Value trees won't have scalar ptr at all, so we need a scalar int printing method anyway. This way we'll be able to share that method between all const representations.
valtree is a version of constants that is inherently safe to be used within types.
This is in contrast to ty::Const which can have different representations of the same value. These representation differences can show up in hashing or equality comparisons, breaking type equality of otherwise equal types.
valtrees do not have this problem.
expand: Do not allocate `Lrc` for `allow_internal_unstable` list unless necessary
This allocation is done for any macro defined in the current crate, or used from a different crate.
EDIT: This also removes an `Lrc` increment from each *use* of such macro, which may be more significant.
Noticed when reviewing https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/82367.
This probably doesn't matter, but let's do a perf run.
Adjust some `#[cfg]`s to take non-Unix non-Windows operating systems into account
This makes compilation to such targets (e.g. `wasm32-wasi`) easier.
cc rust-lang/miri#722bb6d1d0a09 (r48100619)
Eagerly construct bodies of THIR
With this PR:
- the THIR is no longer constructed lazily, but is entirely built before being passed to the MIR Builder
- the THIR is now allocated in arenas instead of `Box`es
However, this PR doesn't make any changes to the way patterns are constructed: they are still boxed, and exhaustiveness checking is unchanged.
Implements MCP rust-lang/compiler-team#409.
Closesrust-lang/project-thir-unsafeck#1.
r? `@ghost` cc `@nikomatsakis` `@oli-obk`
Shorten `rustc_middle::ty::mod`
Related to #60302.
This PR moves all `Adt*`, `Assoc*`, `Generic*`, and `UpVar*` types to separate files.
This, alongside some `use` reordering, puts `mod.rs` at ~2,200 lines, thus removing the `// ignore-tidy-filelength`.
The particular groups were chosen as they had 4 or more "substantive" members.
This pulls in rust-lang/rustc-rayon#8 to fix#81425. (h/t @ammaraskar)
That revealed weak constraints on `rustc_arena::DropArena`, because its
`DropType` was holding type-erased raw pointers to generic `T`. We can
implement `Send` for `DropType` (under `cfg(parallel_compiler)`) by
requiring all `T: Send` before they're type-erased.
The Rust code is often written under an assumption that for generic
methods inline attribute is mostly unnecessary, since for optimized
builds using ThinLTO, a method will be generated in at least one CGU and
available for import.
For example, deref implementations for Box, Vec, MutexGuard, and
MutexGuard are not currently marked as inline, neither is identity
implementation of From trait.
In PGO builds, when functions are determined to be cold, the default
multiplier of zero will stop the import, even for completely trivial
functions.
Increase slightly the default multiplier from 0 to 0.1 to import them
regardless.
Rollup of 9 pull requests
Successful merges:
- #81309 (always eagerly eval consts in Relate)
- #82217 (Edition-specific preludes)
- #82807 (rustdoc: Remove redundant enableSearchInput function)
- #82924 (WASI: Switch to crt1-command.o to enable support for new-style commands)
- #82949 (Do not attempt to unlock envlock in child process after a fork.)
- #82955 (fix: wrong word)
- #82962 (Treat header as first paragraph for shortened markdown descriptions)
- #82976 (fix error message for copy(_nonoverlapping) overflow)
- #82977 (Rename `Option::get_or_default` to `get_or_insert_default`)
Failed merges:
r? `@ghost`
`@rustbot` modify labels: rollup
WASI: Switch to crt1-command.o to enable support for new-style commands
This switches Rust's WASI target to use crt1-command.o instead of
crt1.o, which enables support for new-style commands. By default,
new-style commands work the same way as old-style commands, so nothing
immediately changes here, but this will be needed by later changes to
enable support for typed arguments.
See here for more information on new-style commands:
- https://github.com/WebAssembly/wasi-libc/pull/203
- https://reviews.llvm.org/D81689
r? ```@alexcrichton```
Edition-specific preludes
This changes `{std,core}::prelude` to export edition-specific preludes under `rust_2015`, `rust_2018` and `rust_2021`. (As suggested in https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/51418#issuecomment-395630382.) For now they all just re-export `v1::*`, but this allows us to add things to the 2021edition prelude soon.
This also changes the compiler to make the automatically injected prelude import dependent on the selected edition.
cc `@rust-lang/libs` `@djc`
Implement RFC 2945: "C-unwind" ABI
## Implement RFC 2945: "C-unwind" ABI
This branch implements [RFC 2945]. The tracking issue for this RFC is #74990.
The feature gate for the issue is `#![feature(c_unwind)]`.
This RFC was created as part of the ffi-unwind project group tracked at rust-lang/lang-team#19.
### Changes
Further details will be provided in commit messages, but a high-level overview
of the changes follows:
* A boolean `unwind` payload is added to the `C`, `System`, `Stdcall`,
and `Thiscall` variants, marking whether unwinding across FFI boundaries is
acceptable. The cases where each of these variants' `unwind` member is true
correspond with the `C-unwind`, `system-unwind`, `stdcall-unwind`, and
`thiscall-unwind` ABI strings introduced in RFC 2945 [3].
* This commit adds a `c_unwind` feature gate for the new ABI strings.
Tests for this feature gate are included in `src/test/ui/c-unwind/`, which
ensure that this feature gate works correctly for each of the new ABIs.
A new language features entry in the unstable book is added as well.
* We adjust the `rustc_middle::ty::layout::fn_can_unwind` function,
used to compute whether or not a `FnAbi` object represents a function that
should be able to unwind when `panic=unwind` is in use.
* Changes are also made to
`rustc_mir_build::build::should_abort_on_panic` so that the function ABI is
used to determind whether it should abort, assuming that the `panic=unwind`
strategy is being used, and no explicit unwind attribute was provided.
[RFC 2945]: https://github.com/rust-lang/rfcs/blob/master/text/2945-c-unwind-abi.md
Remove the -Zinsert-sideeffect
This removes all of the code we had in place to work-around LLVM's
handling of forward progress. From this removal excluded is a workaround
where we'd insert a `sideeffect` into clearly infinite loops such as
`loop {}`. This code remains conditionally effective when the LLVM
version is earlier than 12.0, which fixed the forward progress related
miscompilations at their root.
This removes all of the code we had in place to work-around LLVM's
handling of forward progress. From this removal excluded is a workaround
where we'd insert a `sideeffect` into clearly infinite loops such as
`loop {}`. This code remains conditionally effective when the LLVM
version is earlier than 12.0, which fixed the forward progress related
miscompilations at their root.
Store HIR attributes in a side table
Same idea as #72015 but for attributes.
The objective is to reduce incr-comp invalidations due to modified attributes.
Notably, those due to modified doc comments.
Implementation:
- collect attributes during AST->HIR lowering, in `LocalDefId -> ItemLocalId -> &[Attributes]` nested tables;
- access the attributes through a `hir_owner_attrs` query;
- local refactorings to use this access;
- remove `attrs` from HIR data structures one-by-one.
