By splitting the `FnSig` within `TyKind::FnPtr` into `FnSigTys` and
`FnHeader`, which can be packed more efficiently. This reduces the size
of the hot `TyKind` type from 32 bytes to 24 bytes on 64-bit platforms.
This reduces peak memory usage by a few percent on some benchmarks. It
also reduces cache misses and page faults similarly, though this doesn't
translate to clear cycles or wall-time improvements on CI.
Peel off explicit (or implicit) deref before suggesting clone on move error in borrowck, remove some hacks
Also remove a heck of a lot of weird hacks in `suggest_cloning` that I don't think we should have around.
I know this regresses tests, but I don't believe most of these suggestions were accurate, b/c:
1. They either produced type errors (e.g. turning `&x` into `x.clone()`)
2. They don't fix the issue
3. They fix the issue ostensibly, but introduce logic errors (e.g. cloning a `&mut Option<T>` to then `Option::take` out...)
Most of the suggestions are still wrong, but they're not particularly *less* wrong IMO.
Stacked on top of #128241, which is an "obviously worth landing" subset of this PR.
r? estebank
Remove logic to suggest clone of function output
I can't exactly tell, but I believe that this suggestion is operating off of a heuristic that the lifetime of a function's input is correlated with the lifetime of a function's output in such a way that cloning would fix an error. I don't think that actually manages to hit the bar of "actually provides useful suggestions" most of the time.
Specifically, I've hit false-positives due to this suggestion *twice* when fixing ICEs in the compiler, so I don't think it's worthwhile having this logic around. Neither of the two affected UI tests are actually fixed by the suggestion.
Reword E0626 to mention static coroutine, add structured suggestion for adding `static`
Not certain how to make the example feel less artificial. 🤷
My main point though is that we should probably emphasize that the first solution to making a coroutine allow a borrow across an await is making it `static`.
Also adds a structured suggestion.
Invert infer `error_reporting` mod struture
Parallel change to #127493, which moves `rustc_infer::infer::error_reporting` to `rustc_infer::error_reporting::infer`. After this, we should just be able to merge this into `rustc_trait_selection::error_reporting::infer`, and pull down `TypeErrCtxt` into that crate. 👍
r? lcnr
Suggest borrowing on fn argument that is `impl AsRef`
When encountering a move conflict, on an expression that is `!Copy` passed as an argument to an `fn` that is `impl AsRef`, suggest borrowing the expression.
```
error[E0382]: use of moved value: `bar`
--> f204.rs:14:15
|
12 | let bar = Bar;
| --- move occurs because `bar` has type `Bar`, which does not implement the `Copy` trait
13 | foo(bar);
| --- value moved here
14 | let baa = bar;
| ^^^ value used here after move
|
help: borrow the value to avoid moving it
|
13 | foo(&bar);
| +
```
Fix#41708
Consolidate region error reporting in `rustc_infer`
More work on https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/127492. Separate but important step, since I'm gonna likely pull everything else here into another module.
I don't think I'm confident whether `nice_region_error` should be a submodule of the new `rustc_infer::infer::error_reporting::region` module, so I left it alone for now.
r? lcnr
Make casts of pointers to trait objects stricter
This is an attempt to `fix` https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/120222 and https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/120217.
This is done by adding restrictions on casting pointers to trait objects.
Before this PR the rules were as follows:
> When casting `*const X<dyn A>` -> `*const Y<dyn B>`, principal traits in `A` and `B` must refer to the same trait definition (or no trait).
With this PR the rules are changed to
> When casting `*const X<dyn Src>` -> `*const Y<dyn Dst>`
> - if `Dst` has a principal trait `DstP`,
> - `Src` must have a principal trait `SrcP`
> - `dyn SrcP` and `dyn DstP` must be the same type (modulo the trait object lifetime, `dyn T+'a` -> `dyn T+'b` is allowed)
> - Auto traits in `Dst` must be a subset of auto traits in `Src`
> - Not adhering to this is currently a FCW (warn-by-default + `FutureReleaseErrorReportInDeps`), instead of an error
> - if `Src` has a principal trait `Dst` must as well
> - this restriction will be removed in a follow up PR
This ensures that
1. Principal trait's generic arguments match (no `*const dyn Tr<A>` -> `*const dyn Tr<B>` casts, which are a problem for [#120222](https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/120222))
2. Principal trait's lifetime arguments match (no `*const dyn Tr<'a>` -> `*const dyn Tr<'b>` casts, which are a problem for [#120217](https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/120217))
3. No auto traits can be _added_ (this is a problem for arbitrary self types, see [this comment](https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/120248#discussion_r1463835350))
Some notes:
- We only care about the metadata/last field, so you can still cast `*const dyn T` to `*const WithHeader<dyn T>`, etc
- The lifetime of the trait object itself (`dyn A + 'lt`) is not checked, so you can still cast `*mut FnOnce() + '_` to `*mut FnOnce() + 'static`, etc
- This feels fishy, but I couldn't come up with a reason it must be checked
The diagnostics are currently not great, to say the least, but as far as I can tell this correctly fixes the issues.
cc `@oli-obk` `@compiler-errors` `@lcnr`
Support tail calls in mir via `TerminatorKind::TailCall`
This is one of the interesting bits in tail call implementation — MIR support.
