Since rustc doesn't do the assembly parsing itself, it is unable
to detect when inline assembly ends with an instruction prefix,
which doesn't make sense since it would apply to instructions from
the compiler. This fixes#82314 by mentioning that x86 instruction
prefixes must not be used in inline assembly.
Split doc_cfg and doc_auto_cfg features
Part of #90497.
With this feature, `doc_cfg` won't pick up items automatically anymore.
cc `@Mark-Simulacrum`
r? `@jyn514`
Update Clippy dependencies
Clippy has two outdated dependencies, where one indirect dependency has been flagged by rustsec for dropping a lifetime. See [RUSTSEC-2020-0146](https://rustsec.org/advisories/RUSTSEC-2020-0146). This PR updates these dependencies.
With previous dependency updates, it was tried to prevent duplicates in the `Cargo.lock` file of rust-lang/rust. I've tried to keep this in mind with this update.
* Dependency `semver`
* Used in `src/tools/cargo/Cargo.toml` as version `1.0.3`
* Used in `src/tools/rust-analyzer/crates/project_model/Cargo.toml` as version `1`
* Updated in Clippy from `0.11` to `1.0` (Clippy usually defines the major and minor patch version). The `Cargo.lock` file lists `1.0.3` which is one patch version behind the most recent one but prevents a duplicate with cargo's pinned version.
* Dependency `cargo_metadata`
* Used in several tools as `0.14`
* Used in `src/tools/tidy` and `src/tools/rls` as `0.12`
* Updated in Clippy from `0.12` to `0.14`
All updates to the `Cargo.lock` have been done automatically by `x.py`.
There are still some tools with these outdated dependencies. Clippy didn't require any changes, and it would be likely that the others could also be updated without any problem. Let me know if I should try to update them as well 🙃.
Keep up the good work, whoever is reading this 🦀
---
For Clippy:
changelog: none
Document clippy on nightly-rustc
Adding Clippy's docs to nightly-rustc, based on commit 01cf0bde. This PR only adds `clippy_utils` to the documentation. I've decided to only document one crate for now, as `clippy_lints` etc. contain very specific and undocumented functions which aren't really reusable. I'm guessing that they would mostly clutter up the search results with little benefit.
`./x.py --stage 1 doc src/tools/clippy` if working fine now after the help that ```````@jyn514``````` and ```````@ehuss``````` have provided. A big THANK YOU to them!
Make printed message match the code comment
I think this code is getting L0, not L1 cache size, if I'm reading the Intel manual right. (I might not be.) Either way, the code comment and the printed message should match, whichever way is right. :)
Update cargo
3 commits in 6c1bc24b8b49d4bc965f67d7037906dc199c72b7..94ca096afbf25f670e76e07dca754fcfe27134be
2021-10-24 17:51:41 +0000 to 2021-10-29 14:45:06 +0000
- Chore: prefer `HashMap::from` rather than collecting `Vec` of tuples (rust-lang/cargo#10018)
- Change --scrape-examples flag to -Z rustdoc-scrape-examples (rust-lang/cargo#10017)
- Scrape code examples from examples/ directory for Rustdoc (rust-lang/cargo#9525)
CI: Use ubuntu image to download openssl, curl sources, cacert.pem for x86 dist builds
The dist-x86_64 and dist-i686 docker builds are failing again (see [try build](https://github.com/rust-lang-ci/rust/runs/4060836540?check_suite_focus=true)) because python.org renewed its certificate with a CA cert that is too new for debian:6.
In order to solve this once and for all this PR moves the curl and openssl downloads to a new ubuntu:20.04 "stage-0" docker build and copies the downloaded tarballs over to build them in the "stage-1" debian:6 context. It also downloads the cacert.pem file from the curl website and uses it by pointing the `CURL_CA_BUNDLE` environment variable to it.
Collect `panic/panic_bounds_check` during monomorphization
This would prevent link time errors if these functions are `#[inline]` (e.g. when `panic_immediate_abort` is used).
Fix#90405Fixrust-lang/cargo#10019
`@rustbot` label: T-compiler A-codegen
[master] Fix CVE-2021-42574
This PR implements new lints to mitigate the impact of [CVE-2021-42574], caused by the presence of bidirectional-override Unicode codepoints in the compiled source code. [See the advisory][advisory] for more information about the vulnerability.
The changes in this PR will be released in tomorrow's nightly release.