Change in behaviour:
- the HIR visitor traverses all attributes at once instead of parent-by-parent;
- attribute arrays are sometimes duplicated: for statements and variant constructors;
- as a consequence, attributes are marked as used after unused-attribute lint emission to avoid duplicate lints.
~~Current bug: the lint level is not correctly applied in `std::backtrace_rs`, triggering an unused attribute warning on `#![no_std]`. I welcome suggestions.~~
RFC 1240 states that it is unsafe to capture references into a
packed-struct. This PR ensures that when a closure captures a precise
path, we aren't violating this safety constraint.
To acheive so we restrict the capture precision to the struct itself.
An interesting edge case:
```rust
struct Foo(String);
let foo: Foo;
let c = || {
println!("{}", foo.0);
let x = foo.0;
}
```
Given how closures get desugared today, foo.0 will be moved into the
closure, making the `println!`, safe. However this can be very subtle
and also will be unsafe if the closure gets inline.
Closes: https://github.com/rust-lang/project-rfc-2229/issues/33
Don't hardcode the `v1` prelude in diagnostics, to allow for new preludes.
Instead of looking for `std::prelude::v1`, this changes the two places where that was hardcoded to look for `std::prelude::<anything>` instead.
This is needed for https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/82217.
r? `@estebank`
Bump tracing-tree dependency
This bump fixes two small rendering things that were annoying me:
* The first level didn't have an opening line
* When wraparound happens, there was no warning, the levels just disappeared. Now there is a line that shows that wraparound is happening
See https://github.com/davidbarsky/tracing-tree/pull/31/files for how the look changes
Add Option::get_or_default
Tracking issue: #82901
The original issue is #55042, which was closed, but for an invalid reason (see discussion there). Opening this to reconsider (I hope that's okay). It seems like the only gap for `Option` being "entry-like".
I ran into a need for this method where I had a `Vec<Option<MyData>>` and wanted to do `vec[n].get_or_default().my_data_method()`. Using an `Option` as an inner component of a data structure is probably where the need for this will normally arise.
Stabilize `unsafe_op_in_unsafe_fn` lint
This makes it possible to override the level of the `unsafe_op_in_unsafe_fn`, as proposed in https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/71668#issuecomment-729770896.
Tracking issue: #71668
r? ```@nikomatsakis``` cc ```@SimonSapin``` ```@RalfJung```
# Stabilization report
This is a stabilization report for `#![feature(unsafe_block_in_unsafe_fn)]`.
## Summary
Currently, the body of unsafe functions is an unsafe block, i.e. you can perform unsafe operations inside.
The `unsafe_op_in_unsafe_fn` lint, stabilized here, can be used to change this behavior, so performing unsafe operations in unsafe functions requires an unsafe block.
For now, the lint is allow-by-default, which means that this PR does not change anything without overriding the lint level.
For more information, see [RFC 2585](https://github.com/rust-lang/rfcs/blob/master/text/2585-unsafe-block-in-unsafe-fn.md)
### Example
```rust
// An `unsafe fn` for demonstration purposes.
// Calling this is an unsafe operation.
unsafe fn unsf() {}
// #[allow(unsafe_op_in_unsafe_fn)] by default,
// the behavior of `unsafe fn` is unchanged
unsafe fn allowed() {
// Here, no `unsafe` block is needed to
// perform unsafe operations...
unsf();
// ...and any `unsafe` block is considered
// unused and is warned on by the compiler.
unsafe {
unsf();
}
}
#[warn(unsafe_op_in_unsafe_fn)]
unsafe fn warned() {
// Removing this `unsafe` block will
// cause the compiler to emit a warning.
// (Also, no "unused unsafe" warning will be emitted here.)
unsafe {
unsf();
}
}
#[deny(unsafe_op_in_unsafe_fn)]
unsafe fn denied() {
// Removing this `unsafe` block will
// cause a compilation error.
// (Also, no "unused unsafe" warning will be emitted here.)
unsafe {
unsf();
}
}
```
### Add debug assertion to check `AbiDatas` ordering
This makes a small alteration to `Abi::index`, so that we include a
debug assertion to check that the index we are returning corresponds
with the same abi in our data array.
This will help prevent ordering bugs in the future, which can
manifest in rather strange errors.
### Using exhaustive ABI matches
This slightly modifies the changes from our previous commits,
favoring exhaustive matches in place of `_ => ...` fall-through
arms.
This should help with maintenance in the future, when additional
ABI's are added, or when existing ABI's are modified.
### List all `-unwind` ABI's in unstable book
This updates the `c-unwind` page in the unstable book to list _all_
of the other ABI strings that are introduced by this feature gate.
Now, all of the ABI's specified by RFC 2945 are shown.
Co-authored-by: Amanieu d'Antras <amanieu@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Niko Matsakis <niko@alum.mit.edu>
### Changes
This commit implements unwind ABI's, specified in RFC 2945.
We adjust the `rustc_middle::ty::layout::fn_can_unwind` function,
used to compute whether or not a `FnAbi` object represents a
function that should be able to unwind when `panic=unwind` is in
use.
Changes are also made to
`rustc_mir_build::build::should_abort_on_panic` so that the
function ABI is used to determind whether it should abort, assuming
that the `panic=unwind` strategy is being used, and no explicit
unwind attribute was provided.
### Tests
Unit tests, checking that the behavior is correct for `C-unwind`,
`stdcall-unwind`, `system-unwind`, and `thiscall-unwind`, are
included. These alternative `unwind` ABI strings are specified in
RFC 2945, in the "_Other `unwind` ABI strings_" section.
Additionally, a test case is included to assert that the LLVM IR
generated for an external function defined with the `C-unwind` ABI
will be appropriately labeled with the `nounwind` LLVM attribute
when the `panic=abort` compilation flag is used.
### Ignore Directives
This commit uses `ignore-*` directives in two of our `*-unwind` ABI
test cases.
Specifically, the `stdcall-unwind` and `thiscall-unwind` test cases
ignore architectures that do not support `stdcall` and `thiscall`,
respectively.
These directives are cribbed from
`src/test/ui/c-variadic/variadic-ffi-1.rs` for `stdcall`, and
`src/test/ui/extern/extern-thiscall.rs` for `thiscall`.
### Overview
This commit begins the implementation work for RFC 2945. For more
information, see the rendered RFC [1] and tracking issue [2].
A boolean `unwind` payload is added to the `C`, `System`, `Stdcall`,
and `Thiscall` variants, marking whether unwinding across FFI
boundaries is acceptable. The cases where each of these variants'
`unwind` member is true correspond with the `C-unwind`,
`system-unwind`, `stdcall-unwind`, and `thiscall-unwind` ABI strings
introduced in RFC 2945 [3].
### Feature Gate and Unstable Book
This commit adds a `c_unwind` feature gate for the new ABI strings.
Tests for this feature gate are included in `src/test/ui/c-unwind/`,
which ensure that this feature gate works correctly for each of the
new ABIs.
A new language features entry in the unstable book is added as well.
