Add all known `target_feature` configs to check-cfg
This PR adds all the known `target_feature` from ~~`rustc_codegen_ssa`~~ `rustc_target` to the well known list of check-cfg.
It does so by moving the list from `rustc_codegen_ssa` to `rustc_target` ~~`rustc_session` (I not sure about this, but some of the moved function take a `Session`)~~, then using it the `fill_well_known` function.
This already proved to be useful since portable-simd had a bad cfg.
cc `@nnethercote` (since we discussed it in https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/118494)
It's necessary for `derive(Diagnostic)`, but is best avoided elsewhere
because there are clearer alternatives.
This required adding `Handler::struct_almost_fatal`.
Rearrange `default_configuration` and `CheckCfg::fill_well_known`.
There are comments saying these two functions should be kept in sync, but they have very different structures, process symbols in different orders, and there are some inconsistencies.
This commit reorders them so they're both mostly processing symbols in alphabetical order, which makes cross-checking them a lot easier. The commit also adds some macros to factor out repetitive code patterns.
The commit also moves the handling of `sym::test` out of `build_configuration` into `default_configuration`, where all the other symbols are handled.
r? `@bjorn3`
There are comments saying these two functions should be kept in sync,
but they have very different structures, process symbols in different
orders, and there are some inconsistencies.
This commit reorders them so they're both mostly processing symbols in
alphabetical order, which makes cross-checking them a lot easier. The
commit also adds some macros to factor out repetitive code patterns.
Plus it adds `sanitizer_cfi_normalize_{integers,pointers}` to
`fill_well_known`, which were missing.
The commit also moves the handling of `sym::test` out of
`build_configuration` into `default_configuration`, where all the other
symbols are handled.
Implement `--env` compiler flag (without `tracked_env` support)
Part of https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/80792.
Implementation of https://github.com/rust-lang/compiler-team/issues/653.
Not an implementation of https://github.com/rust-lang/rfcs/pull/2794.
It adds the `--env` compiler flag option which allows to set environment values used by `env!` and `option_env!`.
Important to note: When trying to retrieve an environment variable value, it will first look into the ones defined with `--env`, and if there isn't one, then only it will look into the environment variables. So if you use `--env PATH=a`, then `env!("PATH")` will return `"a"` and not the actual `PATH` value.
As mentioned in the title, `tracked_env` support is not added here. I'll do it in a follow-up PR.
r? rust-lang/compiler
Add emulated TLS support
This is a reopen of https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/96317 . many android devices still only use 128 pthread keys, so using emutls can be helpful.
Currently LLVM uses emutls by default for some targets (such as android, openbsd), but rust does not use it, because `has_thread_local` is false.
This commit has some changes to allow users to enable emutls:
1. add `-Zhas-thread-local` flag to specify that std uses `#[thread_local]` instead of pthread key.
2. when using emutls, decorate symbol names to find thread local symbol correctly.
3. change `-Zforce-emulated-tls` to `-Ztls-model=emulated` to explicitly specify whether to generate emutls.
r? `@Amanieu`
Currently LLVM uses emutls by default
for some targets (such as android, openbsd),
but rust does not use it, because `has_thread_local` is false.
This commit has some changes to allow users to enable emutls:
1. add `-Zhas-thread-local` flag to specify
that std uses `#[thread_local]` instead of pthread key.
2. when using emutls, decorate symbol names
to find thread local symbol correctly.
3. change `-Zforce-emulated-tls` to `-Ztls-model=emulated`
to explicitly specify whether to generate emutls.
`build_session` is passed an `EarlyErrorHandler` and then constructs a
`Handler`. But the `EarlyErrorHandler` is still used for some time after
that.
This commit changes `build_session` so it consumes the passed
`EarlyErrorHandler`, and also drops it as soon as the `Handler` is
built. As a result, `parse_cfg` and `parse_check_cfg` now take a
`Handler` instead of an `EarlyErrorHandler`.
These impls are all needed for just a single `IntoDiagnostic` type, not
a family of them.
Note that `ErrorGuaranteed` is the default type parameter for
`IntoDiagnostic`.
Currently, `Handler::fatal` returns `FatalError`. But `Session::fatal`
returns `!`, because it calls `Handler::fatal` and then calls `raise` on
the result. This inconsistency is unfortunate.
This commit changes `Handler::fatal` to do the `raise` itself, changing
its return type to `!`. This is safe because there are only two calls to
`Handler::fatal`, one in `rustc_session` and one in
`rustc_codegen_cranelift`, and they both call `raise` on the result.
`HandlerInner::fatal` still returns `FatalError`, so I renamed it
`fatal_no_raise` to emphasise the return type difference.
rustc_session: Address all `rustc::potential_query_instability` lints
Instead of allowing `rustc::potential_query_instability` on the whole crate we go over each lint and allow it individually if it is safe to do. Turns out all instances were safe to allow in this crate.
Part of #84447 which is **E-help-wanted**.
Report errors in jobserver inherited through environment variables
This pr attempts to catch situations, when jobserver exists, but is not being inherited.
r? `@petrochenkov`
Instead of allowing `rustc::potential_query_instability` on the whole
crate we go over each lint and allow it individually if it is safe to
do. Turns out all instances were safe to allow in this crate.
This is intended to be used for Linux kernel RETHUNK builds.
With this commit (optionally backported to Rust 1.73.0), plus a
patched Linux kernel to pass the flag, I get a RETHUNK build with
Rust enabled that is `objtool`-warning-free and is able to boot in
QEMU and load a sample Rust kernel module.
Signed-off-by: Miguel Ojeda <ojeda@kernel.org>
They're not used in `rustc_session`, and `rustc_metadata` is a more
obvious location.
`MetadataLoader` was originally put into `rustc_session` in #41565 to
avoid a dependency on LLVM, but things have changed a lot since then and
that's no longer relevant, e.g. `rustc_codegen_llvm` depends on
`rustc_metadata`.
Currently we always do this:
```
use rustc_fluent_macro::fluent_messages;
...
fluent_messages! { "./example.ftl" }
```
But there is no need, we can just do this everywhere:
```
rustc_fluent_macro::fluent_messages! { "./example.ftl" }
```
which is shorter.
The `fluent_messages!` macro produces uses of
`crate::{D,Subd}iagnosticMessage`, which means that every crate using
the macro must have this import:
```
use rustc_errors::{DiagnosticMessage, SubdiagnosticMessage};
```
This commit changes the macro to instead use
`rustc_errors::{D,Subd}iagnosticMessage`, which avoids the need for the
imports.
Enable Rust to use the EHCont security feature of Windows
In the future Windows will enable Control-flow Enforcement Technology (CET aka Shadow Stacks). To protect the path where the context is updated during exception handling, the binary is required to enumerate valid unwind entrypoints in a dedicated section which is validated when the context is being set during exception handling.
The required support for EHCONT Guard has already been merged into LLVM, long ago. This change simply adds the Rust codegen option to enable it.
Relevant LLVM change: https://reviews.llvm.org/D40223
This also adds a new `ehcont-guard` option to the bootstrap config which enables EHCont Guard when building std.
We at Microsoft have been using this feature for a significant period of time; we are confident that the LLVM feature, when enabled, generates well-formed code.
We currently enable EHCONT using a codegen feature, but I'm certainly open to refactoring this to be a target feature instead, or to use any appropriate mechanism to enable it.
Remove `feature` from the list of well known check-cfg name
This PR removes `feature` from the list of well known check-cfg.
This is done for multiple reasons:
- Cargo is the source of truth, rustc shouldn't have any knowledge of it
- It creates a conflict between Cargo and rustc when there are no features defined.
In this case Cargo won't pass any `--check-cfg` for `feature` since no feature will ever be passed, but rustc by having in it's list adds a implicit `cfg(feature, values(any()))` which is completely wrong. Having any cfg `feature` is unexpected not allow any `feature` value.
While doing this, I took the opportunity to specialise the diagnostic a bit for the case above.
r? `@petrochenkov`
In the future Windows will enable Control-flow Enforcement Technology
(CET aka Shadow Stacks). To protect the path where the context is
updated during exception handling, the binary is required to enumerate
valid unwind entrypoints in a dedicated section which is validated when
the context is being set during exception handling.
The required support for EHCONT has already been merged into LLVM,
long ago. This change adds the Rust codegen option to enable it.
Reference:
* https://reviews.llvm.org/D40223
This also adds a new `ehcont-guard` option to the bootstrap config which
enables EHCont Guard when building std.
This was made possible by the removal of plugin support, which
simplified lint store creation.
This simplifies the places in rustc and rustdoc that call
`describe_lints`, which are early on. The lint store is now built before
those places, so they don't have to create their own lint store for
temporary use, they can just use the main one.
Add -Z llvm_module_flag
Allow adding values to the `!llvm.module.flags` metadata for a generated module. The syntax is
`-Z llvm_module_flag=<name>:<type>:<value>:<behavior>`
Currently only u32 values are supported but the type is required to be specified for forward compatibility. The `behavior` element must match one of the named LLVM metadata behaviors.viors.
This flag is expected to be perma-unstable.
Remove `-Zperf-stats`.
The included measurements have varied over the years. At one point there were quite a few more, but #49558 deleted a lot that were no longer used. Today there's just four, and it's a motley collection that doesn't seem particularly valuable.
I think it has been well and truly subsumed by self-profiling, which collects way more data.
r? `@wesleywiser`
Remove `-Zkeep-hygiene-data`.
It was added way back in #28585 under the name `-Zkeep-mtwt-tables`. The justification was:
> This is so that the resolution results can be used after analysis,
> potentially for tool support.
There are no uses of significance in the code base, and various Google searches for both option names (and variants) found nothing of interest. I think this can safely be removed.
r? `@davidtwco`
The included measurements have varied over the years. At one point there
were quite a few more, but #49558 deleted a lot that were no longer
used. Today there's just four, and it's a motley collection that doesn't
seem particularly valuable.