This adds a new `TerminatorKind` which represents a tail call:
```rust
TailCall {
func: Operand<'tcx>,
args: Vec<Operand<'tcx>>,
fn_span: Span,
},
```
*Structurally* this is very similar to a normal `Call` but is missing a few fields:
- `destination` — tail calls don't write to destination, instead they pass caller's destination to the callee (such that eventual `return` will write to the caller of the function that used tail call)
- `target` — similarly to `destination` tail calls pass the caller's return address to the callee, so there is nothing to do
- `unwind` — I _think_ this is applicable too, although it's a bit confusing
- `call_source` — `become` forbids operators and is not created as a lowering of something else; tail calls always come from HIR (at least for now)
It might be helpful to read the interpreter implementation to understand what `TailCall` means exactly, although I've tried documenting it too.
-----
There are a few `FIXME`-questions still left, ideally we'd be able to answer them during review ':)
-----
r? `@oli-obk`
cc `@scottmcm` `@DrMeepster` `@JakobDegen`
Rollup of 9 pull requests
Successful merges:
- #123043 (Disable dead variant removal for `#[repr(C)]` enums.)
- #126405 (Migrate some rustc_builtin_macros to SessionDiagnostic)
- #127037 (Remove some duplicated tests)
- #127283 (Reject SmartPointer constructions not serving the purpose)
- #127301 (Tweak some structured suggestions to be more verbose and accurate)
- #127307 (Allow to have different types for arguments of `Rustc::remap_path_prefix`)
- #127309 (jsondocck: add `$FILE` built-in variable)
- #127314 (Trivial update on tidy bless note)
- #127319 (Remove a use of `StructuredDiag`, which is incompatible with automatic error tainting and error translations)
r? `@ghost`
`@rustbot` modify labels: rollup
The rules for casting `*mut X<dyn A>` -> `*mut Y<dyn B>` are as follows:
- If `B` has a principal
- `A` must have exactly the same principal (including generics)
- Auto traits of `B` must be a subset of autotraits in `A`
Note that `X<_>` and `Y<_>` can be identity, or arbitrary structs with last field being the dyn type.
The lifetime of the trait object itself (`dyn ... + 'a`) is not checked.
This prevents a few soundness issues with `#![feature(arbitrary_self_types)]` and trait upcasting.
Namely, these checks make sure that vtable is always valid for the pointee.
Stop using specialization in rustc_index and rustc_borrowck
For rustc_borrowck the version with specialization isn't much more readable anyway IMO. For rustc_index it probably doesn't affect perf in any noticeable way anyway.
Re-implement a type-size based limit
r? lcnr
This PR reintroduces the type length limit added in #37789, which was accidentally made practically useless by the caching changes to `Ty::walk` in #72412, which caused the `walk` function to no longer walk over identical elements.
Hitting this length limit is not fatal unless we are in codegen -- so it shouldn't affect passes like the mir inliner which creates potentially very large types (which we observed, for example, when the new trait solver compiles `itertools` in `--release` mode).
This also increases the type length limit from `1048576 == 2 ** 20` to `2 ** 24`, which covers all of the code that can be reached with craterbot-check. Individual crates can increase the length limit further if desired.
Perf regression is mild and I think we should accept it -- reinstating this limit is important for the new trait solver and to make sure we don't accidentally hit more type-size related regressions in the future.
Fixes#125460
Rewrite handling of universe-leaking placeholder regions into outlives constraints
This commit prepares for Polonius by moving handling of leak check/universe errors out of the inference step by rewriting any universe error into an outlives-static constraint.
This variant is a work in progress but seems to pass most tests.
Note that a few debug assertions no longer hold; a few extra eyes on those changes are appreciated!
This version is a squash-rebased version of a series
of exiermental commits, since large parts of them
were broken out into PR #125069.
It explicitly handles universe violations in higher-kinded
outlives constraints by adding extra outlives static constraints.
Automatically taint InferCtxt when errors are emitted
r? `@nnethercote`
Basically `InferCtxt::dcx` now returns a `DiagCtxt` that refers back to the `Cell<Option<ErrorGuaranteed>>` of the `InferCtxt` and thus when invoking `Diag::emit`, and the diagnostic is an error, we taint the `InferCtxt` directly.
