Add support for the x86_64h-apple-darwin target
See https://github.com/rust-lang/compiler-team/issues/599 for MCP.
r? compiler-team
CC `@BlackHoleFox` who recently overhauled the apple target code in `rustc-target`.
## Target Support Checklist
> - A tier 3 target must have a designated developer or developers (the "target
> maintainers") on record to be CCed when issues arise regarding the target.
> (The mechanism to track and CC such developers may evolve over time.)
I'm the designated developer.
> - Targets must use naming consistent with any existing targets; for instance, a
> target for the same CPU or OS as an existing Rust target should use the same
> name for that CPU or OS. Targets should normally use the same names and
> naming conventions as used elsewhere in the broader ecosystem beyond Rust
> (such as in other toolchains), unless they have a very good reason to
> diverge. Changing the name of a target can be highly disruptive, especially
> once the target reaches a higher tier, so getting the name right is important
> even for a tier 3 target.
This uses the same naming conventions used for the other macOS targets (`-apple-darwin`), combined with the convention used by LLVM for the `x86_64h` targets. LLVM's convention matches the architecture name used when invoking various tools such as `lipo`, `arch`, and (IMO) there's not really a compelling reason to depart from it.
> - Target names should not introduce undue confusion or ambiguity unless
> absolutely necessary to maintain ecosystem compatibility. For example, if
> the name of the target makes people extremely likely to form incorrect
> beliefs about what it targets, the name should be changed or augmented to
> disambiguate it.
I don't think this is especially likely, although I suppose someone could mistake it for `x86_64-apple-darwin`.
> - If possible, use only letters, numbers, dashes and underscores for the name.
> Periods (`.`) are known to cause issues in Cargo.
👍
> - Tier 3 targets may have unusual requirements to build or use, but must not
> create legal issues or impose onerous legal terms for the Rust project or for
> Rust developers or users.
> - The target must not introduce license incompatibilities.
It does not.
> - Anything added to the Rust repository must be under the standard Rust
> license (`MIT OR Apache-2.0`).
It is.
> - The target must not cause the Rust tools or libraries built for any other
> host (even when supporting cross-compilation to the target) to depend
> on any new dependency less permissive than the Rust licensing policy. This
> applies whether the dependency is a Rust crate that would require adding
> new license exceptions (as specified by the `tidy` tool in the
> rust-lang/rust repository), or whether the dependency is a native library
> or binary. In other words, the introduction of the target must not cause a
> user installing or running a version of Rust or the Rust tools to be
> subject to any new license requirements.
There are no new dependencies that don't also apply to `x86_64-apple-darwin`.
> - Compiling, linking, and emitting functional binaries, libraries, or other
> code for the target (whether hosted on the target itself or cross-compiling
> from another target) must not depend on proprietary (non-FOSS) libraries.
> Host tools built for the target itself may depend on the ordinary runtime
> libraries supplied by the platform and commonly used by other applications
> built for the target, but those libraries must not be required for code
> generation for the target; cross-compilation to the target must not require
> such libraries at all. For instance, `rustc` built for the target may
> depend on a common proprietary C runtime library or console output library,
> but must not depend on a proprietary code generation library or code
> optimization library. Rust's license permits such combinations, but the
> Rust project has no interest in maintaining such combinations within the
> scope of Rust itself, even at tier 3.
This has the same requirements as the other macOS targets (e.g. `x86_64-apple-darwin` and similar).
> - "onerous" here is an intentionally subjective term. At a minimum, "onerous"
> legal/licensing terms include but are *not* limited to: non-disclosure
> requirements, non-compete requirements, contributor license agreements
> (CLAs) or equivalent, "non-commercial"/"research-only"/etc terms,
> requirements conditional on the employer or employment of any particular
> Rust developers, revocable terms, any requirements that create liability
> for the Rust project or its developers or users, or any requirements that
> adversely affect the livelihood or prospects of the Rust project or its
> developers or users.
No change here.
> - Neither this policy nor any decisions made regarding targets shall create any
> binding agreement or estoppel by any party. If any member of an approving
> Rust team serves as one of the maintainers of a target, or has any legal or
> employment requirement (explicit or implicit) that might affect their
> decisions regarding a target, they must recuse themselves from any approval
> decisions regarding the target's tier status, though they may otherwise
> participate in discussions.