I think it has been well and truly subsumed by self-profiling, which
collects way more data.
Allow adding values to the `!llvm.module.flags` metadata for a generated
module. The syntax is
`-Z llvm_module_flag=<name>:<type>:<value>:<behavior>`
Currently only u32 values are supported but the type is required to be
specified for forward compatibility. The `behavior` element must match
one of the named LLVM metadata behaviors.viors.
This flag is expected to be perma-unstable.
Add `std:#️⃣:{DefaultHasher, RandomState}` exports (needs FCP)
This implements rust-lang/libs-team#267 to move the libstd hasher types to `std::hash` where they belong, instead of `std::collections::hash_map`.
<details><summary>The below no longer applies, but is kept for clarity.</summary>
This is a small refactor for #27242, which moves the definitions of `RandomState` and `DefaultHasher` into `std::hash`, but in a way that won't be noticed in the public API.
I've opened rust-lang/libs-team#267 as a formal ACP to move these directly into the root of `std::hash`, but for now, they're at least separated out from the collections code in a way that will make moving that around easier.
I decided to simply copy the rustdoc for `std::hash` from `core::hash` since I think it would be ideal for the two to diverge longer-term, especially if the ACP is accepted. However, I would be willing to factor them out into a common markdown document if that's preferred.
</details>
It was added way back in #28585 under the name `-Zkeep-mtwt-tables`. The
justification was:
> This is so that the resolution results can be used after analysis,
> potentially for tool support.
There are no uses of significance in the code base, and various Google
searches for both option names (and variants) found nothing of interest.
@petrochenkov says removing this part (and it's only part) of the
hygiene data is dubious. It doesn't seem that big, so let's just keep it
around.
It currently has the syntax
`current_rustc_version!(env!("CFG_RELEASE"))` where the
`env!("CFG_RELEASE")` part looks like a normal expression but it is
actually parsed and processed by the `current_rustc_version` macro.
The documented rationale for this is that you'll find it if you grep for
`env!("CFG_RELEASE")`. But I think that's of very little use -- I would
personally grep for just "CFG_RELEASE" -- and it complicates the macro,
requiring the use of `syn`.
This commit simplifies the macro.
It was stabilized as `-C strip` in November 2021. The unstable option
was kept around as a temporary measure to ease the transition. Two years
is more than enough!
Add -Zcross-crate-inline-threshold=yes
``@thomcc`` says this would be useful for
> seeing if it makes a difference in some code if i do it when building the sysroot, since -Zbuild-std + lto helps more than it seems like it should
And I've changed the possible values as a reference to ``@Manishearth`` saying
> LLVM's inlining heuristic is "yes".
Remove support for alias `-Z symbol-mangling-version`
(This is very similar to the removal of `-Z instrument-coverage` in #117111.)
`-C symbol-mangling-version` was stabilized back in rustc 1.59.0 (2022-02-24) via #90128, with the old unstable flag kept around (with a warning) as an alias to ease migration.
use global cache when computing proof trees
we're writing the solver while relying on the existence of the global cache to avoid exponential blowup. By disabling the global cache when building proof trees, it is easy to get hangs, e.g. when computing intercrate ambiguity causes.
Removes the unstable `-Zdump_solver_proof_tree_use_cache` option, as we now always return a full proof tree.
r? `@compiler-errors`
Most notably, this commit changes the `pub use crate::*;` in that file
to `use crate::*;`. This requires a lot of `use` items in other crates
to be adjusted, because everything defined within `rustc_span::*` was
also available via `rustc_span::source_map::*`, which is bizarre.
The commit also removes `SourceMap::span_to_relative_line_string`, which
is unused.
- Sort dependencies and features sections.
- Add `tidy` markers to the sorted sections so they stay sorted.
- Remove empty `[lib`] sections.
- Remove "See more keys..." comments.
Excluded files:
- rustc_codegen_{cranelift,gcc}, because they're external.
- rustc_lexer, because it has external use.
- stable_mir, because it has external use.
Despite what I claimed in an earlier commit, the ordering does matter to
some degree. Using `FxIndexSet` prevents changes to the error message
order in `tests/ui/check-cfg/mix.rs`.
`parse_cfgspecs` and `parse_check_cfg` run very early, before the main
interner is running. They each use a short-lived interner and convert
all interned symbols to strings in their output data structures. Once
the main interner starts up, these data structures get converted into
new data structures that are identical except with the strings converted
to symbols.
All is not obvious from the current code, which is a mess, particularly
with inconsistent naming that obscures the parallel string/symbol data
structures. This commit clean things up a lot.
- The existing `CheckCfg` type is generic, allowing both
`CheckCfg<String>` and `CheckCfg<Symbol>` forms. This is really
useful, but it defaults to `String`. The commit removes the default so
we have to use `CheckCfg<String>` and `CheckCfg<Symbol>` explicitly,
which makes things clearer.
- Introduces `Cfg`, which is generic over `String` and `Symbol`, similar
to `CheckCfg`.
- Renames some things.
- `parse_cfgspecs` -> `parse_cfg`
- `CfgSpecs` -> `Cfg<String>`, plus it's used in more places, rather
than the underlying `FxHashSet` type.
- `CrateConfig` -> `Cfg<Symbol>`.
- `CrateCheckConfig` -> `CheckCfg<Symbol>`
- Adds some comments explaining the string-to-symbol conversions.
- `to_crate_check_config`, which converts `CheckCfg<String>` to
`CheckCfg<Symbol>`, is inlined and removed and combined with the
overly-general `CheckCfg::map_data` to produce
`CheckCfg::<String>::intern`.
- `build_configuration` now does the `Cfg<String>`-to-`Cfg<Symbol>`
conversion, so callers don't need to, which removes the need for
`to_crate_config`.
The diff for two of the fields in `Config` is a good example of the
improved clarity:
```
- pub crate_cfg: FxHashSet<(String, Option<String>)>,
- pub crate_check_cfg: CheckCfg,
+ pub crate_cfg: Cfg<String>,
+ pub crate_check_cfg: CheckCfg<String>,
```
Compare that with the diff for the corresponding fields in `ParseSess`,
and the relationship to `Config` is much clearer than before:
```
- pub config: CrateConfig,
- pub check_config: CrateCheckConfig,
+ pub config: Cfg<Symbol>,
+ pub check_config: CheckCfg<Symbol>,
```
The value of `-Cinstrument-coverage=` doesn't need to be `Option`
(Extracted from #117199, since this is a purely internal cleanup that can land independently.)
Not using this flag is identical to passing `-Cinstrument-coverage=off`, so there's no need to distinguish between `None` and `Some(Off)`.
Stop telling people to submit bugs for internal feature ICEs
This keeps track of usage of internal features, and changes the message to instead tell them that using internal features is not supported.
I thought about several ways to do this but now used the explicit threading of an `Arc<AtomicBool>` through `Session`. This is not exactly incremental-safe, but this is fine, as this is set during macro expansion, which is pre-incremental, and also only affects the output of ICEs, at which point incremental correctness doesn't matter much anyways.
See [MCP 620.](https://github.com/rust-lang/compiler-team/issues/596)
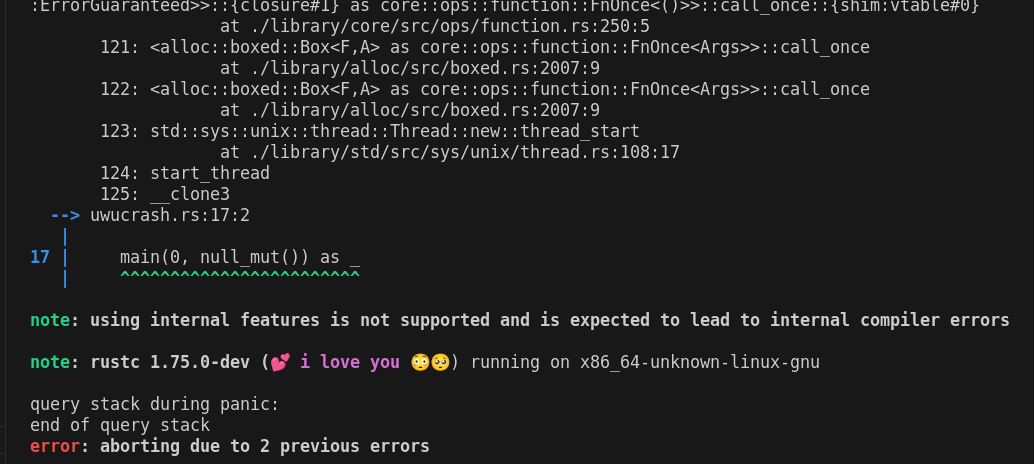
This keeps track of usage of internal features, and changes the message
to instead tell them that using internal features is not supported.
See MCP 620.
Location-insensitive polonius: consider a loan escaping if an SCC has member constraints applied only
The location-insensitive analysis considered loans to escape if there were member constraints, which makes *some* sense for scopes and matches the scopes that NLL computes on all the tests.
However, polonius and NLLs differ on the fuzzed case #116657, where an SCC has member constraints but no applied ones (and is kinda surprising). The existing UI tests with member constraints impacting scopes all have some constraint applied.
This PR changes the location-insensitive analysis to consider a loan to escape if there are applied member constraints, and for extra paranoia/insurance via fuzzing and crater: actually checks the constraint's min choice is indeed a universal region as we expect. (This could be turned into a `debug_assert` and early return as a slight optimization after these periods of verification)
The 4 UI tests where member constraints are meaningful for computing scopes still pass obviously, and this also fixes#116657.
r? `@matthewjasper`
Implement rustc part of RFC 3127 trim-paths
This PR implements (or at least tries to) [RFC 3127 trim-paths](https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/111540), the rustc part. That is `-Zremap-path-scope` with all of it's components/scopes.