### Further Work To Be Done
This commit does not proceed to implement the new unwinding ABIs,
and is intentionally scoped specifically to *defining* the ABIs and
their feature flag.
### One Note on Test Churn
This will lead to some test churn, in re-blessing hash tests, as the
deleted comment in `src/librustc_target/spec/abi.rs` mentioned,
because we can no longer guarantee the ordering of the `Abi`
variants.
While this is a downside, this decision was made bearing in mind
that RFC 2945 states the following, in the "Other `unwind` Strings"
section [3]:
> More unwind variants of existing ABI strings may be introduced,
> with the same semantics, without an additional RFC.
Adding a new variant for each of these cases, rather than specifying
a payload for a given ABI, would quickly become untenable, and make
working with the `Abi` enum prone to mistakes.
This approach encodes the unwinding information *into* a given ABI,
to account for the future possibility of other `-unwind` ABI
strings.
### Ignore Directives
`ignore-*` directives are used in two of our `*-unwind` ABI test
cases.
Specifically, the `stdcall-unwind` and `thiscall-unwind` test cases
ignore architectures that do not support `stdcall` and
`thiscall`, respectively.
These directives are cribbed from
`src/test/ui/c-variadic/variadic-ffi-1.rs` for `stdcall`, and
`src/test/ui/extern/extern-thiscall.rs` for `thiscall`.
This would otherwise fail on some targets, see:
fcf697f902
### Footnotes
[1]: https://github.com/rust-lang/rfcs/blob/master/text/2945-c-unwind-abi.md
[2]: https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/74990
[3]: https://github.com/rust-lang/rfcs/blob/master/text/2945-c-unwind-abi.md#other-unwind-abi-strings
This updates all places where match branches check on StatementKind or UseContext.
This doesn't properly implement them, but adds TODOs where they are, and also adds some best
guesses to what they should be in some cases.
I'm still not totally sure if this is the right way to implement the memcpy, but that portion
compiles correctly now. Now to fix the compile errors everywhere else :).
Change x64 size checks to not apply to x32.
Rust contains various size checks conditional on target_arch = "x86_64", but these checks were never intended to apply to x86_64-unknown-linux-gnux32. Add target_pointer_width = "64" to the conditions.
or-patterns: disallow in `let` bindings
~~Blocked on https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/81869~~
Disallows top-level or-patterns before type ascription. We want to reserve this syntactic space for possible future generalized type ascription.
r? ``@petrochenkov``
This switches Rust's WASI target to use crt1-command.o instead of
crt1.o, which enables support for new-style commands. By default,
new-style commands work the same way as old-style commands, so nothing
immediately changes here, but this will be needed by later changes to
enable support for typed arguments.
See here for more information on new-style commands:
- https://github.com/WebAssembly/wasi-libc/pull/203
- https://reviews.llvm.org/D81689
diagnostics: Be clear about "crate root" and `::foo` paths in resolve diagnostics
Various changes to make sure the diagnostics are clear about the differences in `::foo` paths across editions:
- `::foo` will say "crate root" in 2015 and "list of imported crates" in 2018
- `crate::` will never reference imported crates in 2018
Fixes https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/82876
Refactor confirm_builtin_call, remove partial if
Pass callee expr to `confirm_builtin_call`. This removes a partial
pattern match in `confirm_builtin_call` and the `panic` in the `else`
branch. The diff is large because of indentation changes caused by
removing the if-let.
Disable destination propagation on all mir-opt-levels
The new `// compile-flags: -Zunsound-mir-opts` are inserted without an extra newline to avoid introducing a large mir-opt diff.
Implement built-in attribute macro `#[cfg_eval]` + some refactoring
This PR implements a built-in attribute macro `#[cfg_eval]` as it was suggested in https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/79078 to avoid `#[derive()]` without arguments being abused as a way to configure input for other attributes.
The macro is used for eagerly expanding all `#[cfg]` and `#[cfg_attr]` attributes in its input ("fully configuring" the input).
The effect is identical to effect of `#[derive(Foo, Bar)]` which also fully configures its input before passing it to macros `Foo` and `Bar`, but unlike `#[derive]` `#[cfg_eval]` can be applied to any syntax nodes supporting macro attributes, not only certain items.
`cfg_eval` was the first name suggested in https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/79078, but other alternatives are also possible, e.g. `cfg_expand`.
```rust
#[cfg_eval]
#[my_attr] // Receives `struct S {}` as input, the field is configured away by `#[cfg_eval]`
struct S {
#[cfg(FALSE)]
field: u8,
}
```
Tracking issue: https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/82679
expand: Refactor module loading
This is an accompanying PR to https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/82399, but they can be landed independently.
See individual commits for more details.
Anyone should be able to review this equally well because all people actually familiar with this code left the project.
bypass auto_da_alloc for metadata files
This saves about 0.7% when rerunning the UI test suite. I.e. when the metadata files exist and will be overwritten. No improvements expected for a clean build. So it might show up in incr-patched perf results.
```
regular rename:
Benchmark #1: touch src/tools/compiletest/src/main.rs ; RUSTC_WRAPPER="" schedtool -B -e ./x.py test src/test/ui
Time (mean ± σ): 47.305 s ± 0.170 s [User: 1631.540 s, System: 412.648 s]
Range (min … max): 47.125 s … 47.856 s 20 runs
non-durable rename:
Benchmark #1: touch src/tools/compiletest/src/main.rs ; RUSTC_WRAPPER="" schedtool -B -e ./x.py test src/test/ui
Time (mean ± σ): 46.930 s ± 0.064 s [User: 1634.344 s, System: 396.038 s]
Range (min … max): 46.759 s … 47.043 s 20 runs
```
There are more places that trigger auto_da_alloc behavior by overwriting existing files with O_TRUNC, but those are much harder to locate because `O_TRUNC` is set on `open()` but the writeback is triggered on `close()`. The latter is the part which shows up in profiles.
Let a portion of DefPathHash uniquely identify the DefPath's crate.
This allows to directly map from a `DefPathHash` to the crate it originates from, without constructing side tables to do that mapping -- something that is useful for incremental compilation where we deal with `DefPathHash` instead of `DefId` a lot.
It also allows to reliably and cheaply check for `DefPathHash` collisions which allows the compiler to gracefully abort compilation instead of running into a subsequent ICE at some random place in the code.
The following new piece of documentation describes the most interesting aspects of the changes:
```rust
/// A `DefPathHash` is a fixed-size representation of a `DefPath` that is
/// stable across crate and compilation session boundaries. It consists of two
/// separate 64-bit hashes. The first uniquely identifies the crate this
/// `DefPathHash` originates from (see [StableCrateId]), and the second
/// uniquely identifies the corresponding `DefPath` within that crate. Together
/// they form a unique identifier within an entire crate graph.