👍
> - This requirement does not prevent part or all of this policy from being
> cited in an explicit contract or work agreement (e.g. to implement or
> maintain support for a target). This requirement exists to ensure that a
> developer or team responsible for reviewing and approving a target does not
> face any legal threats or obligations that would prevent them from freely
> exercising their judgment in such approval, even if such judgment involves
> subjective matters or goes beyond the letter of these requirements.
👍
> - Tier 3 targets should attempt to implement as much of the standard libraries
> as possible and appropriate (`core` for most targets, `alloc` for targets
> that can support dynamic memory allocation, `std` for targets with an
> operating system or equivalent layer of system-provided functionality), but
> may leave some code unimplemented (either unavailable or stubbed out as
> appropriate), whether because the target makes it impossible to implement or
> challenging to implement. The authors of pull requests are not obligated to
> avoid calling any portions of the standard library on the basis of a tier 3
> target not implementing those portions.
The standard library tests seem to pass.
> - The target must provide documentation for the Rust community explaining how
> to build for the target, using cross-compilation if possible. If the target
> supports running binaries, or running tests (even if they do not pass), the
> documentation must explain how to run such binaries or tests for the target,
> using emulation if possible or dedicated hardware if necessary.
Documentation is provided.
> - Tier 3 targets must not impose burden on the authors of pull requests, or
> other developers in the community, to maintain the target. In particular,
> do not post comments (automated or manual) on a PR that derail or suggest a
> block on the PR based on a tier 3 target. Do not send automated messages or
> notifications (via any medium, including via ``@`)` to a PR author or others
> involved with a PR regarding a tier 3 target, unless they have opted into
> such messages.
Noted. This target is nearly identical to `x86_64-apple-darwin`, so this is
unlikely to cause issues anyway.
> - Backlinks such as those generated by the issue/PR tracker when linking to
> an issue or PR are not considered a violation of this policy, within
> reason. However, such messages (even on a separate repository) must not
> generate notifications to anyone involved with a PR who has not requested
> such notifications.
👍
> - Patches adding or updating tier 3 targets must not break any existing tier 2
> or tier 1 target, and must not knowingly break another tier 3 target without
> approval of either the compiler team or the maintainers of the other tier 3
> target.
> - In particular, this may come up when working on closely related targets,
> such as variations of the same architecture with different features. Avoid
> introducing unconditional uses of features that another variation of the
> target may not have; use conditional compilation or runtime detection, as
> appropriate, to let each target run code supported by that target.
👍
fix lint regression in `non_upper_case_globals`
Fixes#110573
The issue also exists for inherent associated types (where I copied my impl from). `EarlyContext` is more involved to fix in this way, so I'll leave it be for now (note it's unstable so that's not urgent).
r? `@compiler-errors`
`deny(unsafe_op_in_unsafe_fn)` in `rustc_data_structures`
r? `@Nilstrieb`
I couldn't bring myself to document the safety in big `unsafe` functions but ehh
Make `impl Debug for Span` not panic on not having session globals.
I hit the panic that this patch avoids while messing with the early lints in `rustc_session::config::build_session_options()`. The rest of that project is not finished, but this seemed like a self-contained improvement.
(Should changes like this add tests? I don't see similar unit tests.)
Add suggestion to use closure argument instead of a capture on borrowck error
Fixes#109271
r? `@compiler-errors`
This should probably be refined a bit, but opening a PR so that I don't forget anything.
Support AIX-style archive type
Reading facility of AIX big archive has been supported by `object` since 0.30.0.
Writing facility of AIX big archive has already been supported by `ar_archive_writer`, but we need to bump the version to support the new archive type enum.
While it might *seem* that this does something, it actually doesn't.
`mut_borrow_of_mutable_ref` returns a `bool` that is ignored by the
let-else. This was basically
```rust
if !self.body.local_decls.get(local).is_some() {
return
}
```
Which is pretty useless
Don't transmute `&List<GenericArg>` <-> `&List<Ty>`
In #93505 we allowed safely transmuting between `&List<GenericArg<'_>>` and `&List<Ty<'_>>`. This was possible because `GenericArg` is a tagged pointer and the tag for types is `0b00`, such that a `GenericArg` with a type inside has the same layout as `Ty`.
While this was meant as an optimization, it doesn't look like it was actually any perf or max-rss win (see https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/94799#issuecomment-1064340003, https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/94841, https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/110496#issuecomment-1513799140).