`@rustbot` label: +F-trim-paths
Add `Config::hash_untracked_state` callback
For context, I'm looking to use [late module passes](https://doc.rust-lang.org/nightly/nightly-rustc/rustc_lint/context/struct.LintStore.html#structfield.late_module_passes) in Clippy which unlike regular late passes run incrementally per module
However we have a config file which can change between runs, we need changes to that to invalidate the `lint_mod` query. This PR adds a side channel for us to hash some extra state into `Options` in order to do that
This does not make any changes to Clippy, I plan to do that in a PR to the Clippy repo along with some other required changes
An alternative implementation would be to add a new query to track this state and override the `lint_mod` query in Clippy to first call that
cc `@rust-lang/clippy`
It's a better name, and lets "active features" refer to the features
that are active in a particular program, due to being declared or
enabled by the edition.
The commit also renames `Features::enabled` as `Features::active` to
match this; I changed my mind and have decided that "active" is a little
better thatn "enabled" for this, particularly because a number of
pre-existing comments use "active" in this way.
Finally, the commit renames `Status::Stable` as `Status::Accepted`, to
match `ACCEPTED_FEATURES`.
Streamline `rustc_driver_impl` pretty-printing.
This PR simplifies a lot of unnecessary structure in
`rustc_driver_impl/src/pretty.rs`. It removes some traits and functions,
simplifies some structs, renames some things for increased consistency, and
eliminates some boilerplate code. Overall it cuts more than 150 lines of code.
r? `@compiler-errors`
Remove cgu_reuse_tracker from Session
This removes a bit of global mutable state.
It will now miss post-lto cgu reuse when ThinLTO determines that a cgu doesn't get changed, but there weren't any tests for this anyway and a test for it would be fragile to the exact implementation of ThinLTO in LLVM.
Compute NLL loan scopes using the polonius model
For a *location-insensitive* analysis (that is, without expressiveness improvements for users yet), this PR implements loans going out of scope using reachability and liveness, rather than checking if the issuing region's values contain a given CFG point. This is equivalent to NLL scopes and computes the same data.
r? `@matthewjasper`
A couple of notes:
- there are some assumptions about SCC representatives, placeholders, free regions, and member constraints that I believe hold, and they're documented in the code
- this passes all the UI tests with `-Zpolonius=next` -- the perf is [not terrible](https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/112432#issuecomment-1749685862) and there are a bunch of ways to improve it in the future.
- there's a fixme left, hopefully Matthew you know a clean way to get the information it mentions.
Implement `-Clink-self-contained=-linker` opt out
This implements the `-Clink-self-contained` opt out necessary to switch to lld by changing rustc's defaults instead of cargo's.
Components that are enabled and disabled on the CLI are recorded, for the purpose of being merged with the ones which the target spec will declare (I'll open another PR for that tomorrow, for easier review).
For MCP510, we now check whether using the self-contained linker is disabled on the CLI. Right now it would only be sensible to with `-Zgcc-ld=lld` (and I'll add some checks that we don't both enable and disable a component on the CLI in a future PR), but the goal is to simplify adding the check of the target's enabled components here in the follow-up PRs.
r? `@petrochenkov`
[breaking change] Validate crate name in `--extern` [MCP 650]
Reject non-ASCII-identifier crate names passed to the CLI option `--extern` (`rustc`, `rustdoc`).
Implements [MCP 650](https://github.com/rust-lang/compiler-team/issues/650) (except that we only allow ASCII identifiers not arbitrary Rust identifiers).
Fixes#113035.
[As mentioned on Zulip](https://rust-lang.zulipchat.com/#narrow/stream/233931-t-compiler.2Fmajor-changes/topic/Disallow.20non-identifier-valid.20--extern.20cr.E2.80.A6.20compiler-team.23650/near/376826988), doing a crater run probably doesn't make sense since it wouldn't yield anything. Most users don't interact with `rustc` directly but only ever through Cargo which always passes a valid crate name to `--extern` when it invokes `rustc` and `rustdoc`. In any case, the user wouldn't be able to use such a crate name in the source code anyway.
Note that I'm not using [`rustc_session::output::validate_crate_name`](https://doc.rust-lang.org/nightly/nightly-rustc/rustc_session/output/fn.validate_crate_name.html) (used for `--crate-name` and `#![crate_name]`) since the latter doesn't reject non-ASCII crate names and ones that start with a digit.
As an aside, I've also thought about getting rid of `validate_crate_name` entirely in a separate PR (with another MCP) in favor of `is_ascii_ident` to reject more weird `--crate-name`s, `#![crate_name]`s and file names but I think that would lead to a lot of actual breakage, namely because of file names starting with a digit. In `tests/ui` 9 tests would be impacted for example.
CC `@estebank`
r? `@est31`
Avoid blessing cargo deps's source code in ui tests
Before this PR, the source code of dependencies was included in UI test error messages whenever possible. Unfortunately, "whenever possible" means in some cases the source code wouldn't be injected, resulting in a test failure.
One such case is when `$CARGO_HOME` is remapped to something that is not present on disk [^1]. As the remapped path doesn't exist on disk, the source code wouldn't be showed in `tests/ui/issues/issue-21763.rs`:
```diff
= note: required for `hashbrown::raw::RawTable<(Rc<()>, Rc<()>)>` to implement `Send`
note: required because it appears within the type `HashMap<Rc<()>, Rc<()>, RandomState>`
--> $HASHBROWN_SRC_LOCATION
- |
-LL | pub struct HashMap<K, V, S = DefaultHashBuilder, A: Allocator + Clone = Global> {
- | ^^^^^^^
note: required because it appears within the type `HashMap<Rc<()>, Rc<()>>`
--> $SRC_DIR/std/src/collections/hash/map.rs:LL:COL
note: required by a bound in `foo`
```
This PR fixes the problem by always hiding dependencies source code in the error messages generated during UI tests. This is implemented with a new internal flag, `-Z ignore-directory-in-diagnostics-source-blocks=$path`, which compiletest passes during UI tests. Once this is merged, remapping the Cargo home will be supported.
This PR is best reviewed commit-by-commit.
[^1]: After being puzzled for a bit, I discovered why this never impacted `rust-lang/rust`: we don't remap `$CARGO_HOME` 😅. Instead, we set `$CARGO_HOME` to `/cargo` in CI, which sort-of-but-not-really achieves the same effect.
Make `.rmeta` file in `dep-info` have correct name (`lib` prefix)
Since `filename_for_metadata()` and
`OutputFilenames::path(OutputType::Metadata)` had different logic for the name of the metadata file, the `.d` file contained a file name different from the actual name used. Share the logic to fix the out-of-sync name.
Without this fix, the `.d` file contained
dash-separated_something-extra.rmeta: dash-separated.rs
instead of
libdash_separated_something-extra.rmeta: dash-separated.rs
which is the name of the file that is actually written by the compiler.
Worth noting: It took me several iterations to get all tests to pass, so I am relatively confident that this PR does not break anything.
Closes#68839
Enable incremental-relative-spans by default.
This was enabled on nightly in https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/84762.
It has been a while, without obvious bugs. It's time to enable it by default for incremental runs.
Use `FreezeLock` for `CStore`
This uses `FreezeLock` to protect the `CStore`. `FreezeReadGuard` and `FreezeWriteGuard` are changed to support a `map` operation.
r? `@oli-obk`
Abort if check nightly options failed on stable
Fixes#115680
Also, if there are multiple unstable options passing on stable compiler, printing multiple same `note` and `help` seems noisy.
LLVM already supports emitting compressed debuginfo. In debuginfo=full
builds, the debug section is often a large amount of data, and it
typically compresses very well (3x is not unreasonable.) We add a new
knob to allow debuginfo to be compressed when the matching LLVM
functionality is present. Like clang, if a known-but-disabled
compression mechanism is requested, we disable compression and emit
uncompressed debuginfo sections.
The API is different enough on older LLVMs we just pretend the support
is missing on LLVM older than 16.
Add CL and CMD into to pdb debug info
Partial fix for https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/96475
The Arg0 and CommandLineArgs of the MCTargetOptions cpp class are not set within bb548f9645/compiler/rustc_llvm/llvm-wrapper/PassWrapper.cpp (L378)
This causes LLVM to not neither output any compiler path (cl) nor the arguments that were used when invoking it (cmd) in the PDB file.
This fix adds the missing information to the target machine so LLVM can use it.
Stabilize `PATH` option for `--print KIND=PATH`
This PR propose stabilizing the `PATH` option for `--print KIND=PATH`. This option was previously added in https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/113780 (as insta-stable before being un-stablized in https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/114139).
Description of the `PATH` option:
> A filepath may optionally be specified for each requested information kind, in the format `--print KIND=PATH`, just like for `--emit`. When a path is specified, information will be written there instead of to stdout.
------
Description of the original PR [\[link\]](https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/113780#issue-1807080607):
> **Support --print KIND=PATH command line syntax**
>
> As is already done for `--emit KIND=PATH` and `-L KIND=PATH`.
>
> In the discussion of https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/110785, it was pointed out that `--print KIND=PATH` is nicer than trying to apply the single global `-o path` to `--print`'s output, because in general there can be multiple print requests within a single rustc invocation, and anyway `-o` would already be used for a different meaning in the case of `link-args` and `native-static-libs`.
>
> I am interested in using `--print cfg=PATH` in Buck2. Currently Buck2 works around the lack of support for `--print KIND=PATH` by [indirecting through a Python wrapper script](d43cf3a51a/prelude/rust/tools/get_rustc_cfg.py) to redirect rustc's stdout into the location dictated by the build system.
