ..`), but I also don't think we need to introduce an obtuse bikeshedding name, since `AsyncFn` just makes sense.
## The lending problem: why not add a more fundamental primitive of `LendingFn`/`LendingFnMut`?
Firstly, for `async` closures to be as flexible as possible, they must be allowed to return futures which borrow from the async closure's captures. This can be done by introducing `LendingFn`/`LendingFnMut` traits, or (equivalently) by adding a new generic associated type to `FnMut` which allows the return type to capture lifetimes from the `&mut self` argument of the trait. This was proposed in one of [Niko's blog posts](https://smallcultfollowing.com/babysteps/blog/2023/05/09/giving-lending-and-async-closures/).
Upon further experimentation, for the purposes of closure type- and borrow-checking, I've come to the conclusion that it's significantly harder to teach the compiler how to handle *general* lending closures which may borrow from their captures. This is, because unlike `Fn`/`FnMut`, the `LendingFn`/`LendingFnMut` traits don't form a simple "inheritance" hierarchy whose top trait is `FnOnce`.
```mermaid
flowchart LR
Fn
FnMut
FnOnce
LendingFn
LendingFnMut
Fn -- isa --> FnMut
FnMut -- isa --> FnOnce
LendingFn -- isa --> LendingFnMut
Fn -- isa --> LendingFn
FnMut -- isa --> LendingFnMut
```
For example:
```
fn main() {
let s = String::from("hello, world");
let f = move || &s;
let x = f(); // This borrows `f` for some lifetime `'1` and returns `&'1 String`.
```
That trait hierarchy means that in general for "lending" closures, like `f` above, there's not really a meaningful return type for `<typeof(f) as FnOnce>::Output` -- it can't return `&'static str`, for example.
### Special-casing this problem:
By splitting out these traits manually, and making sure that each trait has its own associated future type, we side-step the issue of having to answer the questions of a general `LendingFn`/`LendingFnMut` implementation, since the compiler knows how to generate built-in implementations for first-class constructs like async closures, including the required future types for the (by-move) `AsyncFnOnce` and (by-ref) `AsyncFnMut`/`AsyncFn` trait implementations.
[^1]: For example, with trait transformers, we may eventually be able to write: `trait AsyncFn = async Fn;`
[^2]: For example, via the introduction of a more fundamental "`LendingFn`" trait, plus a [special desugaring with augmented trait aliases](https://rust-lang.zulipchat.com/#narrow/stream/213817-t-lang/topic/Lending.20closures.20and.20Fn*.28.29.20-.3E.20impl.20Trait/near/408471480).
Change the implicit `Sized` `Obligation` `Span` for call expressions to
include the whole expression. This aids the existing deduplication
machinery to reduce the number of errors caused by a single unsized
expression.
Change return type of unstable `Waker::noop()` from `Waker` to `&Waker`.
The advantage of this is that it does not need to be assigned to a variable to be used in a `Context` creation, which is the most common thing to want to do with a noop waker. It also avoids unnecessarily executing the dynamically dispatched drop function when the noop waker is dropped.
If an owned noop waker is desired, it can be created by cloning, but the reverse is harder to do since it requires declaring a constant. Alternatively, both versions could be provided, like `futures::task::noop_waker()` and `futures::task::noop_waker_ref()`, but that seems to me to be API clutter for a very small benefit, whereas having the `&'static` reference available is a large reduction in boilerplate.
[Previous discussion on the tracking issue starting here](https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/98286#issuecomment-1862159766)
Don't ICE when deducing future output if other errors already occurred
The situation can't really happen outside of erroneous code. What was interesting is that it ICEd before emitting any other diagnostics. This was because the other errors were silenced due to cycle_delay_bug cycle errors.
r? ```@compiler-errors```
fixes#119890
Silence some follow-up errors [3/x]
this is one piece of the requested cleanups from https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/117449
Keep error types around, even in obligations.
