Apply lint restrictions from renamed lints
Previously, if you denied the old name of a renamed lint, it would warn
about using the new name, but otherwise do nothing. Now, it will behave
the same as if you'd used the new name.
Fixes https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/82615.
r? `@ehuss`
make x86_64-pc-solaris the default target for x86-64 Solaris
This change makes `x86_64-pc-solaris` the default compilation target for x86-64 Solaris/Illumos (based on [this exchange](https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/68214#issuecomment-748042054) with `@varkor).`
I tried several ways of doing this (leveraging the alias support added with #61761 and improved/fixed with #80073) and found out that cross-compilation to the new one is by far the simplest way of doing this. It can be achieved by adding the following arguments: `--build x86_64-sun-solaris --host x86_64-pc-solaris --target x86_64-pc-solaris` and enabling the cross compilation with `PKG_CONFIG_ALLOW_CROSS=1` environment variable.
I also removed alias support altogether - `x86_64-pc-solaris` and `x86_64-sun-solaris` are now two separate targets. The problem with aliases is that even if rust internally knows that two are the same, other tools building with rust don't know that, resulting in build issues like the one with firefox mentioned [here](https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/68214#issuecomment-746144229). I think that once the dust settles and `x86_64-pc-solaris` becomes the default, `x86_64-sun-solaris` can be removed.
If you agree with the above, I have two subsequent questions:
1. Is there a preferred way to display deprecation warnings when `x86_64-sun-solaris` is passed into the compiler as an argument? I am not sure whether target deprecation was done before.
2. Where would be the best way to document this change for those using rust on Solaris? Without the cross-compilation arguments (used once to build a new version), the build won't work. Should I add it into [RELEASES.md](https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/blob/master/RELEASES.md)?
Thanks!
Remove storage markers if they won't be used during code generation
The storage markers constitute a substantial portion of all MIR
statements. At the same time, for builds without any optimizations,
the storage markers have no further use during and after MIR
optimization phase.
If storage markers are not necessary for code generation, remove them.
Fixed support for macOS Catalyst on ARM64
When I initially added Arm64 Catalyst support in https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/77484 I had access to a DTK. However, while waiting to merge the PR some other changes were merged which caused conflicts in the branch. When fixing those conflicts I had no access to the DTK anymore and didn't try out if the resulting binaries did indeed work on Apple Silicon. I finally have a M1 and I realized that some small changes were necessary to support Apple Silicon. This PR adds the required changes. I've been running binaries generated with this branch for some time now and they work without issues.
Previously, if you denied the old name of a renamed lint, it would warn
about using the new name, but otherwise do nothing. Now, it will behave
the same as if you'd used the new name.
Remove the x86_64-rumprun-netbsd target
Herein we remove the target from the compiler and the code from libstd intended to support the now-defunct rumprun project.
Closes#81514
The storage markers constitute a substantial portion of all MIR
statements. At the same time, for builds without any optimizations,
the storage markers have no further use during and after MIR
optimization phase.
If storage markers are not necessary for code generation, remove them.
Update measureme dependency to the latest version
This version adds the ability to use `rdpmc` hardware-based performance
counters instead of wall-clock time for measuring duration. This also
introduces a dependency on the `perf-event-open-sys` crate on Linux
which is used when using hardware counters.
r? ```@oli-obk```
Link crtbegin/crtend on musl to terminate .eh_frame
For some targets, rustc uses a "CRT fallback", where it links CRT
object files it ships instead of letting the host compiler link
them.
On musl, rustc currently links crt1, crti and crtn (provided by
libc), but does not link crtbegin and crtend (provided by libgcc).
In particular, crtend is responsible for terminating the .eh_frame
section. Lack of terminator may result in segfaults during
unwinding, as reported in #47551 and encountered by the LLVM 12
update in #81451.
This patch links crtbegin and crtend for musl as well, following
the table at the top of crt_objects.rs.
r? ``@nagisa``
Suggest character encoding is incorrect when encountering random null bytes
This adds a note whenever null bytes are seen at the start of a token unexpectedly, since those tend to come from UTF-16 encoded files without a [BOM](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Byte_order_mark) (if a UTF-16 BOM appears it won't be valid UTF-8, but if there is no BOM it be both valid UTF-16 and valid but garbled UTF-8). This approach was suggested in https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/73979#issuecomment-653976451.
Closes#73979.
Skip Ty w/o infer ty/const in trait select
Remove some allocations & also add `skip_current_subtree` to skip subtrees with no inferred items.
r? `@eddyb` since marked in the FIXME
When token-based attribute handling is implemeneted in #80689,
we will need to access tokens from `HasAttrs` (to perform
cfg-stripping), and we will to access attributes from `HasTokens` (to
construct a `PreexpTokenStream`).
This PR merges the `HasAttrs` and `HasTokens` traits into a new
`AstLike` trait. The previous `HasAttrs` impls from `Vec<Attribute>` and `AttrVec`
are removed - they aren't attribute targets, so the impls never really
made sense.