Additionally the way it was done is quite fragile — `unsafe` code was not properly documented or contained in a module, types were not marked as `repr(C)` (making the transmutes possibly unsound). All of this makes the code maintenance harder and blocks other possible optimizations (as an example I've found out about these `transmutes` when my change caused them to sigsegv compiler).
Thus, I think we can safely (pun intended) remove those transmutes, making maintenance easier, optimizations possible, code less cursed, etc.
r? `@compiler-errors`
Add `rustc_fluent_macro` to decouple fluent from `rustc_macros`
Fluent, with all the icu4x it brings in, takes quite some time to compile. `fluent_messages!` is only needed in further downstream rustc crates, but is blocking more upstream crates like `rustc_index`. By splitting it out, we allow `rustc_macros` to be compiled earlier, which speeds up `x check compiler` by about 5 seconds (and even more after the needless dependency on `serde_json` is removed from `rustc_data_structures`).
Rollup of 7 pull requests
Successful merges:
- #110432 (Report more detailed reason why `Index` impl is not satisfied)
- #110451 (Minor changes to `IndexVec::ensure_contains_elem` & related methods)
- #110476 (Delay a good path bug on drop for `TypeErrCtxt` (instead of a regular delayed bug))
- #110498 (Switch to `EarlyBinder` for `collect_return_position_impl_trait_in_trait_tys`)
- #110507 (boostrap: print output during building tools)
- #110510 (Fix ICE for transmutability in candidate assembly)
- #110513 (make `non_upper_case_globals` lint not report trait impls)
Failed merges:
r? `@ghost`
`@rustbot` modify labels: rollup
make `non_upper_case_globals` lint not report trait impls
We should not lint on trait `impl`s for `non_upper_case_globals`; the user doesn't have control over the name. This brings `non_upper_case_globals` into consistency with other `nonstandard_style` lints.
Switch to `EarlyBinder` for `collect_return_position_impl_trait_in_trait_tys`
Part of the work to finish https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/105779.
This PR adds `EarlyBinder` to the return type of the `collect_return_position_impl_trait_in_trait_tys` query and removes `bound_return_position_impl_trait_in_trait_tys`.
r? `@lcnr`
Delay a good path bug on drop for `TypeErrCtxt` (instead of a regular delayed bug)
r? `@lcnr`
Perhaps we should just delete the `Drop` impl altogether though?
Fixesrust-lang/rust-clippy#10645
`@matthiaskrgr:` I don't know how to make a clippy test for this. Any idea? Clippy's UI tests run with `-D warnings` and I have no idea how to switch it off to make a test that triggers this ICE in the clippy test suite 🤣
Don't allocate on SimplifyCfg/Locals/Const on every MIR pass
Hey! 👋🏾 This is a first PR attempt to see if I could speed up some rustc internals.
Thought process:
```rust
pub struct SimplifyCfg {
label: String,
}
```
in [compiler/src/rustc_mir_transform/simplify.rs](7908a1d654/compiler/rustc_mir_transform/src/simplify.rs (L39)) fires multiple times per MIR analysis. This means that a likely string allocation is happening in each of these runs, which may add up, as they are not being lazily allocated or cached in between the different passes.
...yes, I know that adding a global static array is probably not the future-proof solution, but I wanted to lob this now as a proof of concept to see if it's worth shaving off a few cycles and then making more robust.
Encode hashes as bytes, not varint
In a few places, we store hashes as `u64` or `u128` and then apply `derive(Decodable, Encodable)` to the enclosing struct/enum. It is more efficient to encode hashes directly than try to apply some varint encoding. This PR adds two new types `Hash64` and `Hash128` which are produced by `StableHasher` and replace every use of storing a `u64` or `u128` that represents a hash.