>
> From skimming Cargo's usages of `--print`, it definitely seems like it would benefit from `--print KIND=PATH` too. Currently it is working around the lack of this by inserting `--crate-name=___ --print=crate-name` so that it can look for a line containing `___` as a delimiter between the 2 other `--print` informations it actually cares about. This is commented as a "HACK" and "abuse". 31eda6f7c3/src/cargo/core/compiler/build_context/target_info.rs (L242)
-----
cc `@dtolnay`
r? `@jackh726`
Description of the `PATH` option:
> A filepath may optionally be specified for each requested information
> kind, in the format `--print KIND=PATH`, just like for `--emit`. When
> a path is specified, information will be written there instead of to
> stdout.
Since `filename_for_metadata()` and
`OutputFilenames::path(OutputType::Metadata)` had different logic for
the name of the metadata file, the `.d` file contained a file name
different from the actual name used. Share the logic to fix the
out-of-sync name.
Closes 68839.
Add an (perma-)unstable option to disable vtable vptr
This flag is intended for evaluation of trait upcasting space cost for embedded use cases.
Compared to the approach in #112355, this option provides a way to evaluate end-to-end cost of trait upcasting. Rationale: https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/112355#issuecomment-1658207769
## How this flag should be used (after merge)
Build your project with and without `-Zno-trait-vptr` flag. If you are using cargo, set `RUSTFLAGS="-Zno-trait-vptr"` in the environment variable. You probably also want to use `-Zbuild-std` or the binary built may be broken. Save both binaries somewhere.
### Evaluate the space cost
The option has a direct and indirect impact on vtable space usage. Directly, it gets rid of the trait vptr entry needed to store a pointer to a vtable of a supertrait. (IMO) this is a small saving usually. The larger saving usually comes with the indirect saving by eliminating the vtable of the supertrait (and its parent).
Both impacts only affects vtables (notably the number of functions monomorphized should , however where vtable reside can depend on your relocation model. If the relocation model is static, then vtable is rodata (usually stored in Flash/ROM together with text in embedded scenario). If the binary is relocatable, however, the vtable will live in `.data` (more specifically, `.data.rel.ro`), and this will need to reside in RAM (which may be a more scarce resource in some cases), together with dynamic relocation info living in readonly segment.
For evaluation, you should run `size` on both binaries, with and without the flag. `size` would output three columns, `text`, `data`, `bss` and the sum `dec` (and it's hex version). As explained above, both `text` and `data` may change. `bss` shouldn't usually change. It'll be useful to see:
* Percentage change in text + data (indicating required flash/ROM size)
* Percentage change in data + bss (indicating required RAM size)
CFI: Fix error compiling core with LLVM CFI enabled
Fix#90546 by filtering out global value function pointer types from the type tests, and adding the LowerTypeTests pass to the rustc LTO optimization pipelines.
Fix#90546 by filtering out global value function pointer types from the
type tests, and adding the LowerTypeTests pass to the rustc LTO
optimization pipelines.
Lots of tiny incremental simplifications of `EmitterWriter` internals
ignore the first commit, it's https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/114088 squashed and rebased, but it's needed to use to use `derive_setters`, as they need a newer `syn` version.
Then this PR starts out with removing many arguments that are almost always defaulted to `None` or `false` and replace them with builder methods that can set these fields in the few cases that want to set them.
After that it's one commit after the other that removes or merges things until everything becomes some very simple trait objects
It lints against features that are inteded to be internal to the
compiler and standard library. Implements MCP #596.
We allow `internal_features` in the standard library and compiler as those
use many features and this _is_ the standard library from the "internal to the compiler and
standard library" after all.
Marking some features as internal wasn't exactly the most scientific approach, I just marked some
mostly obvious features. While there is a categorization in the macro,
it's not very well upheld (should probably be fixed in another PR).
We always pass `-Ainternal_features` in the testsuite
About 400 UI tests and several other tests use internal features.
Instead of throwing the attribute on each one, just always allow them.
There's nothing wrong with testing internal features^^
Remove -Z diagnostic-width
This removes the `-Z diagnostic-width` option since it is ignored and does nothing. `-Z diagnostic-width` was stabilized as `--diagnostic-width` in #95635. It is not entirely clear why the `-Z` flag was kept, but in part its final use was removed in #102216, but the `-Z` flag itself was not removed.
Split some functions with many arguments into builder pattern functions
r? `@estebank`
This doesn't resolve all of the ones in rustc, mostly because I need to do other cleanups in order to be able to use some builder derives from crates.io
Works around https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/90672 by making `x test rustfmt --bless` format itself instead of testing that it is formatted
new unstable option: -Zwrite-long-types-to-disk
This option guards the logic of writing long type names in files and instead using short forms in error messages in rustc_middle/ty/error behind a flag. The main motivation for this change is to disable this behaviour when running ui tests.
This logic can be triggered by running tests in a directory that has a long enough path, e.g. /my/very-long-path/where/rust-codebase/exists/
This means ui tests can fail depending on how long the path to their file is.
Some ui tests actually rely on this behaviour for their assertions, so for those we enable the flag manually.
This option guards the logic of writing long type names in files and
instead using short forms in error messages in rustc_middle/ty/error
behind a flag. The main motivation for this change is to disable this
behaviour when running ui tests.
This logic can be triggered by running tests in a directory that has a
long enough path, e.g. /my/very-long-path/where/rust-codebase/exists/
This means ui tests can fail depending on how long the path to their
file is.
Some ui tests actually rely on this behaviour for their assertions,
so for those we enable the flag manually.
Prototype: Add unstable `-Z reference-niches` option
MCP: rust-lang/compiler-team#641
Relevant RFC: rust-lang/rfcs#3204
This prototype adds a new `-Z reference-niches` option, controlling the range of valid bit-patterns for reference types (`&T` and `&mut T`), thereby enabling new enum niching opportunities. Like `-Z randomize-layout`, this setting is crate-local; as such, references to built-in types (primitives, tuples, ...) are not affected.
The possible settings are (here, `MAX` denotes the all-1 bit-pattern):
| `-Z reference-niches=` | Valid range |
|:---:|:---:|
| `null` (the default) | `1..=MAX` |
| `size` | `1..=(MAX- size)` |
| `align` | `align..=MAX.align_down_to(align)` |
| `size,align` | `align..=(MAX-size).align_down_to(align)` |
------
This is very WIP, and I'm not sure the approach I've taken here is the best one, but stage 1 tests pass locally; I believe this is in a good enough state to unleash this upon unsuspecting 3rd-party code, and see what breaks.
Use SHA256 source file checksums by default when targeting MSVC
Currently, when targeting Windows (more specifically, the MSVC toolchain), Rust will use SHA1 source file checksums by default. SHA1 has been superseded by SHA256, and Microsoft recommends migrating to SHA256.
As of Visual Studio 2022, MSVC defaults to SHA256. This change aligns Rust and MSVC.
LLVM can already use SHA256 checksums, so this does not require any change to LLVM.
MSVC docs on source file checksums: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/cpp/build/reference/zh?view=msvc-170
Support `--print KIND=PATH` command line syntax
As is already done for `--emit KIND=PATH` and `-L KIND=PATH`.
In the discussion of #110785, it was pointed out that `--print KIND=PATH` is nicer than trying to apply the single global `-o` path to `--print`'s output, because in general there can be multiple print requests within a single rustc invocation, and anyway `-o` would already be used for a different meaning in the case of `link-args` and `native-static-libs`.
I am interested in using `--print cfg=PATH` in Buck2. Currently Buck2 works around the lack of support for `--print KIND=PATH` by [indirecting through a Python wrapper script](d43cf3a51a/prelude/rust/tools/get_rustc_cfg.py) to redirect rustc's stdout into the location dictated by the build system.
From skimming Cargo's usages of `--print`, it definitely seems like it would benefit from `--print KIND=PATH` too. Currently it is working around the lack of this by inserting `--crate-name=___ --print=crate-name` so that it can look for a line containing `___` as a delimiter between the 2 other `--print` informations it actually cares about. This is commented as a "HACK" and "abuse". 31eda6f7c3/src/cargo/core/compiler/build_context/target_info.rs (L242) (FYI `@weihanglo` as you dealt with this recently in https://github.com/rust-lang/cargo/pull/11633.)
Mentioning reviewers active in #110785: `@fee1-dead` `@jyn514` `@bjorn3`
Resurrect: rustc_llvm: Add a -Z `print-codegen-stats` option to expose LLVM statistics.
This resurrects PR https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/104000, which has sat idle for a while. And I want to see the effect of stack-move optimizations on LLVM (like https://reviews.llvm.org/D153453) :).
I have applied the changes requested by `@oli-obk` and `@nagisa` https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/104000#discussion_r1014625377 and https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/104000#discussion_r1014642482 in the latest commits.
r? `@oli-obk`
-----
LLVM has a neat [statistics](https://llvm.org/docs/ProgrammersManual.html#the-statistic-class-stats-option) feature that tracks how often optimizations kick in. It's very handy for optimization work. Since we expose the LLVM pass timings, I thought it made sense to expose the LLVM statistics too.
-----
(Edit: fix broken link
(Edit2: fix segmentation fault and use malloc
If `rustc` is built with
```toml
[llvm]
assertions = true
```
Then you can see like
```
rustc +stage1 -Z print-codegen-stats -C opt-level=3 tmp.rs
===-------------------------------------------------------------------------===
... Statistics Collected ...
===-------------------------------------------------------------------------===
3 aa - Number of MayAlias results
193 aa - Number of MustAlias results
531 aa - Number of NoAlias results
...
```
And the current default build emits only
```
$ rustc +stage1 -Z print-codegen-stats -C opt-level=3 tmp.rs
===-------------------------------------------------------------------------===
... Statistics Collected ...
===-------------------------------------------------------------------------===
$
```
This might be better to emit the message to tell assertion flag necessity, but now I can't find how to do that...
On nightly, dump ICE backtraces to disk
Implement rust-lang/compiler-team#578.