///
/// There is a very small chance of hash collisions, which would mean that two
/// different `DefPath`s map to the same `DefPathHash`. Proceeding compilation
/// with such a hash collision would very probably lead to an ICE and, in the
/// worst case, to a silent mis-compilation. The compiler therefore actively
/// and exhaustively checks for such hash collisions and aborts compilation if
/// it finds one.
///
/// `DefPathHash` uses 64-bit hashes for both the crate-id part and the
/// crate-internal part, even though it is likely that there are many more
/// `LocalDefId`s in a single crate than there are individual crates in a crate
/// graph. Since we use the same number of bits in both cases, the collision
/// probability for the crate-local part will be quite a bit higher (though
/// still very small).
///
/// This imbalance is not by accident: A hash collision in the
/// crate-local part of a `DefPathHash` will be detected and reported while
/// compiling the crate in question. Such a collision does not depend on
/// outside factors and can be easily fixed by the crate maintainer (e.g. by
/// renaming the item in question or by bumping the crate version in a harmless
/// way).
///
/// A collision between crate-id hashes on the other hand is harder to fix
/// because it depends on the set of crates in the entire crate graph of a
/// compilation session. Again, using the same crate with a different version
/// number would fix the issue with a high probability -- but that might be
/// easier said then done if the crates in questions are dependencies of
/// third-party crates.
///
/// That being said, given a high quality hash function, the collision
/// probabilities in question are very small. For example, for a big crate like
/// `rustc_middle` (with ~50000 `LocalDefId`s as of the time of writing) there
/// is a probability of roughly 1 in 14,750,000,000 of a crate-internal
/// collision occurring. For a big crate graph with 1000 crates in it, there is
/// a probability of 1 in 36,890,000,000,000 of a `StableCrateId` collision.
```
Given the probabilities involved I hope that no one will ever actually see the error messages. Nonetheless, I'd be glad about some feedback on how to improve them. Should we create a GH issue describing the problem and possible solutions to point to? Or a page in the rustc book?
r? `@pnkfelix` (feel free to re-assign)
Use u32 over Option<u32> in DebugLoc
~~Changes `Option<u32>` fields in `DebugLoc` to `Option<NonZeroU32>`. Since the respective fields (`line` and `col`) are guaranteed to be 1-based, this layout optimization is a freebie.~~
EDIT: Changes `Option<u32>` fields in `DebugLoc` to `u32`. As `@bugadani` pointed out, an `Option<NonZeroU32>` is probably an unnecessary layer of abstraction since the `None` variant is always used as `UNKNOWN_LINE_NUMBER` (which is just `0`). Also, `SourceInfo` in `metadata.rs` already uses a `u32` instead of an `Option<u32>` to encode the same information, so I think this change is warranted.
Since `@jyn514` raised some concerns over measuring performance in a similar PR (#82255), does this need a perf run?
Sync rustc_codegen_cranelift
The main highlight of this sync is removal of support for the old x86 Cranelift backend. This made it possible to use native atomic instructions rather than hackishly using a global mutex. 128bit integer support has also seen a few bugfixes and performance improvements. And finally I have formatted everything using the same rustfmt config as the rest of this repo.
r? ````@ghost````
````@rustbot```` label +A-codegen +A-cranelift +T-compiler
Cleanup rustdoc warnings
## Clean up error reporting for deprecated passes
Using `error!` here goes all the way back to the original commit, https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/8540. I don't see any reason to use logging; rustdoc should use diagnostics wherever possible. See https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/81932#issuecomment-785291244 for further context.
- Use spans for deprecated attributes
- Use a proper diagnostic for unknown passes, instead of error logging
- Add tests for unknown passes
- Improve some wording in diagnostics
## Report that `doc(plugins)` doesn't work using diagnostics instead of `eprintln!`
This also adds a test for the output.
This was added in https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/52194. I don't see any particular reason not to use diagnostics here, I think it was just missed in https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/50541.
Change built-in kernel targets to be os = none throughout
Whether for Rust's own `target_os`, LLVM's triples, or GNU config's, the
OS-related have fields have been for code running *on* that OS, not code
hat is *part* of the OS.
The difference is huge, as syscall interfaces are nothing like
freestanding interfaces. Kernels are (hypervisors and other more exotic
situations aside) freestanding programs that use the interfaces provided
by the hardware. It's *those* interfaces, the ones external to the
program being built and its software dependencies, that are the content
of the target.
For the Linux Kernel in particular, `target_env: "gnu"` is removed for
the same reason: that `-gnu` refers to glibc or GNU/linux, neither of
which applies to the kernel itself.
Relates to #74247
Move check only relevant in error case out of critical path
Move the check for potentially forgotten `return` in a tail expression
of arbitrary expressions into the coercion error branch to avoid
computing unncessary coercion checks on successful code.
Follow up to #81458.
Rust contains various size checks conditional on target_arch = "x86_64",
but these checks were never intended to apply to
x86_64-unknown-linux-gnux32. Add target_pointer_width = "64" to the
conditions.
Warn on `#![doc(test(...))]` on items other than the crate root and use future incompatible lint
Part of #82672.
This PR does multiple things:
* Create a new `INVALID_DOC_ATTRIBUTE` lint which is also "future incompatible", allowing us to use it as a warning for the moment until it turns (eventually) into a hard error.
* Use this link when `#![doc(test(...))]` isn't used at the crate level.
* Make #82702 use this new lint as well.
r? ``@jyn514``
When rustdoc lints were changed to be tool lints, the `rustdoc` group
was removed, leading to spurious warnings like
```
warning: unknown lint: `rustdoc`
```
The lint group still worked when rustdoc ran, since rustdoc added the group itself.
This renames the group to `rustdoc::all` for consistency with
`clippy::all` and the rest of the rustdoc lints.
Add diagnostic item to `Default` trait
This PR adds diagnostic item to `Default` trait to be used by rust-lang/rust-clippy#6562 issue.
Also fixes the obsolete path to the `symbols.rs` file in the comment.
Add suggestion `.collect()` for iterators in iterators
Closes#81584
```
error[E0515]: cannot return value referencing function parameter `y`
--> main3.rs:4:38
|
4 | ... .map(|y| y.iter().map(|x| x + 1))
| -^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
| |
| returns a value referencing data owned by the current function
| `y` is borrowed here
| help: Maybe use `.collect()` to allocate the iterator
```
Added the suggestion: `help: Maybe use `.collect()` to allocate the iterator`
resolve: Reduce scope of `pub_use_of_private_extern_crate` deprecation lint
This lint was deny-by-default since July 2017, crater showed 7 uses on crates.io back then (https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/42894#issuecomment-311921147).
Unfortunately, the construction `pub use foo as bar` where `foo` is `extern crate foo;` was used by an older version `bitflags`, so turning it into an error causes too many regressions.
So, this PR reduces the scope of the lint instead of turning it into a hard error, and only turns some more rarely used components of it into errors.
Implement NOOP_METHOD_CALL lint
Implements the beginnings of https://github.com/rust-lang/lang-team/issues/67 - a lint for detecting noop method calls (e.g, calling `<&T as Clone>::clone()` when `T: !Clone`).