Distribution of the byte lengths of leb128 encodings, from `x build --stage 2` with `incremental = true`
Before:
```
( 1) 373418203 (53.7%, 53.7%): 1
( 2) 196240113 (28.2%, 81.9%): 3
( 3) 108157958 (15.6%, 97.5%): 2
( 4) 17213120 ( 2.5%, 99.9%): 4
( 5) 223614 ( 0.0%,100.0%): 9
( 6) 216262 ( 0.0%,100.0%): 10
( 7) 15447 ( 0.0%,100.0%): 5
( 8) 3633 ( 0.0%,100.0%): 19
( 9) 3030 ( 0.0%,100.0%): 8
( 10) 1167 ( 0.0%,100.0%): 18
( 11) 1032 ( 0.0%,100.0%): 7
( 12) 1003 ( 0.0%,100.0%): 6
( 13) 10 ( 0.0%,100.0%): 16
( 14) 10 ( 0.0%,100.0%): 17
( 15) 5 ( 0.0%,100.0%): 12
( 16) 4 ( 0.0%,100.0%): 14
```
After:
```
( 1) 372939136 (53.7%, 53.7%): 1
( 2) 196240140 (28.3%, 82.0%): 3
( 3) 108014969 (15.6%, 97.5%): 2
( 4) 17192375 ( 2.5%,100.0%): 4
( 5) 435 ( 0.0%,100.0%): 5
( 6) 83 ( 0.0%,100.0%): 18
( 7) 79 ( 0.0%,100.0%): 10
( 8) 50 ( 0.0%,100.0%): 9
( 9) 6 ( 0.0%,100.0%): 19
```
The remaining 9 or 10 and 18 or 19 are `u64` and `u128` respectively that have the high bits set. As far as I can tell these are coming primarily from `SwitchTargets`.
rustc_metadata: Remove `Span` from `ModChild`
It can be decoded on demand from regular `def_span` tables.
Partially mitigates perf regressions from https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/109500.
Fluent, with all the icu4x it brings in, takes quite some time to
compile. `fluent_messages!` is only needed in further downstream rustc
crates, but is blocking more upstream crates like `rustc_index`. By
splitting it out, we allow `rustc_macros` to be compiled earlier, which
speeds up `x check compiler` by about 5 seconds (and even more after the
needless dependency on `serde_json` is removed from
`rustc_data_structures`).
Spelling compiler
This is per https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/110392#issuecomment-1510193656
I'm going to delay performing a squash because I really don't expect people to be perfectly happy w/ my changes, I really am a human and I really do make mistakes.
r? Nilstrieb
I'm going to be flying this evening, but I should be able to squash / respond to reviews w/in a day or two.
I tried to be careful about dropping changes to `tests`, afaict only two files had changes that were likely related to the changes for a given commit (this is where not having eagerly squashed should have given me an advantage), but, that said, picking things apart can be error prone.
Rollup of 7 pull requests
Successful merges:
- #109981 (Set commit information environment variables when building tools)
- #110348 (Add list of supported disambiguators and suffixes for intra-doc links in the rustdoc book)
- #110409 (Don't use `serde_json` to serialize a simple JSON object)
- #110442 (Avoid including dry run steps in the build metrics)
- #110450 (rustdoc: Fix invalid handling of nested items with `--document-private-items`)
- #110461 (Use `Item::expect_*` and `ImplItem::expect_*` more)
- #110465 (Assure everyone that `has_type_flags` is fast)
Failed merges:
r? `@ghost`
`@rustbot` modify labels: rollup
Don't use `serde_json` to serialize a simple JSON object
This avoids `rustc_data_structures` depending on `serde_json` which allows it to be compiled much earlier, unlocking most of rustc.
This used to not matter, but after #110407 we're not blocked on fluent anymore, which means that it's now a blocking edge.
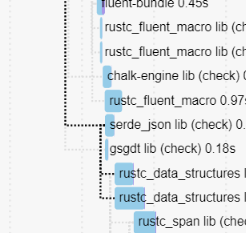
This saves a few more seconds.
cc ````@Zoxc```` who added it recently
Implement StableHasher::write_u128 via write_u64
In https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/110367#issuecomment-1510114777 the cachegrind diffs indicate that nearly all the regression is from this:
```
22,892,558 ???:<rustc_data_structures::sip128::SipHasher128>::slice_write_process_buffer
-9,502,262 ???:<rustc_data_structures::sip128::SipHasher128>::short_write_process_buffer::<8>
```
Which happens because the diff for that perf run swaps a `Hash::hash` of a `u64` to a `u128`. But `slice_write_process_buffer` is a `#[cold]` function, and is for handling hashes of arbitrary-length byte arrays.
Using the much more optimizer-friendly `u64` path twice to hash a `u128` provides a nice perf boost in some benchmarks.
Tagged pointers, now with strict provenance!