When an ICE is encountered on nightly releases, the new rustc panic handler will also write the contents of the backtrace to disk. If any `delay_span_bug`s are encountered, their backtrace is also added to the file. The platform and rustc version will also be collected.
<img width="1032" alt="Screenshot 2023-03-03 at 2 13 25 PM" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/1606434/222842420-8e039740-4042-4563-b31d-599677171acf.png">
The current behavior will *always* write to disk on nightly builds, regardless of whether the backtrace is printed to the terminal, unless the environment variable `RUSTC_ICE_DISK_DUMP` is set to `0`. This is a compromise and can be changed.
Make it clearer that edition functions are `>=`, not `==`
r? `@Nilstrieb`
We could also perhaps derive `Ord` on `Edition` and use comparison operators.
Implement rust-lang/compiler-team#578.
When an ICE is encountered on nightly releases, the new rustc panic
handler will also write the contents of the backtrace to disk. If any
`delay_span_bug`s are encountered, their backtrace is also added to the
file. The platform and rustc version will also be collected.
LLVM has a neat [statistics] feature that tracks how often optimizations kick
in. It's very handy for optimization work. Since we expose the LLVM pass
timings, I thought it made sense to expose the LLVM statistics too.
[statistics]: https://llvm.org/docs/ProgrammersManual.html#the-statistic-class-stats-option
Replace RPITIT current impl with new strategy that lowers as a GAT
This PR replaces the current implementation of RPITITs with the new implementation that we had under -Zlower-impl-trait-in-trait-to-assoc-ty flag that lowers the RPIT as a GAT on the trait and on the impls that implement that trait.
Opening this PR as a draft because this goes after #112682, ~#112981~ and ~#112983~.
As soon as those are merged, I can rebase and we should run perf, crater and test a lot.
r? `@compiler-errors`
Add simple markdown formatting to `rustc --explain` output
This is a second attempt at #104540, which is #63128 without dependencies.
This PR adds basic markdown formatting to `rustc --explain` output when available. Currently, the output just displays raw markdown: this works of course, but it really doesn't look very elegant. (output is `rustc --explain E0038`)
<img width="583" alt="image" src="https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/assets/13724985/ea418117-47af-455b-83c0-6fc59276efee">
After this patch, sample output from the same file:
<img width="693" alt="image" src="https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/assets/13724985/12f7bf9b-a3fe-4104-b74b-c3e5227f3de9">
This also obeys the `--color always/auto/never` command option. Behavior:
- If pager is available and supports color, print with formatting to the pager
- If pager is not available or fails print with formatting to stdout - otherwise without formatting
- Follow `--color always/never` if suppied
- If everything fails, just print plain text to stdout
r? `@oli-obk`
cc `@estebank`
(since the two of you were involved in the previous discussion)
add flag for enabling global cache usage for proof trees and printing proof trees on error
This adds a few new things:
- `-Zdump-solver-proof-tree=always/never/on-error`
- `always`/`never` were previosuly specifiable by whether the flag exists or not, th new flag is `on_error` which reruns obligations of fulfillment and selection errors with proof tree generation enabled and prints them out
- `-Zdump-solver-proof-tree-uses-cache`
- allows forcing global cache to be used or unused for all generated proof trees, global cache is enabled by default for `always` so that it accurately represents what happend. This flag currently would affect misc uses of `GenerateProofTree::Yes` which will be added in the future for things like diagnostics logic and rustdoc's auto_trait file. We can fix this when we start using proof tree generation for those use cases if it's desirable.
I also changed the output to go straight to stdout instead of going through `debug!` so that `-Zdump-solver-proof-tree` can be adequately used on `nightly` not just a locally built toolchain.
The idea for `on-error` is that it should hopefully make it easier to quickly figure out "why doesnt this code compile"- you just pass in `-Zdump-solver-proof-tree=on-error` and you'll only get proof trees you care about.
---
r? `@lcnr` `@compiler-errors`
Currently, the output of `rustc --explain foo` displays the raw markdown in a
pager. This is acceptable, but using actual formatting makes it easier to
understand.
This patch consists of three major components:
1. A markdown parser. This is an extremely simple non-backtracking recursive
implementation that requires normalization of the final token stream
2. A utility to write the token stream to an output buffer
3. Configuration within rustc_driver_impl to invoke this combination for
`--explain`. Like the current implementation, it first attempts to print to
a pager with a fallback colorized terminal, and standard print as a last
resort.
If color is disabled, or if the output does not support it, or if printing
with color fails, it will write the raw markdown (which matches current
behavior).
Pagers known to support color are: `less` (with `-r`), `bat` (aka `catbat`),
and `delta`.
The markdown parser does not support the entire markdown specification, but
should support the following with reasonable accuracy:
- Headings, including formatting
- Comments
- Code, inline and fenced block (no indented block)
- Strong, emphasis, and strikethrough formatted text
- Links, anchor, inline, and reference-style
- Horizontal rules
- Unordered and ordered list items, including formatting
This parser and writer should be reusable by other systems if ever needed.
Add `-Zremark-dir` unstable flag to write LLVM optimization remarks to YAML
This PR adds an option for `rustc` to emit LLVM optimization remarks to a set of YAML files, which can then be digested by existing tools, like https://github.com/OfekShilon/optview2. When `-Cremark-dir` is passed, and remarks are enabled (`-Cremark=all`), the remarks will be now written to the specified directory, **instead** of being printed to standard error output. The files are named based on the CGU from which they are being generated.
Currently, the remarks are written using the LLVM streaming machinery, directly in the diagnostics handler. It seemed easier than going back to Rust and then form there back to C++ to use the streamer from the diagnostics handler. But there are many ways to implement this, of course, so I'm open to suggestions :)
I included some comments with questions into the code. Also, I'm not sure how to test this.
r? `@tmiasko`
linker flavors
- only the stable values for `-Clink-self-contained` can be used on stable until we
have more feedback on the interface
- `-Zunstable-options` is required to use unstable linker flavors
Per the discussion in #106380 plt=no isn't a great default, and
rust-lang/compiler-team#581 decided that the default should be PLT=yes
for everything except x86_64. Not everyone agrees about the x86_64 part
of this change, but this at least is an improvement in the state of
things without changing the x86_64 situation, so I've attempted making
this change in the name of not letting the perfect be the enemy of the
good.
Collect VTable stats & add `-Zprint-vtable-sizes`
This is a bit hacky/buggy, but I'm not entirely sure how to fix it, so I want to ask reviewers for help...
To try this, use either of those:
- `cargo clean && RUSTFLAGS="-Zprint-vtable-sizes" cargo +toolchain b`
- `cargo clean && cargo rustc +toolchain -Zprint-vtable-sizes`
- `rustc +toolchain -Zprint-vtable-sizes ./file.rs`
Because tiny CGUs make compilation less efficient *and* result in worse
generated code.
We don't do this when the number of CGUs is explicitly given, because
there are times when the requested number is very important, as
described in some comments within the commit. So the commit also
introduces a `CodegenUnits` type that distinguishes between default
values and user-specified values.
This change has a roughly neutral effect on walltimes across the
rustc-perf benchmarks; there are some speedups and some slowdowns. But
it has significant wins for most other metrics on numerous benchmarks,
including instruction counts, cycles, binary size, and max-rss. It also
reduces parallelism, which is good for reducing jobserver competition
when multiple rustc processes are running at the same time. It's smaller
benchmarks that benefit the most; larger benchmarks already have CGUs
that are all larger than the minimum size.
Here are some example before/after CGU sizes for opt builds.
- html5ever
- CGUs: 16, mean size: 1196.1, sizes: [3908, 2992, 1706, 1652, 1572,
1136, 1045, 948, 946, 938, 579, 471, 443, 327, 286, 189]
- CGUs: 4, mean size: 4396.0, sizes: [6706, 3908, 3490, 3480]
- libc
- CGUs: 12, mean size: 35.3, sizes: [163, 93, 58, 53, 37, 8, 2 (x6)]
- CGUs: 1, mean size: 424.0, sizes: [424]
- tt-muncher
- CGUs: 5, mean size: 1819.4, sizes: [8508, 350, 198, 34, 7]
- CGUs: 1, mean size: 9075.0, sizes: [9075]
Note that CGUs of size 100,000+ aren't unusual in larger programs.
Write to stdout if `-` is given as output file
With this PR, if `-o -` or `--emit KIND=-` is provided, output will be written to stdout instead. Binary output (those of type `obj`, `llvm-bc`, `link` and `metadata`) being written this way will result in an error unless stdout is not a tty. Multiple output types going to stdout will trigger an error too, as they will all be mixded together.
This implements https://github.com/rust-lang/compiler-team/issues/431
The idea behind the changes is to introduce an `OutFileName` enum that represents the output - be it a real path or stdout - and to use this enum along the code paths that handle different output types.
Removed use of iteration through a HashMap/HashSet in rustc_incremental and replaced with IndexMap/IndexSet
This allows for the `#[allow(rustc::potential_query_instability)]` in rustc_incremental to be removed, moving towards fixing #84447 (although a LOT more modules have to be changed to fully resolve it). Only HashMaps/HashSets that are being iterated through have been modified (although many structs and traits outside of rustc_incremental had to be modified as well, as they had fields/methods that involved a HashMap/HashSet that would be iterated through)
I'm making a PR for just 1 module changed to test for performance regressions and such, for future changes I'll either edit this PR to reflect additional modules being converted, or batch multiple modules of changes together and make a PR for each group of modules.
If `-o -` or `--emit KIND=-` is provided, output will be written
to stdout instead. Binary output (`obj`, `llvm-bc`, `link` and
`metadata`) being written this way will result in an error unless
stdout is not a tty. Multiple output types going to stdout will
trigger an error too, as they will all be mixded together.