That change on its own has no effect at all, because `InferCtxt` already tracks whether errors have been emitted by recording the global error count when it gets opened, and checking at the end whether the count changed. So I removed that error count check, which had a bit of fallout that I immediately fixed by invoking `InferCtxt::dcx` instead of `TyCtxt::dcx` in a bunch of places.
The remaining new errors are because an error was reported in another query, and never bubbled up. I think they are minor enough for this to be ok, and sometimes it actually improves diagnostics, by not silencing useful diagnostics anymore.
fixes#126485 (cc `@olafes)`
There are more improvements we can do (like tainting in hir ty lowering), but I would rather do that in follow up PRs, because it requires some refactorings.
Do not ICE when suggesting dereferencing closure arg
Account for `for` lifetimes when constructing closure to see if dereferencing the return value would be valid.
Fix#125634, fix#124563.
Remove confusing `use_polonius` flag and do less cloning
The `use_polonius` flag is both redundant and confusing since every function it's propagated to also checks if `all_facts` is `Some`, the true test of whether to generate Polonius facts for Polonius or for external consumers. This PR makes that path clearer by simply doing away with the argument and handling the logic in precisely two places: where facts are populated (check for `Some`), and where `all_facts` are initialised. It also delays some statements until after that check to avoid the miniscule performance penalty of executing them when Polonius is disabled.
This also addresses `@lqd's` concern in #125652 by reducing the size of what is cloned out of Polonius facts to just the facts being added, as opposed to the entire vector of potential inputs, and added descriptive comments.
*Reviewer note*: the comments in `add_extra_drop_facts` should be inspected by a reviewer, in particular the one on [L#259](https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/compare/master...amandasystems:you-dropped-this-again?expand=1#diff-aa727290e6670264df2face84f012897878e11a70e9c8b156543cfcd9619bac3R259) in this PR, which should be trivial for someone with the right background knowledge to address.
I also included some lints I found on the way there that I couldn't help myself from addressing.
Rename `InstanceDef` -> `InstanceKind`
Renames `InstanceDef` to `InstanceKind`. The `Def` here is confusing, and makes it hard to distinguish `Instance` and `InstanceDef`. `InstanceKind` makes this more obvious, since it's really just describing what *kind* of instance we have.
Not sure if this is large enough to warrant a types team MCP -- it's only 53 files. I don't personally think it does, but happy to write one if anyone disagrees. cc ``@rust-lang/types``
r? types
Convert a `span_bug` to a `span_delayed_bug`.
PR #121208 converted this from a `span_delayed_bug` to a `span_bug` because nothing in the test suite caused execution to hit this path. But now fuzzing has found a test case that does hit it. So this commit converts it back to `span_delayed_bug` and adds the relevant test.
Fixes#126385.
r? `@lcnr`
Make suggestion to change `Fn` to `FnMut` work with methods as well
Fixes#125325
The issue occurred because the code that emitted the suggestion to change `Fn` to `FnMut` worked only for function calls and not method calls. This PR makes it work with methods as well.
PR #121208 converted this from a `span_delayed_bug` to a `span_bug`
because nothing in the test suite caused execution to hit this path. But
now fuzzing has found a test case that does hit it. So this commit
converts it back to `span_delayed_bug` and adds the relevant test.
Fixes#126385.
Make uninitialized_error_reported a set of locals
Another artifact of how places used to be able to be based on statics and not just locals. This set is exclusively filled with PlaceRefs that are just locals, so it should just contain locals directly.
smir: merge identical Constant and ConstOperand types
The first commit renames the const operand visitor functions on regular MIR to match the type name, that was forgotten in the original rename.
The second commit changes stable MIR, fixing https://github.com/rust-lang/project-stable-mir/issues/71. Previously there were two different smir types for the MIR type `ConstOperand`, one used in `Operand` and one in `VarDebugInfoContents`.
Maybe we should have done this with https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/125967, so there's only a single breaking change... but I saw that PR too late.
Fixes https://github.com/rust-lang/project-stable-mir/issues/71
Use `Variance` glob imported variants everywhere
Fully commit to using the globbed variance. Could be convinced the other way, and change this PR to not use the globbed variants anywhere, but I'd rather we do one or the other.
r? lcnr
Extend SCC construction to enable extra functionality
Do YOU feel like your SCC construction doesn't do enough? Then I have a patch for you! SCCs can now do *everything*! Well, almost.
