Fix incorrect panic message in example
The panic message when calling the `connect()` should probably be a message about connection failure, not a message about binding address failure.
Document valid values of the char type
As discussed at #93392, the current documentation on what constitutes a valid char isn't very detailed and is partly on the MAX constant rather than the type itself.
This PR expands on that information, stating the actual numerical range, giving examples of what won't work, and also mentions how a `char` might be a valid USV but still not be a defined character (terminology checked against [Unicode 14.0, table 2-3](https://www.unicode.org/versions/Unicode14.0.0/ch02.pdf#M9.61673.TableTitle.Table.22.Types.of.Code.Points)).
Change Termination::report return type to ExitCode
Related to https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/43301
The goal of this change is to minimize the forward compatibility risks in stabilizing Termination. By using the opaque type `ExitCode` instead of an `i32` we leave room for us to evolve the API over time to provide what cross-platform consistency we can / minimize footguns when working with exit codes, where as stabilizing on `i32` would limit what changes we could make in the future in how we represent and construct exit codes.
kmc-solid: Increase the default stack size
This PR increases the default minimum stack size on the [`*-kmc-solid_*`](https://doc.rust-lang.org/nightly/rustc/platform-support/kmc-solid.html) Tier 3 targets to 64KiB (Arm) and 128KiB (AArch64).
This value was chosen as a middle ground between supporting a relatively complex program (e.g., an application using a full-fledged off-the-shelf web server framework) with no additional configuration and minimizing resource consumption for the embedded platform that doesn't support lazily-allocated pages nor over-commitment (i.e., wasted stack spaces are wasted physical memory). If the need arises, the users can always set the `RUST_MIN_STACK` environmental variable to override the default stack size or use the platform API directly.
kmc-solid: Inherit the calling task's base priority in `Thread::new`
This PR fixes the initial priority calculation of spawned threads on the [`*-kmc-solid_*`](https://doc.rust-lang.org/nightly/rustc/platform-support/kmc-solid.html) Tier 3 targets.
Fixes a spawned task (an RTOS object on top of which threads are implemented for this target; unrelated to async tasks) getting an unexpectedly higher priority if it's spawned by a task whose priority is temporarily boosted by a priority-protection mutex.
unix: Use metadata for `DirEntry::file_type` fallback
When `DirEntry::file_type` fails to match a known `d_type`, we should
fall back to `DirEntry::metadata` instead of a bare `lstat`, because
this is faster and more reliable on targets with `fstatat`.
Fixes a spawned task getting an unexpectedly higher priority if it's
spawned by a task whose priority is temporarily boosted by a priority-
protection mutex.
When `DirEntry::file_type` fails to match a known `d_type`, we should
fall back to `DirEntry::metadata` instead of a bare `lstat`, because
this is faster and more reliable on targets with `fstatat`.
fs: Don't copy d_name from struct dirent
The dirent returned from readdir() is only guaranteed to be valid for
d_reclen bytes on common platforms. Since we copy the name separately
anyway, we can copy everything except d_name into DirEntry::entry.
Fixes#93384.
Move unstable is_{arch}_feature_detected! macros to std::arch
These macros are unstable, except for `is_x86_feature_detected` which is still exported from the crate root for backwards-compatibility.
This should unblock the stabilization of `is_aarch64_feature_detected`.
r? ```@m-ou-se```
The dirent returned from readdir() is only guaranteed to be valid for
d_reclen bytes on common platforms. Since we copy the name separately
anyway, we can copy everything except d_name into DirEntry::entry.
Fixes#93384.
kmc-solid: Implement `net::FileDesc::duplicate`
This PR implements `std::sys::solid::net::FileDesc::duplicate`, which was accidentally left out when this target was added by #86191.
Bump libc and fix remove_dir_all on Fuchsia after CVE fix
With the previous `is_dir` impl, we would attempt to unlink
a directory in the None branch, but Fuchsia supports returning
ENOTEMPTY from unlinkat() without the AT_REMOVEDIR flag because
we don't currently differentiate unlinking files and directories
by default.