[CVE-2021-42574]: https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2021-42574
[advisory]: https://blog.rust-lang.org/2021/11/01/cve-2021-42574.html
Until `external_traits` is cleaned up (i.e., no longer behind a
`RefCell`), `DocVisitor` will have to `take` `external_traits` -- just
like `DocFolder` -- to prevent `RefCell` runtime errors.
* Flip conjuncts of `&&` in rustdoc
The `CrateNum` comparison should be very cheap, while
`span.filename()` fetches and clones a `FileName`.
* Use `into_local_path()` instead of `local_path().clone()`
`DocFolder` allows transforming the docs, accomplished by making its
methods take and return types by-value. However, several of the rustdoc
`DocFolder` impls only *visit* the docs; they don't change anything.
Passing around types by-value is thus unnecessary, confusing, and
potentially inefficient for those impls.
`DocVisitor` is very similar to `DocFolder`, except that its methods
take shared references and return nothing (i.e., the unit type). This
should both be more efficient and make the code clearer.
There is an additional reason to add `DocVisitor`, too. As part of my
cleanup of `external_traits`, I'm planning to add a `fn cache(&mut self)
-> &mut Cache` method to `DocFolder` so that `external_traits` can be
retrieved explicitly from the `Cache`, rather than implicitly via
`Crate.external_traits` (which is an `Rc<RefCell<...>>`). However, some
of the `DocFolder` impls that could be turned into `DocVisitor` impls
only have a shared reference to the `Cache`, because they are used
during rendering. (They have to access the `Cache` via
`html::render::Context.shared.cache`, which involves an `Rc`.)
Since `DocVisitor` does not mutate any of the types it's visiting, its
equivalent `cache()` method will only need a shared reference to the
`Cache`, avoiding the problem described above.
Also, contrary to the comment, the clone is not that small, since
`Variant` contains `Item`s, which are quite large when you factor in
both stack- and heap-allocated memory.
Test that promotion follows references when looking for drop
Noticed that this wasn't covered by any of existing tests.
The const checking and const qualification, which currently shares the
implementation with promotion, will likely need a different behaviour
here (see issue #90193).
Fix rare ICE during typeck in rustdoc scrape_examples
While testing the `--scrape-examples` extension on the [wasmtime](https://github.com/bytecodealliance/wasmtime) repository, I found some additional edge cases. Specifically, when asking to typecheck a body containing a function call, I would sometimes get an ICE if:
* The body doesn't exist
* The function's HIR node didn't have a type
This adds checks for both of those conditions.
(Also this updates a test to check that the sources of a reverse-dependency are correctly generated and linked.)
r? `@jyn514`
rustdoc: remove flicker during page load
The search bar has a `:disabled` style that makes it grey, which creates a distracting flicker from grey to white when the page finishes loading. The search bar should stay the same color throughout page load.
A blank white search bar might create an incorrect impression for users with JS turned off. Since they can't use the search functionality, I've hidden the search bar in noscript.css.
Fixes#90246
r? `@GuillaumeGomez`
Demo: https://rustdoc.crud.net/jsha/flashy-searchbar/std/string/struct.String.html
Handling submodule update failures more gracefully from x.py
Addresses #80498
Handling the case where x.py can't check out the right commit of a submodule, because the submodule has local edits that would be overwritten by the checkout, more gracefully.
The error is printed in detail, with some hints on how to revert the local changes to the submodule.
Add new tier 3 target: `x86_64-unknown-none`
Adds support for compiling OS kernels or other bare-metal applications for the x86-64 architecture.
Below are details on how this target meets the requirements for tier 3:
> A tier 3 target must have a designated developer or developers (the "target maintainers") on record to be CCed when issues arise regarding the target. (The mechanism to track and CC such developers may evolve over time.)
I would be willing to be a target maintainer, though I would appreciate if others volunteered to help with that as well.
> Targets must use naming consistent with any existing targets; for instance, a target for the same CPU or OS as an existing Rust target should use the same name for that CPU or OS. Targets should normally use the same names and naming conventions as used elsewhere in the broader ecosystem beyond Rust (such as in other toolchains), unless they have a very good reason to diverge. Changing the name of a target can be highly disruptive, especially once the target reaches a higher tier, so getting the name right is important even for a tier 3 target.
Uses the same naming as the LLVM target, and the same convention as many other bare-metal targets.