This patch has been extracted from #123720. It specifically enhances
`Sccs` to allow tracking arbitrary commutative properties (think min/max mappings on nodes vs arbitrary closures) of strongly connected components, including
- reachable values (max/min)
- SCC-internal values (max/min)
This helps with among other things universe computation. We can now identify
SCC universes as a reasonably straightforward "find max/min" operation during SCC construction. This is also included in this patch.
It's also more or less zero-cost; don't use the new features, don't pay for them.
This commit also vastly extends the documentation of the SCCs module, which I had a very hard time following. It may or may not have gotten easier to read for someone else.
I believe this logic can also be used in leak check, but haven't checked. Ha. ha. Ha.
This patch has been extracted from #123720. It specifically enhances
`Sccs` to allow tracking arbitrary commutative properties of SCCs, including
- reachable values (max/min)
- SCC-internal values (max/min)
This helps with among other things universe computation: we can now identify
SCC universes as a straightforward "find max/min" operation during SCC construction.
It's also more or less zero-cost; don't use the new features, don't pay for them.
This commit also vastly extends the documentation of the SCCs module, which I had a very hard time following.
Use `tidy` to sort crate attributes for all compiler crates.
We already do this for a number of crates, e.g. `rustc_middle`, `rustc_span`, `rustc_metadata`, `rustc_span`, `rustc_errors`.
For the ones we don't, in many cases the attributes are a mess.
- There is no consistency about order of attribute kinds (e.g. `allow`/`deny`/`feature`).
- Within attribute kind groups (e.g. the `feature` attributes), sometimes the order is alphabetical, and sometimes there is no particular order.
- Sometimes the attributes of a particular kind aren't even grouped all together, e.g. there might be a `feature`, then an `allow`, then another `feature`.
This commit extends the existing sorting to all compiler crates, increasing consistency. If any new attribute line is added there is now only one place it can go -- no need for arbitrary decisions.
Exceptions:
- `rustc_log`, `rustc_next_trait_solver` and `rustc_type_ir_macros`, because they have no crate attributes.
- `rustc_codegen_gcc`, because it's quasi-external to rustc (e.g. it's ignored in `rustfmt.toml`).
r? `@davidtwco`
We already do this for a number of crates, e.g. `rustc_middle`,
`rustc_span`, `rustc_metadata`, `rustc_span`, `rustc_errors`.
For the ones we don't, in many cases the attributes are a mess.
- There is no consistency about order of attribute kinds (e.g.
`allow`/`deny`/`feature`).
- Within attribute kind groups (e.g. the `feature` attributes),
sometimes the order is alphabetical, and sometimes there is no
particular order.
- Sometimes the attributes of a particular kind aren't even grouped
all together, e.g. there might be a `feature`, then an `allow`, then
another `feature`.
This commit extends the existing sorting to all compiler crates,
increasing consistency. If any new attribute line is added there is now
only one place it can go -- no need for arbitrary decisions.
Exceptions:
- `rustc_log`, `rustc_next_trait_solver` and `rustc_type_ir_macros`,
because they have no crate attributes.
- `rustc_codegen_gcc`, because it's quasi-external to rustc (e.g. it's
ignored in `rustfmt.toml`).
The `use_polonius` flag is both redundant and confusing since every
function it's propagated to also checks if `all_facts` is `Some`,
the true test of whether to generate Polonius facts for Polonius
or for external consumers. This PR makes that path clearer by
simply doing away with the argument and handling the logic in
precisely two places: where facts are populated (check for `Some`),
and where `all_facts` are initialised. It also delays some statements
until after that check to avoid the miniscule performance penalty
of executing them when Polonius is disabled.
This also addresses @lqd's concern in #125652 by reducing
the size of what is cloned out of Polonius facts to just the
facts being added, as opposed to the entire vector of potential
inputs, and added descriptive comments.
*Reviewer note*: the comments in [add_extra_drop_facts](85f90a4612/compiler/rustc_borrowck/src/type_check/liveness/trace.rs (L219)) should be inspected by a reviewer,
in particular the one on L#259 in this PR, which should be trivial
for someone with the right background knowledge.
I also included some minor lints I found on the way there that I
couldn't help myself from addressing.
Silence follow-up errors directly based on error types and regions
During type_of, we used to just return an error type if there were any errors encountered. This is problematic, because it means a struct declared as `struct Foo<'static>` will end up not finding any inherent or trait impls because those impl blocks' `Self` type will be `{type error}` instead of `Foo<'re_error>`. Now it's the latter, silencing nonsensical follow-up errors about `Foo` not having any methods.
Unfortunately that now allows for new follow-up errors, because borrowck treats `'re_error` as `'static`, causing nonsensical errors about non-error lifetimes not outliving `'static`. So what I also did was to just strip all outlives bounds that borrowck found, thus never letting it check them. There are probably more nuanced ways to do this, but I worried there would be other nonsensical errors if some outlives bounds were missing. Also from the test changes, it looked like an improvement everywhere.