On the Fuchsia side I've opened https://fxbug.dev/92273 to discuss
whether this is the correct behavior, but it doesn't seem like
addressing the error code is necessary to make our tests happy.
Depends on https://github.com/rust-lang/libc/pull/2654 since we
apparently haven't needed to reference DT_UNKNOWN before this.
With the previous `is_dir` impl, we would attempt to unlink
a directory in the None branch, but Fuchsia supports returning
ENOTEMPTY from unlinkat() without the AT_REMOVEDIR flag because
we don't currently differentiate unlinking files and directories
by default.
On the Fuchsia side I've opened https://fxbug.dev/92273 to discuss
whether this is the correct behavior, but it doesn't seem like
addressing the error code is necessary to make our tests happy.
Updates std's libc crate to include DT_UNKNOWN for Fuchsia.
Avoid double panics when using `TempDir` in tests
`TempDir` could panic on drop if `remove_dir_all` returns an error. If this happens while already panicking, the test process would abort and therefore not show the test results.
This PR tries to avoid such double panics.
Add os::unix::net::SocketAddr::from_path
Creates a new SocketAddr from a path, supports both regular paths and
abstract namespaces.
Note that `SocketAddr::from_abstract_namespace` could be removed after this as `SocketAddr::unix` also supports abstract namespaces.
Updates #65275
Unblocks https://github.com/tokio-rs/mio/issues/1527
r? `@m-ou-se`
With the addition of `sock_accept()` to snapshot1, simple networking via
a passed `TcpListener` is possible. This patch implements the basics to
make a simple server work.
Signed-off-by: Harald Hoyer <harald@profian.com>
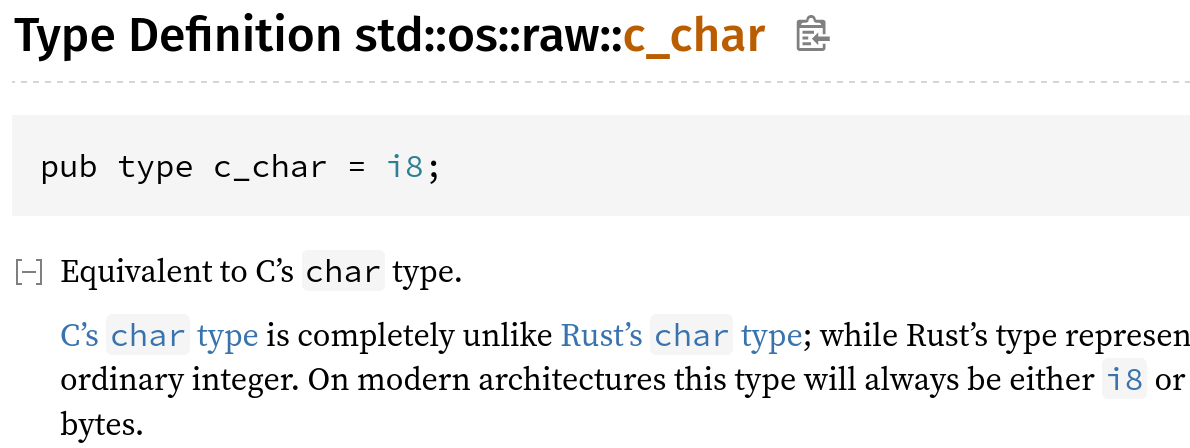
Define c_char using cfg_if rather than repeating 40-line cfg
Libstd has a 40-line cfg that defines the targets on which `c_char` is unsigned, and then repeats the same cfg with `not(…)` for the targets on which `c_char` is signed.
This PR replaces it with a `cfg_if!` in which an `else` takes care of the signed case.