These help silence follow-up errors, as we now figure out that some types (most notably inference variables) are equal to an error type.
But it also allows figuring out more types in the presence of errors, possibly causing more errors.
Wrap coroutine variant fields in MaybeUninit to indicate that they
might be uninitialized. Otherwise an uninhabited field will make
the entire variant uninhabited and introduce undefined behaviour.
The analogous issue in the prefix of coroutine layout was addressed by
6fae7f8071.
This is an extension of the previous commit. It means the output of
something like this:
```
stringify!(let a: Vec<u32> = vec![];)
```
goes from this:
```
let a: Vec<u32> = vec![] ;
```
With this PR, it now produces this string:
```
let a: Vec<u32> = vec![];
```
`tokenstream::Spacing` appears on all `TokenTree::Token` instances,
both punct and non-punct. Its current usage:
- `Joint` means "can join with the next token *and* that token is a
punct".
- `Alone` means "cannot join with the next token *or* can join with the
next token but that token is not a punct".
The fact that `Alone` is used for two different cases is awkward.
This commit augments `tokenstream::Spacing` with a new variant
`JointHidden`, resulting in:
- `Joint` means "can join with the next token *and* that token is a
punct".
- `JointHidden` means "can join with the next token *and* that token is a
not a punct".
- `Alone` means "cannot join with the next token".
This *drastically* improves the output of `print_tts`. For example,
this:
```
stringify!(let a: Vec<u32> = vec![];)
```
currently produces this string:
```
let a : Vec < u32 > = vec! [] ;
```
With this PR, it now produces this string:
```
let a: Vec<u32> = vec![] ;
```
(The space after the `]` is because `TokenTree::Delimited` currently
doesn't have spacing information. The subsequent commit fixes this.)
The new `print_tts` doesn't replicate original code perfectly. E.g.
multiple space characters will be condensed into a single space
character. But it's much improved.
`print_tts` still produces the old, uglier output for code produced by
proc macros. Because we have to translate the generated code from
`proc_macro::Spacing` to the more expressive `token::Spacing`, which
results in too much `proc_macro::Along` usage and no
`proc_macro::JointHidden` usage. So `space_between` still exists and
is used by `print_tts` in conjunction with the `Spacing` field.
This change will also help with the removal of `Token::Interpolated`.
Currently interpolated tokens are pretty-printed nicely via AST pretty
printing. `Token::Interpolated` removal will mean they get printed with
`print_tts`. Without this change, that would result in much uglier
output for code produced by decl macro expansions. With this change, AST
pretty printing and `print_tts` produce similar results.
The commit also tweaks the comments on `proc_macro::Spacing`. In
particular, it refers to "compound tokens" rather than "multi-char
operators" because lifetimes aren't operators.
recurse into refs when comparing tys for diagnostics
before:

after:
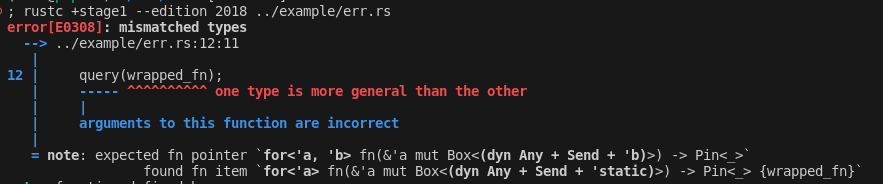
this diff from the test suite is also quite nice imo:
```diff
`@@` -4,8 +4,8 `@@` error[E0308]: mismatched types
LL | debug_assert_eq!(iter.next(), Some(value));
| ^^^^^^^^^^^ expected `Option<<I as Iterator>::Item>`, found `Option<&<I as Iterator>::Item>`
|
- = note: expected enum `Option<<I as Iterator>::Item>`
- found enum `Option<&<I as Iterator>::Item>`
+ = note: expected enum `Option<_>`
+ found enum `Option<&_>`
```