Replace const eval limit by a lint and add an exponential backoff warning
The lint triggers at the first power of 2 that comes after 1 million function calls or traversed back-edges (takes less than a second on usual programs). After the first emission, an unsilenceable warning is repeated at every following power of 2 terminators, causing it to get reported less and less the longer the evaluation runs.
cc `@rust-lang/wg-const-eval`
fixes#93481closes#67217
linker: Report linker flavors incompatible with the current target
The linker flavor is checked for target compatibility even if linker is never used (e.g. we are producing a rlib).
If it causes trouble, we can move the check to `link.rs` so it will run if the linker (flavor) is actually used.
And also feature gate explicitly specifying linker flavors for tier 3 targets.
The next step is supporting all the internal linker flavors in user-visible interfaces (command line and json).
Stop normalizing so many different prefixes
Previously, we would normalize *all* of
- the absolute path to the repository checkout
- the /rustc/$sha for stage1 (if `remap-debuginfo` was enabled)
- the /rustc/$sha for download-rustc
- the sysroot for download-rustc
Now, we consistently only normalize /rustc/FAKE_PREFIX. Not only is this much simpler, but it also avoids ongoing maintenance for download-rustc and makes it much less likely that tests break by accident.
- Change `tests/ui/track-diagnostics/track6.rs` to use a relative path instead of an absolute one. I am not actually sure why `track_caller` works here, but it does seem to work 🤷
- Pass `-Zsimulate-remapped-rust-src-base=/rustc/FAKE_PREFIX` to all suites, not just UI. In particular, mir-opt tests emit /rustc/ paths in their output.
r? ```@cjgillot``` since you reviewed https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/110699 - this is the test that it doesn't regress :)
Remove `-Zcgu-partitioning-strategy`.
This option was introduced three years ago, but it's never been meaningfully used, and `default` is the only acceptable value.
Also, I think the `Partition` trait presents an interface that is too closely tied to the existing strategy and would probably be wrong for other strategies. (My rule of thumb is to not make something generic until there are at least two instances of it, to avoid this kind of problem.)
Also, I don't think providing multiple partitioning strategies to the user is a good idea, because the compiler already has enough obscure knobs.
This commit removes the option, along with the `Partition` trait, and the `Partitioner` and `DefaultPartitioning` types. I left the existing code in `compiler/rustc_monomorphize/src/partitioning/default.rs`, though I could be persuaded that moving it into
`compiler/rustc_monomorphize/src/partitioning/mod.rs` is better.
r? ``@wesleywiser``
This option was introduced three years ago, but it's never been
meaningfully used, and `default` is the only acceptable value.
Also, I think the `Partition` trait presents an interface that is too
closely tied to the existing strategy and would probably be wrong for
other strategies. (My rule of thumb is to not make something generic
until there are at least two instances of it, to avoid this kind of
problem.)
Also, I don't think providing multiple partitioning strategies to the
user is a good idea, because the compiler already has enough obscure
knobs.
This commit removes the option, along with the `Partition` trait, and
the `Partitioner` and `DefaultPartitioning` types. I left the existing
code in `compiler/rustc_monomorphize/src/partitioning/default.rs`,
though I could be persuaded that moving it into
`compiler/rustc_monomorphize/src/partitioning/mod.rs` is better.
Each of `{D,Subd}iagnosticMessage::{Str,Eager}` has a comment:
```
// FIXME(davidtwco): can a `Cow<'static, str>` be used here?
```
This commit answers that question in the affirmative. It's not the most
compelling change ever, but it might be worth merging.
This requires changing the `impl<'a> From<&'a str>` impls to `impl
From<&'static str>`, which involves a bunch of knock-on changes that
require/result in call sites being a little more precise about exactly
what kind of string they use to create errors, and not just `&str`. This
will result in fewer unnecessary allocations, though this will not have
any notable perf effects given that these are error paths.
Note that I was lazy within Clippy, using `to_string` in a few places to
preserve the existing string imprecision. I could have used `impl
Into<{D,Subd}iagnosticMessage>` in various places as is done in the
compiler, but that would have required changes to *many* call sites
(mostly changing `&format("...")` to `format!("...")`) which didn't seem
worthwhile.
Adds support for LLVM [SafeStack] which provides backward edge control
flow protection by separating the stack into two parts: data which is
only accessed in provable safe ways is allocated on the normal stack
(the "safe stack") and all other data is placed in a separate allocation
(the "unsafe stack").
SafeStack support is enabled by passing `-Zsanitizer=safestack`.
[SafeStack]: https://clang.llvm.org/docs/SafeStack.html
Previously, we would normalize *all* of
- the absolute path to the repository checkout
- the /rustc/$sha for stage1 (if `remap-debuginfo` was enabled)
- the /rustc/$sha for download-rustc
- the sysroot for download-rustc
Now, we consistently only normalize /rustc/FAKE_PREFIX. Not only is this
much simpler, but it also avoids ongoing maintenance for download-rustc
and makes it much less likely that tests break by accident.
- Change `tests/ui/track-diagnostics/track6.rs` to use a relative path
instead of an absolute one. I am not actually sure why `track_caller`
works here, but it does seem to work 🤷
- Pass `-Zsimulate-remapped-rust-src-base=/rustc/FAKE_PREFIX` to all
suites, not just UI. In particular, mir-opt tests emit /rustc/ paths
in their output.
very minor cleanups
- add `must_use` to `early_error_no_abort`
this was already being used at its only callsite, but this ensures that new code remembers to use it if it's called in the future. found this while investigating https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/110090.
- remove outdated and incorrect comment in `builder.rs`. `doc_rust_lang_org_channel` doesn't exist in rustdoc, it gets it from an env var instead: b275d2c30b/src/librustdoc/clean/utils.rs (L569-L573)
fix(resolve): replace bindings to dummy for unresolved imports
close#109343
In #109343, `f` in `pub use f as g` points to:
|namespace| binding|
|-|-|
|type| `external crate f`|
|value| `None` |
|macro| `None` |
When resolve `value_ns` during `resolve_doc_links`, the value of the binding of single_import `pub use f as g` goes to `pub use inner::f`, and since it does not satisfy [!self.is_accessible_from(binding.vis, single_import.parent_scope.module)](https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/blob/master/compiler/rustc_resolve/src/ident.rs#L971) and returns `Err(Undetermined)`, which eventually goes to `PathResult::Indeterminate => unreachable!`.
This PR replace all namespace binding to `dummy_binding` for indeterminate import, so, the bindings of `pub use f as g` had been changed to followings after finalize:
|namespace| binding|
|-|-|
|type| `dummy`|
|value| `dummy` |
|macro| `dummy` |
r?`@petrochenkov`
Only depend on CFG_VERSION in rustc_interface
This avoids having to rebuild the whole compiler on each commit when `omit-git-hash = false`.
cc https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/76720 - this won't fix it, and I'm not suggesting we turn this on by default, but it will make it less painful for people who do have `omit-git-hash` on as a workaround.
- add `must_use` to `early_error_no_abort`
this was already being used at its only callsite, but this ensures
that new code remembers to use it if it's called in the future.
- remove outdated and incorrect comment in `builder.rs`.
`doc_rust_lang_org_channel` doesn't exist in rustdoc, it gets it from
an env var instead.
Error message all end up passing into a function as an `impl
Into<{D,Subd}iagnosticMessage>`. If an error message is creatd as
`&format("...")` that means we allocate a string (in the `format!`
call), then take a reference, and then clone (allocating again) the
reference to produce the `{D,Subd}iagnosticMessage`, which is silly.
This commit removes the leading `&` from a lot of these cases. This
means the original `String` is moved into the
`{D,Subd}iagnosticMessage`, avoiding the double allocations. This
requires changing some function argument types from `&str` to `String`
(when all arguments are `String`) or `impl
Into<{D,Subd}iagnosticMessage>` (when some arguments are `String` and
some are `&str`).
Introduce `DynSend` and `DynSync` auto trait for parallel compiler
part of parallel-rustc #101566
This PR introduces `DynSend / DynSync` trait and `FromDyn / IntoDyn` structure in rustc_data_structure::marker. `FromDyn` can dynamically check data structures for thread safety when switching to parallel environments (such as calling `par_for_each_in`). This happens only when `-Z threads > 1` so it doesn't affect single-threaded mode's compile efficiency.
r? `@cjgillot`
Add support for `cfg(overflow_checks)`
This PR adds support for detecting if overflow checks are enabled in similar fashion as `debug_assertions` are detected. Possible use-case of this, for example, if we want to use checked integer casts in builds with overflow checks, e.g.
```rust
pub fn cast(val: usize)->u16 {
if cfg!(overflow_checks) {
val.try_into().unwrap()
}
else{
vas as _
}
}
```
Resolves#91130.
bump windows crate 0.46 -> 0.48
This drops duped version of crate(0.46), reduces `rustc_driver.dll` ~800kb and reduces exported functions number from 26k to 22k.
Also while here, added `tidy-alphabetical` sorting to lists in tidy allowed lists.
This PR adds support for detecting if overflow checks are enabled in similar fashion as debug_assertions are detected.
Possible use-case of this, for example, if we want to use checked integer casts in builds with overflow checks, e.g.
```rust
pub fn cast(val: usize)->u16 {
if cfg!(overflow_checks) {
val.try_into().unwrap()
}
else{
vas as _
}
}
```
Resolves#91130.
Tracking issue: #111466.
Support linking to rust dylib with --crate-type staticlib
This allows for example dynamically linking libstd, while statically linking the user crate into an executable or C dynamic library. For this two unstable flags (`-Z staticlib-allow-rdylib-deps` and `-Z staticlib-prefer-dynamic`) are introduced. Without the former you get an error. The latter is the equivalent to `-C prefer-dynamic` for the staticlib crate type to indicate that dynamically linking is preferred when both options are available, like for libstd. Care must be taken to ensure that no crate ends up being merged into two distinct staticlibs that are linked together. Doing so will cause a linker error at best and undefined behavior at worst. In addition two distinct staticlibs compiled by different rustc may not be combined under any circumstances due to some rustc private symbols not being mangled.