Use parenthetical notation for `Fn` traits
Always use the `Fn(T) -> R` format when printing closure traits instead of `Fn<(T,), Output = R>`.
Address #67100:
```
error[E0277]: expected a `Fn()` closure, found `F`
--> file.rs:6:13
|
6 | call_fn(f)
| ------- ^ expected an `Fn()` closure, found `F`
| |
| required by a bound introduced by this call
|
= note: wrap the `F` in a closure with no arguments: `|| { /* code */ }`
note: required by a bound in `call_fn`
--> file.rs:1:15
|
1 | fn call_fn<F: Fn() -> ()>(f: &F) {
| ^^^^^^^^^^ required by this bound in `call_fn`
help: consider further restricting this bound
|
5 | fn call_any<F: std::any::Any + Fn()>(f: &F) {
| ++++++
```
Revert propagation of drop-live information from Polonius
#64749 introduced a flow of drop-use data from Polonius to `LivenessResults::add_extra_drop_facts()`, which makes `LivenessResults` agree with Polonius on liveness in the presence of free regions that may be dropped. Later changes accidentally removed this flow. This PR restores it.
Rename HIR `TypeBinding` to `AssocItemConstraint` and related cleanup
Rename `hir::TypeBinding` and `ast::AssocConstraint` to `AssocItemConstraint` and update all items and locals using the old terminology.
Motivation: The terminology *type binding* is extremely outdated. "Type bindings" not only include constraints on associated *types* but also on associated *constants* (feature `associated_const_equality`) and on RPITITs of associated *functions* (feature `return_type_notation`). Hence the word *item* in the new name. Furthermore, the word *binding* commonly refers to a mapping from a binder/identifier to a "value" for some definition of "value". Its use in "type binding" made sense when equality constraints (e.g., `AssocTy = Ty`) were the only kind of associated item constraint. Nowadays however, we also have *associated type bounds* (e.g., `AssocTy: Bound`) for which the term *binding* doesn't make sense.
---
Old terminology (HIR, rustdoc):
```
`TypeBinding`: (associated) type binding
├── `Constraint`: associated type bound
└── `Equality`: (associated) equality constraint (?)
├── `Ty`: (associated) type binding
└── `Const`: associated const equality (constraint)
```
Old terminology (AST, abbrev.):
```
`AssocConstraint`
├── `Bound`
└── `Equality`
├── `Ty`
└── `Const`
```
New terminology (AST, HIR, rustdoc):
```
`AssocItemConstraint`: associated item constraint
├── `Bound`: associated type bound
└── `Equality`: associated item equality constraint OR associated item binding (for short)
├── `Ty`: associated type equality constraint OR associated type binding (for short)
└── `Const`: associated const equality constraint OR associated const binding (for short)
```
r? compiler-errors
Always use the `Fn(T) -> R` format when printing closure traits instead of `Fn<(T,), Output = R>`.
Fix#67100:
```
error[E0277]: expected a `Fn()` closure, found `F`
--> file.rs:6:13
|
6 | call_fn(f)
| ------- ^ expected an `Fn()` closure, found `F`
| |
| required by a bound introduced by this call
|
= note: wrap the `F` in a closure with no arguments: `|| { /* code */ }`
note: required by a bound in `call_fn`
--> file.rs:1:15
|
1 | fn call_fn<F: Fn() -> ()>(f: &F) {
| ^^^^^^^^^^ required by this bound in `call_fn`
help: consider further restricting this bound
|
5 | fn call_any<F: std::any::Any + Fn()>(f: &F) {
| ++++++
```
This shunts all the complexity of siphoning off the drop-use facts
into `LivenessResults::add_extra_drop_facts()`, which may or may
not be a good approach.
Follow-up fixes to `report_return_mismatched_types`
Some renames, simplifications, fixes, etc. Follow-ups to #123804. I don't think it totally disentangles this code, but it does remove some of the worst offenders on the "I am so confused" scale (e.g. `get_node_fn_decl`).
Uplift `RegionVid`, `TermKind` to `rustc_type_ir`, and `EagerResolver` to `rustc_next_trait_solver`
- Uplift `RegionVid`. This was complicated due to the fact that we implement `polonius_engine::Atom` for `RegionVid` -- but I just separated that into `PoloniusRegionVid`, and added `From`/`Into` impls so it can be defined in `rustc_borrowck` separately. Coherence 😵
- Change `InferCtxtLike` to expose `opportunistically_resolve_{ty,ct,lt,int,float}_var` so that we can uplift `EagerResolver` for use in the canonicalization methods.