This is a big refactor of tagged pointers in rustc, with three main goals:
1. Porting the code to the strict provenance
2. Cleanup the code
3. Document the code (and safety invariants) better
This PR has grown quite a bit (almost a complete rewrite at this point...), so I'm not sure what's the best way to review this, but reviewing commit-by-commit should be fine.
r? `@Nilstrieb`
Bypass the varint path when encoding InitMask
The data in a `InitMask` is stored as `u64` but it is a large bitmask (not numbers) so varint encoding doesn't make sense.
Check freeze with right param-env in `deduced_param_attrs`
We're checking if a trait (`Freeze`) holds in a polymorphic function, but not using that function's own (reveal-all) param-env. This causes us to try to eagerly normalize a specializable projection type that has no default value, which causes an ICE.
Fixes#110171
Various minor Idx-related tweaks
Nothing particularly exciting here, but a couple of things I noticed as I was looking for more index conversions to simplify.
cc https://github.com/rust-lang/compiler-team/issues/606
r? `@WaffleLapkin`
Remove some suspicious cast truncations
These truncations were added a long time ago, and as best I can tell without a perf justification. And with rust-lang/rust#110410 it has become perf-neutral to not truncate anymore. We worked hard for all these bits, let's use them.
Rollup of 7 pull requests
Successful merges:
- #110038 (Erase regions when confirming transmutability candidate)
- #110341 (rustdoc: stop passing a title to `replaceState` second argument)
- #110388 (Add a message for if an overflow occurs in `core::intrinsics::is_nonoverlapping`.)
- #110404 (fix clippy::toplevel_ref_arg and ::manual_map)
- #110421 (Spelling librustdoc)
- #110423 (Spelling srcdoc)
- #110433 (Windows: map a few more error codes to ErrorKind)
Failed merges:
r? `@ghost`
`@rustbot` modify labels: rollup
Alloc `hir::Lit` in an arena to remove the destructor from `Expr`
This allows allocating `Expr`s into a dropless arena, which is useful for using length prefixed thing slices in HIR, since these can only be allocated in the dropless arena and not in a typed arena.
Permit MIR inlining without #[inline]
I noticed that there are at least a handful of portable-simd functions that have no `#[inline]` but compile to an assign + return.
I locally benchmarked inlining thresholds between 0 and 50 in increments of 5, and 50 seems to be the best. Interesting. That didn't include check builds though, ~maybe perf will have something to say about that~.
Perf has little useful to say about this. We generally regress all the check builds, as best as I can tell, due to a number of small codegen changes in a particular hot function in the compiler. Probably this is because we've nudged the inlining outcomes all over, and uses of `#[inline(always)]`/`#[inline(never)]` might need to be adjusted.
This allows allocating `Expr`s into a dropless arena, which is useful
for using length prefixed thing slices in HIR, since these can only be
allocated in the dropless arena and not in a typed arena. This is
something I'm working on.
Remove the loop in `Align::from_bytes`
Perf is almost certainly irrelevant, but might as well simplify it, since `trailing_zeros` does exactly what's needed.
Remove `TypeSuper{Foldable,Visitable}` impls for `Region`.
These traits exist so that folders/visitors can recurse into types of interest: binders, types, regions, predicates, and consts. But `Region` is non-recursive and cannot contain other types of interest, so its methods in these traits are trivial.
This commit inlines and removes those trivial methods.
r? `@compiler-errors`
Remove `remap_env_constness` in queries
This removes some of the complexities with const traits. #88119 used to be caused by this but was fixed by `param_env = param_env.without_const()`.
This allows us to get rid of the `rustc_const_eval->rustc_borrowck`
dependency edge which was delaying the compilation of borrowck.
The added utils in `rustc_middle` are small and should not affect
compile times there.
Don't `use rustc_hir as ast`(!)
It makes for confusing code.
This was introduced in a large commit in #67886 that rearranged a lot of `use` statements. I suspect it was an accident.
I suspect this macro was around before `TypeFoldable`/`TypeVisitable`
were derivable. But now it's only used for two types, `Result` and
`Option`. Removing the macro and implementing the traits for those types
by hand makes the code much simpler.
suggest lifetime for closure parameter type when mismatch
This is a draft PR, will add test cases later and be ready for review.
This PR fixes https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/105675 by adding a diagnostics suggestion. Also a partial fix to https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/105528.