To successfully link a staticlib, `--print native-static-libs` can be used while compiling to ask rustc for the linker flags necessary when linking the staticlib. This is an existing flag which previously only listed native libraries. It has been extended to list rust dylibs too. Trying to locate libstd yourself to link against it is not supported and may break if for example the libstd of multiple rustc versions are put in the same directory.
For an example on how to use this see the `src/test/run-make-fulldeps/staticlib-dylib-linkage/` test.
Add `force` option for `--extern` flag
When `--extern force:foo=libfoo.so` is passed to `rustc` and `foo` is not actually used in the crate, ~inject an `extern crate foo;` statement into the AST~ force it to be resolved anyway in `CrateLoader::postprocess()`. This allows you to, for instance, inject a `#[panic_handler]` implementation into a `#![no_std]` crate without modifying its source so that it can be built as a `dylib`. It may also be useful for `#![panic_runtime]` or `#[global_allocator]`/`#![default_lib_allocator]` implementations.
My work previously involved integrating Rust into an existing C/C++ codebase which was built with Buck and shipped on, among other platforms, Android. When targeting Android, Buck builds all "native" code with shared linkage* so it can be loaded from Java/Kotlin. My project was not itself `#![no_std]`, but many of our dependencies were, and they would fail to build with shared linkage due to a lack of a panic handler. With this change, that project can add the new `force` option to the `std` dependency it already explicitly provides to every crate to solve this problem.
*This is an oversimplification - Buck has a couple features for aggregating dependencies into larger shared libraries, but none that I think sustainably solve this problem.
~The AST injection happens after macro expansion around where we similarly inject a test harness and proc-macro harness. The resolver's list of actually-used extern flags is populated during macro expansion, and if any of our `--extern` arguments have the `force` option and weren't already used, we inject an `extern crate` statement for them. The injection logic was added in `rustc_builtin_macros` as that's where similar injections for tests, proc-macros, and std/core already live.~
(New contributor - grateful for feedback and guidance!)
Stabilize raw-dylib, link_ordinal, import_name_type and -Cdlltool
This stabilizes the `raw-dylib` feature (#58713) for all architectures (i.e., `x86` as it is already stable for all other architectures).
Changes:
* Permit the use of the `raw-dylib` link kind for x86, the `link_ordinal` attribute and the `import_name_type` key for the `link` attribute.
* Mark the `raw_dylib` feature as stable.
* Stabilized the `-Zdlltool` argument as `-Cdlltool`.
* Note the path to `dlltool` if invoking it failed (we don't need to do this if `dlltool` returns an error since it prints its path in the error message).
* Adds tests for `-Cdlltool`.
* Adds tests for being unable to find the dlltool executable, and dlltool failing.
* Fixes a bug where we were checking the exit code of dlltool to see if it failed, but dlltool always returns 0 (indicating success), so instead we need to check if anything was written to `stderr`.
NOTE: As previously noted (https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/104218#issuecomment-1315895618) using dlltool within rustc is temporary, but this is not the first time that Rust has added a temporary tool use and argument: https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/104218#issuecomment-1318720482
Big thanks to ``````@tbu-`````` for the first version of this PR (#104218)
Improve check-cfg implementation
This PR makes multiple improvements into the implementation of check-cfg, it is a prerequisite to a follow-up PR that will introduce a simpler and more explicit syntax.
The 2 main area of improvements are:
1. Internal representation of expected values:
- now uses `FxHashSet<Option<Symbol>>` instead of `FxHashSet<Symbol>`, it made the no value expected case only possible when no values where in the `HashSet` which is now represented as `None` (same as cfg represent-it).
- a enum with `Some` and `Any` makes it now clear if some values are expected or not, necessary for `feature` and `target_feature`.
2. Diagnostics: Improve the diagnostics in multiple case and fix case where a missing value could have had a new name suggestion instead of the value diagnostic; and some drive by improvements
I highly recommend reviewing commit by commit.
r? `@petrochenkov`
This is done to simplify to relationship between names() and values()
but also make thing clearer (having an Any to represent that any values
are allowed) but also to allow the (none) + values expected cases that
wasn't possible before.
Add cross-language LLVM CFI support to the Rust compiler
This PR adds cross-language LLVM Control Flow Integrity (CFI) support to the Rust compiler by adding the `-Zsanitizer-cfi-normalize-integers` option to be used with Clang `-fsanitize-cfi-icall-normalize-integers` for normalizing integer types (see https://reviews.llvm.org/D139395).
It provides forward-edge control flow protection for C or C++ and Rust -compiled code "mixed binaries" (i.e., for when C or C++ and Rust -compiled code share the same virtual address space). For more information about LLVM CFI and cross-language LLVM CFI support for the Rust compiler, see design document in the tracking issue #89653.
Cross-language LLVM CFI can be enabled with -Zsanitizer=cfi and -Zsanitizer-cfi-normalize-integers, and requires proper (i.e., non-rustc) LTO (i.e., -Clinker-plugin-lto).
Thank you again, ``@bjorn3,`` ``@nikic,`` ``@samitolvanen,`` and the Rust community for all the help!
This commit adds cross-language LLVM Control Flow Integrity (CFI)
support to the Rust compiler by adding the
`-Zsanitizer-cfi-normalize-integers` option to be used with Clang
`-fsanitize-cfi-icall-normalize-integers` for normalizing integer types
(see https://reviews.llvm.org/D139395).
It provides forward-edge control flow protection for C or C++ and Rust
-compiled code "mixed binaries" (i.e., for when C or C++ and Rust
-compiled code share the same virtual address space). For more
information about LLVM CFI and cross-language LLVM CFI support for the
Rust compiler, see design document in the tracking issue #89653.
Cross-language LLVM CFI can be enabled with -Zsanitizer=cfi and
-Zsanitizer-cfi-normalize-integers, and requires proper (i.e.,
non-rustc) LTO (i.e., -Clinker-plugin-lto).
Remove `QueryEngine` trait
This removes the `QueryEngine` trait and `Queries` from `rustc_query_impl` and replaced them with function pointers and fields in `QuerySystem`. As a side effect `OnDiskCache` is moved back into `rustc_middle` and the `OnDiskCache` trait is also removed.
This has a couple of benefits.
- `TyCtxt` is used in the query system instead of the removed `QueryCtxt` which is larger.
- Function pointers are more flexible to work with. A variant of https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/107802 is included which avoids the double indirection. For https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/108938 we can name entry point `__rust_end_short_backtrace` to avoid some overhead. For https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/108062 it avoids the duplicate `QueryEngine` structs.
- `QueryContext` now implements `DepContext` which avoids many `dep_context()` calls in `rustc_query_system`.
- The `rustc_driver` size is reduced by 0.33%, hopefully that means some bootstrap improvements.
- This avoids the unsafe code around the `QueryEngine` trait.
r? `@cjgillot`
Report allocation errors as panics
OOM is now reported as a panic but with a custom payload type (`AllocErrorPanicPayload`) which holds the layout that was passed to `handle_alloc_error`.
This should be review one commit at a time:
- The first commit adds `AllocErrorPanicPayload` and changes allocation errors to always be reported as panics.
- The second commit removes `#[alloc_error_handler]` and the `alloc_error_hook` API.
ACP: https://github.com/rust-lang/libs-team/issues/192Closes#51540Closes#51245
Enable flatten-format-args by default.
Part of https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/99012.
This enables the `flatten-format-args` feature that was added by https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/106824:
> This change inlines string literals, integer literals and nested format_args!() into format_args!() during ast lowering, making all of the following pairs result in equivalent hir:
>
> ```rust
> println!("Hello, {}!", "World");
> println!("Hello, World!");
> ```
>
> ```rust
> println!("[info] {}", format_args!("error"));
> println!("[info] error");
> ```
>
> ```rust
> println!("[{}] {}", status, format_args!("error: {}", msg));
> println!("[{}] error: {}", status, msg);
> ```
>
> ```rust
> println!("{} + {} = {}", 1, 2, 1 + 2);
> println!("1 + 2 = {}", 1 + 2);
> ```
>
> And so on.
>
> This is useful for macros. E.g. a `log::info!()` macro could just pass the tokens from the user directly into a `format_args!()` that gets efficiently flattened/inlined into a `format_args!("info: {}")`.
>
> It also means that `dbg!(x)` will have its file, line, and expression name inlined:
>
> ```rust
> eprintln!("[{}:{}] {} = {:#?}", file!(), line!(), stringify!(x), x); // before
> eprintln!("[example.rs:1] x = {:#?}", x); // after
> ```
>
> Which can be nice in some cases, but also means a lot more unique static strings than before if dbg!() is used a lot.
This is mostly an optimization, except that it will be visible through [`fmt::Arguments::as_str()`](https://doc.rust-lang.org/nightly/std/fmt/struct.Arguments.html#method.as_str).
In https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/106823, there was already a libs-api FCP about the documentation of `fmt::Arguments::as_str()` to allow it to give `Some` rather than `None` depending on optimizations like this. That was just a documentation update though. This PR is the one that actually makes the user visible change:
```rust
assert_eq!(format_args!("abc").as_str(), Some("abc")); // Unchanged.
assert_eq!(format_args!("ab{}", "c").as_str(), Some("abc")); // Was `None` before!
```
Add `rustc_fluent_macro` to decouple fluent from `rustc_macros`
Fluent, with all the icu4x it brings in, takes quite some time to compile. `fluent_messages!` is only needed in further downstream rustc crates, but is blocking more upstream crates like `rustc_index`. By splitting it out, we allow `rustc_macros` to be compiled earlier, which speeds up `x check compiler` by about 5 seconds (and even more after the needless dependency on `serde_json` is removed from `rustc_data_structures`).