- Uplift `TermKind` much like `GenericArgKind`
All of this is miscellaneous dependencies for making more `EvalCtxt` methods generic.
Coroutines can be prefixed with the `static` keyword to make them
`!Unpin`.
However, given the following function:
```rust
fn check() -> impl Sized {
let x = 0;
#[coroutine]
static || {
yield;
x
}
}
```
We currently suggest prefixing `move` before `static`, which is
syntactically incorrect:
```
error[E0373]: coroutine may outlive the current function, but it borrows
...
--> src/main.rs:6:5
|
6 | static || {
| ^^^^^^^^^ may outlive borrowed value `x`
7 | yield;
8 | x
| - `x` is borrowed here
|
note: coroutine is returned here
--> src/main.rs:6:5
|
6 | / static || {
7 | | yield;
8 | | x
9 | | }
| |_____^
help: to force the coroutine to take ownership of `x` (and any other
referenced variables), use the `move` keyword
| // this is syntactically incorrect, it should be `static move ||`
6 | move static || {
| ++++
```
This PR suggests adding `move` after `static` for these coroutines.
chore: Remove repeated words (extension of #124924)
When I saw #124924 I thought "Hey, I'm sure that there are far more than just two typos of this nature in the codebase". So here's some more typo-fixing.
Some found with regex, some found with a spellchecker. Every single one manually reviewed by me (along with hundreds of false negatives by the tools)
Rename Unsafe to Safety
Alternative to #124455, which is to just have one Safety enum to use everywhere, this opens the posibility of adding `ast::Safety::Safe` that's useful for unsafe extern blocks.
This leaves us today with:
```rust
enum ast::Safety {
Unsafe(Span),
Default,
// Safe (going to be added for unsafe extern blocks)
}
enum hir::Safety {
Unsafe,
Safe,
}
```
We would convert from `ast::Safety::Default` into the right Safety level according the context.
Rename some `FulfillmentErrorCode`/`ObligationCauseCode` variants to be less redundant
1. Rename some `FulfillmentErrorCode` variants.
2. Always use `ObligationCauseCode::` to prefix a code, rather than using a glob import and naming them through `traits::`.
3. Rename some `ObligationCauseCode` variants -- I wasn't particularly thorough with thinking of a new names for these, so could workshop them if necessary.
4. Misc stuff from renaming.
r? lcnr
Eliminate some `FIXME(lcnr)` comments
In some cases this involved changing code. In some cases the comment was able to removed or replaced.
r? ``@lcnr``
Rename `Generics::params` to `Generics::own_params`
I hope this makes it slightly more obvious that `generics.own_params` is insufficient when considering nested items. I didn't actually audit any of the usages, for the record.
r? lcnr
`InferCtxt::next_{ty,const}_var*` all take an origin, but the
`param_def_id` is almost always `None`. This commit changes them to just
take a `Span` and build the origin within the method, and adds new
methods for the rare cases where `param_def_id` might not be `None`.
This avoids a lot of tedious origin building.
Specifically:
- next_ty_var{,_id_in_universe,_in_universe}: now take `Span` instead of
`TypeVariableOrigin`
- next_ty_var_with_origin: added
- next_const_var{,_in_universe}: takes Span instead of ConstVariableOrigin
- next_const_var_with_origin: added
- next_region_var, next_region_var_in_universe: these are unchanged,
still take RegionVariableOrigin
The API inconsistency (ty/const vs region) seems worth it for the
large conciseness improvements.
When encountering a move conflict, on an expression that is `!Copy` passed as an argument to an `fn` that is `impl AsRef`, suggest borrowing the expression.
```
error[E0382]: use of moved value: `bar`
--> f204.rs:14:15
|
12 | let bar = Bar;
| --- move occurs because `bar` has type `Bar`, which does not implement the `Copy` trait
13 | foo(bar);
| --- value moved here
14 | let baa = bar;
| ^^^ value used here after move
|
help: borrow the value to avoid moving it
|
13 | foo(&bar);
| +
```
Fix#41708
It provides a way to effectively embed a linked list within an
`IndexVec` and also iterate over that list. It's written in a very
generic way, involving two traits `Links` and `LinkElem`. But the
`Links` trait is only impl'd for `IndexVec` and `&IndexVec`, and the
whole thing is only used in one module within `rustc_borrowck`. So I
think it's over-engineered and hard to read. Plus it has no comments.
This commit removes it, and adds a (non-generic) local iterator for the
use within `rustc_borrowck`. Much simpler.