I confirmed that `x.py doc library/std` inlines the type alias because c_char_definition is not a publicly accessible path:
Make available the remaining float intrinsics that require runtime support
from a platform's libm, and thus cannot be included in a no-deps libcore,
by exposing them through a sealed trait, `std::simd::StdFloat`.
We might use the trait approach a bit more in the future, or maybe not.
Ideally, this trait doesn't stick around, even if so.
If we don't need to intermesh it with std, it can be used as a crate,
but currently that is somewhat uncertain.
The creation of libc::sockaddr_un is a safe operation, no need for it to
be unsafe.
This also uses the more performant copy_nonoverlapping instead of an
iterator.
Add a `try_clone()` function to `OwnedFd`.
As suggested in #88564. This adds a `try_clone()` to `OwnedFd` by
refactoring the code out of the existing `File`/`Socket` code.
r? ``@joshtriplett``
Fix STD compilation for the ESP-IDF target (regression from CVE-2022-21658)
Commit 54e22eb7db broke the compilation of STD for the ESP-IDF embedded "unix-like" Tier 3 target, because the fix for [CVE-2022-21658](https://blog.rust-lang.org/2022/01/20/Rust-1.58.1.html) uses [libc flags](https://github.com/esp-rs/esp-idf-svc/runs/4892221554?check_suite_focus=true) which are not supported on the ESP-IDF platform.
This PR simply redirects the ESP-IDF compilation to the "classic" implementation, similar to REDOX. This should be safe because:
* Neither of the two filesystems supported by ESP-IDF (spiffs and fatfs) support [symlinks](https://github.com/natevw/fatfs/blob/master/README.md) in the first place
* There is no notion of fs permissions at all, as the ESP-IDF is an embedded platform that does not have the notion of users, groups, etc.
* Similarly, ESP-IDF has just one "process" - the firmware itself - which contains the user code and the "OS" fused together and running with all permissions
Print a helpful message if unwinding aborts when it reaches a nounwind function
This is implemented by routing `TerminatorKind::Abort` back through the panic handler, but with a special flag in the `PanicInfo` which indicates that the panic handler should *not* attempt to unwind the stack and should instead abort immediately.
This is useful for the planned change in https://github.com/rust-lang/lang-team/issues/97 which would make `Drop` impls `nounwind` by default.
### Code
```rust
#![feature(c_unwind)]
fn panic() {
panic!()
}
extern "C" fn nounwind() {
panic();
}
fn main() {
nounwind();
}
```
### Before
```
$ ./test
thread 'main' panicked at 'explicit panic', test.rs:4:5
note: run with `RUST_BACKTRACE=1` environment variable to display a backtrace
Illegal instruction (core dumped)
```
### After
```
$ ./test
thread 'main' panicked at 'explicit panic', test.rs:4:5
note: run with `RUST_BACKTRACE=1` environment variable to display a backtrace
thread 'main' panicked at 'panic in a function that cannot unwind', test.rs:7:1
stack backtrace:
0: 0x556f8f86ec9b - <std::sys_common::backtrace::_print::DisplayBacktrace as core::fmt::Display>::fmt::hdccefe11a6ac4396
1: 0x556f8f88ac6c - core::fmt::write::he152b28c41466ebb
2: 0x556f8f85d6e2 - std::io::Write::write_fmt::h0c261480ab86f3d3
3: 0x556f8f8654fa - std::panicking::default_hook::{{closure}}::h5d7346f3ff7f6c1b
4: 0x556f8f86512b - std::panicking::default_hook::hd85803a1376cac7f
5: 0x556f8f865a91 - std::panicking::rust_panic_with_hook::h4dc1c5a3036257ac
6: 0x556f8f86f079 - std::panicking::begin_panic_handler::{{closure}}::hdda1d83c7a9d34d2
7: 0x556f8f86edc4 - std::sys_common::backtrace::__rust_end_short_backtrace::h5b70ed0cce71e95f
8: 0x556f8f865592 - rust_begin_unwind
9: 0x556f8f85a764 - core::panicking::panic_no_unwind::h2606ab3d78c87899
10: 0x556f8f85b910 - test::nounwind::hade6c7ee65050347
11: 0x556f8f85b936 - test::main::hdc6e02cb36343525
12: 0x556f8f85b7e3 - core::ops::function::FnOnce::call_once::h4d02663acfc7597f
13: 0x556f8f85b739 - std::sys_common::backtrace::__rust_begin_short_backtrace::h071d40135adb0101
14: 0x556f8f85c149 - std::rt::lang_start::{{closure}}::h70dbfbf38b685e93
15: 0x556f8f85c791 - std::rt::lang_start_internal::h798f1c0268d525aa
16: 0x556f8f85c131 - std::rt::lang_start::h476a7ee0a0bb663f
17: 0x556f8f85b963 - main
18: 0x7f64c0822b25 - __libc_start_main
19: 0x556f8f85ae8e - _start
20: 0x0 - <unknown>
thread panicked while panicking. aborting.