This PR does not fully realize the vision and has a few limitations that need to be addressed either before merging or in subsequent PRs:
* [ ] No UFCS support
* [ ] The warning message is pretty plain
* [ ] Doesn't work for `ToOwned`
The implementation uses [`Instance::resolve`](https://doc.rust-lang.org/nightly/nightly-rustc/rustc_middle/ty/instance/struct.Instance.html#method.resolve) which is normally later in the compiler. It seems that there are some invariants that this function relies on that we try our best to respect. For instance, it expects substitutions to have happened, which haven't yet performed, but we check first for `needs_subst` to ensure we're dealing with a monomorphic type.
Thank you to ```@davidtwco,``` ```@Aaron1011,``` and ```@wesleywiser``` for helping me at various points through out this PR ❤️.
Inherit `#[stable(..)]` annotations in enum variants and fields from its item
Lint changes for #65515. The stdlib will have to be updated once this lands in beta and that version is promoted in master.
This ownership kind is only constructed in the case of path attributes like `#[path = ".."]` without a file name segment, which always represent some kind of directories and will produce and error on attempt to parse them as a module file.
Fix polymorphization ICE on associated types in trait decls using const generics in bounds
r? `@davidtwco`
only the last commit actually changes something
Upgrade to LLVM 12
This implements the necessary adjustments to make rustc work with LLVM 12. I didn't encounter any major issues so far.
r? `@cuviper`
Pass callee expr to `confirm_builtin_call`. This removes a partial
pattern match in `confirm_builtin_call` and the `panic` in the `else`
branch. The diff is large because of indentation changes caused by
removing the if-let.
Add `-Z unpretty` flags for the AST
Implements rust-lang/compiler-team#408.
Builds on #82269, but if that PR is rejected or stalls out, I can implement this without #82269.
cc rust-lang/rustc-dev-guide#1062
Move the check for potentially forgotten `return` in a tail expression
of arbitrary expressions into the coercion error branch to avoid
computing unncessary coercion checks on successful code.
Follow up to #81458.
This works around a design defect in the LLVM 12 pass builder
implementation. In LLVM 13, the PreLink ThinLTO pipeline properly
respects the OptimizerLastEPCallbacks.
Update tracing to 0.1.25
* Update tracing from 0.1.18 to 0.1.25
* Update tracing-subscriber from 0.2.13 to 0.2.16
* Update tracing-tree from 0.1.6 to 0.1.8
* Add pin-project-lite to the list of allowed dependencies (it is now a direct dependency of tracing).
Revert non-power-of-two vector restriction
Removes the power of two restriction from rustc. As discussed in https://github.com/rust-lang/stdsimd/issues/63
r? ```@calebzulawski```
cc ```@workingjubilee``` ```@thomcc```
Optimize counting digits in line numbers during error reporting further
This one-ups #82248 by switching the strategy: Instead of dividing the value by 10 repeatedly, we compare with a limit that we multiply by 10 repeatedly. In my benchmarks, this took between 50% and 25% of the original time. The reasons for being faster are:
1. While LLVM is able to replace a division by constant with a multiply + shift, a plain multiplication is still faster. However, this doesn't even factor, because
2. Multiplication, unlike division, is const. We also use a simple for-loop instead of a more complex loop + break, which allows
3. rustc to const-fold the whole loop, and indeed the assembly output simply shows a series of comparisons.
Rollup of 10 pull requests
Successful merges:
- #80189 (Convert primitives in the standard library to intra-doc links)
- #80874 (Update intra-doc link documentation to match the implementation)
- #82376 (Add option to enable MIR inlining independently of mir-opt-level)
- #82516 (Add incomplete feature gate for inherent associate types.)
- #82579 (Fix turbofish recovery with multiple generic args)
- #82593 (Teach rustdoc how to display WASI.)
- #82597 (Get TyCtxt from self instead of passing as argument in AutoTraitFinder)
- #82627 (Erase late bound regions to avoid ICE)
- #82661 (⬆️ rust-analyzer)
- #82691 (Update books)
Failed merges:
r? `@ghost`
`@rustbot` modify labels: rollup
Add incomplete feature gate for inherent associate types.
Mentored by ``````@oli-obk``````
So far the only change is that instead of giving an automatic error, the following code compiles:
```rust
struct Foo;
impl Foo {
type Bar = isize;
}
```
The backend work to make it actually usable isn't there yet. In particular, this:
```rust
let x : Foo::Bar;
```
will give you:
```sh
error[E0223]: ambiguous associated type
--> /$RUSTC_DIR/src/test/ui/assoc-inherent.rs:15:13
|
LL | let x : Foo::Bar;
| ^^^^^^^^ help: use fully-qualified syntax: `<Foo as Trait>::Bar`
```
Add option to enable MIR inlining independently of mir-opt-level
Add `-Zinline-mir` option that enables MIR inlining independently of the
current MIR opt level. The primary use-case is enabling MIR inlining on the
default MIR opt level.
Turn inlining thresholds into optional values to make it possible to configure
different defaults depending on the current mir-opt-level (although thresholds
are yet to be used in such a manner).
Remove an old FIXME comment and inline attribute
Apparently #35870 caused a problem in this code (which originally
returned an impl trait) and `#[inline]` was added as a workaround, in
ade79d7609.
The issue is now fixed and the comment and `#[inline]` can now be
removed.
Note that the FIXME was removed because this can't be fixed,
`register_renamed` calls LintId::of and there's no LintId for rustdoc
lints when rustc is running.
- Move MISSING_CRATE_LEVEL_DOCS to rustdoc directly
- Update documentation
This also takes the opportunity to make the `no-crate-level-doc-lint`
test more specific.
- Use `register_renamed` when rustdoc is running so the lint will still
be active and use a structured suggestion
- Test the behavior for rustc, not just for rustdoc (because it differs)
- Rename `broken_intra_doc_links` to `rustdoc::broken_intra_doc_links`
- Ensure that the old lint names still work and give deprecation errors
- Register lints even when running doctests
Otherwise, all `rustdoc::` lints would be ignored.
- Register all existing lints as removed
This unfortunately doesn't work with `register_renamed` because tool
lints have not yet been registered when rustc is running. For similar
reasons, `check_backwards_compat` doesn't work either. Call
`register_removed` directly instead.
- Fix fallout
+ Rustdoc lints for compiler/
+ Rustdoc lints for library/
Note that this does *not* suggest `rustdoc::broken_intra_doc_links` for
`rustdoc::intra_doc_link_resolution_failure`, since there was no time
when the latter was valid.
Highlight identifier span instead of whole pattern span in `unused` lint
Fixes#81314
This pretty much just changes the span highlighted in the lint from `pat_sp` to `ident.span`. There's however an exception, which is in patterns with shorthands like `Point { y, ref mut x }`, where a suggestion to change just `x` would be invalid; in those cases I had to keep the pattern span. Another option would be suggesting something like `Point { y, x: ref mut _x }`.