> Target names should not introduce undue confusion or ambiguity unless absolutely necessary to maintain ecosystem compatibility. For example, if the name of the target makes people extremely likely to form incorrect beliefs about what it targets, the name should be changed or augmented to disambiguate it.
I don't believe there is any ambiguity here.
> Tier 3 targets may have unusual requirements to build or use, but must not create legal issues or impose onerous legal terms for the Rust project or for Rust developers or users.
I don't see any legal issues here.
> The target must not introduce license incompatibilities.
> Anything added to the Rust repository must be under the standard Rust license (MIT OR Apache-2.0).
> The target must not cause the Rust tools or libraries built for any other host (even when supporting cross-compilation to the target) to depend on any new dependency less permissive than the Rust licensing policy. This applies whether the dependency is a Rust crate that would require adding new license exceptions (as specified by the tidy tool in the rust-lang/rust repository), or whether the dependency is a native library or binary. In other words, the introduction of the target must not cause a user installing or running a version of Rust or the Rust tools to be subject to any new license requirements.
>If the target supports building host tools (such as rustc or cargo), those host tools must not depend on proprietary (non-FOSS) libraries, other than ordinary runtime libraries supplied by the platform and commonly used by other binaries built for the target. For instance, rustc built for the target may depend on a common proprietary C runtime library or console output library, but must not depend on a proprietary code generation library or code optimization library. Rust's license permits such combinations, but the Rust project has no interest in maintaining such combinations within the scope of Rust itself, even at tier 3.
> Targets should not require proprietary (non-FOSS) components to link a functional binary or library.
> "onerous" here is an intentionally subjective term. At a minimum, "onerous" legal/licensing terms include but are not limited to: non-disclosure requirements, non-compete requirements, contributor license agreements (CLAs) or equivalent, "non-commercial"/"research-only"/etc terms, requirements conditional on the employer or employment of any particular Rust developers, revocable terms, any requirements that create liability for the Rust project or its developers or users, or any requirements that adversely affect the livelihood or prospects of the Rust project or its developers or users.
I see no issues with any of the above.
> Neither this policy nor any decisions made regarding targets shall create any binding agreement or estoppel by any party. If any member of an approving Rust team serves as one of the maintainers of a target, or has any legal or employment requirement (explicit or implicit) that might affect their decisions regarding a target, they must recuse themselves from any approval decisions regarding the target's tier status, though they may otherwise participate in discussions.
> This requirement does not prevent part or all of this policy from being cited in an explicit contract or work agreement (e.g. to implement or maintain support for a target). This requirement exists to ensure that a developer or team responsible for reviewing and approving a target does not face any legal threats or obligations that would prevent them from freely exercising their judgment in such approval, even if such judgment involves subjective matters or goes beyond the letter of these requirements.
Only relevant to those making approval decisions.
> Tier 3 targets should attempt to implement as much of the standard libraries as possible and appropriate (core for most targets, alloc for targets that can support dynamic memory allocation, std for targets with an operating system or equivalent layer of system-provided functionality), but may leave some code unimplemented (either unavailable or stubbed out as appropriate), whether because the target makes it impossible to implement or challenging to implement. The authors of pull requests are not obligated to avoid calling any portions of the standard library on the basis of a tier 3 target not implementing those portions.
`core` and `alloc` can be used. `std` cannot be used as this is a bare-metal target.
> The target must provide documentation for the Rust community explaining how to build for the target, using cross-compilation if possible. If the target supports running tests (even if they do not pass), the documentation must explain how to run tests for the target, using emulation if possible or dedicated hardware if necessary.
Use `--target=x86_64-unknown-none-elf` option to cross compile, just like any target. The target does not support running tests.
> Tier 3 targets must not impose burden on the authors of pull requests, or other developers in the community, to maintain the target. In particular, do not post comments (automated or manual) on a PR that derail or suggest a block on the PR based on a tier 3 target. Do not send automated messages or notifications (via any medium, including via `@)` to a PR author or others involved with a PR regarding a tier 3 target, unless they have opted into such messages.
> Backlinks such as those generated by the issue/PR tracker when linking to an issue or PR are not considered a violation of this policy, within reason. However, such messages (even on a separate repository) must not generate notifications to anyone involved with a PR who has not requested such notifications.
I don't foresee this being a problem.
> Patches adding or updating tier 3 targets must not break any existing tier 2 or tier 1 target, and must not knowingly break another tier 3 target without approval of either the compiler team or the maintainers of the other tier 3 target.