Fluent, with all the icu4x it brings in, takes quite some time to
compile. `fluent_messages!` is only needed in further downstream rustc
crates, but is blocking more upstream crates like `rustc_index`. By
splitting it out, we allow `rustc_macros` to be compiled earlier, which
speeds up `x check compiler` by about 5 seconds (and even more after the
needless dependency on `serde_json` is removed from
`rustc_data_structures`).
Validate `ignore` and `only` compiletest directive, and add human-readable ignore reasons
This PR adds strict validation for the `ignore` and `only` compiletest directives, failing if an unknown value is provided to them. Doing so uncovered 79 tests in `tests/ui` that had invalid directives, so this PR also fixes them.
Finally, this PR adds human-readable ignore reasons when tests are ignored due to `ignore` or `only` directives, like *"only executed when the architecture is aarch64"* or *"ignored when the operative system is windows"*. This was the original reason why I started working on this PR and #108659, as we need both of them for Ferrocene.
The PR is a draft because the code is extremely inefficient: it calls `rustc --print=cfg --target $target` for every rustc target (to gather the list of allowed ignore values), which on my system takes between 4s and 5s, and performs a lot of allocations of constant values. I'll fix both of them in the coming days.
r? `@ehuss`
Avoid a few locks
We can use atomics or datastructures tuned for specific access patterns instead of locks. This may be an improvement for parallel rustc, but it's mostly a cleanup making various datastructures only usable in the way they are used right now (append data, never mutate), instead of having a general purpose lock.
`-Cdebuginfo=1` was never line tables only and
can't be due to backwards compatibility issues.
This was clarified and an option for line tables only
was added. Additionally an option for line info
directives only was added, which is well needed for
some targets. The debug info options should now
behave the same as clang's debug info options.
Add `try_canonicalize` to `rustc_fs_util` and use it over `fs::canonicalize`
This adds `try_canonicalize` which tries to call `fs::canonicalize`, but falls back to `std::path::absolute` if it fails. Existing `canonicalize` calls are replaced with it. `fs::canonicalize` is not guaranteed to work on Windows.
Add `-Z time-passes-format` to allow specifying a JSON output for `-Z time-passes`
This adds back the `-Z time` option as that is useful for [my rustc benchmark tool](https://github.com/Zoxc/rcb), reverting https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/102725. It now uses nanoseconds and bytes as the units so it is renamed to `time-precise`.
Avoid unnecessary hashing
I noticed some stable hashing being done in a non-incremental build. It turns out that some of this is necessary to compute the crate hash, but some of it is not. Removing the unnecessary hashing is a perf win.
r? `@cjgillot`
This makes it easier to open the messages file while developing on features.
The commit was the result of automatted changes:
for p in compiler/rustc_*; do mv $p/locales/en-US.ftl $p/messages.ftl; rmdir $p/locales; done
for p in compiler/rustc_*; do sed -i "s#\.\./locales/en-US.ftl#../messages.ftl#" $p/src/lib.rs; done
This is fixed by simply using the currently registered target in the
current session. We need to use it because of target json that are not
by design included in the rustc list of targets.
Do not implement HashStable for HashSet (MCP 533)
This PR removes all occurrences of `HashSet` in query results, replacing it either with `FxIndexSet` or with `UnordSet`, and then removes the `HashStable` implementation of `HashSet`. This is part of implementing [MCP 533](https://github.com/rust-lang/compiler-team/issues/533), that is, removing the `HashStable` implementations of all collection types with unstable iteration order.
The changes are mostly mechanical. The only place where additional sorting is happening is in Miri's override implementation of the `exported_symbols` query.
The crate hash is needed:
- if debug assertions are enabled, or
- if incr. comp. is enabled, or
- if metadata is being generated, or
- if `-C instrumentation-coverage` is enabled.
This commit avoids computing the crate hash when these conditions are
all false, such as when doing a release build of a binary crate.
It uses `Option` to store the hashes when needed, rather than
computing them on demand, because some of them are needed in multiple
places and computing them on demand would make compilation slower.
The commit also removes `Owner::hash_without_bodies`. There is no
benefit to pre-computing that one, it can just be done in the normal
fashion.
Implement -Zlink-directives=yes/no
`-Zlink-directives=no` will ignored `#[link]` directives while compiling a crate, so nothing is emitted into the crate's metadata. The assumption is that the build system already knows about the crate's native dependencies and can provide them at link time without these directives.
This is another way to address issue # #70093, which is currently addressed by `-Zlink-native-libraries` (implemented in #70095). The latter is implemented at link time, which has the effect of ignoring `#[link]` in *every* crate. This makes it a very large hammer as it requires all native dependencies to be known to the build system to be at all usable, including those in sysroot libraries. I think this means its effectively unused, and definitely under-used.
Being able to control this on a crate-by-crate basis should make it much easier to apply when needed.
I'm not sure if we need both mechanisms, but we can decide that later.
cc `@pcwalton` `@cramertj`
`-Zlink-directives=no` will ignored `#[link]` directives while compiling a
crate, so nothing is emitted into the crate's metadata. The assumption is
that the build system already knows about the crate's native dependencies
and can provide them at link time without these directives.
This is another way to address issue # #70093, which is currently addressed
by `-Zlink-native-libraries` (implemented in #70095). The latter is
implemented at link time, which has the effect of ignoring `#[link]`
in *every* crate. This makes it a very large hammer as it requires all
native dependencies to be known to the build system to be at all usable,
including those in sysroot libraries. I think this means its effectively
unused, and definitely under-used.
Being able to control this on a crate-by-crate basis should make it much
easier to apply when needed.
I'm not sure if we need both mechanisms, but we can decide that later.
errors: generate typed identifiers in each crate
Instead of loading the Fluent resources for every crate in `rustc_error_messages`, each crate generates typed identifiers for its own diagnostics and creates a static which are pulled together in the `rustc_driver` crate and provided to the diagnostic emitter.
There are advantages and disadvantages to this change..
#### Advantages
- Changing a diagnostic now only recompiles the crate for that diagnostic and those crates that depend on it, rather than `rustc_error_messages` and all crates thereafter.
- This approach can be used to support first-party crates that want to supply translatable diagnostics (e.g. `rust-lang/thorin` in https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/102612#discussion_r985372582, cc `@JhonnyBillM)`
- We can extend this a little so that tools built using rustc internals (like clippy or rustdoc) can add their own diagnostic resources (much more easily than those resources needing to be available to `rustc_error_messages`)
#### Disadvantages
- Crates can only refer to the diagnostic messages defined in the current crate (or those from dependencies), rather than all diagnostic messages.
- `rustc_driver` (or some other crate we create for this purpose) has to directly depend on *everything* that has error messages.
- It already transitively depended on all these crates.
#### Pending work
- [x] I don't know how to make `rustc_codegen_gcc`'s translated diagnostics work with this approach - because `rustc_driver` can't depend on that crate and so can't get its resources to provide to the diagnostic emission. I don't really know how the alternative codegen backends are actually wired up to the compiler at all.
- [x] Update `triagebot.toml` to track the moved FTL files.
r? `@compiler-errors`
cc #100717
Extend `CodegenBackend` trait with a function returning the translation
resources from the codegen backend, which can be added to the complete
list of resources provided to the emitter.
Signed-off-by: David Wood <david.wood@huawei.com>
Instead of loading the Fluent resources for every crate in
`rustc_error_messages`, each crate generates typed identifiers for its
own diagnostics and creates a static which are pulled together in the
`rustc_driver` crate and provided to the diagnostic emitter.
Signed-off-by: David Wood <david.wood@huawei.com>
Use a lock-free datastructure for source_span
follow up to the perf regression in https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/105462
The main regression is likely the CStore, but let's evaluate the perf impact of this on its own
remove unstable `pick_stable_methods_before_any_unstable` flag
This flag was only added in #90329 in case there was any issue with the impl so that it would be easy to tell nightly users to use the flag to disable the new logic to fix their code. It's now been enabled for two years and also I can't find any issues corresponding to this new functionality? This flag made it way harder to understand how this code works so it would be nice to remove it and simplify what's going on.
cc `@nbdd0121`
r? `@oli-obk`
Add `kernel-address` sanitizer support for freestanding targets
This PR adds support for KASan (kernel address sanitizer) instrumentation in freestanding targets. I included the minimal set of `x86_64-unknown-none`, `riscv64{imac, gc}-unknown-none-elf`, and `aarch64-unknown-none` but there's likely other targets it can be added to. (`linux_kernel_base.rs`?) KASan uses the address sanitizer attributes but has the `CompileKernel` parameter set to `true` in the pass creation.
Implement partial support for non-lifetime binders
This implements support for non-lifetime binders. It's pretty useless currently, but I wanted to put this up so the implementation can be discussed.
Specifically, this piggybacks off of the late-bound lifetime collection code in `rustc_hir_typeck::collect::lifetimes`. This seems like a necessary step given the fact we don't resolve late-bound regions until this point, and binders are sometimes merged.
Q: I'm not sure if I should go along this route, or try to modify the earlier nameres code to compute the right bound var indices for type and const binders eagerly... If so, I'll need to rename all these queries to something more appropriate (I've done this for `resolve_lifetime::Region` -> `resolve_lifetime::ResolvedArg`)
cc rust-lang/types-team#81
r? `@ghost`
Most tests involving save-analysis were removed, but I kept a few where
the `-Zsave-analysis` was an add-on to the main thing being tested,
rather than the main thing being tested.
For `x.py install`, the `rust-analysis` target has been removed.
For `x.py dist`, the `rust-analysis` target has been kept in a
degenerate form: it just produces a single file `reduced.json`
indicating that save-analysis has been removed. This is necessary for
rustup to keep working.
Closes#43606.