Use small hash set in `mir_inliner_callees`
Use small hash set in `mir_inliner_callees` to avoid temporary
allocation when possible and quadratic behaviour for large number of
callees.
Improve anonymous lifetime note to indicate the target span
Improvement for #81650
Cc #81995
Message after this improvement:
(Improve note in the middle)
```
error[E0311]: the parameter type `T` may not live long enough
--> src/main.rs:25:11
|
24 | fn play_with<T: Animal + Send>(scope: &Scope, animal: T) {
| -- help: consider adding an explicit lifetime bound...: `T: 'a +`
25 | scope.spawn(move |_| {
| ^^^^^
|
note: the parameter type `T` must be valid for the anonymous lifetime defined on the function body at 24:40...
--> src/main.rs:24:40
|
24 | fn play_with<T: Animal + Send>(scope: &Scope, animal: T) {
| ^^^^^
note: ...so that the type `[closure@src/main.rs:25:17: 27:6]` will meet its required lifetime bounds
--> src/main.rs:25:11
|
25 | scope.spawn(move |_| {
| ^^^^^
```
r? ``````@estebank``````
Replace const_cstr with cstr crate
This PR replaces the `const_cstr` macro inside `rustc_data_structures` with `cstr` macro from [cstr](https://crates.io/crates/cstr) crate.
The two macros basically serve the same purpose, which is to generate `&'static CStr` from a string literal. `cstr` is better because it validates the literal at compile time, while the existing `const_cstr` does it at runtime when `debug_assertions` is enabled. In addition, the value `cstr` generates can be used in constant context (which is seemingly not needed anywhere currently, though).
Set codegen thread names
Set names on threads spawned during codegen. Various debugging and profiling tools can take advantage of this to show a more useful identifier for threads.
For example, gdb will show thread names in `info threads`:
```
(gdb) info threads
Id Target Id Frame
1 Thread 0x7fffefa7ec40 (LWP 2905) "rustc" __pthread_clockjoin_ex (threadid=140737214134016, thread_return=0x0, clockid=<optimized out>, abstime=<optimized out>, block=<optimized out>)
at pthread_join_common.c:145
2 Thread 0x7fffefa7b700 (LWP 2957) "rustc" 0x00007ffff125eaa8 in llvm::X86_MC::initLLVMToSEHAndCVRegMapping(llvm::MCRegisterInfo*) ()
from /home/wesley/.rustup/toolchains/stage1/lib/librustc_driver-f866439e29074957.so
3 Thread 0x7fffeef0f700 (LWP 3116) "rustc" futex_wait_cancelable (private=0, expected=0, futex_word=0x7fffe8602ac8) at ../sysdeps/nptl/futex-internal.h:183
* 4 Thread 0x7fffeed0e700 (LWP 3123) "rustc" rustc_codegen_ssa:🔙:write::spawn_work (cgcx=..., work=...) at /home/wesley/code/rust/rust/compiler/rustc_codegen_ssa/src/back/write.rs:1573
6 Thread 0x7fffe113b700 (LWP 3150) "opt foof.7rcbfp" 0x00007ffff2940e62 in llvm::CallGraph::populateCallGraphNode(llvm::CallGraphNode*) ()
from /home/wesley/.rustup/toolchains/stage1/lib/librustc_driver-f866439e29074957.so
8 Thread 0x7fffe0d39700 (LWP 3158) "opt foof.7rcbfp" 0x00007fffefe8998e in malloc_consolidate (av=av@entry=0x7ffe2c000020) at malloc.c:4492