The following code will have a compile error now:
```
fn const_if_unit(input: bool) -> impl for<'a> FnOnce(&'a ()) -> usize {
let x = |_| 1;
x
}
```
Before this PR:
```
error[E0308]: mismatched types
--> src/lib.rs:3:5
|
3 | x
| ^ one type is more general than the other
|
= note: expected trait `for<'a> FnOnce<(&'a (),)>`
found trait `FnOnce<(&(),)>`
note: this closure does not fulfill the lifetime requirements
--> src/lib.rs:2:13
|
2 | let x = |_| 1;
| ^^^
error: implementation of `FnOnce` is not general enough
--> src/lib.rs:3:5
|
3 | x
| ^ implementation of `FnOnce` is not general enough
|
= note: closure with signature `fn(&'2 ()) -> usize` must implement `FnOnce<(&'1 (),)>`, for any lifetime `'1`...
= note: ...but it actually implements `FnOnce<(&'2 (),)>`, for some specific lifetime `'2`
For more information about this error, try `rustc --explain E0308`.
error: could not compile `rust-test` due to 2 previous errors
```
After this PR:
```
error[E0308]: mismatched types
--> src/lib.rs:3:5
|
3 | x
| ^ one type is more general than the other
|
= note: expected trait `for<'a> FnOnce<(&'a (),)>`
found trait `FnOnce<(&(),)>`
note: this closure does not fulfill the lifetime requirements
--> src/lib.rs:2:13
|
2 | let x = |_| 1;
| ^^^
help: consider changing the type of the closure parameters
|
2 | let x = |_: &_| 1;
| ~~~~~~~
error: implementation of `FnOnce` is not general enough
--> src/lib.rs:3:5
|
3 | x
| ^ implementation of `FnOnce` is not general enough
|
= note: closure with signature `fn(&'2 ()) -> usize` must implement `FnOnce<(&'1 (),)>`, for any lifetime `'1`...
= note: ...but it actually implements `FnOnce<(&'2 (),)>`, for some specific lifetime `'2`
For more information about this error, try `rustc --explain E0308`.
error: could not compile `rust-test` due to 2 previous errors
```
After applying the suggestion, it compiles. The suggestion might not always be correct as the generation procedure of that suggestion is quite simple...
These traits exist so that folders/visitors can recurse into types of
interest: binders, types, regions, predicates, and consts. But `Region`
is non-recursive and cannot contain other types of interest, so its
methods in these traits are trivial.
This commit inlines and removes those trivial methods.
explicit `adt_dtorck_constraint` for `ManuallyDrop`
the only reason we didn't add outlives requirements when dropping `ManuallyDrop` was a fast-path in `trivial_dropck_outlives`. Explicitly acknowledge that fast-path in `adt_dtorck_constraint`
Do not attempt to commute comparison and cast to codegen discriminants
The general algorithm to compute a discriminant is:
```
relative_tag = tag - niche_start
is_niche = relative_tag <= (ule) relative_max
discr = if is_niche {
cast(relative_tag) + niche_variants.start()
} else {
untagged_variant
}
```
We have an optimization branch which attempts to merge the addition and the subtraction by commuting them with the cast. We currently get this optimization wrong.
This PR takes the easiest and safest way: remove the optimization, and let LLVM handle it. (Perf may not agree with that course of action 😅)
There may be a less invasive solution, but I don't have the necessary knowledge of LLVM semantics to find it. Cranelift has the same optimization, which should be handled similarly.
cc `@nikic` and `@bjorn3` if you have a better solution.
Fixes https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/110128
Reformulate `point_at_expr_source_of_inferred_type` to be more accurate
Be more accurate when deducing where along the several usages of a binding it is constrained to be some type that is incompatible with an expectation.
This also renames the method to `note_source_of_type_mismatch_constraint` because I prefer that name, though I guess I can revert that. (Also drive-by rename `note_result_coercion` -> `suggest_coercing_result_via_try_operator`, because it's suggesting, not noting!)
This PR is (probably?) best reviewed per commit, but it does regress a bit only to fix it later on, so it could also be reviewed as a whole if that makes the final results more clear.
r? `@estebank`
Add a stable MIR way to get the main function
This is useful for analysis tools that only analyze the code paths that a specific program actually goes through. Or for code generators built on top of stable MIR.
Switch to `EarlyBinder` for `impl_subject` query
Part of the work to finish https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/105779.