I also added a new test since there weren't any test that checked the `unused` lint with optional patterns.
The definition of this struct changes in LLVM 12 due to the addition
of branch coverage support. To avoid future mismatches, declare our
own struct and then convert between them.
Whether for Rust's own `target_os`, LLVM's triples, or GNU config's, the
OS-related have fields have been for code running *on* that OS, not code
that is *part* of the OS.
The difference is huge, as syscall interfaces are nothing like
freestanding interfaces. Kernels are (hypervisors and other more exotic
situations aside) freestanding programs that use the interfaces provided
by the hardware. It's *those* interfaces, the ones external to the
program being built and its software dependencies, that are the content
of the target.
For the Linux Kernel in particular, `target_env: "gnu"` is removed for
the same reason: that `-gnu` refers to glibc or GNU/linux, neither of
which applies to the kernel itself.
Relates to #74247
Thanks @ojeda for catching some things.
Apply lint restrictions from renamed lints
Previously, if you denied the old name of a renamed lint, it would warn
about using the new name, but otherwise do nothing. Now, it will behave
the same as if you'd used the new name.
Fixes https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/82615.
r? `@ehuss`
make x86_64-pc-solaris the default target for x86-64 Solaris
This change makes `x86_64-pc-solaris` the default compilation target for x86-64 Solaris/Illumos (based on [this exchange](https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/68214#issuecomment-748042054) with `@varkor).`
I tried several ways of doing this (leveraging the alias support added with #61761 and improved/fixed with #80073) and found out that cross-compilation to the new one is by far the simplest way of doing this. It can be achieved by adding the following arguments: `--build x86_64-sun-solaris --host x86_64-pc-solaris --target x86_64-pc-solaris` and enabling the cross compilation with `PKG_CONFIG_ALLOW_CROSS=1` environment variable.
I also removed alias support altogether - `x86_64-pc-solaris` and `x86_64-sun-solaris` are now two separate targets. The problem with aliases is that even if rust internally knows that two are the same, other tools building with rust don't know that, resulting in build issues like the one with firefox mentioned [here](https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/68214#issuecomment-746144229). I think that once the dust settles and `x86_64-pc-solaris` becomes the default, `x86_64-sun-solaris` can be removed.
If you agree with the above, I have two subsequent questions:
1. Is there a preferred way to display deprecation warnings when `x86_64-sun-solaris` is passed into the compiler as an argument? I am not sure whether target deprecation was done before.
2. Where would be the best way to document this change for those using rust on Solaris? Without the cross-compilation arguments (used once to build a new version), the build won't work. Should I add it into [RELEASES.md](https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/blob/master/RELEASES.md)?
Thanks!
Remove storage markers if they won't be used during code generation
The storage markers constitute a substantial portion of all MIR
statements. At the same time, for builds without any optimizations,
the storage markers have no further use during and after MIR
optimization phase.
If storage markers are not necessary for code generation, remove them.
Fixed support for macOS Catalyst on ARM64
When I initially added Arm64 Catalyst support in https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/77484 I had access to a DTK. However, while waiting to merge the PR some other changes were merged which caused conflicts in the branch. When fixing those conflicts I had no access to the DTK anymore and didn't try out if the resulting binaries did indeed work on Apple Silicon. I finally have a M1 and I realized that some small changes were necessary to support Apple Silicon. This PR adds the required changes. I've been running binaries generated with this branch for some time now and they work without issues.
Apparently #35870 caused a problem in this code (which originally
returned an impl trait) and `#[inline]` was added as a workaround, in
ade79d7609.
The issue is now fixed and the comment and `#[inline]` can now be
removed.
The first argument to an x86-interrupt ABI function was implicitly
treated as byval prior to LLVM 12. Since LLVM 12, it has to be
marked as such explicitly: 2e0e03c6a0
Previously, if you denied the old name of a renamed lint, it would warn
about using the new name, but otherwise do nothing. Now, it will behave
the same as if you'd used the new name.
Remove the x86_64-rumprun-netbsd target
Herein we remove the target from the compiler and the code from libstd intended to support the now-defunct rumprun project.
Closes#81514
The storage markers constitute a substantial portion of all MIR
statements. At the same time, for builds without any optimizations,
the storage markers have no further use during and after MIR
optimization phase.
If storage markers are not necessary for code generation, remove them.
Update measureme dependency to the latest version
This version adds the ability to use `rdpmc` hardware-based performance
counters instead of wall-clock time for measuring duration. This also
introduces a dependency on the `perf-event-open-sys` crate on Linux
which is used when using hardware counters.
r? ```@oli-obk```
Link crtbegin/crtend on musl to terminate .eh_frame
For some targets, rustc uses a "CRT fallback", where it links CRT
object files it ships instead of letting the host compiler link
them.
On musl, rustc currently links crt1, crti and crtn (provided by
libc), but does not link crtbegin and crtend (provided by libgcc).
In particular, crtend is responsible for terminating the .eh_frame
section. Lack of terminator may result in segfaults during
unwinding, as reported in #47551 and encountered by the LLVM 12
update in #81451.
This patch links crtbegin and crtend for musl as well, following
the table at the top of crt_objects.rs.
r? ``@nagisa``
Suggest character encoding is incorrect when encountering random null bytes
This adds a note whenever null bytes are seen at the start of a token unexpectedly, since those tend to come from UTF-16 encoded files without a [BOM](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Byte_order_mark) (if a UTF-16 BOM appears it won't be valid UTF-8, but if there is no BOM it be both valid UTF-16 and valid but garbled UTF-8). This approach was suggested in https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/73979#issuecomment-653976451.
Closes#73979.
Skip Ty w/o infer ty/const in trait select
Remove some allocations & also add `skip_current_subtree` to skip subtrees with no inferred items.
r? `@eddyb` since marked in the FIXME
This adds recovery when in array type syntax user writes
[X; Y<Z, ...>]
instead of
[X; Y::<Z, ...>]
Fixes#82566
Note that whenever we parse an expression and know that the next token
cannot be `,`, we should be calling
check_mistyped_turbofish_with_multiple_type_params for this recovery.
Previously we only did this for statement parsing (e.g. `let x = f<a,
b>;`). We now also do it when parsing the length field in array type
syntax.
check_mistyped_turbofish_with_multiple_type_params was previously
expecting type arguments between angle brackets, which is not right, as
we can also see const expressions. We now use generic argument parser
instead of type parser.
Test with one, two, and three generic arguments added to check
consistentcy between
1. check_no_chained_comparison: Called after parsing a nested binop
application like `x < A > ...` where angle brackets are interpreted as
binary operators and `A` is an expression.
2. check_mistyped_turbofish_with_multiple_type_params: called by
`parse_full_stmt` when we expect to see a semicolon after parsing an
expression but don't see it.
(In `T2<1, 2>::C;`, the expression is `T2 < 1`)
When token-based attribute handling is implemeneted in #80689,
we will need to access tokens from `HasAttrs` (to perform
cfg-stripping), and we will to access attributes from `HasTokens` (to
construct a `PreexpTokenStream`).