Remove many `#[macro_use] extern crate foo` items
This requires the addition of more `use` items, which often make the code more verbose. But they also make the code easier to read, because `#[macro_use]` obscures where macros are defined.
r? `@fee1-dead`
Remove optionality from MoveData::base_local
This is an artifact from when Places could be based on statics and not just locals. Now, all move paths either are locals or have parents, so this doesn't need to return Option anymore.
```
error[E0499]: cannot borrow `foo` as mutable more than once at a time
--> $DIR/suggest-split-at-mut.rs:13:18
|
LL | let a = &mut foo[..2];
| --- first mutable borrow occurs here
LL | let b = &mut foo[2..];
| ^^^ second mutable borrow occurs here
LL | a[0] = 5;
| ---- first borrow later used here
|
= help: use `.split_at_mut(position)` or similar method to obtain two mutable non-overlapping sub-slices
```
Address most of #58792.
For follow up work, we should emit a structured suggestion for cases where we can identify the exact `let (a, b) = foo.split_at_mut(2);` call that is needed.
```
error[E0507]: cannot move out of `bar`, a captured variable in an `FnMut` closure
--> $DIR/borrowck-move-by-capture.rs:9:29
|
LL | let bar: Box<_> = Box::new(3);
| --- captured outer variable
LL | let _g = to_fn_mut(|| {
| -- captured by this `FnMut` closure
LL | let _h = to_fn_once(move || -> isize { *bar });
| ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^ ----
| | |
| | variable moved due to use in closure
| | move occurs because `bar` has type `Box<isize>`, which does not implement the `Copy` trait
| `bar` is moved here
|
help: clone the value before moving it into the closure
|
LL ~ let value = bar.clone();
LL ~ let _h = to_fn_once(move || -> isize { value });
|
```
```
error[E0382]: use of moved value: `t`
--> $DIR/use_of_moved_value_copy_suggestions.rs:7:9
|
LL | fn duplicate_t<T>(t: T) -> (T, T) {
| - move occurs because `t` has type `T`, which does not implement the `Copy` trait
...
LL | (t, t)
| - ^ value used here after move
| |
| value moved here
|
help: if `T` implemented `Clone`, you could clone the value
--> $DIR/use_of_moved_value_copy_suggestions.rs:4:16
|
LL | fn duplicate_t<T>(t: T) -> (T, T) {
| ^ consider constraining this type parameter with `Clone`
...
LL | (t, t)
| - you could clone this value
help: consider restricting type parameter `T`
|
LL | fn duplicate_t<T: Copy>(t: T) -> (T, T) {
| ++++++
```
The `help` is new. On ADTs, we also extend the output with span labels:
```
error[E0507]: cannot move out of static item `FOO`
--> $DIR/issue-17718-static-move.rs:6:14
|
LL | let _a = FOO;
| ^^^ move occurs because `FOO` has type `Foo`, which does not implement the `Copy` trait
|
note: if `Foo` implemented `Clone`, you could clone the value
--> $DIR/issue-17718-static-move.rs:1:1
|
LL | struct Foo;
| ^^^^^^^^^^ consider implementing `Clone` for this type
...
LL | let _a = FOO;
| --- you could clone this value
help: consider borrowing here
|
LL | let _a = &FOO;
| +
```
Start pointing to where bindings were declared when they are captured in closures:
```
error[E0597]: `x` does not live long enough
--> $DIR/suggest-return-closure.rs:23:9
|
LL | let x = String::new();
| - binding `x` declared here
...
LL | |c| {
| --- value captured here
LL | x.push(c);
| ^ borrowed value does not live long enough
...
LL | }
| -- borrow later used here
| |
| `x` dropped here while still borrowed
```
Suggest cloning in more cases involving closures:
```
error[E0507]: cannot move out of `foo` in pattern guard
--> $DIR/issue-27282-move-ref-mut-into-guard.rs:11:19
|
LL | if { (|| { let mut bar = foo; bar.take() })(); false } => {},
| ^^ --- move occurs because `foo` has type `&mut Option<&i32>`, which does not implement the `Copy` trait
| |
| `foo` is moved here
|
= note: variables bound in patterns cannot be moved from until after the end of the pattern guard
help: consider cloning the value if the performance cost is acceptable
|
LL | if { (|| { let mut bar = foo.clone(); bar.take() })(); false } => {},
| ++++++++
```
deref patterns: lower deref patterns to MIR
This lowers deref patterns to MIR. This is a bit tricky because this is the first kind of pattern that requires storing a value in a temporary. Thanks to https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/123324 false edges are no longer a problem.
The thing I'm not confident about is the handling of fake borrows. This PR ignores any fake borrows inside a deref pattern. We are guaranteed to at least fake borrow the place of the first pointer value, which could be enough, but I'm not certain.