> In particular, this may come up when working on closely related targets, such as variations of the same architecture with different features. Avoid introducing unconditional uses of features that another variation of the target may not have; use conditional compilation or runtime detection, as appropriate, to let each target run code supported by that target.
No other targets should be affected by the pull request.
Noticed that this wasn't covered by any of existing tests.
The const checking and const qualification, which currently shares the
implementation with promotion, will likely need a different behaviour
here (see issue #90193).
Add #[must_use] to mem/ptr functions
There's a lot of low-level / unsafe stuff here. Are there legit use cases for ignoring any of these return values?
* No regressions in `./x.py test --stage 1 library/std src/tools/clippy`.
* One regression in `./x.py test --stage 1 src/test/ui`. Fixed.
* I am unable to run `./x.py doc` on my machine so I'll need to wait for the CI to verify doctests pass. I eyeballed all the adjacent tests and they all look okay.
Parent issue: #89692
r? ```@joshtriplett```
rustdoc: Compute some fields of `clean::Crate` on-demand to reduce size
`clean::Crate` is frequently moved by-value -- for example, in `DocFolder`
implementations -- so reducing its size should improve performance.
This PR reduces the size of `clean::Crate` from 168 bytes to 104 bytes.
r? `@jyn514`
Skipping verbose diagnostic suggestions when calling .as_ref() on type not implementing AsRef
Addresses #89806
Skipping suggestions when calling `.as_ref()` for types that do not implement the `AsRef` trait.
r? `@estebank`
Use `is_global` in `candidate_should_be_dropped_in_favor_of`
This manifistated in #90195 with compiler being unable to keep
one candidate for a trait impl, if where is a global impl and more
than one trait bound in the where clause.
Before #87280 `candidate_should_be_dropped_in_favor_of` was using
`TypeFoldable::is_global()` that was enough to discard the two
`ParamCandidate`s. But #87280 changed it to use
`TypeFoldable::is_known_global()` instead, which is pessimistic, so
now the compiler drops the global impl instead (because
`is_known_global` is not sure) and then can't decide between the
two `ParamCandidate`s.
Switching it to use `is_global` again solves the issue.
Fixes#90195.
Improve and test cross-crate hygiene
- Decode the parent expansion for traits and enums in `rustc_resolve`, this was already being used for resolution in typeck
- Avoid suggesting importing names with def-site hygiene, since it's often not useful
- Add more tests
r? `@petrochenkov`
Show all Deref implementations recursively
Fixes#87783.
This is a re-implementation of #80653, so taking the original PR comment:
This changes `rustdoc` to recursively follow `Deref` targets so that methods from all levels are added to the rendered output. This implementation displays the methods from all levels in the expanded state with separate sections for each level.
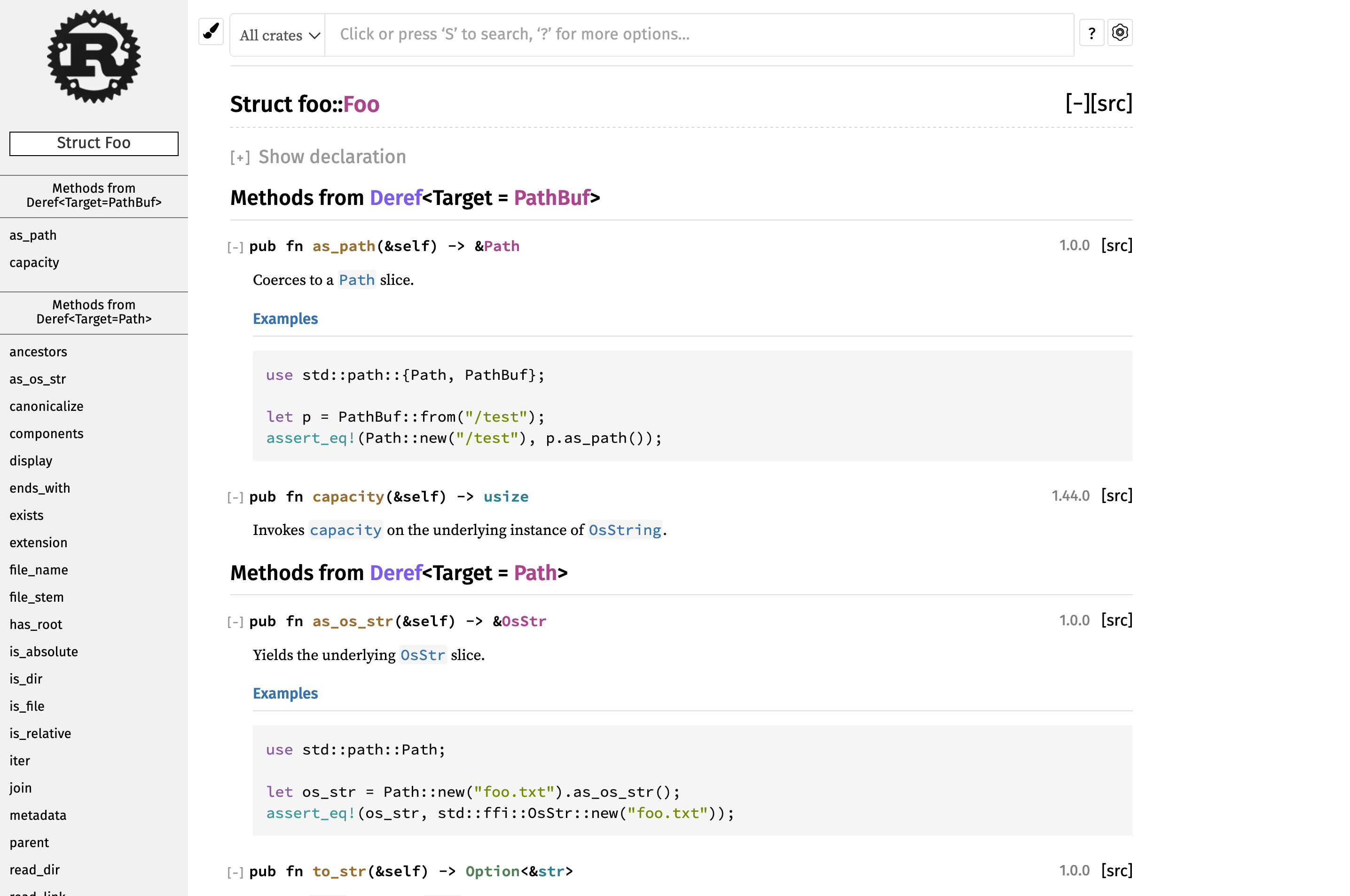
cc `@camelid`
r? `@jyn514`
It is only used in one place; `src` was about a third of `Crate`'s total
size; `Crate` is frequently moved by-value; and `src` can be easily
computed on-demand.
Repace use of `static_nobundle` with `native_link_modifiers` within Rust codebase
This fixes warnings when building Rust and running tests:
```
warning: library kind `static-nobundle` has been superseded by specifying `-bundle` on library kind `static`. Try `static:-bundle`
warning: `rustc_llvm` (lib) generated 2 warnings (1 duplicate)
```
Unify titles in rustdoc book doc attributes chapter
As discussed in https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/90339.
I wasn't able to find out where the link to the titles was used so let's see if the CI fails. :)
r? ``@camelid``
rustdoc: Fix generics generation in search index
The generics were not added to the search index as they should, instead they were added as arguments. I used this opportunity to allow generics to have generics themselves (will come in very handy for my current rewrite of the search engine!).
r? `@jyn514`
rustdoc: Switch to mainline rayon
The rustc fork of rayon integrates with Cargo's jobserver to limit the
amount of parallelism. However, rustdoc's use case is concurrent I/O,
which is not CPU-heavy, so it should be able to use mainline rayon.
See [this discussion][1] for more details.
[1]: https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/90227#issuecomment-952468618
Note: I chose rayon 1.3.1 so that the rayon version used elsewhere in
the workspace does not change.
r? `@Mark-Simulacrum`
cc `@jyn514`
Use type based qualification for unions
Union field access is currently qualified based on the qualification of
a value previously assigned to the union. At the same time, every union
access transmutes the content of the union, which might result in a
different qualification.
For example, consider constants A and B as defined below, under the
current rules neither contains interior mutability, since a value used
in the initial assignment did not contain `UnsafeCell` constructor.
```rust
#![feature(untagged_unions)]
union U { i: u32, c: std::cell::Cell<u32> }
const A: U = U { i: 0 };
const B: std::cell::Cell<u32> = unsafe { U { i: 0 }.c };
```
To avoid the issue, the changes here propose to consider the content of
a union as opaque and use type based qualification for union types.
Fixes#90268.
`@rust-lang/wg-const-eval`