Aborted (core dumped)
```
delete `Stdin::split` forwarder
Part of #87096. Delete the `Stdin::split` forwarder because it's seen as too niche to expose at this level.
`@rustbot` label T-libs-api A-io
Improve `Arc` and `Rc` documentation
This makes two changes (I can split the PR if necessary, but the changes are pretty small):
1. A bunch of trait implementations claimed to be zero cost; however, they use the `Arc<T>: From<Box<T>>` impl which is definitely not free, especially for large dynamically sized `T`.
2. The code in deferred initialization examples unnecessarily used excessive amounts of `unsafe`. This has been reduced.
readdir() is preferred over readdir_r() on Linux and many other
platforms because it more gracefully supports long file names. Both
glibc and musl (and presumably all other Linux libc implementations)
guarantee that readdir() is thread-safe as long as a single DIR* is not
accessed concurrently, which is enough to make a readdir()-based
implementation of ReadDir safe. This implementation is already used for
some other OSes including Fuchsia, Redox, and Solaris.
See #40021 for more details. Fixes#86649. Fixes#34668.
Help optimize out backtraces when disabled
The comment in `rust_backtrace_env` says:
> // If the `backtrace` feature of this crate isn't enabled quickly return
> // `None` so this can be constant propagated all over the place to turn
> // optimize away callers.
but this optimization has regressed, because the only caller of this function had an alternative path that unconditionally (and pointlessly) asked for a full backtrace, so the disabled state couldn't propagate.
I've added a getter for the full format that respects the feature flag, so that the caller will now be able to really optimize out the disabled backtrace path. I've also made `rust_backtrace_env` trivially inlineable when backtraces are disabled.
Little improves in CString `new` when creating from slice
Old code already contain optimization for cases with `&str` and `&[u8]` args. This commit adds a specialization for `&mut[u8]` too.
Also, I added usage of old slice in search for zero bytes instead of new buffer because it produce better code for constant inputs on Windows LTO builds. For other platforms, this wouldn't cause any difference because it calls `libc` anyway.
Inlined `_new` method into spec trait to reduce amount of code generated to `CString::new` callers.
Remove deprecated LLVM-style inline assembly
The `llvm_asm!` was deprecated back in #87590 1.56.0, with intention to remove
it once `asm!` was stabilized, which already happened in #91728 1.59.0. Now it
is time to remove `llvm_asm!` to avoid continued maintenance cost.
Closes#70173.
Closes#92794.
Closes#87612.