Several queries `X` have a `bound_X` variant that wraps the output in `EarlyBinder`. This adds `EarlyBinder` to the return type of the `impl_subject` query and removes `bound_impl_subject`.
r? ```@lcnr```
Remove all but one of the spans in `BoundRegionKind::BrAnon`
There are only three places where `BoundRegionKind::BrAnon` uses `Some(span)` instead of `None`. Two of them are easy to remove, which this PR does.
r? ```@jackh726```
don't uniquify regions when canonicalizing
uniquifying causes a bunch of issues, most notably it causes `AliasEq(<?x as Trait<'a>>::Assoc, <?x as Trait<'a>>::Assoc)` to result in ambiguity because both `normalizes-to` paths result in ambiguity and substs equate should trivially succeed but doesn't because we uniquified `'a` to two different regions.
I originally added uniquification to make it easier to deal with requirement 6 from the dev-guide: https://rustc-dev-guide.rust-lang.org/solve/trait-solving.html#requirements
> ### 6. Trait solving must be (free) lifetime agnostic
>
> Trait solving during codegen should have the same result as during typeck. As we erase
> all free regions during codegen we must not rely on them during typeck. A noteworthy example
> is special behavior for `'static`.
cc https://github.com/rust-lang/rustc-dev-guide/pull/1671
Relying on regions being identical may cause ICE during MIR typeck, but even without this PR we can end up relying on that as type inference vars can resolve to types which contain an identical region. Let's land this and deal with any ICE that crop up as we go. Will look at this issue again before stabilization.
r? ```@compiler-errors```
Improve safe transmute error reporting
This patch updates the error reporting when Safe Transmute is not possible between 2 types by including the reason.
Also, fix some small bugs that occur when computing the `Answer` for transmutability.
resolve: Pre-compute non-reexport module children
Instead of repeating the same logic by walking HIR during metadata encoding.
The only difference is that we are no longer encoding `macro_rules` items, but we never currently need them as a part of this list. They can be encoded separately if this need ever arises.
`module_reexports` is also un-querified, because I don't see any reasons to make it a query, only overhead.
This patch updates the error reporting when Safe Transmute is not
possible between 2 types by including the reason.
Also, fix some small bugs that occur when computing the `Answer` for
transmutability.
Check for body owner fallibly in error reporting
Sometimes the "body id" we use for an obligation cause is not actually a body owner, like when we're doing WF checking on items.
Fixes#110157
Add inline assembly support for m68k
I believe this should be correct, to the extent I understand the logic around inline assembly. M68k is fairly straightforward here, other than having separate address registers.
cleanup our region error API
- require `TypeErrCtxt` to always result in an error, closing #108810
- move `resolve_regions_and_report_errors` to the `ObligationCtxt`
- call `process_registered_region_obligations` in `resolve_regions`
- move `resolve_regions` into the `outlives` submodule
- add `#[must_use]` to functions returning lists of errors
r? types
Erase lifetimes above `ty::INNERMOST` when probing ambiguous types
Turns out that `TyCtxt::replace_escaping_bound_vars_uncached` only erases bound vars exactly at `ty::INNERMOST`, and not everything above. This regresses the suggestions for non-lifetime binders, but oh well, I don't really care about those.
Fixes#110052
I'm surprised the compiler doesn't warn about these. It appears having
an `impl` on a struct is enough to avoid a warning about it never being
constructed.
Preserve argument indexes when inlining MIR
We store argument indexes on VarDebugInfo. Unlike the previous method of relying on the variable index to know whether a variable is an argument, this survives MIR inlining.
We also no longer check if var.source_info.scope is the outermost scope. When a function gets inlined, the arguments to the inner function will no longer be in the outermost scope. What we care about though is whether they were in the outermost scope prior to inlining, which we know by whether we assigned an argument index.
Fixes#83217
I considered using `Option<NonZeroU16>` instead of `Option<u16>` to store the index. I didn't because `TypeFoldable` isn't implemented for `NonZeroU16` and because it looks like due to padding, it currently wouldn't make any difference. But I indexed from 1 anyway because (a) it'll make it easier if later it becomes worthwhile to use a `NonZeroU16` and because the arguments were previously indexed from 1, so it made for a smaller change.
This is my first PR on rust-lang/rust, so apologies if I've gotten anything not quite right.
Do not use ImplDerivedObligationCause for inherent impl method error reporting
We were constructing a `TraitRef` out of impl substs, for an *inherent* impl that has no corresponding trait. Instead of doing that, let's construct a meaningful obligation cause code, and instead adjust the error reporting machinery to handle that correctly.
Fixes#110131
cc #106702, which introduced this regression