9 Thread 0x7fffe0f3a700 (LWP 3162) "opt foof.7rcbfp" 0x00007fffefef27c4 in __libc_open64 (file=0x7fffe0f38608 "foof.foof.7rcbfp3g-cgu.6.rcgu.o", oflag=524865) at ../sysdeps/unix/sysv/linux/open64.c:48
(gdb)
```
and Windows Performance Analyzer will also show this information when profiling:
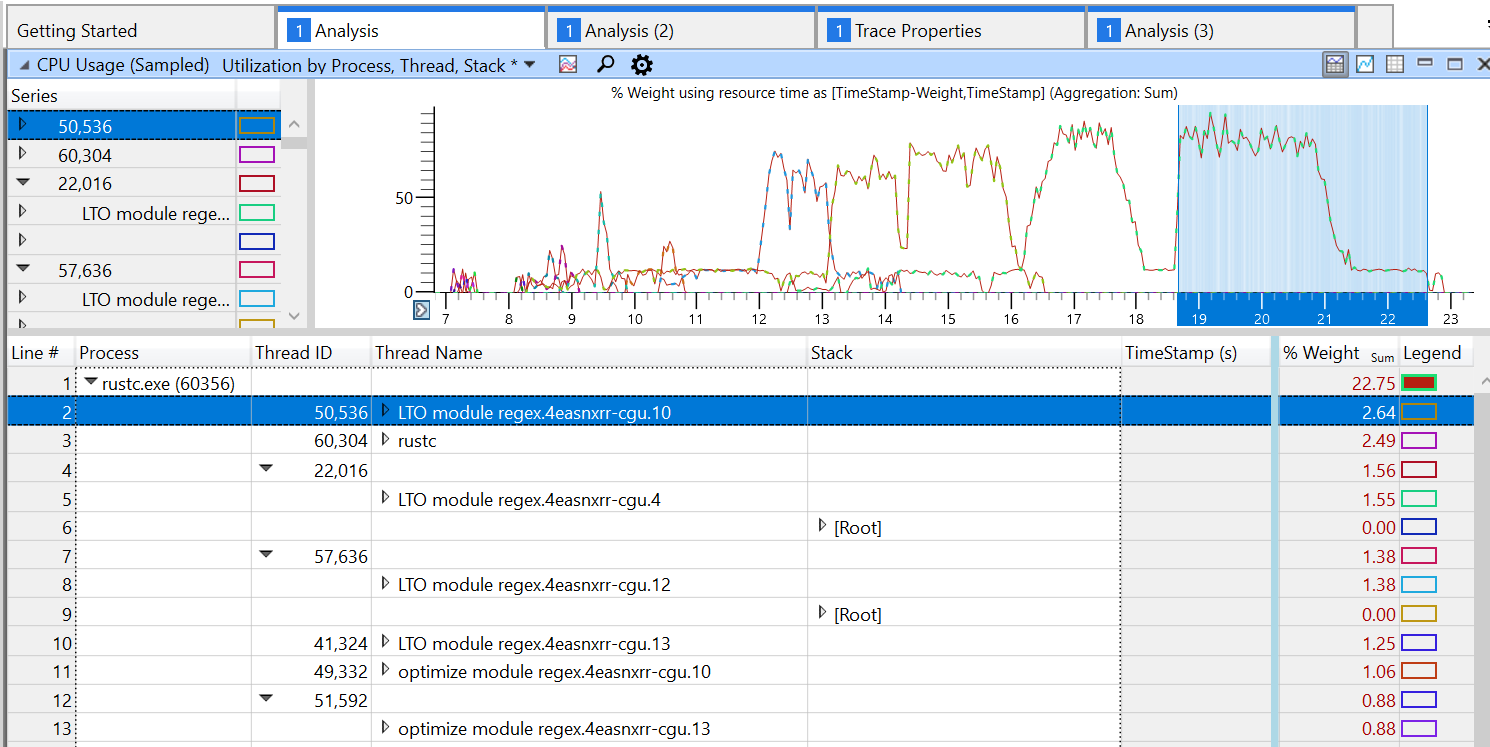
Consider inexpensive inlining criteria first
Refactor inlining decisions so that inexpensive criteria are considered first:
1. Based on code generation attributes.
2. Based on MIR availability (examines call graph).
3. Based on MIR body.
Reword labels on E0308 involving async fn return type
Fix for #80658.
When someone writes code like this:
```rust
fn foo() -> u8 {
async fn async_fn() -> () {}
async_fn()
}
```
And they try to compile it, they will see an error that looks like this:
```bash
error[E0308]: mismatched types
--> test.rs:4:5
|
1 | fn foo() -> u8 {
| -- expected `u8` because of return type
2 | async fn async_fn() -> () {}
| -- checked the `Output` of this `async fn`, found opaque type
3 |
4 | async_fn()
| ^^^^^^^^^^ expected `u8`, found opaque type
|
= note: while checking the return type of this `async fn`
= note: expected type `u8`
found opaque type `impl Future`
```
For some targets, rustc uses a "CRT fallback", where it links CRT
object files it ships instead of letting the host compiler link
them.
On musl, rustc currently links crt1, crti and crtn (provided by
libc), but does not link crtbegin and crtend (provided by libgcc).
In particular, crtend is responsible for terminating the .eh_frame
section. Lack of terminator may result in segfaults during
unwinding, as reported in #47551 and encountered by the LLVM 12
update in #81451.
This patch links crtbegin and crtend for musl as well, following
the table at the top of crt_objects.rs.
[librustdoc] Only split lang string on `,`, ` `, and `\t`
Split markdown lang strings into tokens on `,`.
The previous behavior was to split lang strings into tokens on any
character that wasn't a `_`, `_`, or alphanumeric.
This is a potentially breaking change, so please scrutinize! See discussion in #78344.
I noticed some test cases that made me wonder if there might have been some reason for the original behavior:
```
t("{.no_run .example}", false, true, Ignore::None, true, false, false, false, v(), None);
t("{.sh .should_panic}", true, false, Ignore::None, false, false, false, false, v(), None);
t("{.example .rust}", false, false, Ignore::None, true, false, false, false, v(), None);
t("{.test_harness .rust}", false, false, Ignore::None, true, true, false, false, v(), None);
```
It seemed pretty peculiar to specifically test lang strings in braces, with all the tokens prefixed by `.`.
I did some digging, and it looks like the test cases were added way back in [this commit from 2014](https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/commit/3fef7a74ca9a) by `@skade.`
It looks like they were added just to make sure that the splitting was permissive, and aren't testing that those strings in particular are accepted.
Closes https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/78344.