Closes#82065.
cc `@rust-lang/wg-inline-asm`
r? `@Amanieu`
Add diagnostic items for macros
For use in Clippy, it adds diagnostic items to all the stable public macros
Clippy has lints that look for almost all of these (currently by name or path), but there are a few that aren't currently part of any lint, I could remove those if it's preferred to add them as needed rather than ahead of time
Implement `panic::update_hook`
Add a new function `panic::update_hook` to allow creating panic hooks that forward the call to the previously set panic hook, without race conditions. It works by taking a closure that transforms the old panic hook into a new one, while ensuring that during the execution of the closure no other thread can modify the panic hook. This is a small function so I hope it can be discussed here without a formal RFC, however if you prefer I can write one.
Consider the following example:
```rust
let prev = panic::take_hook();
panic::set_hook(Box::new(move |info| {
println!("panic handler A");
prev(info);
}));
```
This is a common pattern in libraries that need to do something in case of panic: log panic to a file, record code coverage, send panic message to a monitoring service, print custom message with link to github to open a new issue, etc. However it is impossible to avoid race conditions with the current API, because two threads can execute in this order:
* Thread A calls `panic::take_hook()`
* Thread B calls `panic::take_hook()`
* Thread A calls `panic::set_hook()`
* Thread B calls `panic::set_hook()`
And the result is that the original panic hook has been lost, as well as the panic hook set by thread A. The resulting panic hook will be the one set by thread B, which forwards to the default panic hook. This is not considered a big issue because the panic handler setup is usually run during initialization code, probably before spawning any other threads.
Using the new `panic::update_hook` function, this race condition is impossible, and the result will be either `A, B, original` or `B, A, original`.
```rust
panic::update_hook(|prev| {
Box::new(move |info| {
println!("panic handler A");
prev(info);
})
});
```
I found one real world use case here: 988cf403e7/src/detection.rs (L32) the workaround is to detect the race condition and panic in that case.
The pattern of `take_hook` + `set_hook` is very common, you can see some examples in this pull request, so I think it's natural to have a function that combines them both. Also using `update_hook` instead of `take_hook` + `set_hook` reduces the number of calls to `HOOK_LOCK.write()` from 2 to 1, but I don't expect this to make any difference in performance.
### Unresolved questions:
* `panic::update_hook` takes a closure, if that closure panics the error message is "panicked while processing panic" which is not nice. This is a consequence of holding the `HOOK_LOCK` while executing the closure. Could be avoided using `catch_unwind`?
* Reimplement `panic::set_hook` as `panic::update_hook(|_prev| hook)`?
Remove `&mut` from `io::read_to_string` signature
``@m-ou-se`` [realized][1] that because `Read` is implemented for `&mut impl
Read`, there's no need to take `&mut` in `io::read_to_string`.
Removing the `&mut` from the signature allows users to remove the `&mut`
from their calls (and thus pass an owned reader) if they don't use the
reader later.
r? `@m-ou-se`
[1]: https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/80218#issuecomment-874322129
Inline std::os::unix::ffi::OsStringExt methods
Those methods essentially do nothing at assembly level. On Unix systems, `OsString` is represented as a `Vec` without performing any transformations.
Partially stabilize `maybe_uninit_extra`
This covers:
```rust
impl<T> MaybeUninit<T> {
pub unsafe fn assume_init_read(&self) -> T { ... }
pub unsafe fn assume_init_drop(&mut self) { ... }
}
```
It does not cover the const-ness of `write` under `const_maybe_uninit_write` nor the const-ness of `assume_init_read` (this commit adds `const_maybe_uninit_assume_init_read` for that).
FCP: https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/63567#issuecomment-958590287.
Signed-off-by: Miguel Ojeda <ojeda@kernel.org>
`@m-ou-se` [realized][1] that because `Read` is implemented for `&mut impl
Read`, there's no need to take `&mut` in `io::read_to_string`.
Removing the `&mut` from the signature allows users to remove the `&mut`
from their calls (and thus pass an owned reader) if they don't use the
reader later.
[1]: https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/80218#issuecomment-874322129
Add `std::error::Report` type
This is a continuation of https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/90174, split into a separate PR since I cannot push to ```````@seanchen1991``````` 's fork