Make `suggest_deref_closure_return` more idiomatic/easier to understand
The only functional change here really is just making it not use a fresh type variable for upvars. I'll point that out in the code.
The rest of the changes are just stylistic, because reading this code was really confusing me (variable names were vague, ways of accessing types were unidiomatic, order of operations was kind of strange, etc).
This is stacked on #123989.
r? oli-obk since you approved #122213
Better graphviz output for SCCs and NLL constraints
This PR modifies the output for `-Z dump-mir-graphviz=yes`. Specifically, it changes the output of the files `.-------.nll.0.regioncx.all.dot` and `nll.0.regioncx.scc.dot` to be easier to read and contain some information that helped me during debugging. In particular:
- SCC indices are contracted to `SCC(n)` instead of `ConstraintSccIndex(n)` to compress the nodes
- SCC regions are in `{}` rather than `[]` (controversial since they are technically ordered by index, but I figured they're more sets than arrays conceptually since they're equivalence classes).
- For regions in other universes than the root, also show the region universe (as ?8/U1)
- For regions with external names, show the external name in parenthesis
- For the region graph where edges are locations, render the All variant of the enum without the file since it's extremely long and often destroys the rendering
- For region graph edge annotations for single locations, remove the wrapping around the Location variant and just add its contents since this can be unambiguously done
Example output (from the function `foo()` of `tests/ui/error-codes/E0582.rs`) for an SCC graph:
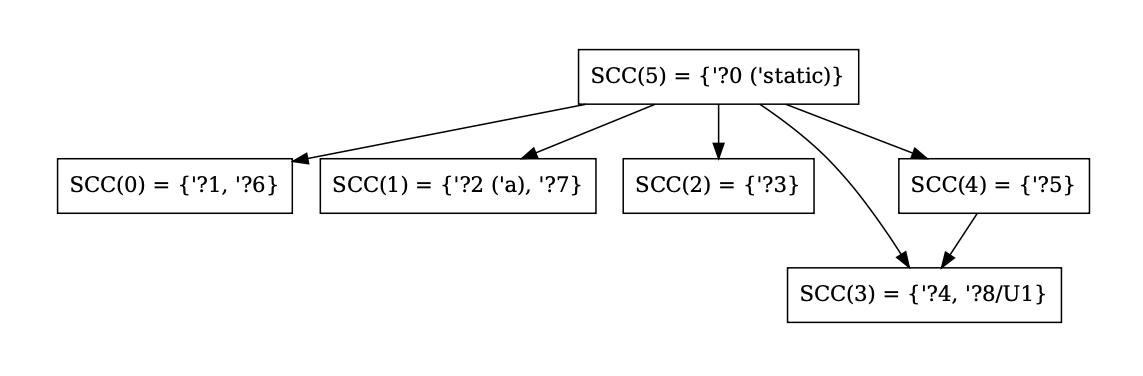
...and for the constraints:
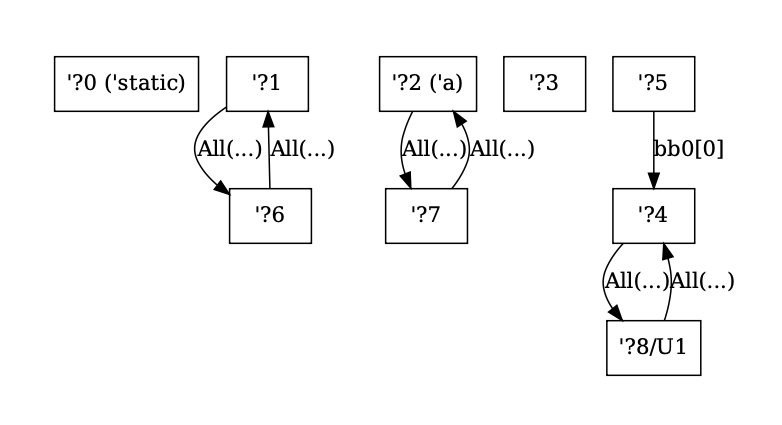
This PR also gives `UniverseIndex`es the `is_root()` method since this is now an operation that happens three times in the borrowck crate.
Remove `TypeVariableOriginKind` and `ConstVariableOriginKind`
It's annoying to have to import `TypeVariableOriginKind` just to fill it with `MiscVariable` for almost every use. Every other usage other than `TypeParameterDefinition` wasn't even used -- I can see how it may have been useful once for debugging, but I do quite a lot of typeck debugging and I've never really needed it.
So let's just remove it, and keep around the only useful thing which is the `DefId` of the param for `var_for_def`.
This is based on #123006, which removed the special use of `TypeVariableOriginKind::OpaqueInference`, which I'm pretty sure I was the one that added.
r? lcnr or re-roll to types