This PR merges the `HasAttrs` and `HasTokens` traits into a new
`AstLike` trait. The previous `HasAttrs` impls from `Vec<Attribute>` and `AttrVec`
are removed - they aren't attribute targets, so the impls never really
made sense.
Use small hash set in `mir_inliner_callees`
Use small hash set in `mir_inliner_callees` to avoid temporary
allocation when possible and quadratic behaviour for large number of
callees.
Improve anonymous lifetime note to indicate the target span
Improvement for #81650
Cc #81995
Message after this improvement:
(Improve note in the middle)
```
error[E0311]: the parameter type `T` may not live long enough
--> src/main.rs:25:11
|
24 | fn play_with<T: Animal + Send>(scope: &Scope, animal: T) {
| -- help: consider adding an explicit lifetime bound...: `T: 'a +`
25 | scope.spawn(move |_| {
| ^^^^^
|
note: the parameter type `T` must be valid for the anonymous lifetime defined on the function body at 24:40...
--> src/main.rs:24:40
|
24 | fn play_with<T: Animal + Send>(scope: &Scope, animal: T) {
| ^^^^^
note: ...so that the type `[closure@src/main.rs:25:17: 27:6]` will meet its required lifetime bounds
--> src/main.rs:25:11
|
25 | scope.spawn(move |_| {
| ^^^^^
```
r? ``````@estebank``````
Replace const_cstr with cstr crate
This PR replaces the `const_cstr` macro inside `rustc_data_structures` with `cstr` macro from [cstr](https://crates.io/crates/cstr) crate.
The two macros basically serve the same purpose, which is to generate `&'static CStr` from a string literal. `cstr` is better because it validates the literal at compile time, while the existing `const_cstr` does it at runtime when `debug_assertions` is enabled. In addition, the value `cstr` generates can be used in constant context (which is seemingly not needed anywhere currently, though).
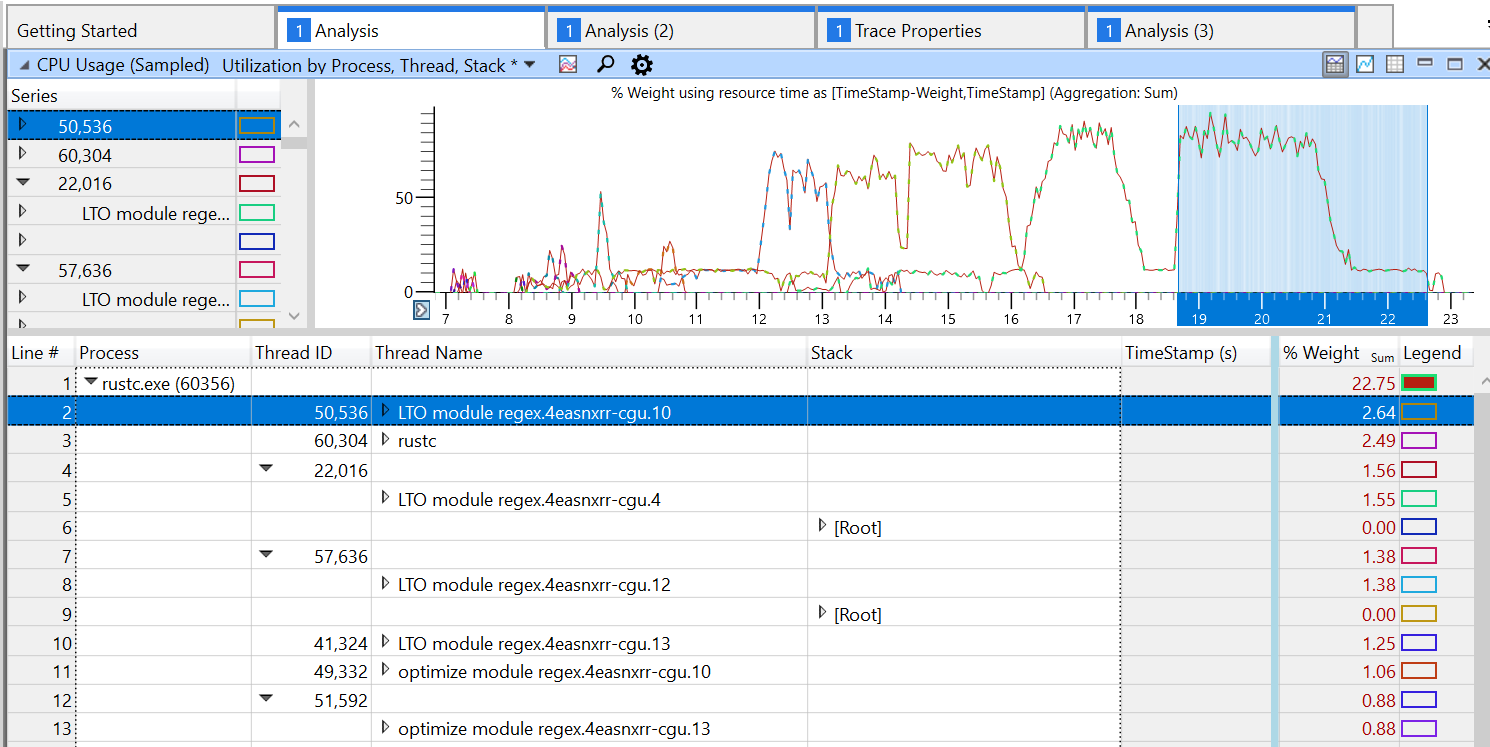
Set codegen thread names
Set names on threads spawned during codegen. Various debugging and profiling tools can take advantage of this to show a more useful identifier for threads.
For example, gdb will show thread names in `info threads`:
```
(gdb) info threads
Id Target Id Frame
1 Thread 0x7fffefa7ec40 (LWP 2905) "rustc" __pthread_clockjoin_ex (threadid=140737214134016, thread_return=0x0, clockid=<optimized out>, abstime=<optimized out>, block=<optimized out>)
at pthread_join_common.c:145
2 Thread 0x7fffefa7b700 (LWP 2957) "rustc" 0x00007ffff125eaa8 in llvm::X86_MC::initLLVMToSEHAndCVRegMapping(llvm::MCRegisterInfo*) ()
from /home/wesley/.rustup/toolchains/stage1/lib/librustc_driver-f866439e29074957.so
3 Thread 0x7fffeef0f700 (LWP 3116) "rustc" futex_wait_cancelable (private=0, expected=0, futex_word=0x7fffe8602ac8) at ../sysdeps/nptl/futex-internal.h:183
* 4 Thread 0x7fffeed0e700 (LWP 3123) "rustc" rustc_codegen_ssa:🔙:write::spawn_work (cgcx=..., work=...) at /home/wesley/code/rust/rust/compiler/rustc_codegen_ssa/src/back/write.rs:1573
6 Thread 0x7fffe113b700 (LWP 3150) "opt foof.7rcbfp" 0x00007ffff2940e62 in llvm::CallGraph::populateCallGraphNode(llvm::CallGraphNode*) ()
from /home/wesley/.rustup/toolchains/stage1/lib/librustc_driver-f866439e29074957.so
8 Thread 0x7fffe0d39700 (LWP 3158) "opt foof.7rcbfp" 0x00007fffefe8998e in malloc_consolidate (av=av@entry=0x7ffe2c000020) at malloc.c:4492
9 Thread 0x7fffe0f3a700 (LWP 3162) "opt foof.7rcbfp" 0x00007fffefef27c4 in __libc_open64 (file=0x7fffe0f38608 "foof.foof.7rcbfp3g-cgu.6.rcgu.o", oflag=524865) at ../sysdeps/unix/sysv/linux/open64.c:48
(gdb)
```
and Windows Performance Analyzer will also show this information when profiling:
Consider inexpensive inlining criteria first
Refactor inlining decisions so that inexpensive criteria are considered first:
1. Based on code generation attributes.
2. Based on MIR availability (examines call graph).
3. Based on MIR body.
Reword labels on E0308 involving async fn return type
Fix for #80658.
When someone writes code like this:
```rust
fn foo() -> u8 {
async fn async_fn() -> () {}
async_fn()
}
```
And they try to compile it, they will see an error that looks like this:
```bash
error[E0308]: mismatched types
--> test.rs:4:5
|
1 | fn foo() -> u8 {
| -- expected `u8` because of return type
2 | async fn async_fn() -> () {}
| -- checked the `Output` of this `async fn`, found opaque type
3 |
4 | async_fn()
| ^^^^^^^^^^ expected `u8`, found opaque type
|
= note: while checking the return type of this `async fn`
= note: expected type `u8`
found opaque type `impl Future`
```
For some targets, rustc uses a "CRT fallback", where it links CRT
object files it ships instead of letting the host compiler link
them.
On musl, rustc currently links crt1, crti and crtn (provided by
libc), but does not link crtbegin and crtend (provided by libgcc).
In particular, crtend is responsible for terminating the .eh_frame
section. Lack of terminator may result in segfaults during
unwinding, as reported in #47551 and encountered by the LLVM 12
update in #81451.
This patch links crtbegin and crtend for musl as well, following
the table at the top of crt_objects.rs.
[librustdoc] Only split lang string on `,`, ` `, and `\t`
Split markdown lang strings into tokens on `,`.
The previous behavior was to split lang strings into tokens on any
character that wasn't a `_`, `_`, or alphanumeric.
This is a potentially breaking change, so please scrutinize! See discussion in #78344.
I noticed some test cases that made me wonder if there might have been some reason for the original behavior:
```
t("{.no_run .example}", false, true, Ignore::None, true, false, false, false, v(), None);
t("{.sh .should_panic}", true, false, Ignore::None, false, false, false, false, v(), None);
t("{.example .rust}", false, false, Ignore::None, true, false, false, false, v(), None);
t("{.test_harness .rust}", false, false, Ignore::None, true, true, false, false, v(), None);
```
It seemed pretty peculiar to specifically test lang strings in braces, with all the tokens prefixed by `.`.
I did some digging, and it looks like the test cases were added way back in [this commit from 2014](https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/commit/3fef7a74ca9a) by `@skade.`
It looks like they were added just to make sure that the splitting was permissive, and aren't testing that those strings in particular are accepted.
Closes https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/78344.
This version adds the ability to use `rdpmc` hardware-based performance
counters instead of wall-clock time for measuring duration. This also
introduces a dependency on the `perf-event-open-sys` crate on Linux
which is used when using hardware counters.
Move pick_by_value_method docs above function header
- Currently style triggers #81183 so we can't add `#[instrument]` to
this function.
- Having docs above the header is more consistent with the rest of the
code base.
Cleanup `PpMode` and friends
This PR:
- Separates `PpSourceMode` and `PpHirMode` to remove invalid states
- Renames the variant to remove the redundant `Ppm` prefix
- Adds basic documentation for the different pretty-print modes
- Cleanups some code to make it more idiomatic
Not sure if this is actually useful, but it looks cleaner to me.
Add #[rustc_legacy_const_generics]
This is the first step towards removing `#[rustc_args_required_const]`: a new attribute is added which rewrites function calls of the form `func(a, b, c)` to `func::<{b}>(a, c)`. This allows previously stabilized functions in `stdarch` which use `rustc_args_required_const` to use const generics instead.
This new attribute is not intended to ever be stabilized, it is only intended for use in `stdarch` as a replacement for `#[rustc_args_required_const]`.
```rust
#[rustc_legacy_const_generics(1)]
pub fn foo<const Y: usize>(x: usize, z: usize) -> [usize; 3] {
[x, Y, z]
}
fn main() {
assert_eq!(foo(0 + 0, 1 + 1, 2 + 2), [0, 2, 4]);
assert_eq!(foo::<{1 + 1}>(0 + 0, 2 + 2), [0, 2, 4]);
}
```
r? `@oli-obk`
Improve error msgs when found type is deref of expected
This improves help messages in two cases:
- When expected type is `T` and found type is `&T`, we now look through blocks
and suggest dereferencing the expression of the block, rather than the whole
block.
- In the above case, if the expression is an `&`, we not suggest removing the
`&` instead of adding `*`.
Both of these are demonstrated in the regression test. Before this patch the
first error in the test would be:
error[E0308]: `if` and `else` have incompatible types
--> test.rs:8:9
|
5 | / if true {
6 | | a
| | - expected because of this
7 | | } else {
8 | | b
| | ^ expected `usize`, found `&usize`
9 | | };
| |_____- `if` and `else` have incompatible types
|
help: consider dereferencing the borrow
|
7 | } else *{
8 | b
9 | };
|
Now:
error[E0308]: `if` and `else` have incompatible types
--> test.rs:8:9
|
5 | / if true {
6 | | a
| | - expected because of this
7 | | } else {
8 | | b
| | ^
| | |
| | expected `usize`, found `&usize`
| | help: consider dereferencing the borrow: `*b`
9 | | };
| |_____- `if` and `else` have incompatible types
The second error:
error[E0308]: `if` and `else` have incompatible types
--> test.rs:14:9
|
11 | / if true {
12 | | 1
| | - expected because of this
13 | | } else {
14 | | &1
| | ^^ expected integer, found `&{integer}`
15 | | };
| |_____- `if` and `else` have incompatible types
|
help: consider dereferencing the borrow
|
13 | } else *{
14 | &1
15 | };
|
now:
error[E0308]: `if` and `else` have incompatible types
--> test.rs:14:9
|
11 | / if true {
12 | | 1
| | - expected because of this
13 | | } else {
14 | | &1
| | ^-
| | ||
| | |help: consider removing the `&`: `1`
| | expected integer, found `&{integer}`
15 | | };
| |_____- `if` and `else` have incompatible types
Fixes#82361
---
r? ````@estebank````